|
Exhibition Hall 14:30 - 15:30 |
|
|
|
Computer # |
|
3476.
 |
73 |
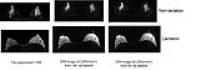
Simple and robust cardiac diffusion weighted imaging using
single-shot Turbo Spin-Echo with peripheral pulse gating 
Yasuhiro Goto1, Kenji Fukushima2,
Masami Yoneyama3, Atsushi Takemura3,
Hitoshi Tadenuma1, Mamoru Takeyama1,
and Shuji Sakai2
1Department of Radioligical Service, Tokyo
Women's Medical University Hospital, TOKYO, Japan, 2Department
of Diagnostic imaging & Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Women`s
Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan,3Philips
Electronics Japan, Tokyo, Japan
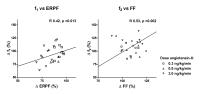
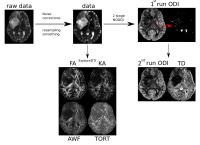
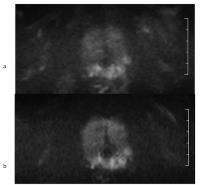
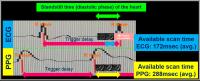
We evaluated the feasibility of optimal gating method and
imaging parameters for Single-Shot Turbo Spin Echo (ssTSE) diffusion
weighted image (DWI). As a result, The Peripheral pulse
gating (PPG) synchronization method was significantly higher
in visual scoring than that of the ECG synchronization
method (p=0.02) and ssTSE-DWI using SENSE-factor 4.0 brought
about the best image quality. Refocusing Flip Angle (RFA)
tended to be higher in images with higher visual score.
Visualizing cardiac DWI was feasible under above conditions.
In conclusion, it is expected that ssTSE-DWI using PPG has a
possibility to detect abnormal signal from myocardium by
non-contrast MRI.
|
|
3477.
 |
74 |
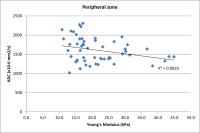
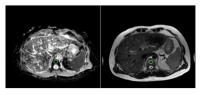
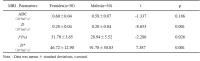
The Study of Vertebral Marrow Microstructure in Healthy Young
Adults with Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-weighted
Imaging 
Jinliang Niu1, Wenqi Wu1, Tong Gong1,
Wenjin Li1, Dandan Zheng2, Zheng Zhong3,
Hongwei Wang1, and Xiaohong Joe Zhou3
1The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical
University, Taiyuan, China, People's Republic of, 2GE
Healthcare MR Research China, Beijing, China, People's
Republic of, 3Center
for Magnetic Resonance Research, University of Illinois
Hospital &Health Sciences System, Chicago, IL, United States
MRI has become preferred over other imaging modalities in
evaluating marrow compositions. Although the routine MRI can
evaluate the cellularity of marrow according to signal
intensity, it’s not quantitative analysis. IVIM provides
both diffusion and perfusion quantification using a single
imaging study at the same time, without intravenous contrast
injection. IVIM has been applied in various diseases, but
the application of IVIM in marrow composition is less. As
the preliminary study, we will adopt the parameters of IVIM
to assess the vertebral bone marrow microstructure, then to
investigate gender-related cellular and capillary network of
vertebral marrow in healthy young adults.
|
|
3478.
 |
75 |
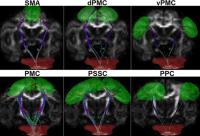
Corticospinal Tract Distribution in Motor Cortices of Adult
Macaque Brains Revealed by High Angular Resolution Diffusion
Imaging Tractography 
Yuguang Meng1 and
Xiaodong Zhang1,2
1Yerkes Imaging Center, Yerkes National Primate
Research Center, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, United
States, 2Division
of Neuropharmacology and Neurologic Diseases, Yerkes
National Primate Research Center, Emory University, Atlanta,
GA, United States
Non-human primates mimick most aspects of humans and
are widely used in preclinical or medical studies.
