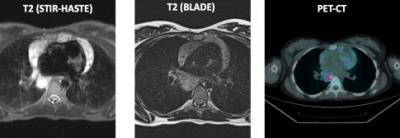
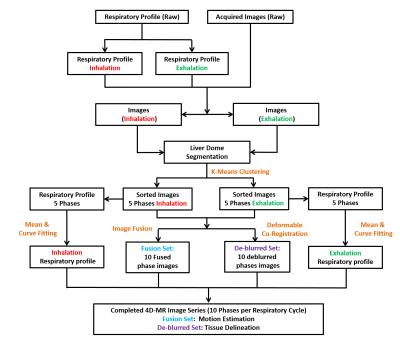
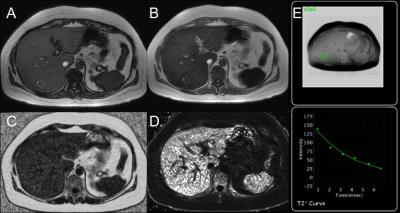
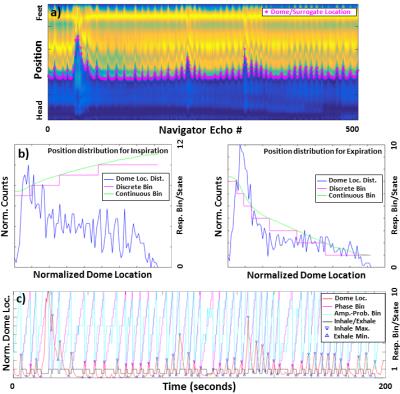
Gastrointestinal MRI
Electronic Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Wednesday, 26 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
14:45 - 15:45 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4972.
 |
55 |
Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging using Non-contrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography using Balanced Steady-State Free-Precession Sequence and Time-Spatial Labeling Inversion Pulse: Measuring Left Gastric Vein Flow Velocity to Predict Esophageal Varices Development and Rupture - permission withheld
Akihiro Furuta, Hiroyoshi Isoda, Shigeshi Kohno, Koji Tokunaga, Ayako Ono, Rinpei Imamine, Rikiya Yamashita, Shigeki Arizono, Aki Kido, Naotaka Sakashita, Kaori Togashi
LGV flow velocity is clinically important to foresee esophageal varices development and rupture. But it is difficult to measure it's velocity exactly by echo or only phase contrast MRI (PC-MRI). To measure LGV flow velocity, 2D PC-MRI were set perpendicularly across vessel segments in the cross-sectional slice position determined from 3D selective visualized LGV using non-contrast-enhanced MRA with balanced steady-state free-precession sequence and time-spatial labeling inversion pulse. LGV flow velocity of all subjects could be measured exactly. This method is useful to measure LGV flow velocity.
|
|
4973.
 |
56 |
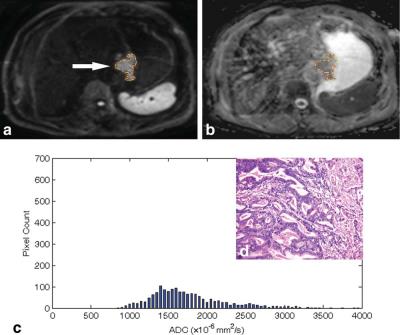
Assessment of Histological Differentiation in Gastric Cancers Using Whole-Volume Histogram Analysis of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps 
Zhengyang Zhou, Song Liu, Jian He, Weibo Chen
Seventy-eight patients with gastric cancer were underwent MRI to investigate whether the histogram analysis of the entire tumor volume in ADC maps could differentiate between histological grades. A series of histogram parameters were calculated and correlated with the histological grade of the surgical specimen. There were significant differences in the 5th, 10th, 25th, and 50th percentiles, skew, and kurtosis between poorly and well-differentiated gastric cancers. There were correlations between the degrees of differentiation and histogram parameters, including the 10th percentile, skew, kurtosis, and max frequency. Histogram analysis of the ADC maps can be useful in differentiating between histological grades.
|
|
4974.
