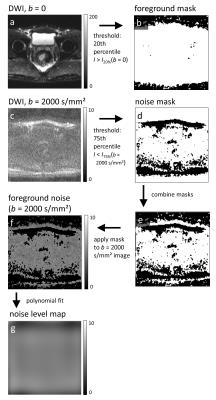
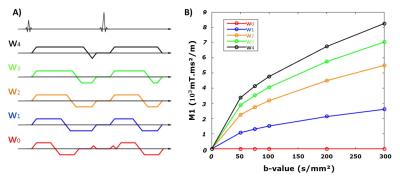
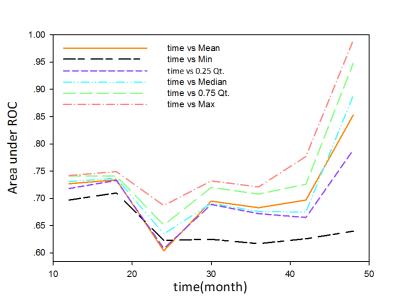
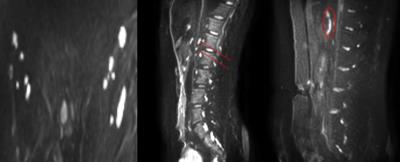
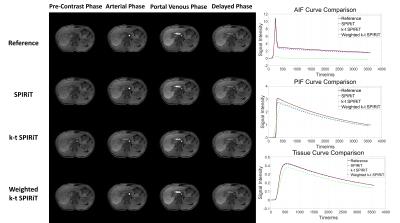
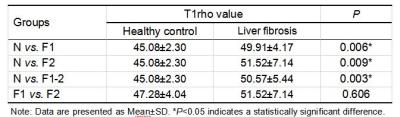
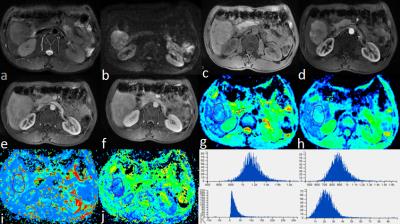
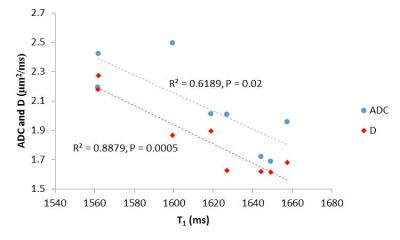
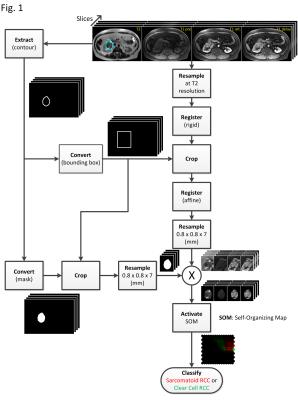
Thoracic MRI-2
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Monday, 24 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
09:15 - 10:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
3307.
 |
97 |
Respiratory motion-resolved MRI of the lung and liver for evaluation of cystic fibrosis 
Alexander B. Hilario T., Eduardo Baum, Alexandre Franco, Li Feng, Marilisa Baldissera, Ricardo Soder, Bruno Hochhegger, Matteo Baldisserotto, Ricardo Otazo
Free-breathing MRI with reconstruction of respiratory phases using the XD-GRASP technique is demonstrated for evaluation of cystic fibrosis patients. A platform for automated data processing is developed for robust utilization in a clinical setting. XD-GRASP is validated in a cohort of 9 patients against the conventional technique.
|
|
3308.
