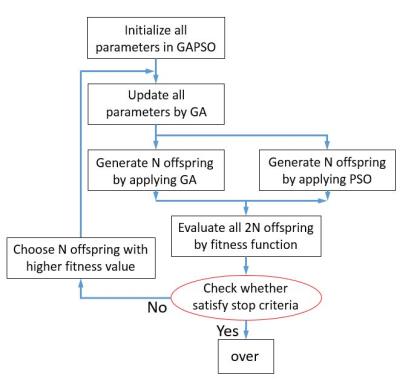
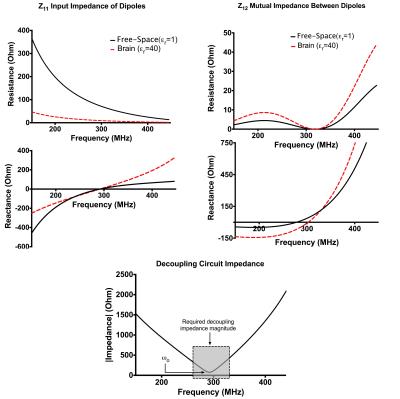
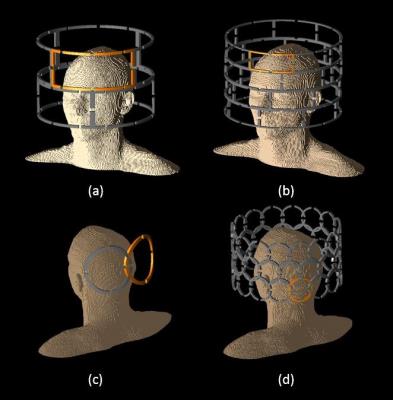
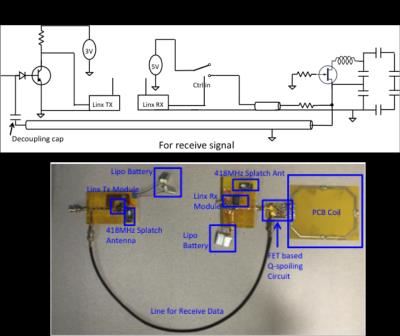
UHF Imaging & Spectroscopy
Electronic Poster
Engineering
Tuesday, 25 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
17:15 - 18:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4399.
 |
73 |
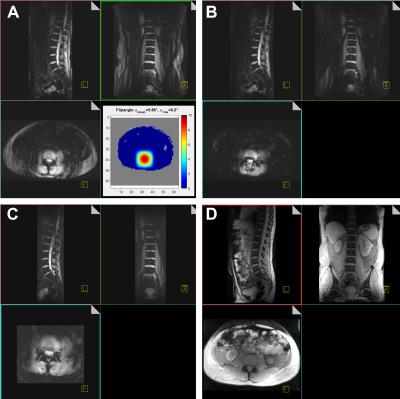
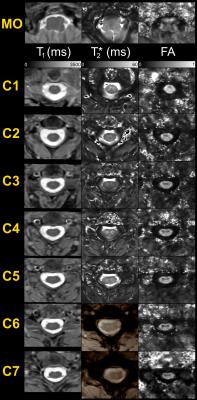
From medulla to lower cervical levels, a multi-parametric quantitative MR investigation dedicated to the diffuse alterations of the spinal cord at 7T: first insights into Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 
Aurélien Massire, Henitsoa Rasoanandrianina, Thorsten Feiweier , Manuel Taso, Aude-Marie Grapperon, Shahram Attarian, Maxime Guye, Jean-Philippe Ranjeva, Annie Verschueren, Virginie Callot
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) may benefit from unique contrasts and high-spatial resolutions provided by ultra-high field brain MRI. This also stands for spinal cord; nevertheless spinal cord imaging at 7T has lagged considerably behind brain investigations until recently. In this work, we propose a multi-parametric quantitative MR imaging protocol (T1, T2*, DTI, CSA), in an acquisition time compatible with clinical research (50min), to comprehensively investigate spinal cord diffuse alterations in neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS. With imaging along the whole cervical cord and medulla, theses multi-parametric acquisitions have the potential to provide new insights for the study of ALS.
|
|
4412.
