ISMRT Oral
1st & 2nd Place Research Abstract Winner Presentations, JAK Winner Presentations
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 03-08 June 2023 • Toronto, ON, Canada

| 11:30 |
5432. |
VitaLenz: A Convolutional Neural Network for the Detection of
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Artifacts
Brian Johnson1,
Joel Batey1,
Dave Hitt1,
Robert Lay1,
Tom Lowe1,
Michael Pawlak1,
John Penatzer1,
Elaine Petrilla1,
Jim Snicer1,
Marcie Stopchinski1,
Greg Thomas1,
Kristen Williams1,
Paul Worthington1,
and Jonathan Chia 1
1Philips, Cleveland, OH, United States
Advances in MR acceleration techniques have produced a
paradigm shift in MR productivity. In addition, the
integration of artificial intelligence offers even more
promise to integrate MR workflow and accelerate image
acquisition. Recognizing the absence of operator assisted
technologies we created VitaLenz, a convolutional neural
network, to test the ability of artificial intelligence in
detecting common MR imaging artifacts. VitaLenz was able to
identify common MR image artifacts with high sensitivity,
accuracy, and speed. Creation and use of this type of
assistive technology can help ensure image quality and can
also lead to faster clinical adoption of newer imaging
techniques.
|
| 11:40 |
5433.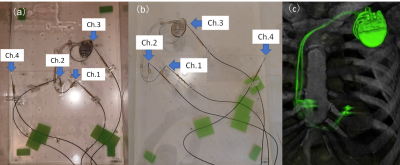 |
MR-safety of mixed-brand of cardiac implantable electronic
devices: Comparison of RF induced heating with approved
single-brand at 1.5 T and 3.0 T
Issei Fukunaga1,
Shuhei Shibukawa1,
Satoshi Yatsushiro2,
Kazuya Tawara2,
Toshiko Nakai3,
Haruhiko Abe4,
Shigeki Aoki5,
Atsuko Miyajima6,
and Kagayaki Kuroda7
1Department of Radiological Technology, Juntendo University, Tokyo, Japan, 2BioView, Inc., Tokyo, Japan, 3Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Nihon University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan, 4Department of Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental Health, Fukuoka, Japan, 5Department of Radiology, Juntendo University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 6Division of Medical Devices, National Institute of Health Sciences, Kanagawa, Japan, 7School of Information Science and Technology, Tokai University, Kanagawa, Japan
Radio-frequency-induced heating around MR-conditional
cardiac implantable electronic devices with mixed brand
combinations of generator and lead were compared with the
approved single brand combinations at 1.5 T and 3.0 T. The
generator-lead combinations were selected from three
high-share vendors (Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and St.
Jude) based on the frequency in clinical practice.
Temperature measurements were conducted along with ASTM2182
and ISO10974 at locations corresponding to the right
ventricle, right atrium, the generator edge, and
contralateral of in the ASTM phantom. The results evaluated
by Mann-Whitney's U-test showed no significant difference in
temperature increases between the mixed and approved
combinations.
|
| 11:50 | 5435. |
Improving the patient experience for paediatrics in Magnetic
Resonance Imaging through Play Therapy.
Charlotte Elizabeth Swain1,
Carolyn Costigan1,
and Selene Rowe1
1MRI, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust, Nottingham, United Kingdom Play Therapy has been shown to be a successful alternative for children allowing them to have an MRI scan awake instead of with a general anaesthetic. With funding through local hospital charities, a dedicated Play Specialist List runs once a week to scan predominantly 3-13yr olds. With fun and engaging play methods, it has been possible to acquire diagnostic images in 98% of children scanned. With no risk when compared to a general anaesthetic and a more relaxed atmosphere and process, this has vastly improved the patient experience, for not only the children, but also their parents/carers. |
| 11:50 |
5434.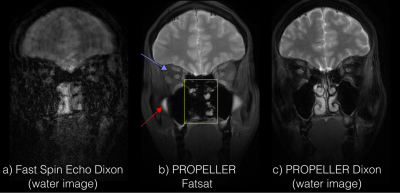 |
Efficient fat suppression and motion correction using a Dixon
PROPELLER sequence with interleaved echoes and asymmetric
readout waveforms
Matea Borbas1,
Mikael Skorpil2,
and Henric Rydén3
1Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden, 2Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, 3Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
A novel fat/water separated Propeller Dixon sequence is
described. Its performance is tested against fatsat.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.