 |
57 |
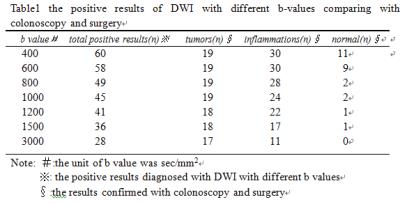
Diffusion-weighted MR Enterography imaging of the ileocecal segment: optimizing b-value for visually differentiating inflammatory and neoplastic lesions 
Hao Yu, Daoyu Hu, Yaqi Shen, Zhen Li, Jianjun Li, Zi Wang, Yanchun Wang
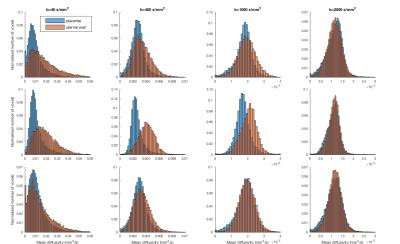
To evaluate the ability of conventional MR Enterography (MRE) including coronal and axial T1/T2 weighted imaging and Diffusion-weighted imaging with different b-values(b=400,600,800,1000,1200,1500,3000 sec/mm2)to visually illustrate inflammatory lesions and neoplastic lesions in the ileocecal region comparing with colonoscopy or surgical results.As a result,MRE and DWI were capable of revealing the lesions in the ileocecal segment. DWI was superior to detect lesions especially inflammations comparing with conventional MRE, and the optimal b value of DWI for MRE was 800 sec/mm2 at 3T. Hyperintensity of ileocecal lesion on DWI with high b(?1000 sec/mm2) value wes more favor for tumor-like lesion.
|
|
4975.
 |
58 |
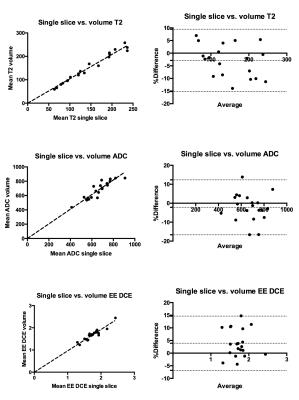
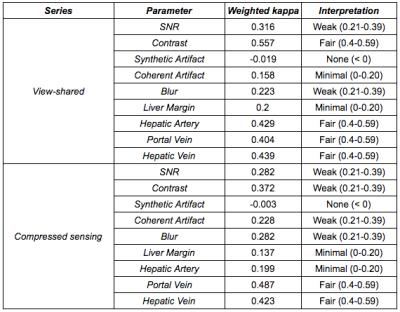
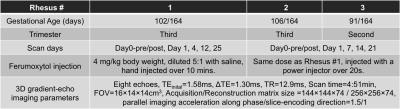
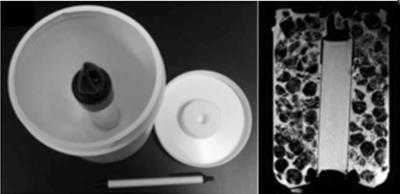
Ultra-fast abdominal imaging with high parallel-imaging factors: Comparative study of a 60-channel receiver coil with the standard coil set-up 
Ahmed Othman, Petros Martirosian, Wilhelm Horger, Jakob Weiss, Jana Taron, Karsten Jahns, Konstantin Nikolaou, Mike Notohamiprodjo
In this study, we evaluated a novel 60-channel coil setup for ultra-fast abdominal imaging using high PAT factors in a phantom, in healthy volunteers and in patients. We found that the 60-channel coil-setup is superior to a conventional 30-channel coil-setup yielding higher SNR and superior image quality and enabling ultra-fast image acquisition with diagnostic image quality.
|
|
4976.
 |
59 |
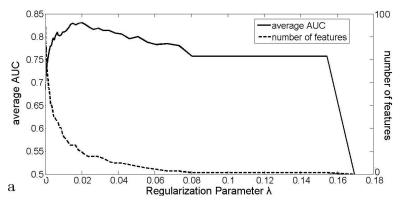
Radiomics Model for Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Rectal Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemoradiatherapy Therapy 
Haitao Zhu, Xiaoyan Zhang, Xiaoting Li, Yanjie Shi, Huici Zhu, Yingshi Sun
Preoperative evaluation of lymph node metastasis in locally advanced rectal cancer remains a problem especially after neoadjuvant chemoradiatherapy treatment (NCT). This study proposed a MRI-based radiomics method to predict lymph node involvement in rectal after NCT. Beside the features from the tumor, features from the lymph nodes were also included for the construction of the radiomics model to increase the accuracy of prediction. 10-fold cross-validation among 300 patients produced ROC with average AUC=0.78. Independent validation with 118 patients produced ROC with AUC=0.81.