 |
98 |
Optimized 3D ultrashort echo-time lung imaging of young children without sedation 
Wingchi Kwok, Jacqueline Wameling, Mitchell Chess, Clement Ren, Gloria Pryhuber, Jason Woods
Our purpose was to develop an optimized study design for 3D ultrashort TE lung imaging of young children without sedation. Eight preterm born subjects all at age 4 were recruited. Siemens work-in-progress PETRA_D sequence was used with respiratory triggering. Repeated short scans were acquired to reduce motion artifacts. Various techniques, including video watching, practicing lying still at home and gift incentive, were employed to help achieve subject compliance. Five subjects were scanned successfully. The images revealed abnormalities including peribronchial thickening, pneumatocele and atelectasis. Our study design allows the monitoring of lung development and evaluation of lung diseases in young children.
|
|
3309.
 |
99 |
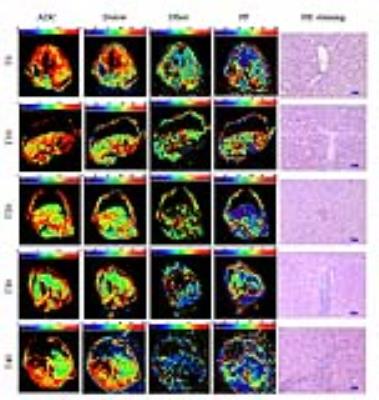
A preliminary study of in-vivo visualization of oxide oxide enhancement in focal inflammatory lesion of lung parenchyma using a 3D radial gradient-echo-based UTE sequence (CODE) - permission withheld
Soon Ho Yoon, Suh-Young Lee, Chanhee Lee, Jinil Park, Jin Mo Goo, Jang-Yeon Park
Dual-echo ultrashort echo-time CODE pulmonary MRI preliminarily succeeded in generating a positive contrast of iron oxide in rabbits with granulomatous lung disease, by using clinically-usable superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles, ferumoxytol, which was hardly achievable via conventional T2* MR sequence. This new pulmonary MR imaging biomarker possibly gives a chance to differentiate a benign inflammatory lesion from malignancy.
|
|
3310.
 |
100 |
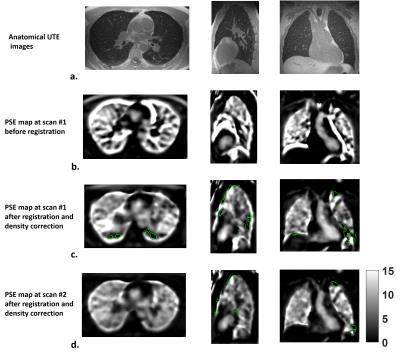
Repeatability of global percent enhancement and regional defect quantification in oxygen-enhanced 3D radial ultrashort echo time MRI - permission withheld
Wei Zha, Stanley Kruger, Kevin Johnson, Robert Cadman, Andrew Hahn, Scott Nagle, Sean Fain
Oxygen-enhanced 3D radial UTE MRI (OE-MRI) shows promise as an alternative to hyperpolarized gas MRI for evaluation of ventilation abnormalities. Ten subjects (2 normal, 2 asthmatics and 6 cystic fibrosis) underwent OE-MRI for multiple scans (test/re-test) during visits separated ≤15 days apart. The intra-subject percent signal enhancement (PSE) maps from OE-MRI were compared for median whole-lung PSE, ventilation defect percent (VDP) and spatial agreement between defects. The results suggest good agreement on two global measures, Median PSE and VDP, with low-to-moderate spatial alignment on the inter-visit segmented defects. Improvement of spatial defect repeatability will be a goal of future work.
|
|
3311.
 |
101 |
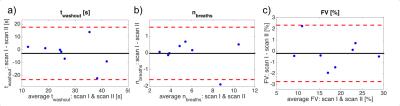
Repeatability of regional lung ventilation quantification using 19F fluorinated gas washout magnetic resonance imaging in free breathing 
Marcel Gutberlet, Andreas Voskrebenzev, Agilo Kern, Till Kaireit, Jens Hohlfeld, Frank Wacker, Jens Vogel-Claussen
Since quantification of regional lung ventilation using 19F fluorinated gas washout imaging in free breathing is feasible even in obstructed lungs, it may improve diagnosis, monitoring and therapy of obstructive lung diseases like asthma and COPD. However, for application in clinical studies the knowledge of the accuracy of this technique is important. Repeatability of the 19F gas washout parameters washout time, number of breaths and fractional ventilation between to scans was assessed in eight healthy volunteers. Due to the excellent repeatability of the number of breaths and fractional ventilation, regional lung ventilation can be accurately quantified using 19F gas washout MRI in free breathing.