Understanding the structural connectivity in non-human
primate brains can provide essential reference for
translational research. The characterization of the
corticospinal tracts plays a crucial role in motor function
and has been well studied in human brain. However, it
remains not fully understood in non-human primates. In this
work, high angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI)
tractography was utilized to evaluate the corticospinal
tracts distribution in sub-regions of motor cortices of
adult macaque monkeys, and high similarity to prior ex-vivo
results was observed.
|
|
3479.
 |
76 |
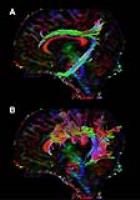
White matter lesions highly influence group comparison of
diffusion tensor imaging metrics 
Daniel Svärd1,2, Markus Nilsson3,
Björn Lampinen4, Jimmy Lätt2, Pia
Sundgren1,2, Erik Stomrud5, Lennart
Minthon5, Katarina Nägga5, Oskar
Hansson5,6, and Danielle van Westen1,2
1Diagnostic Radiology, Clinical Sciences, Lund
University, Lund, Sweden, 2Center
for Medical Imaging and Physiology, Skåne University
Hospital, Lund, Sweden, 3Lund
University Bioimaging Center, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 4Department
of Medical Radiation Physics, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 5Clinical
Memory Research Unit, Clinical Sciences, Lund University,
Malmö, Sweden, 6Neurology,
Clinical Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
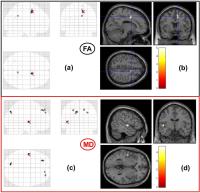
White matter lesions (WML) are common in cognitively healthy
elderly and their presence in a brain region is associated
with elevated mean diffusivity (MD) and reduced fractional
anisotropy (FA). We compared patients with amnestic mild
cognitive impairment (aMCI) to control groups with different
prevalence of WML. Our results showed that including
subjects with WML in the control group highly influence the
outcome of statistical analysis of diffusion tensor imaging
(DTI) metrics. We conclude that WML should be taken into
consideration when designing and interpreting DTI studies.
|
|
3480.
 |
77 |
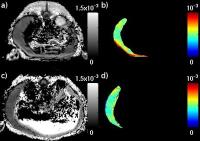
Quantitative Diffusion MRI of Hematopoietic Acute Radiation
Syndrome using a Minipig Model 
Frederick C. Damen1,2, Matthew Lindeblad3,
Kejia Cai2,4, Michael Flannery2, Yi
Sui2, Amelia M Bartholomew5,
Aleksander V Lyubimov3, and Xiaohong Joe Zhou2,4,6,7
1Radiology, University of Illinois at Chicago,
Chicago, IL, United States, 2Center
for Magnetic Resonance Research, University of Illinois at
Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States, 3Pharmacology,
University of Illinois Medical Center, Chicago, IL, United
States, 4Bioengineering,
University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, United
States, 5Surgery,
University of Illinois Medical Center, Chicago, IL, United
States, 6Radiology,
Chicago, IL, United States, 7Neurosurgery,
University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, United
States
The purpose of this study is to characterize Hematopoietic
Acute Radiation Syndrome (hARS) and assess the effect of
total body irradiation in a Göttingen minipig model using
quantitative diffusion MRI. The minipigs were irradiated at
a total dose of either 1.65 Gy (LD30/45 days) or 1.90 Gy
(LD70/45 days). The animals underwent diffusion MRI scans
prior to and again at 8, 15, or 22 days following
irradiation. The consistent diffusion value prior to
irradiation and the significant changes post-irradiation,
both observed in this study, suggest that quantitative
diffusion MR can be a viable marker for studying the effect
of total body irradiation.
|
|
3481.
 |
78 |
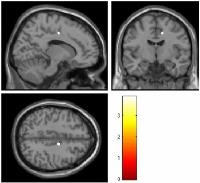
White matter microstructure among perinatally HIV-infected
youth: A diffusion tensor imaging study 
Manoj Kumar Sarma1, Margaret Keller2,
Rajakumar Nagarajan1, David E Michalik3,
Judy Hayes2, Karin Nielsen-Saines4,
Jaime Deville4, Joseph A Church5,
Irwin Walot6, and M. Albert Thomas1
1Radiological Sciences, UCLA School of Medicine,
Los angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Pediatrics,
Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Torrance, CA, United States, 3Infectious
disease-Pediatrics, Miller’s Children’s Hospital of Long
Beach, Long Beach, CA, United States, 4Pediatrics,
UCLA School of Medicine, Los angeles, Los Angeles, CA,
United States, 5Pediatrics,
Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United
States,6Radiology, Harbor-UCLA Medical Center,
Torrance, CA, United States
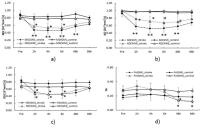
DTI was used to derive in vivo tissue status measurements of
subcortical brain regions that are vulnerable to injury in
perinatally HIV-infected youths. Quantitative measurements,
including the mean diffusivity (MD), fractional anisotropy
(FA), axial diffusivity (AD) and radial diffusivity (RD)
were determined in of the whole brain in 12
well-characterized HIV youths and in 12 healthy control
subjects. We observed widespread brain regions with
increased AD values in perinatally HIV-infected youths
compared to healthy controls, indicating axonal changes. We
also observed increased FA, MD and RD. To confirm these
findings a correlation study with neurodevelopement and
neurocognitive changes as well as ART effect is needed.