|
|
4977.
 |
60 |
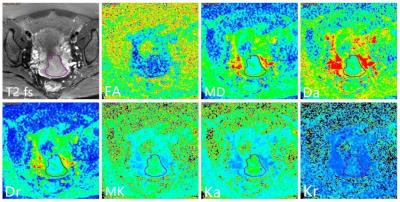
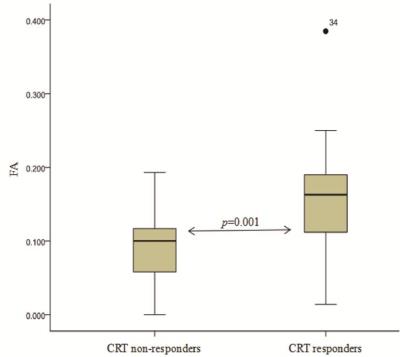
Pretreatment diffusion kurtosis imaging for predicting the response of locally advanced rectal cancer to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy 
Hongliang Sun, Yanyan Xu, Kaining Shi, Wu Wang
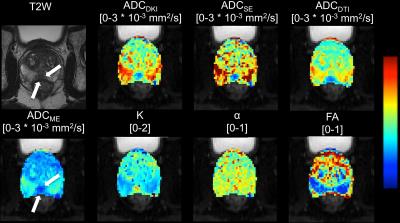
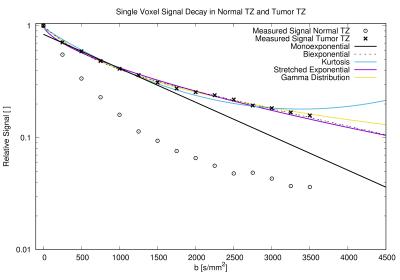
Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) is an emerging technique, which could reflect restricted water diffusion within the complex microstructure of most tissues based on non-Gaussian diffusion model. It has been reported that DKI was used in central system diseases, tumor grade, even assessment of treatment response. However, there is limited research reported about the clinical application of DKI in rectal cancer, and the value of DKI in monitoring rectal cancer treatment was still unclear.
|
|
4978.
 |
61 |
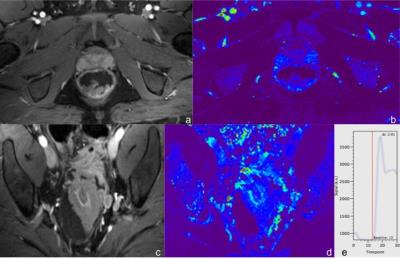
Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Imaging of the Rectum Using Golden-Angle Radial Sparse Parallel MRI (GRASP): Initial Experience and Comparison to a Conventional Approach Using Time-resolved Angiography With Interleaved Stochastic Trajectories (TWIST). 
Daniel Hausmann, Jing Liu, Philipp Riffel, Johannes Budjan, Robert Grimm , Tobias Block, Stefan Schoenberg, Ulrike Attenberger
MR perfusion images to discriminate between normal rectal wall and rectal cancers with less variance of perfusion values and superior image quality compared to conventional TWIST-Angiography can be generated using time-resolved free-breathing MRI with continuous golden-angle radial sampling and iterative reconstruction (GRASP). Additional morphologic assessment (“one-stop-shop”) with high spatial resolution, artifact-insensitive, multiphase, contrast-enhanced imaging may increase accuracy and diagnostic confidence of the examination.
|
|
4979.