|
|
3312.
 |
102 |
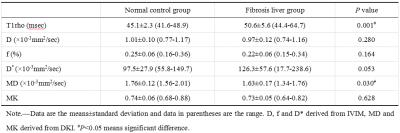
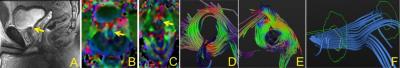
MR Elastography vs. Diffusion-weighted MRI in Characterization of Anterior Mediastinal Solid Tumours - permission withheld
Wei Tang, Ning Wu, Yao Huang
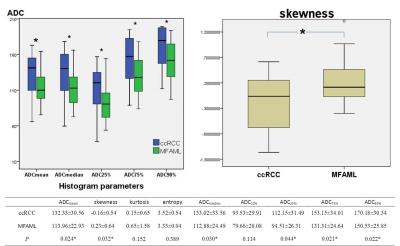
Anterior mediastinal solid tumours were routinely interpreted on CT and MR imaging. However, imaging features of these tumours could be non-specific; evidence suggestive of definitive diagnosis was needed and obtained with invasive procedure of biopsy for some cases. In the present study, we attempted to extent the application of MR elastography to the mediastinum in characterization of anterior mediastinal solid tumours, with the comparison to diffusion-weighted MRI. Thirty-four patients histologically-confirmed with thymic carcinoma in 10, thymoma in 10 and lymphoma in 14 were evaluated. It was found that stiffness value measured on elastogram was significantly higher in thymic carcinoma than that of thymoma and lymphoma. However, measurements of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) were not significantly different among three groups. It was demonstrated that MR elastography reflecting the mechanical properties of tumours can be used to characterize anterior mediastinal solid tumours, particularly in distinguishing thymic carcinoma from lymphoma.
|
|
3313.
 |
103 |
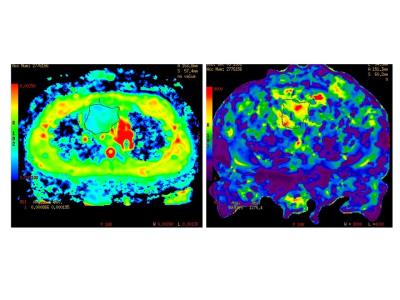
Mapping Vascular Behaviour in Lung Perfusion of two-year old children after Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Repair using Tissue Similarity Maps 
Dimitrios Markellos, Meike Weis, Thomas Schaible, Stefan Schoenberg, Lothar Schad, Frank Zöllner
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH) is associated with lung hypoplasia reflected in decreased pulmonary microcirculation and secondary pulmonary hypertension. Using tissue similarity maps (TSM), Haacke et al. demonstrated mapping vascular behaviour and calculating relative pulmonary blood volume (rPBV) maps in perfusion weighted imaging of the brain. In this study we have investigated the significance of the TSM technqiue for lung perfusion imaging in two-year old children after CDH repair.
|
|
3314.
 |
104 |
Diagnosing Lung Nodules on various MRI Imaging: comparison of T1-Weighted-3D VIBE-dixon sequence and T1-weighted 3D star vibe sequence 
Chuangbo Yang, Nan Yu, Qi Yang, Shaoyu Yu, Youmin Guo, Liya Ma
T1-weighted 3D Star VIBE sequence obtaining scan under free breathing can provide high-resolution imaging. Therefore, our study was to assess the accuracy of various MRI sequences for the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules and to estimate the ability of MRI for display the morphology of pulmonary nodules. We concluded that T1-weighted 3D Star VIBE sequence allow for identification of patients with pulmonary nodules with high detection rate. It can also provide more information of nodules than routine T1-weighted 3D VIBE sequence dose.