 |
86 |
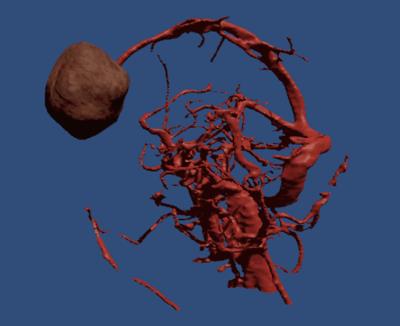
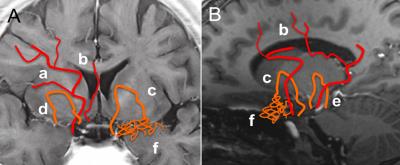
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Collateral Networks in Moyamoya Angiopathy at 7 Tesla - permission withheld
Bixia Chen, Toshinori Matsushige, Markus Kraemer, Philipp Dammann, Sören Johst, Stefan Maderwald, Marc Schlamann, Harald Quick, Mark Ladd, Ulrich Sure, Karsten Wrede
Collateral networks in Moyamoya angiopathy (MMA) have a complex angioarchitecture. Delineation of deeply seated collateral networks (DSCNs) and image quality were prospectively evaluated in 10 patients using 7 Tesla TOF MRA and MPRAGE in comparison with conventional DSA. Seventy DSCNs were detected in DSA, 79 in TOF MRA, and 54 in MPRAGE. Detection of DSCNs was significantly better in TOF MRA than in DSA and MPRAGE. TOF MRA and DSA image quality were comparable, both were better than MPRAGE. Delineation of DSCN pathways in MMA using 7 Tesla TOF MRA was excellent and comparable to DSA.
|
|
4400.
 |
74 |
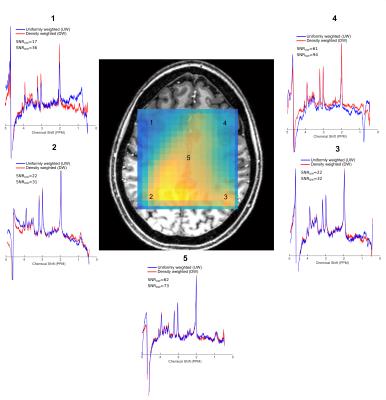
Density Weighted Concentric Rings K-Space Trajectory for 1H MRSI with gradient offset independent adiabatic pulses at 7T 
Mark Chiew, Wenwen Jiang, Peder Larson, Brian Burns, Peter Jezzard, Albert Thomas, Uzay Emir
In this study, we have developed and demonstrated a GOIA-semi-LASER sequence with density-weighted (DW)-concentric rings trajectory (CRT) that performs robustly at 7 Tesla and within a clinically feasible acquisition time. DW-CRT has been validated in a series of phantom experiments and its feasibility assessed in a healthy volunteer with an in-plane resolution of 5×5 mm2. Experiments qualitatively demonstrate the advantage of DW-CRT over uniformly-weighted (UW)-CRT in terms of its improved resolution and reduced contamination of spectra from neighboring voxels.
|
|
4401.
 |
75 |
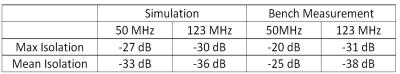
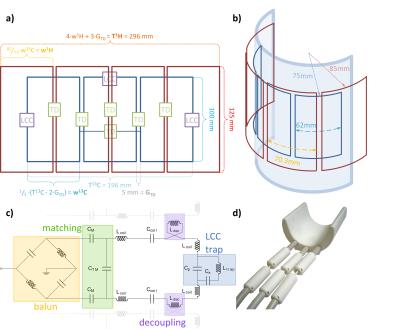
A form-fitted 1H/13C transceive coil array for MR spectroscopy in the human calf muscles at 7 T: initial results 
Sigrun Goluch, Roberta Frass-Kriegl, Michael Pichler, Martin Gajdošík, Juergen Sieg, Ewald Moser, Martin Meyerspeer, Martin Krššák, Elmar Laistler
Carbon-13 (13C) MR spectroscopy (MRS) requires RF coils enabling acquisition at two different Larmor frequencies, namely at the 1H frequency (f1H=297.2 MHz) for scout imaging, B0 shimming and proton decoupling, as well as at the 13C frequency (f13C=74.7 MHz) for acquisition of the carbon spectra at 7T. In this work we present preliminary data on the development of a dual tuned 13C/1H coil array for calf muscle studies at 7 T, including simulation, bench and MR measurements in a glucose phantom.
|
|
4402.
 |
76 |
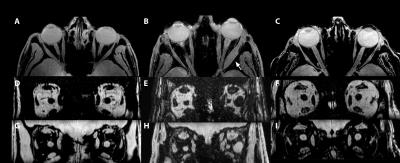
Quantitative MRI of extra-ocular muscles in the clinical evaluation of systemic diseases 
Luc van Vught, Robert de Meel, Jedrzej Burakiewicz, Stijn Genders, Martine Jager, Irene Notting, Jan Verschuuren, Hermien Kan, Jan-Willem Beenakker
Current diagnostic tools fail to accurately assess the condition of the eye muscles and orbital fat in ocular diseases. We have developed a high-resolution 7 Tesla quantitative MRI-protocol of the eye and evaluated its clinical value for Graves' orbitopathy and myasthenia gravis. The scan protocol proved to be robust against eye-motion and extra-ocular muscles were easily segmented from the orbital fat. Patient data showed elevated muscle fat fractions for both conditions compared to healthy subjects. Since the method quantifies the condition of the tissues, which otherwise can only be assess via an invasive biopsy, it potentially is an efficient technique to assess treatment response.