Understanding the impact of HIV disease severity on white
matter integrity provides potentially useful clinical tools
for evaluating ART efficacy during a dynamic period of brain
development.
|
|
3482.
 |
79 |
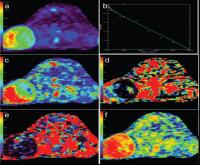
Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging in evaluating the radio-sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts 
Youping Xiao1, Yunbin Chen1, Jianji
Pan2, Dechun Zheng1, Xiang Zheng1,
and Ying Chen1
1Radiology, Fujian Provincial Cancer Hospital,
Fuzhou, China, People's Republic of, 2Radiation
Oncology, Fujian Provincial Cancer Hospital, Fuzhou, China,
People's Republic of
In this present study, by applying the special mouse coil(4
channel), IVIM-DWI with 14 b-factors(0~1000s/mm2) was successfully conducted on
nude mice with different radio-sensitive
NPC xenografts(CNE-1 and CNE-2) during the course of fractional radiations. The IVIM-DWI parameters of xenografts
were found to change
characteristically after fractional radiations and were significantly different between different radio-sensitive NPC xenografts,
and their corresponding changes also
behaved significant correlations with the pathological features of
NPC
xenografts. Thus, it is suggested IVIM-DWI parameters be valuable in evaluating the micro-structures and radio-sensitivity of NPC xenografts.
|
|
3483.
 |
80 |
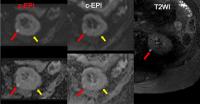
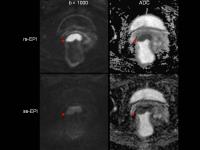
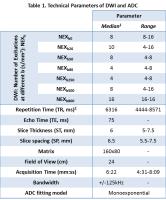
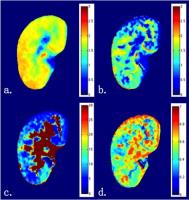
Combining Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Model and Reduced FOV for
Evaluation of Single Renal Diffusion and Perfusion 
CY Wang1, R Zhang2, L Jiang3,
R Wang4, XD Zhang4, H Wang3,
K Zhao4, LX Jin3, J Zhang1,2,
XY Wang1,4, and J Fang1,2
1Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies,
Peking University, Beijing, China, People's Republic of, 2College
of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, China, People's
Republic of, 3Philips
Healthcare, Suzhou, China, People's Republic of, 4Department
of Radiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing,
China, People's Republic of
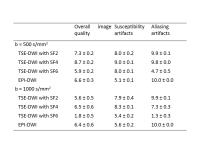
The sequence most commonly used in renal DWI is based on
single-shot echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI), which is prone to
artifacts and distortions related to susceptibility and eddy
currents. Reducing these artifacts and distortions in SS-EPI
generally requires a reduced field of view (rFOV) in the
phase-encoding direction and/or reduced spatial resolution.
To resolve these problems, a 2D rFOV-DWI sequence was
introduced for imaging and further IVIM modeling. Compared
with conventional full-FOV single-shot DWI techniques,
rFOV-DWI methods generally produced images of superior
quality. With the application of IVIM model, it is possible
to evaluate single renal diffusion and perfusion
simultaneously.
|
|
3484.