|
|
3315.
 |
105 |
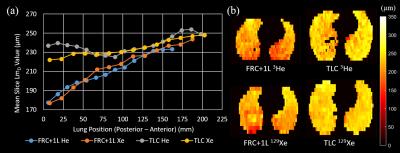
Exploring Lung Inflation Mechanisms with 3D 3He and 129Xe Whole Lung Morphometry Mapping 
Ho-Fung Chan, Juan Parra-Robles, Guilhem Collier, Jim Wild
Alveolar dimensions change with lung inflation, however, there is currently no consensus on whether this change is primarily due to expansion and if alveolar recruitment plays a role. Here, multiple b-value DW-MRI was used to investigate lung inflation mechanisms in-vivo, and 3D 3He and 129Xe whole lung morphometry (LmD) maps were acquired in five healthy volunteers at lung inflation states of FRC+1L and TLC. Decreases in the anterior to posterior gravitational gradient were observed between FRC+1L and TLC with both nuclei. Smaller than predicted LmDvalues at TLC suggests that both alveolar expansion and recruitment may occur during lung inflation.
|
|
3316.
 |
106 |
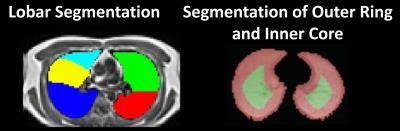
Analysis of Regional Lung Function Detected by Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 MRI in Subjects with Interstitial Lung Diseases 
Kun Qing, Talissa Altes, John Mugler, III, Nicholas Tustison, Kai Ruppert, Jaime Mata, Yun Shim, G.Wilson Miller, Iulian Ruset, F.William Hersman, Borna Mehrad
Previous study showed that hyperpolarized xenon-129 MRI is highly sensitive in detecting functional changes in lungs with interstitial lung diseases (ILD). The degree to which these changes vary regionally in the lung has not been determined, however. In this work, we compared abnormalities in lung function in different regions of the lung, and found significant differences in xenon-129 gas uptake between subjects with ILD and controls. These results support that xenon-129 MRI may provide unique information about lung physiology associated with lung fibrosis.
|
|
3317.
 |
107 |
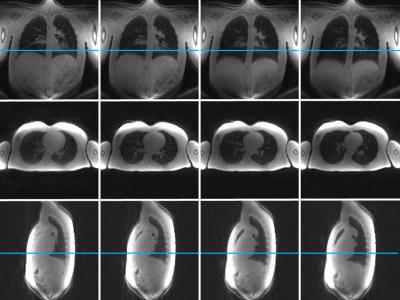
Self-gated ultra-short echo time lung MRI for quantitative ventilation assessment 
Lenon Pereira, Tobias Wech, Andreas Weng, Andreas Kunz, Simon Veldhoen, Thorsten Bley, Herbert Köstler
Self-gated Non-Contrast-enhanced Functional Lung MRI (SENCEFUL) is a technique based on a FLASH sequence that can assess ventilation and perfusion in free-breathing without the use of contrast agents. However, SENCEFUL suffers from the fast T2-induced signal decay in the lung parenchyma and offers no real 3D coverage. Thus, this work presents the use of a 3D ultra-short echo time (UTE) sequence in SENCEFUL MRI for the generation of ventilation-weighted maps.
|
|
3318.
 |
108 |
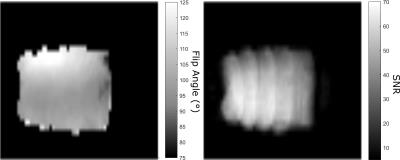
Steady-state Free Precession for Improved Signal to Noise in Lung Ventilation Imaging with 19F Perfluoropropane at 1.5 T 
Adam Maunder, Neil Stewart, Madhwesha Rao, Fraser Robb, Jim Wild
Fluorinated gas MRI is a promising method for pulmonary ventilation imaging that does not require additional polarization equipment. To date, short echo time spoiled gradient echo sequences with long repetition times relative to T1 have been employed for lung ventilation imaging in humans. Here, we present an optimization of steady state free precession sequences for imaging of C3F8 gas in lungs, and demonstrate that image signal-to-noise ratio may be improved by exploiting the short T1, and relatively long T2.