|
|
4403.
 |
77 |
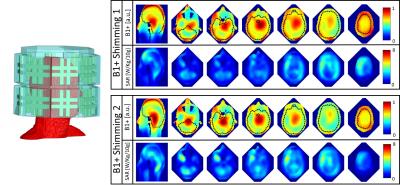
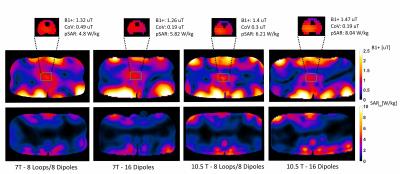
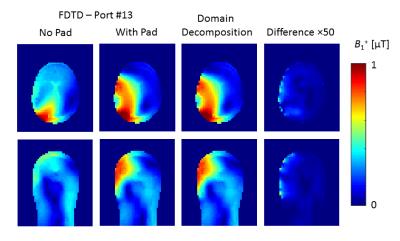
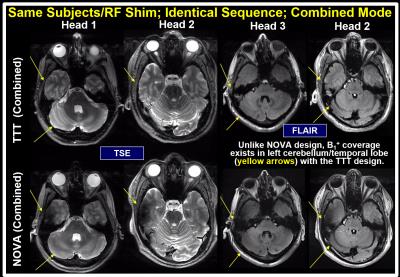
Towards Homogeneous 7T Neuro Imaging: Findings and Comparisons between 7T TTT and NOVA RF Coil Systems 
Tamer Ibrahim, Tales Santini, Shailesh Raval, Narayanan Krishnamurthy, Sossena Wood, Jung-Hwan Kim, Yujuan Zhao, Xiaoping Wu, Essa Yacoub, Howard Aizenstein, Tiejun Zhao
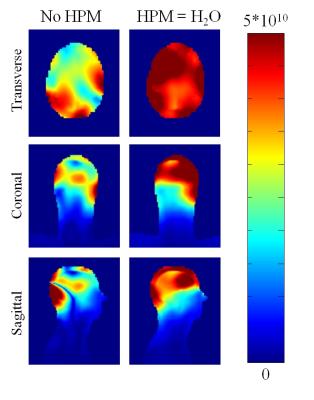
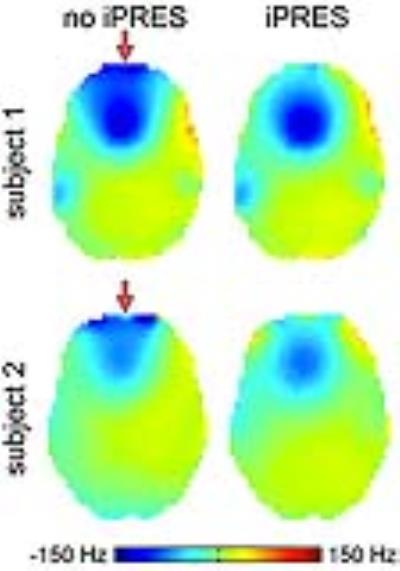
Several major obstacles still face neuro UHF imaging including scanning and preparation time for every subject (for TX arrays) and RF intensity limitations due to increased local/global power deposition. The solutions provided and compared in this work represent non-subject specific configurations (combined mode NOVA coil system, PTX NOVA coil system operating in quadrature, and combined mode 16Tx/32Rx Tic-Tac-Toe coil system) and subject specific configurations (PTX NOVA coil system RF-shimmed for each subject). Experimental results shows significant drop in the B1+ field intensity in the left temporal lobe and cerebellum in the NOVA coil systems, issue alleviated with the Tic-Tac-Toe design.
|
|
4404.
 |
78 |
A Feasibility Study on Bilateral Monopole Antenna with Two Common Grounds for 7T MRI 
Han-Joong Kim, Hyunwoo Song, Sang-Doc Han, Phil Heo, Donghyuk Kim, Yeonjin Choi, Kyoung-Nam Kim
In this study, a bilateral monopole antenna was proposed to have ring element of existing ring-monopole as common ground and to consist of two interlocking monopole antennas along z-axis to improve lopsided |B1| field toward the ground plate. Geometry of the proposed bilateral monopole antenna was optimized with EM simulation then optimized antenna was compared with a transceiver array coil and a birdcage coil for quality verification. Even with worse power consumption, the proposed bilateral monopole antenna can be an alternative for existing RF coils such as transceiver array coil and birdcage coil due to its improved |B1+| field uniformity.
|
|
4405.