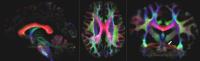 |
81 |
Super-Resolution Track Density Imaging of 1.4 mm isotropic 7T
Whole-Brain Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Images 
Ralf Lützkendorf1, Robin M. Heidemann2,
Thorsten Feiweier2, Michael Luchtmann3,
Sebastian Baecke1, Joern Kaufmann4,
Joerg Stadler5, Eike Budinger5, and
Johannes Bernarding1
1Biometry and Medical Informatics, University of
Magdeburg, Magdeburg, Germany, 2Siemens
Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 3Department
of Neurosurgery, University of Magdeburg, Magdeburg,
Germany, 4Department
of Neurology, University of Magdeburg, Magdeburg, Germany, 5Leibniz
Institute for Neurobiology, Magdeburg, Germany
Track-density imaging (TDI) is a method to generate
super-resolution images from fiber-tracking data (1). Here,
we applied this technique to 1.4 mm isotropic 7T whole brain
diffusion MR imaging data (dMRI). Besides the well-known
large and medium-sized fiber tracts the high resolution of
the data allowed visualizing the complex interwoven courses
of fiber tracts in the cerebellar-pontine angle as well as
showing parts of the trigeminus nerve. Combining TDI with
high-resolved diffusion data has a great potential for
analyzing the anatomy in vivo of brain structures across
different scales as well as the neuronal connectome
throughout the whole brain.
|
|
3485.
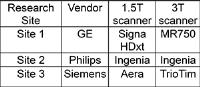 |
82 |
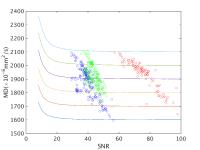
Multi-Center Validation of an Acetone-D2O Quantitative Diffusion
Phantom 
Xiaoke Wang1, Samir D Sharma2, Mustafa
R Bashir3, Jean H Brittain2, Jean
Shaffer3, Takeshi Yokoo4, Qing Yuan4,
Scott B Reeder1,2,5,6,7, and Diego Hernando2
1Biomedical Engineering, University of
Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Radiology,
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Radiology,
Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 4Radiology,
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX,
United States, 5Medical
Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI,
United States, 6Medicine,
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 7Emergency
Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI,
United States
A recently proposed acetone-D2O phantom, which
has ADC tunable over the entire physiological range, has
shown promise for the development and quality assurance of
quantitative diffusion MRI. In this study, this phantom was
shipped between three sites with different MRI vendors to
demonstrate consistent diffusion quantification across
imaging protocols, platforms, and field strengths. The
results demonstrated consistent ADC measurements across
sites/vendors, field strength, choice of b-values,
intra-exam and inter-exam repetition. In conclusion, the
acetone-D2O phantom is a promising tool for
future multi-center validation and quality assurance of
quantitative diffusion MRI techniques.
|
|
3486.
 |
83 |
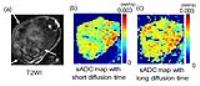
Measuring diffusion time dependence of pseudo-diffusion using
flow compensated pulsed and oscillating gradient sequences 
Dan Wu1 and
Jiangyang Zhang1,2
1Radiology, Johns Hopkins University School of
Medicine, BALTIMORE, MD, United States, 2Radiology,
New York University School of Medicine, New Yourk, NY,
United States
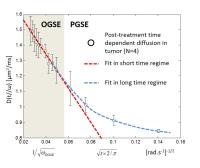
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in the capillaries
reflects capillary geometry and flow velocity, which may be
probed by diffusion MRI measured at varying diffusion times.
In this study, we employed flow-compensated pulsed and
oscillating gradient sequences to investigate the diffusion
time dependence of pseudo-diffusion in the mouse brain with
diffusion times ranging from 2.5 ms to 40 ms. We used a
simplified IVIM model to characterize the pseudo-diffusion
compartment and flow compartment based on the relation
between capillary segments and diffusion time/distance. Our
results clearly demonstrated diffusion time dependence and
suggested that the pseudo-diffusion fraction increased with
increasing diffusion time.
|
|
3487.
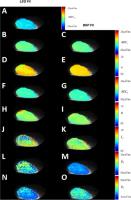 |
84 |
Diffusion weighted imaging of prostate cancer xenografts:
comparison of bayesian modeling and independent least squares
fitting - Permission Withheld
Parisa Movahedi1, Hanne Hakkarainen2,
Harri Merisaari1, Heidi Liljenbäck1,
Helena Virtanen1, Hannu Juhani Aronen1,
Heikki Minn1, Matti Poutanen1, Anne
Roivainen1, Timo Liimatainen2, and
Ivan Jambor1
1University of Turku, Turku, Finland, 2A.I.