|
|
3319.
 |
109 |
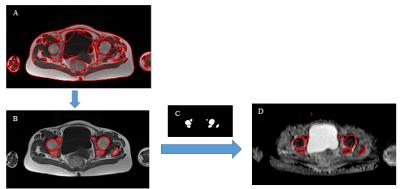
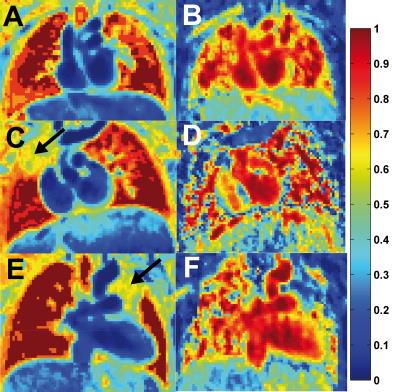
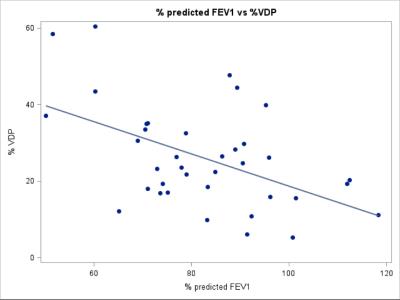
Hyperpolarized Helium-3 MRI Insights into Subtypes of Emphysema in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 
Yanping Sun, Christian Lo Cascio, Pallavi Balte, Jia Guo, Emilia Hermann, Firas Ahmed, Belinda Dsouza, Robert Steiner, Jay Leb, Casandra Almonte, Paul Hughes, Stephen Dashnaw, James Wild, Martin Prince, Emlyn Hughes, Benjamin Smith, Eric Hoffman, R. Graham Barr
To examine the association of ventilation defects on 3He MRI with emphysema subtypes, participants (n=41) between 60 and 85 years of age with 10 or more packyears of smoking were studied. Ventilation defect percentage (VDP) was associated with percent emphysema (r =0.43; p=0.008) and, with borderline statistical significance, extent of visual emphysema (r=0.31; p=0.07). There was no relationship between VDP and extent of centrilobular (p=0.61) or panlobular (P=0.98) emphysema. VDP was associated with extent of paraseptal emphysema (PSE) (r=0.42; p=0.01). These findings suggest that small airways disease may be a component of PSE but not other subtypes of emphysema.
|
|
3320.
 |
110 |
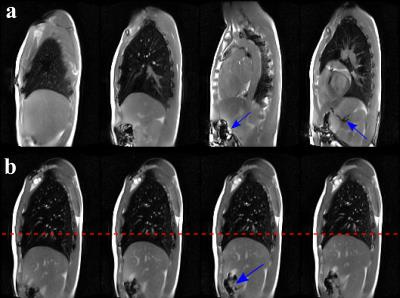
Temporally-resolved volumetric imaging (4DMRI) of the lungs 
Zarko Celicanin, Alina Giger, Grzegorz Bauman, Philippe Cattin, Oliver Bieri
Treatment planning relies on accurate organ motion modeling. Temporally-resolved volumetric imaging (4DMRI) of the lungs using a recently developed ultra fast steady state free precession sequence was attempted. No artifacts were present in the lungs, while image stacking was accurate with no significant image sorting issues.
|
|
3321.
 |
111 |
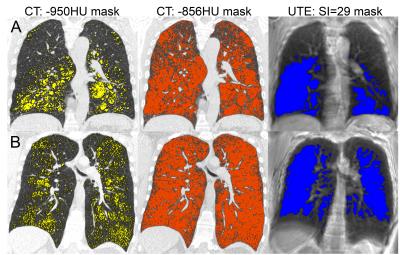
Ultra-Short Echo Time MRI Quantification of Airspace Enlargement in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency: Parenchyma Destruction, Air trapping or Both? 