 |
79 |
Unified Proton and Fluorine Imaging of Small and Low Spin Density Samples at a Human Whole-Body 7 T MRI 
Christian Bruns, Tim Herrmann, Markus Plaumann, Chang-Hyun Oh, Chulhyun Lee , Suchit Kumar, Johannes Bernarding
In order to provide a system, which allows imaging of 19F MR contrast agents, an in-house-built 19F/1H transmit/receive system for 7 T was successfully tested in a human whole-body 7 T MRI system. This system enables the measurement of concentrations of 1.85 mM. For this approach we used a 19F tuned coil which provided still enough signal gain at the proton frequency to allow 1H imaging for comparison. This showed the possibility of using 19F as contrast agents with a quite simple coil design in comparison to other dual tuned approaches.
|
|
4406.
 |
80 |
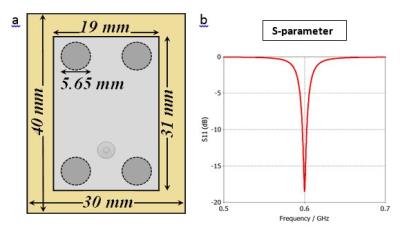
Newly Designed Miniaturized Patch Antenna with High Dielectric Material Plugs 
Gangchea Lee, Navid Gandji, Seokwon Jung, Elena Semouchkina, Michael Lanagan, Thomas Neuberger
High performance Radio Frequency resonators (RF resonators) produce strong and homogeneous magnetic fields. Due to their large sizes, patch antennas have hardly been considered to be used as RF resonators in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), especially at high fields. In this work, a newly developed miniaturized patch antenna with high dielectric material plugs was designed, simulated, built and tested at 14.1 T. The simulated and experimental magnetic fields were compared to confirm the performance of the fabricated patch antenna as a RF resonator for MRI.
|
|
4408.
 |
82 |
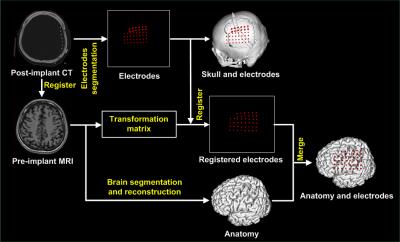
Co-localization of individual neuroanatomical structures and intracranial electrodes to assist brain mapping for pre-surgical evaluation of epilepsy - video not available
Syu-Jyun Peng, Yue-Loong Hsin
We proposed a method to precisely visualize subdural strip and grid electrodes in relation to underlying Brodmann’s area labeled cortical gyration. We transformed a reference brain labeled with Brodmann’s areas to match individual brain. Then we registered the digitalized electrodes from post-implant CT onto the anatomically labeled brain MRI.
|
|
4409.
 |
83 |
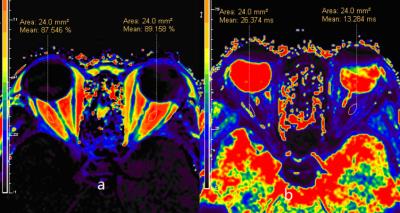
Characteristics of fat in orbits of patients with early-stage hyperthyroidism - video not available
Huajie Jiao, Rongrong Zhu, Kaining Shi, Yong Yang, Weiheng He
Summary: Exophthalmos caused by muscle thickening and fat increasing in orbit is the typical symptom in hyperthyroidism, which impairs multiple systems as the auto-immune disease. From this study, we found the increase of percentage of fat and T2* value using the fat quantification analysis package, which indicate the accumulation and differentiation of fat-oriented cells, inflammation cells infiltration and collagen mucous change. Therefore, the characteristics of fat change in orbit can be evaluated by the transverse six-echo proton density fat fraction (PDFF) sequence (mDIXON-quant) technique in early-stage hyperthyroidism without significant manifestation of eyes.
|
|
4407.
 |
81 |
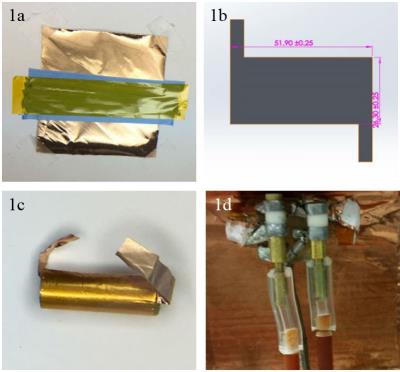
Multi Scroll Coil Setup for Simultaneous Acquisition of MR Microscopy Data of 3D Printed Cells 
Gangchea Lee, Jeongin Choi, Eberhard Munz, Ibrahim Ozbolat , Michael Lanagan, Thomas Neuberger
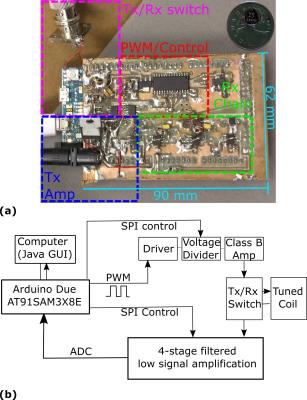
High resolution, and high Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) images in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) require long imaging times. In this work a setup for two separate shielded scroll coils with a common gradient and magnet was introduced to produce two independent three dimensional MRI data sets for MR microscopy. The RF coils and shields were designed, fabricated, and tested. 3-D printed cell samples were imaged using the fabricated set up. Overall, two samples could be acquired with a larger field of view and a similar SNR in the same time compared to a single sample in a solenoid.