Virtanen Institute for Molecular Sciences, Kuopio, Finland
Tumor growth in mice preclinical prostate cancer model
(human prostate cancer cells, PC-3) was followed for 4 weeks
by weekly DWI in control group (n=10) and treatment group
(n=9) receiving Docetaxel. DWI data sets were acquired
using 15 b-values in the range of 0-500s/mm2 and
12 b-values the range of 0-2000 s/mm2. The DWI
signal decays were fitted using monoexponential,
biexponential, kurtosis and stretched exponential
models/functions. Bayesian shrinkage prior method and
independent least squares fitting have been applied and
fitting quality evaluated by corrected Akaike Information
Criteria. Bayesian modeling improved quality of DWI
parametric maps derived using high b-value DWI data sets.
Our result does not support the use of biexponential,
kurtosis and stretched exponential models/functions for low
b value DWI data sets of PC-3 mice preclinical prostate
cancer model.
|
|
3488.
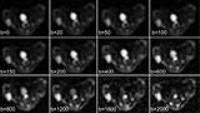 |
85 |
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-weighted Magnetic
Resonance Imaging for Monitoring the Early Response to ZD6474
from Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Nude Mouse -
Video Not Available
Yong Zhang1 and
Yanfen Cui2
1GE Healthcare China, Shanghai, China, Shanghai,
China, People's Republic of, 2Department
of Radiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of
Medicine, Shanghai, China, People's Republic of
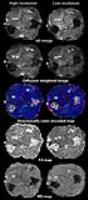
This study was to investigate the feasibility of IVIM DWI to
evaluate the early therapeutic effects of ZD6474 upon human
NPC xenografts in nude mouse. NPC mice underwent IVIM DWI at
baseline and after 1, 3, and 7 days of treatment. In the
treated group, the f and D* decreased significantly on day 1
while the ADC and D were significantly higher from day 3
compared with the control group, demonstrating that IVIM DWI
is sensitive to detect the ZD6474-induced changes in human
NPC nude mouse, and the D* and f parameters could predict
early response to anti-angiogenic treatment.
|
|
3489.
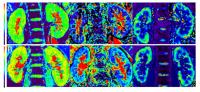 |
86 |
Comparison of IVIM and BOLD MR imaging in Functional Evaluation
of Diabetic nephropathy 
Lihua Chen1, Tao Ren1, Yu Zhang2,
Chenglong Wen1, and Wen Shen1
1Tianjin First Center Hospital, Tianjin, China,
People's Republic of, 2Philips
healthcare, Beijing, China, People's Republic of
To detect the changes of kidney diseases, magnetic resonance
imaging(MRI) as a noninvasive approach has been proved to be
more suitable for detecting and monitoring diabetic
nephropathy(DN). Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) and
blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) MR imaging have
been confirmed their high potential in detecting changes of
renal function in patients with chronic renal diseases and
transplanted kidneys. We compared the parameters of IVIM and
BOLD in patients with DN and heathy controls. The results
demonstrated the capacity of IVIM and BOLD for reflecting
renal perfusion, diffusion and oxygenation changes in
patients with DN.
|
|
3490.
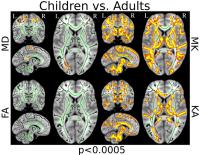 |
87 |
Diffusion Kurtosis Metrics as Biomarker of Fibre Maturity 
Grinberg Farida1,2, Ivan I. Maximov1,3,
Ezequiel Farrher1, Irene Neuner1,4,5,
Eileen Oberwelland6,7, Kerstin Konrad5,6,8,
and N. Jon Shah1,2,5
1Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine - 4,
Forschungszentrum Juelich GmbH, Juelich, Germany, 2Department
of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, RWTH Aachen University,
Aachen, Germany, 3Experimental
Physics III, TU Dortmund University, Dortmund, Germany, 4Department
of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, RWTH Aachen
University, Aachen, Germany, 5JARA
- BRAIN - Translational Medicine, Aachen, Germany, 6Institute
of Neuroscience and Medicine – 3, Forschungszentrum Jülich
GmbH, Juelich, Germany, 7Translational
Brain Research in Psychiatry and Neurology, Department of
Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Psychosomatics and
Psychotherapy, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, 8Child
Neuropsychology Section, Department of Child and Adolescent
Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, RWTH Aachen University,
Aachen, Germany
Diffusion tensor imaging has enabled the examination of
white matter connectivity and microstructural changes across
the lifespan. However, the detection of subtle
microstructural changes during typical brain maturation
still remains challenging. Recently, diffusion kurtosis
imaging has attracted much attention as an efficient method
for characterising non-Gaussian water diffusion in brain
tissue. Here, we tested whether diffusion kurtosis imaging
can extend our knowledge of changes in brain tissue
microstructure related to normal brain development. We
showed that diffusion kurtosis imaging provides useful
biomarkers sensitive to the level of maturity in
association, projection and commissural fibres.
|
|
3491.