 |
62 |
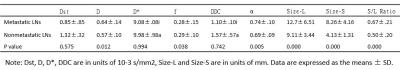
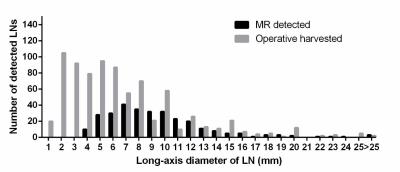
The Limitation in Predicting Lymph Nodes Stage by Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging on the Criterion of Size with Histopathological Analysis as Reference - permission withheld
Caizhen Feng, Jin Cheng, Jing Wu, Gongwei Wang, Yingjiang Ye, Yi Wang
In spite of LN status is critical to the prognosis of patients with gastric cancer, MDCT and MRI cannot accurately assess metastatic LNs prior to surgery.In our study, 802 LNs of 30 patients with gastric carcinoma were harvested.during D2 lymphadenectomy. Only 36.7% (295/802) LNs were detected on preoperative MRI.. 31.5% (217/688) LNs (<8mm) were identified as malignant by pathology, whereas, 44.7% (51/114) LNs (≥8mm) were defined as metastatic. Forty-one metastatic LNs (19%, 41/215) with(?3mm) were found in 7 patients (23.3%, 7/30) and caused N stage upstaging in 3 patients, which could not be detected by MRI.
|
|
4980.
 |
63 |
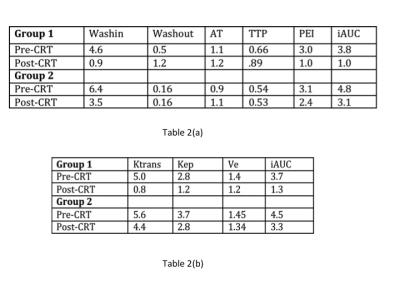
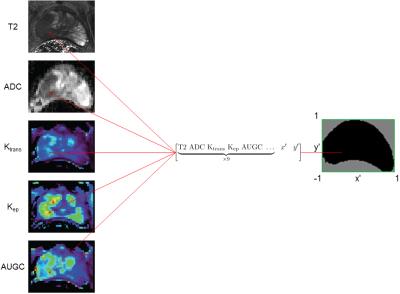
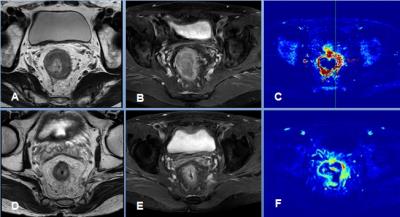
Dynamic contrast enhanced MR imaging for therapeutic response assessment after neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in patient with local advanced rectal cancer - video not available
Yanfen Cui, Xiaotang Yang , Ning Huang
The pre-CRT Ktrans value and the percentage decrease in the Ktrans after CRT could be helpful to predict good therapeutic response to CRT for LARC. This may allow for personalized treatment-options in rectal cancer patients.
|
|
4981.
 |
64 |
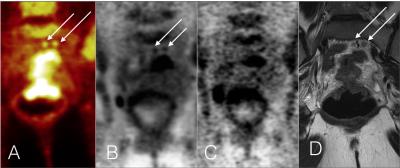
PET/MRI for rectal cancer staging: Longer PET acquisition times result in increased identification of nodal metastatic disease. 
Colin Burke, Thomas Hope, Michael Ohliger, Zhen Wang, Katherine Van Loon, Madhulika Varma
Rectal cancer nodal staging guides the decision to whether neo-adjuvant chemoradiation is needed prior to surgical resection and is a predictor of survival and recurrence. However, staging based on size and morphologic criteria alone is limited. Our data suggests that increased PET acquisition times with PET/MRI increases the identification of nodal metastatic disease in rectal cancer, particularly in small nodes sized 5 mm or less.
|
|
4982.
 |
65 |
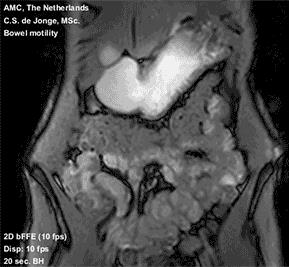
Dynamic MRI For Bowel Motility Imaging – How Fast And How Long? 