|
|
4410.
 |
84 |
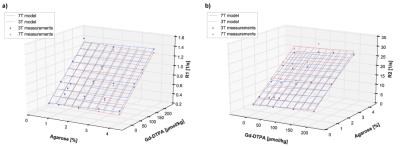
Human brain tissue equivalent MRI phantom for well defined T1 and T2 times at 3 and 7 Tesla 
Michael Woletz, Sigrun Goluch, Allan Hummer, Christian Windischberger
Tissue-equivalent phantoms with well-defined T1- and T2-relaxation behaviour are often required for sequence optimisation and quality control purposes. Based on numerous T1 and T2measurements at 3T and 7T with varying concentrations of Agarose and gadopentetate dimeglumine (Magnevist), we herein present a formula for creating phantoms with T1-values between 700 ms and 3000 ms and T2-values between 30 ms to 250 ms at both field strengths.
|
|
4411.
 |
85 |
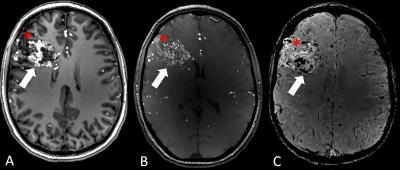
Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Arteriovenous Malformation Architecture at 7 Tesla - permission withheld
Bixia Chen, Toshinori Matsushige, Sören Johst, Stefan Maderwald, Lale Umutlu, Ulrich Sure, Harald Quick, Mark Ladd, Karsten Wrede
General advantages of ultra-high-field MRI at 7 T in cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVM) imaging have been shown recently. This prospective clinical study (10 adult patients) aims to evaluate signal characteristics of AVM feeders, nidus and drainage using 7 T MRI (TOF, MPRAGE, SWI). AVM feeders, nidus and drainage were evaluated by 2 raters. Additionally, AVMs were segmented manually and signal intensity histograms were calculated for the extracted feeders, nidus and drainage, respectively. As previously shown, 7 T MRI has excellent imaging results regarding vessel delineation in AVMs. However, identification of the AVM architecture remains challenging due to signal heterogeneity.
|
|
4413.
 |
87 |
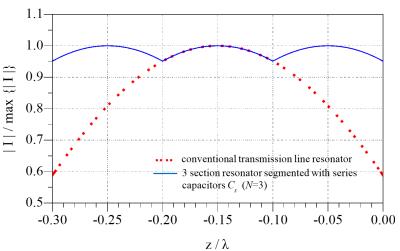
Microstrip Resonator for High Field MRI with Capacitor-Segmented Strip and Ground Plane 
Vitaliy Zhurbenko, Vincent Boer , Esben Petersen
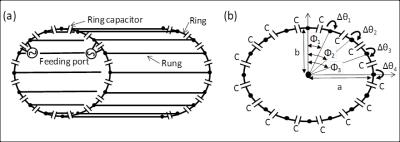
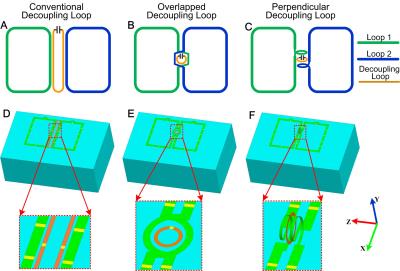
High field MRI coils are often based on transmission line resonators. Due to relatively short wavelength of RF fields, such coils produce uneven field patterns. Here we show, that it is possible to manipulate magnetic field patterns of microstrip resonators in both planes (sagittal and transverse) segmenting stripe and ground plane of the resonator with series capacitors. The design equations for capacitors providing symmetric current distribution are derived. The performance of two types of segmented resonators are investigated experimentally. To authors’ knowledge, a microstrip resonator, where both, strip and ground plane are capacitor-segmented, is shown here for the first time.
|
|
4414.
