ISMRT Oral
Winning Research Oral Presentations
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 04-09 May 2024 • Singapore

| 15:30 |
5187.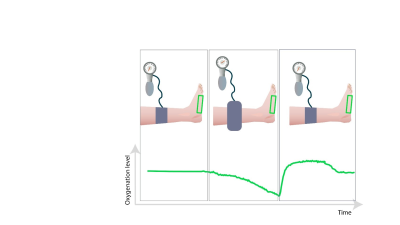 |
MRI-based methods for measuring foot perfusion
Malene Bisgaard1,2,3,
Kim Christian Houlind2,4,
Anne Dorte Blankholm5,6,
Steffen Ringgaard7,
Johnny Christensen3,
and Helle Preht1,3,8
1Health Sciences Research Centre, UCL University College Odense, Odense, Denmark, 2Regional Health Research,, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark, 3Radiology, Lillebealt Hospital, Kolding, Denmark, 4Vascular Surgery, Lillebealt Hospital, Kolding, Denmark, 5Radiology, Aarhus University Hospital,, Aarhus, Denmark, 6Institute of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, 7MR Research Center, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, 8Regional Health Research, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark Motivation: For patients with peripheral artery disease knowing the perfusion in different areas of the foot might have clinical relevance when treating ischemia. Goal(s): The aim was to measure the reliability of five different MR sequences with quantitative parameters for measuring perfusion when imaging the foot. Approach: We used a cuff induced ischemia protocol in a test/retest study of 16 healthy volunteers Results: Flow-sensitive Alternating Inversion Recovery pulsed arterial spin labelling (FAIR) and Blood Oxygenation Level-Dependent (BOLD) sequences had high reliability and were able to distinguish between occluded blood flow and hyperactive response flow Impact: Reliability test of five different MR sequences for quantitative perfusion measurements in the foot. |
| 15:45 |
5188.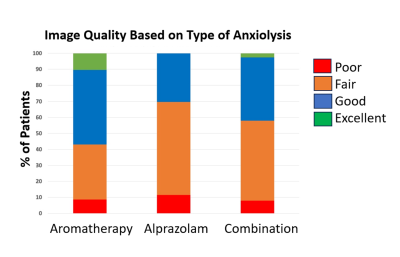 |
Exploring the therapeutic benefits of aromatherapy compared
traditional medicine for patients undergoing Cardiac Magnetic
Resonance Imaging.
Angel G Houston1,
Molly Haberkorn1,
Darcy Loviscek1,
Paul Schoenhagen1,
Danielle Kara2,
Deborah Kwon3,
and Christopher T Nguyen1,2,4,5
1Imaging Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Cardiovascular Innovation Research Center, Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 3Cardiovascular Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 4Cardiovascular Medicine, Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 5Biomedical Engineering, Case Western Reserve University and Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States Keywords: Motivation: Many individuals undergoing MRI scans experience claustrophobia. The resulting anxiety often leads to reduced image quality and even the abandonment of exams. Goal(s): Our goal is to use aromatherapy in a comprehensive stress reduction approach that we’ve developed to help improve MRI image quality, decrease nursing intervention and improve patient experience. Approach: More than 300 patients were involved in retrospective and prospective studies offering aromatherapy and alprazolam for anxiety during Cardiac MRI. Results: Aromatherapy was associated with improved image quality compared to alprazolam and was a strong predictor of reduced scan duration, nursing time, and number of repeat images. Impact: Aromatherapy has the ability to mitigate anxiety during MRI scans for patients with claustrophobia, yielding improved quality images and reduced scan time. As a result, implementation of aromatherapy has the ability to improve patient experience and clinical outcomes. |
| 16:00 |
5189.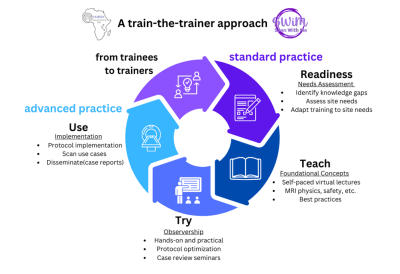 |
Scan With Me (SWiM): A promising train-the-trainer program
tailored for resource-limited settings
Cristian Montalba1,
Abdul Nashirudeen Mumuni2,
Aduluwa Harrison3,
Surendra Maharjan4,
Francis Botwe5,
Marina Fernandez 6,
Abderrazek Zeraii7,
Katerina Eyre8,
Matthias Friedrich8,
Fatade Abiodun9,
Ntobeko Ntusi10,
Tchoyoson Lim11,
Ria Garg12,
Muhammad Umair13,
Hameed Naniwolo14,
Chinedum Anosike15,16,
Farouk Dako17,18,
Sola Adeleke19,
and Udunna Anazodo6,9
1Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Chile, 2Department of Medical Imaging, University for Development Studies, Tamale, Ghana, 3Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 4Department of Radiology & Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN, United States, 5Clinical Imaging Sciences Centre, University of Sussex, Brighton, United Kingdom, 6Consortium for Advancement of MRI Education and Research in Africa (CAMERA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7Biophysics department, Higher Institute of Medical Technologies of Tunis., Tunis, Tunisia, 8Division of Experimental Medicine, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 9Crestview Radiology Ltd, Lagos, Nigeria, 10Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 11National Neuroscience Institute, Singapore, Singapore, 12Department of Internal Medicine, Geisinger Wyoming Valley Hospital, Wilkes-Barre, PA, United States, 13John Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States, 14IRDOCNIGERIA, Lagos, Nigeria, 15Accuread Radiology, Nigeria Ltd, Lagos, Nigeria, 16Warrington and Halton Hospitals National Health Service Foundation Trust, Warrington, United Kingdom, 17RAD-AID International, Chevy Chase, MD, United States, 18Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 19Department of Oncology, Guy's & St Thomas' Hospital, London, United Kingdom Keywords: Motivation: There is a wide discrepancy in MRI accessibility globally, which has created an insurmountable challenge to fulfill the diagnostic healthcare needs of low- and middle- income countries. Goal(s): To train MRI radiographers who can train their peers in a growing network. Approach: The RAD-AID Teach-Try-Use approach was used within 6 weeks to deploy basic to advanced cardiac MRI (CMR) knowledge, followed by expert image acquisition demonstrations, and the use of cases to simulate, analyze and optimize scanner-specific imaging protocols for pathologies. Results: 43 Participants from 16 countries gained practical CMR experience and implemented their own optimized protocols to generate high-quality images. Impact: A sustainable skill set training approach was used to provide expertise to MRI radiographers who will then serve as trainers of their peers in resource-limited settings. Outcome of the training was measured by trainee evaluations and engagement and the high-quality images acquired by participants. |
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.