C.S. de Jonge, R.M. Gollifer, A.J. Nederveen, D. Atkinson, S.A. Taylor, J. Stoker, A. Menys
Dynamic (cine) MRI of bowel motility is now routinely performed in clinical practice and advances in post-processing have enabled robust quantitation of this data facilitating numerous research applications. Generally, motility sequences are acquired in a 20 second breath hold at a temporal resolution of 1 fps. In this study, we investigate these core assumptions and provide guidance information for future studies. In summary, we show that a temporal resolution of at least 1 fps is necessary for a scan duration of at least 10 seconds. This is consistent with the majority of small bowel motility studies to date.
|
|
4983.
 |
66 |
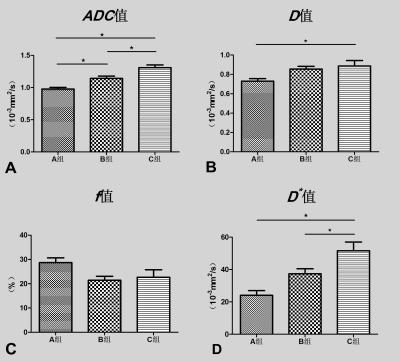
Optimization of high b values for intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of rectal cancer : a pilot study - video not available
Yankai Meng, Chongda Zhang , Hongmei Zhang, Chunwu Zhou
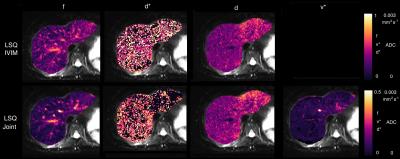
To optimize the high b values (>200s/mm2) for intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of rectal cancer and to observe the effect of high b values variation on IVIM parameters. Three groups (A group with all 16 b values: 0,10,20,30,40,60,80,100,150,200,400,800,1000,1200,1500,2000, B group with 14 b values: 0,10,20,30,40,60,80,100,150,200,400,800,1000,1200 and C group with 12 b values: 0,10,20,30,40,60,80,100,150,200,400,800) were selected respectively for measurement by a radiologist. The average values of each measurement were used for statistical analysis. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post-hoc test were performed on the mean values of IVIM parameters in groups A, B, and C, with a significance level of P<0.05. The p values of ANVOA results in ADC?D?D* values were less than 0.05, the differences were statistically significant. The p values of Bonferroni post-hoc test in D?D*?f values were not statistically significant differences in group A and B. With the number of high b values decrease, the values of ADC?D?D* values and standard error were increased, while of f values was not changed significantly. In our study, the reproducibility of the IVIM parameters caused by high b value variation was not significant. The value of selected b > 1500 need to be further studied.
|
|
4984.
 |
67 |
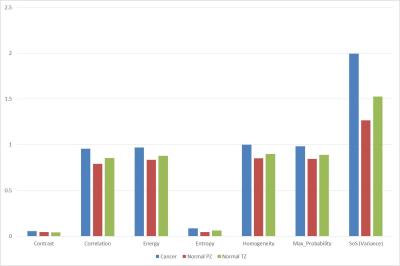
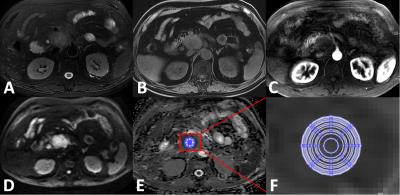
Optimized ROI size on ADC measurements of normal pancreas, pancreatic cancer and mass-forming chronic pancreatitis 
Chao Ma, Jing Li, Mbaiaourer Bouka, Panpan Yang, Li Wang, Luguang Chen, Li Su, Yong Zhang, Jianxun Qu, Shiyue Chen, Qiang Hao, Jianping Lu
The effect of ROI size on ADC measurements in normal pancreatic tissue or pancreatic lesions have rarely been studied. This study investigated the influences of ROI size in ADC measurements for the differentiation between normal pancreas (NP), mass-forming chronic pancreatitis (MFCP) and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
|
|
4985.