 |
88 |
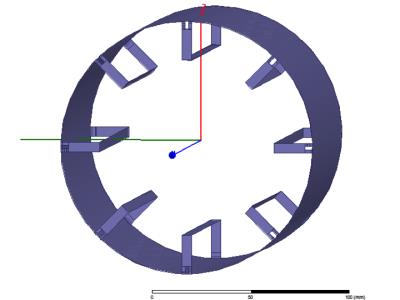
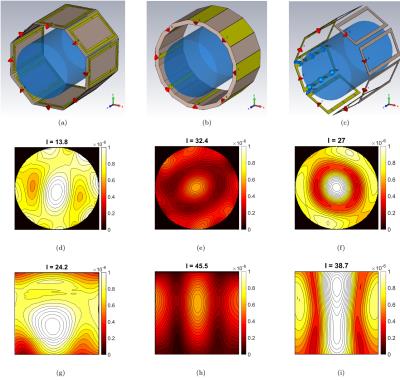
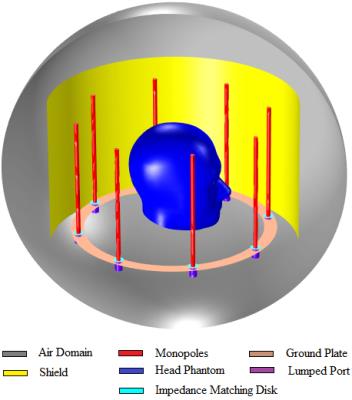
Monopole Antenna Array for UHF Magnetic Resonance Imaging 
A S M Zahid Kausar, David Reutens, Ewald Weber, Viktor Vegh
Birdcage coils have a number of limitations, especially at ultra-high field. Monopole antenna arrays have been proposed as an alternative to birdcage coils, as the design is simpler and they do not use capacitors. We evaluated the potential of using monopole arrays for 3T and 7T MRI brain scans. To be able to benchmark performance, we compared the field produced by the monopole array with the field produced by the birdcage coil. We show that monopole arrays can potentially achieve better field homogeneity and sensitivity than the birdcage coil. We fabricated a monopole array and demonstrated decoupling between individual monopoles.
|
|
4415.
 |
89 |
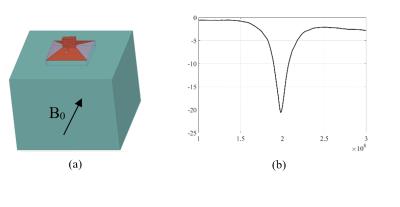
The TEM horn: A new array element for high-field imaging - permission withheld
Atefeh Kordzadeh, Nicola De Zanche
This abstract introduces the TEM horn antenna as an efficient element for imaging the human body at high fields. The horn was designed for 200.4 MHz, simulated in HFSS adjacent to a torso-size phantom, and fabricated using 3-D printing. Transmit/receive imaging measurements were performed at 4.7T. Flip angle maps are compared to the simulation results.
|
|
4416.
 |
90 |
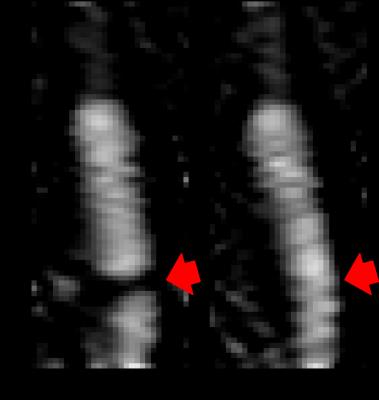
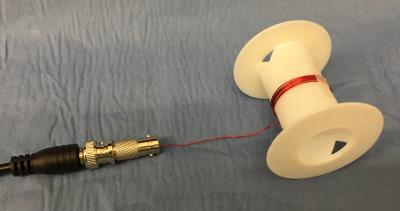
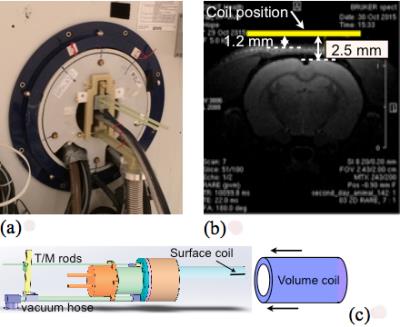
34 µm Isotropic Resolution MRI of Rat Brain using 55K cryo-probe - permission withheld
Kurt Bockhorst, Jarek Wosik, Ponnada Narayana
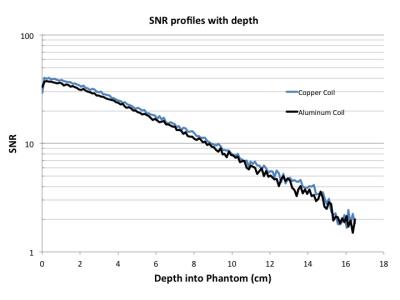
We report on the performance and development of a 300-MHz (7 T) cryogenic receive- only surface coil for MRI of rat brain. Practical performance limits of the cryo-coil were tested such as SNR gains at 55 K for a 19 mm in diameter Cu coil and its frequency stability over long (up to a few days) scans. 3D-RARE isotropic images of ex-vivo rat brain up to 512 slices with outstanding isotropic resolution of 34 μm were acquired showing structural details not seen with conventional small animals coils. In addition, a comparison of such images with matching histological plates is discussed.