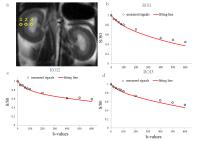 |
88 |
Using intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging to measure renal
diffusion and perfusion in contrast-induced acute kidney injury -
Video Not Available
Bin Zhang1, Long Liang1, Yuhao Dong1,
Kannie W.Y. Chan2, Guanshu Liu2,
Changhong Liang1, and Shuixing Zhang1
1Department of Radiology, Guangdong Academy of
Medical Sciences/Guangdong General Hospital, Guangzhou,
China, People's Republic of, 2Russell
H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences,
Division of MR Research, The Johns Hopkins University School
of Medicine, Baltimore 21287, USA, Baltimore, AL, United
States
Contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) is a common
iatrogenic event caused by the injection of iodinated
contrast agent, and remains the third major source of
in-hospital acquired acute renal failure.The objective of
our study is to examine the feasibility of using Intravoxel
Incoherent Motion (IVIM) MRI to simultaneously measure the
pathological changes in kidney diffusion and perfusion in
the course of CI-AKI. Our results showed that the kidney
perfusion and diffusion as measured by IVIM are
well-correlated with those measured using conventional
methods, indicating IVIM MRI can be used as an effective
tool for the diagnosis and staging of CI-AKI.
|
|
3492.
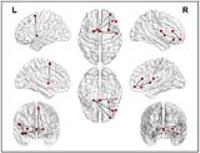 |
89 |
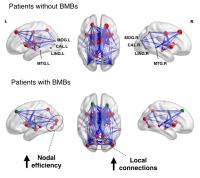
Assessment of brain structural network alterations in major
depressive disorder using generalized q-sampling imaging and
connectome analysis 
Chao-Yu Shen1,2,3, Zhen-Hui Li1,
Vincent Chin-Hung Chen4, Ming-Chou Ho5,
Yeu-Sheng Tyan1,2, and Jun-Cheng Weng1,2
1Department of Medical Imaging and Radiological
Sciences, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, 2Department
of Medical Imaging, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital,
Taichung, Taiwan,3Institute of Medicine, Chung
Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, 4Department
of Psychiatry, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi, Taiwan, 5Department
of Psychology, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung,
Taiwan
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is the most common mood
disorder in the world and the most important precursor of
suicide. Despite decades of research, the pathophysiology of
MDD remains not well understood. Recently, several MRI
studies have focused on structural and functional
connectivity evaluation and suggested that alterations of
some specific regions of the brain, in both gray and white
matter structures and some specific cortical–subcortical
neuronal circuits, may play important roles of MDD.
Generalized q-sampling imaging (GQI) is a more accurate and
sophisticated diffusion MR approach compared to diffusion
tensor imaging (DTI), which can extract additional
information about the altered diffusion environments to
resolve the complicated neural structure changes of neural
disease. In this study, we used GQI and graph theoretical
analysis to evaluate brain structure and connectivity change
of MDD compared to healthy controls and correlation with
symptom severity. Our results indicated GQI indices can
help to detect structural and connective abnormalities of
MDD patients and these alterations are correlated with
depressive severity.
|
|
3493.