|
68 |
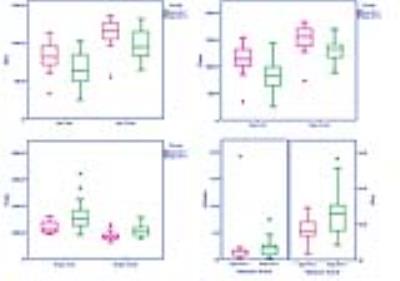
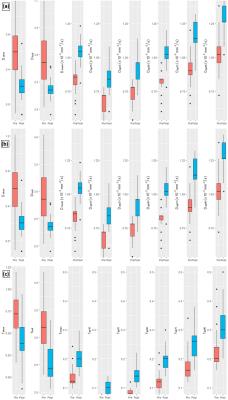
Diffusion kurtosis imaging for differentiating tumor KRAS mutation status in rectal cancer 
Yanyan Xu, Hongliang Sun, Kaining Shi, Wu Wang
Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI), which is a non-Gaussian diffusion-weighted model proposed by Jensen et al 1, has the potential to characterize both normal and pathologic tissue 1-3, meanwhile, providing a new option for tumor garde 4 and assessment of treatment response 5-7. Previous studies 1-3, 8 found that DKI could better account for restricted water diffusion within the complex microstructure of most tissues. To our knowledge, however, no study has included evaluation of DKI characteristic in rectal cancer, especially in the aspect of KRAS mutant, which associated with clinical treatment and prognosis of colorectal cancers 9.
|
|
4986.
 |
69 |
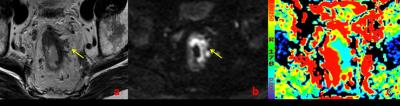
The utilization of DDC value in detecting the status of LVI in rectal cancer patients at 3.0T MRI 
Guangwen Zhang, Jinsong Zhang
In this study, we aimed to investigate the value of DDC in assessing the status of lymphovascular invasion in patients with rectal cancer. Ninety-eight patients with rectal adenocarcinoma underwent DWI with 16 b-values at 3.0T MR system. We found there was an significant difference in DDC value between the LVI presence group (DDC=0. 893±0.151×10-3mm2/s, n=46) and the LVI absent group (DDC=0. 825±0.127×10-3mm2/s, n=52), (P=0.018). We speculate that DDC value derived from multi-b value DWI could be a useful functional parameter in detecting the status of LVI in rectal cancer patients.
|
|
4987.
 |
70 |
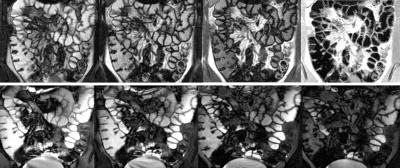
Measuring T1 and T2 of the small bowel wall at 3T 
Hannah Williams, Penny Gowland, Luca Marciani, Robert Scott, Guruprasad Aithal, Caroline Hoad
Available techniques to measure in-vivo bowel permeability are inadequate for stratifying patients to identify those at risk of complications from increased bowel permeability. T1 and T2measurements could potentially be indicators of changes in bowel wall structure and thus permeability. We have measured the T1 and T2 of the bowel wall to be 1.68±0.57 s and 0.08 ±0.02 s respectively. We found significant variations between and within subjects. However it is currently unknown whether some of these variations are real and some due to errors in the measurement process.
|
|
4988.
 |
71 |
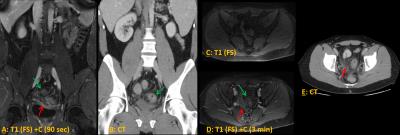
MR versus CT Imaging for Identifying the Etiology of Abdominal Pain in Emergency Department Patients 
Michael Repplinger, Perry Pickhardt, Rebecca Bracken, Douglas Kitchin, Jessica Robbins, Timothy Ziemlewicz, Scott Reeder
Our study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of MR versus CT for identifying the etiology of abdominal pain in emergency department patients. This is a prospective study that included patients ≥12-years-old who were being evaluated for possible appendicitis. All patients underwent both MR and CT; images were interpreted by three radiologists who were blind to the patient’s outcome. There were 113 instances of acute abdominal processes (15 different diagnoses). The overall accuracy of NC-MR, CE-MR, and CT was 77%, 83%, and 90% for individual reads and 82%, 84%, and 94% for consensus reads.
|
|
4967.