|
|
4417.
 |
91 |
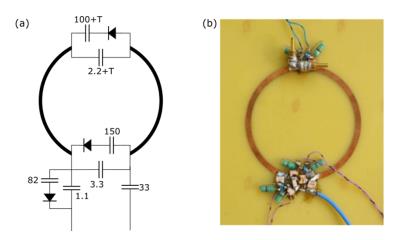
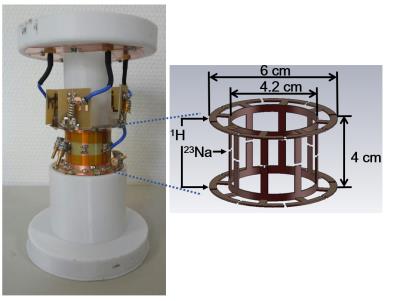
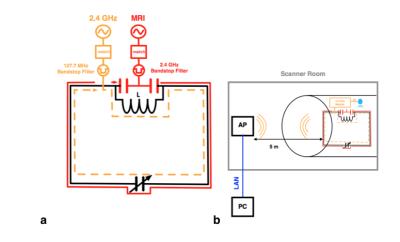
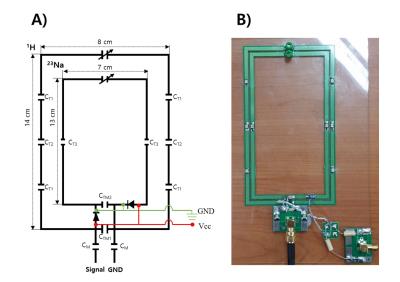
A simple frequency selectable method controlled by PIN diode in the double layered multi-nuclei RF coil at 7T 
Sang-Doc Han, Hyunwoo Song, Phil Heo, Han-Joong Kim, Donghyuk Kim, Yeonjin Choi, Yeunchul Ryu, Kyoung-Nam Kim
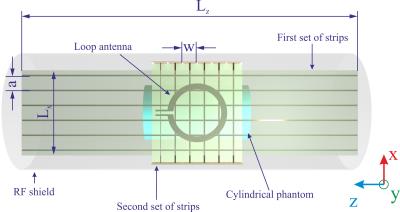
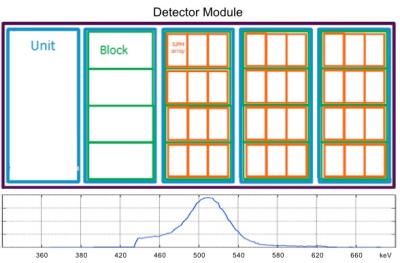
With the facilitated approach of ultra-high frequency (UHF, over 7T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, multi-nuclei (MN)-MRI can be regarded as one of critical means for diagnose due to its capability of acquiring non-invasive metabolic information1, 2. In this study, a radiofrequency (RF) coil that can selectively receive two nuclei signals, the proton (1H) and the sodium (23Na), by controlling PIN diodes is proposed. Since 1H images show clear anatomical structure where 23Na show critical in-vivo metabolisms, acquired MN magnetic resonance (MR) images using the proposed MN RF coil have capabilities to assist diagnose visually3.
|
|
4418.
 |
92 |
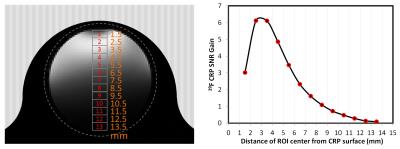
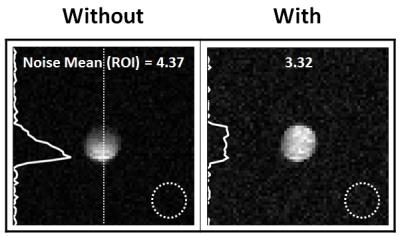
Improvement of Magnetic Field Uniformity of 19F Imaging using the Inductive Coupling at 7.0T 
Bu Park, Sunder Rajan, Joe Murphy-Boesch, William Koch, Charity Stagg, Brent McCright
Numerical simulations and experimental verification of the feasibility are shown to improve B1 uniformity of a commercial 19F RF coil with addition of a secondary resonator using inductive coupling without changing the RF coil at 7.0T animal MRI. The designed resonator was placed on the opposite side of the imaging object from the 19F surface coil to improve the field uniformity. Numerical simulations and related experiments using a 19F phantom show significant improvement of |B1+| and image uniformity, i.e., about 26%. The mouse leg image of 19F/1H with the designed resonator is shown as an example of potential pre-clinical applications.
|
|
4419.