Heather Young, Dante Capaldi, Khadija Sheikh, David McCormack, Cory Yamashita, Grace Parraga
UTE MRI signal-intensity has not yet been evaluated in young patients with AATD and BPD, where there may be different mechanisms of parenchyma and airway destruction. There is the potential to demonstrate UTE MRI as a quantitative-measurement-tool for longitudinal and treatment-response evaluations in these vulnerable patients. We evaluated UTE MRI and CT using -950HU and -856HU radiodensity-thresholds, and a ‘sliding-threshold’ for the UTE image, identifying regions with low-signal-intensity for multiple threshold values. Regions of normalized UTE signal-intensity <29 suggest airspace enlargement, and demonstrate the potential utility of UTE MRI in quantifying this without ionizing-radiation in AATD and BPD subjects.
|
|
3322.
 |
112 |
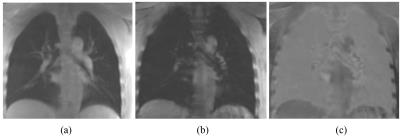
T2* Quantification of the Lung Using 3D Ultrashort Echo Time Cones Sequences - permission withheld
Amin Nazaran, Michael Carl, Yanchun Zhu, Yajun Ma, Eric Chang, Jiang Du
Imaging of the lungs without a contrast agent is a challenging task due to the low SNR. The main challenge stems from the air in the lungs, which causes low proton density and high magnetic susceptibility at interfaces with tissue. Ultra short echo time (UTE) techniques have the potential to acquire high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) images due to their short achievable TEs, much less than 1ms. The lung imaging based on 3D radial UTE sequences were previously reported. In this work, we applied three-dimensional UTE with Cones trajectories (3D UTE-Cones) to quantify lungs’ tissue.
|
|
3323.
 |
113 |
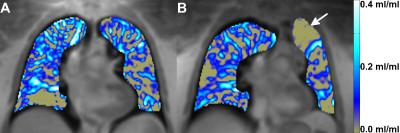
Self-gated Non–Contrast-Enhanced Functional Lung (SENCEFUL) MRI for Evaluation of Endoscopic Lung Volume Reduction in Patients with Lung Emphysema 
Simon Veldhoen, Andreas Weng, Tobias Wech, Andreas Kunz, Stephanie Sauer, Thorsten Bley, Herbert Köstler
Purpose of the study was to assess the feasibility of SENCEFUL ventilation imaging for evaluation of therapy success after endoscopic lung volume reduction. Two patients with lung emphysema who underwent bronchial valve implantation were scanned before and after the procedure using SENCEFUL-MRI. Color-coded lung ventilation maps and quantitative ventilation values were pre- and postinterventionally compared. The first patient showed a ventilation defect corresponding to the location of the implanted valves with reduction of the quantitative ventilation. The second patient did not present such alterations and was later classified as non-responder to therapy. SENCEFUL-MRI detected clinically successful and non-successful outcomes correctly.
|
|
3324.
 |
114 |
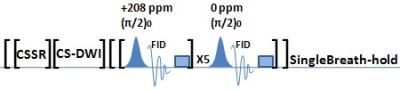
Single Breath CSSR-DWI: A New Method to Simultaneously and Quantitatively Assess the Changes of Respiratory Membrane and Pulmonary Microstructure in Human 
Junshuai Xie, Huiting Zhang, Xiuchao Zhao, Haidong Li, Sa Xiao, Ke Wang, Hao Yang, Xianping Sun, Guangyao Wu, Chaohui Ye, Xin Zhou
The blood-gas exchange function and the pulmonary microstructure are generally affected by the lung inflation levels. Here We developed a new method Single Breath CSSR-DWI to simultaneously quantify the respiratory membrane and the pulmonary microstructure via hyperpolarized 129Xe in a single breath. A new parameter SVRd/g was defined from ADC and SVRd to characterize the ‘%-predicted dissolved SVR’. Human pulmonary functional and structure information were successfully obtained in a single breath via hyperpolarized 129Xe. Compared to the healthy young subjects, SVRd/g of the asymptomatic aged subjects decreases while the size of the pulmonary microstructure increases.