 |
50 |
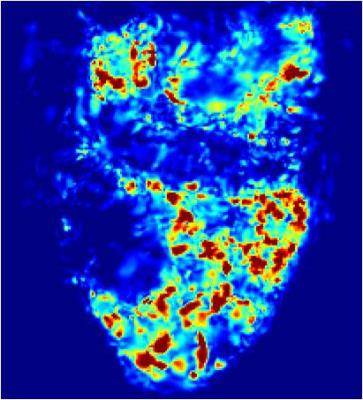
Analysis of motility in apparently normal small bowel – relationship to Crohn’s symptoms 
Ruaridh Gollifer, Alex Menys, Jesica Makanyanga, Carl Puylaert, Frans Vos, Jaap Stoker, David Atkinson, Stuart Taylor
Crohn’s disease (CD) patients often suffer abdominal symptoms even when their disease is apparently in remission with no identifiable active inflammation.1 Ongoing aberrant gut motility has been postulated as a cause, and this can now be quantified using MRI.2 This study tested the association between abdominal symptoms based on the Harvey-Bradshaw Index (HBI) and MRI derived motility metrics in morphologically healthy small bowel in CD patients. An inverse association was found between reduced motility spatial variation across the small bowel and symptoms, particularly diarrhoea. This association was strongest when HBI scores were higher.
|
|
4968.
 |
51 |
Feasibility of Performing Dynamic and Delayed Enhancement and Magnetization Transfer Ratios in pediatric patients undergoing clinically-indicated MRE: pilot study to assess image quality for quantitative evaluation 
Mary-Louise Greer, Susan Shelmerdine, Kedar Patil, Claire Cuscaden, Debra Drossman, Logi Vidarsson
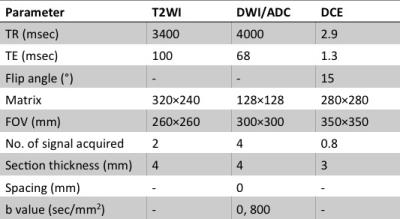
Purpose: Assess feasibility of applying magnetization transfer (MT) and dynamic and delayed enhancement (DCE) sequences during MR Enterography(MRE) in children. Methods: REB approved, in this prospective study, patients =/< 18 years undergoing MRE for suspected or proven inflammatory bowel disease were consented for application of MT and DCE sequenced in addition to standard clinical sequences. These were assessed and prospectively recruited and imaging sequences applied. Imaging was subjectively analysed by two radiologists or a radiologists and physicist in the first arm by consensus for sequence modification.
Results: Inter and intra-reader analysis was undertaken.
Conclusion: DCE is robust, MTR requires further modification.
|
|
4969.
 |
52 |
Magnetization transfer MRI for evaluating bowel fibrosis and inflammation in patients with stricturing Crohn’s disease - video not available
Xuehua Li, Zhuangnian Fang, Siyun Huang, Li Huang, Zhongwei Zhang, Xu Yan, Xiaolei Zhu, Jinjiang Lin, Mengchen Zhang, Mengjie Jiang, Shiting Feng, Canhui Sun, Ziping Li
This study aimed to assess the efficacy of Magnetization Transfer MRI (MTI) for evaluating bowel fibrosis and inflammation in patients with stricturing Crohn’s Disease (CD). Bowel wall MTR with normalization to skeletal muscle was calculated and correlated to histologic fibrosis and inflammation as well as amount of type I collagen and vessel density. The results showed that normalized MTRs correlated with histologic fibrosis and type I collagen scores, but did not correlate with inflammation scores or vessel densities. Thus, MTI can accurately detect and distinguish varying degrees of bowel fibrosis with or without coexisting inflammation in human CD.
|
|
4970.
 |
53 |
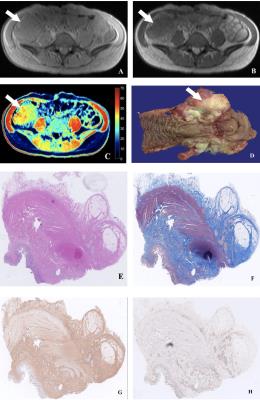
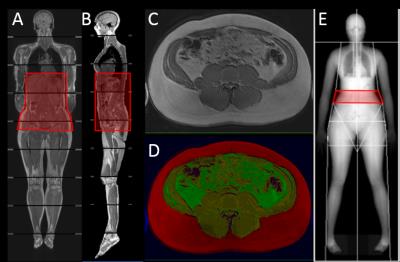
Comparison of Measurement of Abdominal Visceral Adipose Tissue in Men and Women by MRI vs. DXA 
Cherie Shook, Bret Goodpaster, Heather Cornnell
Visceral adipose tissue (VAT) has been identified as a significant contributing factor to the metabolic complications of obesity and cardio-metabolic disease, thus its precise measurement is becoming more clinically relevant. Both MRI and DXA were used to measure different components of body composition including VAT, and these results were compared by gender. Both scan acquisitions took similar amounts of time, but DXA results were calculated automatically while MR data processing was completed offline, thus took more time. The results from this study indicate that DXA is a precise measure of only a portion of VAT while MRI can give a more accurate measurement of total VAT across the entire abdomen, potentially avoiding gender bias.