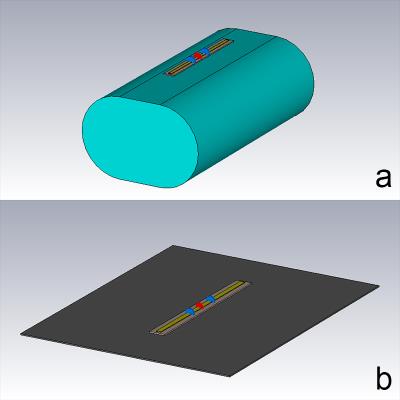 |
93 |
A method to experimentally assess “coil loss” of a dipole antenna for Ultra-High-Field (UHF) MRI 
Gang Chen, Christopher Collins, Daniel Sodickson, Graham Wiggins
At clinical field strengths, the contribution of coil noise is often characterized by the Q-ratio, the ratio of the loaded Q and unloaded Q. Because of the inconsistent contribution of radiation loss and frequency drift in unloaded and loaded cases, it is difficult to characterize the body noise dominance of a dipole antenna by conventional Q ratio at 7T. Here we propose a new approach using a measure of Q when a dipole antenna is well shielded. The shielded/loaded Q ratio estimates the relative noise contribution from coil loss, similar to unloaded/loaded Q ratio for surface coil at low frequencies.
|
|
4420.
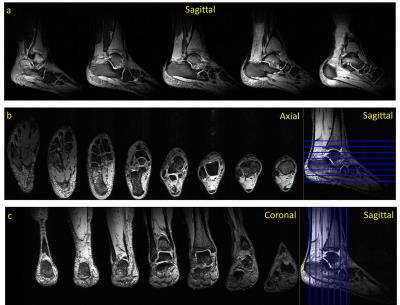 |
94 |
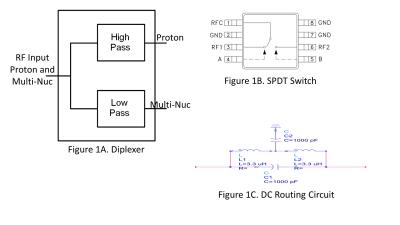
A new RF coil for foot and ankle imaging at 7T MRI 
Tales Santini, Junghwan Kim, Sossena Wood, Narayanan Krishnamurthy, Shailesh Raval, Tamer Ibrahim
7T Foot and ankle has been previously explored1. A four-channel Tic-Tac-Toe (TTT) transmit-only (Tx-only) array2,3 and a four-channel receive-only array were developed and combined to demonstrate the feasiability of high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) foot and ankle imaging at 7T MRI. The experimental measurements of magnetic field distribution responsible for excitation (B1+) is in agreement with the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulations and the SAR is within the FDA safety limits for the entire lower leg and foot (peak SAR ~ 7W/Kg/10g of tissue, average SAR ~ 1W/Kg/10g of tissue per continuous average field B1+ = 1.97uT). In-vivo proton density TSE and T2DESS images were acquired.
|
|
4421.
 |
95 |
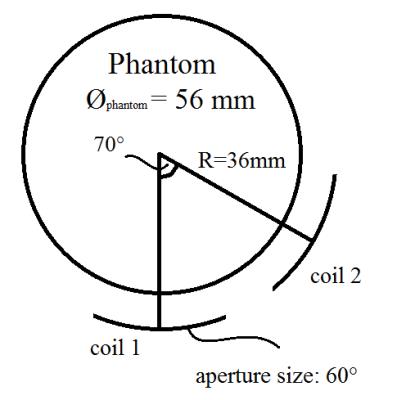
Improving Image Quality by Adjusting Relative Phases of Channels with a Two-element Rotating Coil Array at 9.4T 
Mingyan Li, Ewald Weber, Jin Jin, Yasvir Tesiram, Thimo Hugger, Simon Stark, Feng Liu, Sven Junge, Stuart Crozier
This work investigates the feasibility of incorporating an additional RF element to the rotating RF coil (RRFC) to improve imaging performance. The transmit profiles of the two-element rotating coil array were optimised by adjusting the interference patterns formed by two channels with varied relative phase. Combined with the previously developed rotating imaging scheme, an optimal relative phase was determined to produce an image uniformity of 93%.
|
|
4422.
 |
96 |
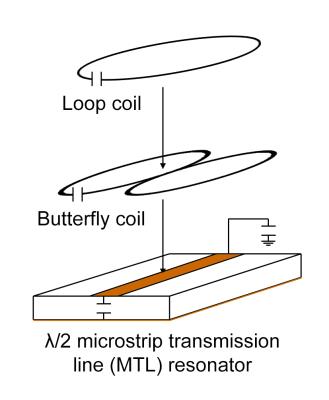
A Compact Planar Triple-Nuclear Coil for Small Animal 1H, 13C, and 31P Metabolic MR Imaging at 14.1 T 
Andrew Leynes, Yiran Chen, Subramaniam Sukumar, Duan Xu, Xiaoliang Zhang
The development and test of a triple-nuclear surface coil for simultaneous 1H, 13C, and 31P small animal imaging at 14.1 Tesla.
|
|