 |
90 |
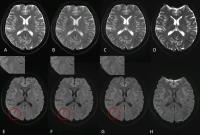
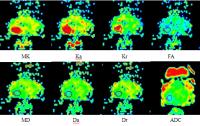
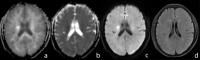
Evaluation of Acute Cerebral Infarction Using a Fast Kurtosis
Diffusion imaging Protocol 
Chengxu Li1, Tianyi Qian2, Jinsuh Kim3,
Philip Zhe Sun4, Jie Lu1, and Kuncheng
Li1
1Department of Radiology, Xuanwu Hospital,
Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, People's
Republic of, 2MR
Collaborations NE Asia, Siemens Healthcare, Beijing, China,
People's Republic of, 3Department
of Radiology, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago,
IL, United States, 4Martinos
Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology,
Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School,
Boston, MA, United States
Conventional DKI is limited in use for detecting acute
stroke because of its relatively long scan time and current
need of offline processing. Here we used a 13 directions
protocol combined with simultaneous multi-slice technique
with inline reconstruction to test the diffusion pattern at
different time points. The results shows the lesion size
observed within 24hr on MK matched with the lesion size on
T2-FLAIR after one month, which was better than lesion size
observed within 24hr on DWI. Early application of the fast
DKI to detect the anomalous range of MK was beneficial to
predict the range of the eventual infarction for clinical
treatment.
|
|
3494.
 |
91 |
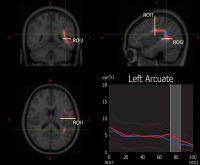
High resolution tract density tract-based spatial statistics and
automating fiber-tract quantification analysis in patients
suffering from major depressive disorder 
Stefan Sommer1,2, Nadja Doerig3,4,
Janis Brakowski2, Martin grosse Holtforth5,
Sebastian Kozerke1, Erich Seifritz2,4,
Simona Spinelli2,4, and Philipp Stämpfli2
1Institute for Biomedical Engineering, ETH and
University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2Department
of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics Psychiatric
Hospital, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland,3Division
Neuropsychology, Departement of Psychology, University of
Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 4Neuroscience
Center, University and ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 5Department
of Psychology, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
In the last few years, tract base spatial statistics (TBSS)
and automating fiber-tract quantification (AFQ) have become
prominent tools for analyzing diffusion data in group
studies. In this study, we introduce optimized
high-resolution tract density (optTD) images and analyze
these maps using TBSS and AFQ in patients with major
depressive disorders. We show a higher sensitivity in the
newly introduced optTD compared to traditional FA analyses.
Significant group differences were found using both methods
indicating robust findings. High resolution optTD maps
derived from optimized tractograms provide a promising tool
for investigating white-matter abnormalities in mental
disorders.
|
|
3495.
 |
92 |
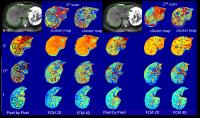
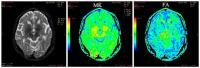
Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study Of Parkinson Disease 
Xilun Ma1, Jitian Guan1, Zhiyan Zhang1,
Miaomiao Chen1, Yanzi Chen1, Zhiwei
Shen1, and Renhua Wu1
1Department of Medical Imaging, the 2nd
Affiliated Hospital, Medical College of Shantou University,
Shantou 515041, China, Shantou, China, People's Republic of
Eighteen Parkinson Disease’s (PD) patients and four healthy
controls(HC) underwent the diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI)
and then we tested the PD’s patients with Hoehn-Yahr scale
and Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale(UPDRS). As a
result, we found a significant decrease of Mean kurtosis
(MK) values in the left substantia nigra between PD’s
patients and healthy controls. Moreover, the kurtosis
fractional anisotropy (KFA) values in right red nucleus of
the PD’s patients were positively associated with the UPDRS
scores in our study.
|
|
3496.
 |
93 |
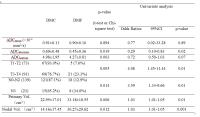
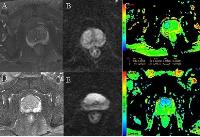
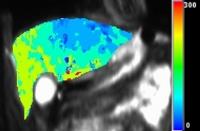
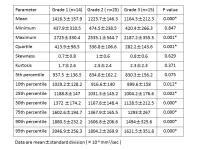
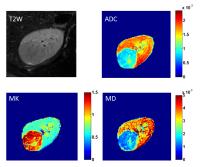
Characterization of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging: Correlation between Diffusion Kurtosis Parameters and Tumor Cellularity 
Guangyu Wu1 and
Yongming Dai2
1renji hospital, shangha, China, People's
Republic of, 2MR,
Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, People's Republic of
A wide spectrum of the use of DKI to characterize
non-Gaussian diffusion pattern in microstructural tumor
tissue has been developed involving a variety of tumors.