|
|
3325.
 |
115 |
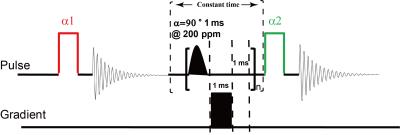
Quantify Pulmonary Gas-Exchange Function with Hyperpolarized 129Xe CEST MRI 
Haidong Li, Zhiying Zhang, Xiuchao Zhao, Yeqing Han, Xianping Sun, Chaohui Ye, Xin Zhou
In this study, the pulmonary gas-exchange function was quantitatively evaluated globally and regionally by hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI using the method of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST). A new parameter, named as pulmonary gas consumption time constant (Toc), was proposed to characterize the gas exchange function. The parameter showed significant difference between the COPD and healthy rats, and we believe it will be a useful parameter in evaluating the pulmonary function.
|
|
3326.
 |
116 |
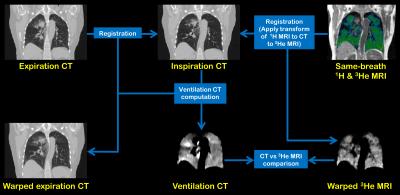
A spatial comparison of CT-based surrogates of ventilation with hyperpolarized Helium-3 & Xenon-129 MRI 
Bilal Tahir, Paul Hughes, Helen Marshall, Neil Stewart, Felix Horn, Guilhem Collier, Graham Norquay, Kerry Hart, James Swinscoe, Matthew Hatton, Jim Wild, Rob Ireland
Synopsis: Image registration of lung CT images acquired at different inflation levels has been proposed as a surrogate method to map lung ‘ventilation’. However, this technique requires validation against established ventilation modalities such as hyperpolarised gas MRI. Here, we develop an image acquisition and analysis strategy to facilitate direct spatial correlation of ventilation CT with both hyperpolarised 3He & 129Xe MRI and apply our method to a cohort of lung cancer patients.
|
|
3327.
 |
117 |
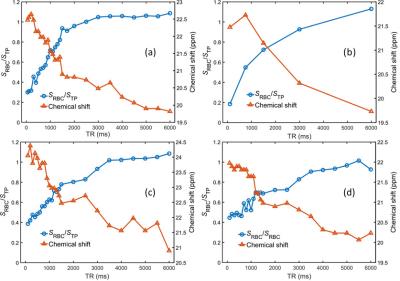
Evaluation of 129Xe-RBC signal dynamics and chemical shift in the cardiopulmonary circuit using hyperpolarized 129Xe NMR 
Graham Norquay, Neil Stewart, Jim Wild
The signal dynamics of hyperpolarized 129Xe in the pulmonary capillaries and veins was evaluated by employing multi-TR pulse sequences, with TR values ranging from 100-6000ms. The ratio of signal from 129Xe dissolved in red blood cells (RBC) and tissue/plasma (TP) was found to increase for longer TRs whilst the 129Xe-RBC chemical shift was observed to decrease with increasing TR. This observed chemical shift difference is unprecedented, and understanding the nature of the underlying mechanisms causing this shift is crucial for future in vivo experiments using 129Xe-RBC chemical shift as a measure of blood oxygenation.
|
|
3328.
 |
118 |
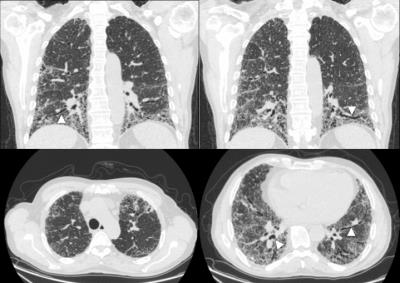
Assessment of acinar destruction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with hyperpolarised 3He gas diffusion-weighted MRI: reproducibility of ADC metrics and correlation with physiological parameters of disease severity. 