However, the feasibility of DKI in kidney has been assessed
in healthy volunteers only. The study was assigned to assess
the quantitative DKI in grading of clear cell renal
carcinoma (ccRCC) and to compare the correlation between DKI
parameters and tumor cellularity and found that DKI could
not only quantitatively characterize ccRCC with different
grades but also provide valuable information on the
diffusion properties related to tumor microenvironment
changes or tissue complexity in tumor.
|
|
3497.
 |
94 |
Diffusional kurtosis imaging study in idiopathic normal pressure
hydrocephalus patients, before and after shunt placement surgery
analysis 
Chanon Ngamsombat 1,
Zhe Zhang2, Hua Gua2, Theerapol
Witthiwej3, Weerasak Muangpaisan4,
Sith Sathornsumetee5, Suwit Charoensak6,
Panida Charnchaowanish1, and Orasa Chawalparit1
1Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine
Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand,
Bangkok, Thailand, 2Center
for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical
Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University,
Beijing, China, Beijing, China, People's Republic of, 3Department
of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol
University, Bangkok, Thailand, Bangkok, Thailand,4Department
of Preventive and Social Medicine, Faculty of Medicine
Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand,
Bangkok, Thailand, 5Departments
of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol
University, Bangkok, Thailand, Bangkok, Thailand, 6Department
of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol
University, Bangkok, Thailand, Bangkok, Thailand
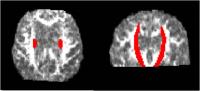
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus(iNPH) is important
reversible cause of dementia and gait abnormality in elderly
patients. Diffusional kurtosis imaging(DKI) moreover
explains the complexity of white matter abnormality with
inclusion of non-Gaussian effects. We aim to identify
difference of complexity of white matter alteration in iNPH
patients before and after shunt placement surgery by using
high resolution DKI. We report significant increase of mean
diffusional kurtosis(Kmean), mean diffusivity(MD) and
decrease of radial diffusional kurtosis(Krad) , fractional
ansiotropy(FA) after shunt placement surgery. High
resolution DKI can be used for monitoring and detection
complexity of white matter alteration in iNPH patients.
|
|
3498.
 |
95 |
The Investigation of Cerebral Microstructure Changes of
Pediatric Patients With Type ? Gaucher Disease Using Diffusion
Kurtosis Imaging 
Huiying Kang1, Ningning Zhang, Kaining Shi2,
Yanqiu Lv1, Di Hu1, and Yun Peng1
1Imaging center, Beijing Children’s Hospital,
Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, People's
Republic of, 2Imaging
Systems Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Beijing,
China, People's Republic of
Increasing clinical studies suggested that there are some
type ? Gaucher disease (GD?) patients suffering neurological
symptom, which was originally defined as non-neuropathlogical
involved. This study recruited 38 patients and 32 normal
children to investigate morphological changes of brain in GD?
patients by using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging. Our results
showed significant decreased MD in bilateral olfactory gyrus,
increased MD in right calcarine and substantia nigra and
significant increased MK in right olfactory gyrus. Our study
suggests a necessity of adjusting the opinion regarding the
CNS-involvement of GD?, and DKI analysis is a potential
imaging marker in clinical studies of GD?.
|
|
3499.
 |
96 |
Differentiating Minimal Fat Angiomyolipoma from clear cell Renal
Cell Carcinoma: comparison of monoexponential, biexponential,
and stretched exponential Diffusion-weighted imaging -
Video Not Available
Haojie Li1, Lili Liang1, Anqin Li1,
Qiong Li1, Yao Hu1, Hui Lin2,
Daoyu Hu1, and Zhen Li1
1Departments of Radiology, Tongji Hospital,
Tongji Medical College, WU HAN, China, People's Republic of, 2GE
Healthcare,MR Research China,WU HAN, WU HAN, China, People's
Republic of
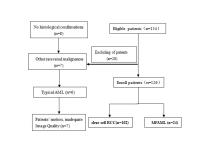
Since DWI with different models may demonstrate different
aspects of tissue properties, it should be valuable to
compare and explore their roles in renal tumors. To our
knowledge, however, no comparison of these different
diffusion imaging approaches for the differential diagnosis
in renal tumors has been investigated so far. The purpose of
this study was to quantitatively compare and evaluate the
potential clinical value of various diffusion parameters
obtained from monoexponential, biexponential, and stretched
exponential DWI models for differentiation of MFAML from
ccRCC.
|
|