Nicholas Weatherley, Ho-Fung Chan, Neil Stewart, Laura Saunders, Guilhem Collier, Graham Norquay, Madhwesha Rao, Laurie Smith, Matthew Austin, Stephen Renshaw, Stephen Bianchi, Jim Wild
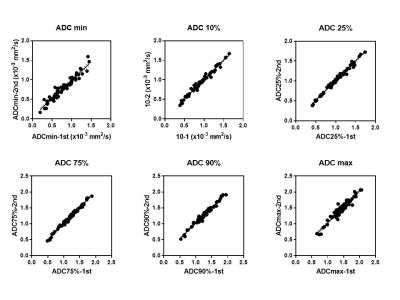
Outcome metrics from diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI) were evaluated for reproducibility and clinical correlation in a cohort of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). It was hypothesized that fibrotic lung tissue in IPF undergoes changes that increase the rate of intra-acinar Brownian diffusion. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) mean, median and histogram metrics are highly reproducible and correlate both quantitatively with regional fibrosis on CT and qualitatively with carbon monoxide transfer coefficient (KCO) from pulmonary function tests. DW-MRI imaging metrics may provide novel insights into microstructural disease severity in IPF and may prove to be a useful non-ionising imaging biomarker of disease.
|
|
3329.
 |
119 |
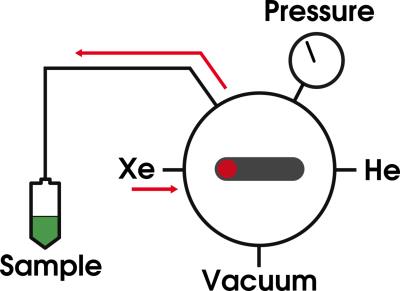
Hyperpolarized xenon by d-DNP using the clinical GE SpinLab polarizer system 
Christian Mariager, Steffen Ringgaard, Jan Ardenkjær-Larsen, Christoffer Laustsen
Hyperpolarized (HP) 129Xe have been demonstrated as a useful probe for magnetic resonance (MR) lung imaging and show promise for in vivo perfusion imaging and brown adipose tissue characterization. Reports of large polarization enhancements for 129Xe using dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) have raised expectations that DNP can be an alternative to the standard spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We show that it is possible to produce HP 129Xe gas using the clinical GE SpinLab polarizer, thus extending the practical use of the system beyond the primary purpose of hyperpolarizing liquid biomolecules.
|
|
3330.
 |
120 |
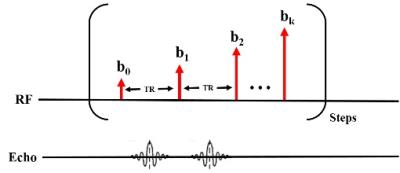
Combination of Variable and Constant Flip Angles for Hyperpolarized 129Xe Multi-b Diffusion MRI in a Single Breath-hold 
Weiwei Ruan, Jianping Zhong, Ming Zhang, He Deng, Yeqing Han, Chaohui Ye, Xin Zhou
To propose a novel flip angle scheme for hyperpolarized gas multi-b diffusion MRI. It combined the variable and constant flip angles and was named as the combination of variable and constant flip angle (CVCFA). Computer simulation was used to systematically compare the proposed flip angle scheme with the common-used flip angle schemes, including the interleaved constant flip angle (ICFA) and the variable flip angle (VFA) schemes. The CVCFA scheme was used for hyperpolarized xenon diffusion MRI to measure the pulmonary morphology in rats, noninvasively. The results showed the CVCFA was suited for the hyperpolarized gas multi-b diffusion MRI.
|
|