|
|
4971.
 |
54 |
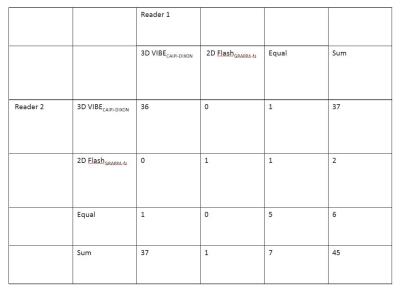
Clinical application of 3D VIBECAIPI-DIXON for enhanced imaging of the small intestine 
Yang Yu, Lu Liang, Tao Jiang
The abstract discussed the clinical application of a fast 3D VIBE sequence with Dixon fat saturation and CAIPIRINHA acceleration techniques (3D VIBECAIPI-DIXON) by compare to a standard 2D FLASH sequence with spectral fat saturation and conventional GRAPPA acceleration technique (2D FlashGRAPPA-fs) for enhanced imaging of the small intestine
|
|
4966.
 |
49 |
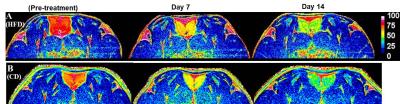
Metabolic Imaging of ß3-adrenoreceptor Activated BAT and its Systemic Effect on Abdominal Fat in Diet Induced Obese Model 
Jadegoud Yaligar, Sanjay Kumar Verma , Venkatesh Gopalan , Anantharaj Rengaraj, Tian Xianfeng, Anna Ulyanova, Bhanu Prakash K.N, Suresh Anand Sadananthan, Navin Michael, S. Sendhil Velan
Imbalance in dietary intake and energy expenditure are associated with obesity, diabetes and metabolic disorders. Adipocyte size and expansion of adipose tissue plays a critical role towards the progression of diet induced obesity. Brown adipose tissue (BAT) plays a critical role in modulating different fat depots in the body. BAT can be functionally activated by administering the β3-adrenergic agonist. Understanding the mechanisms associated with BAT activation and the possibility of reversing insulin resistance and its impact on whole body metabolism is of current clinical interest for combating diabetes. In the current study, we investigated the fat partitioning in high fat diet induced obese rodent model by β-adrenergic-mediated BAT activation.
|
|
4989.
 |
72 |
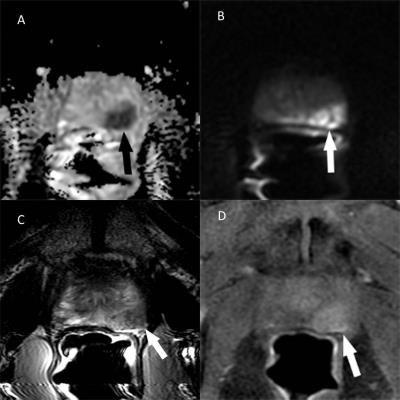
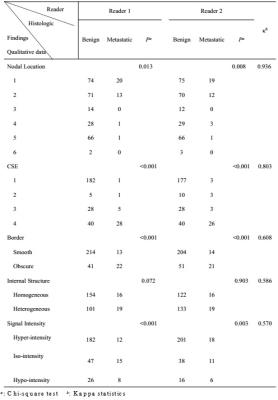
Chemical Shift Effect Predicting Lymph Node Status in Rectal Cancer using High-Resolution MR Imaging with Node-for-node Matched Histopathological Validation - video not available
chongda zhang, hongmei zhang, feng ye, yuan liu, chunwu zhou
To evaluate the value of chemical shift effect (CSE), as well as other criteria for the prediction of lymph node status. Lymph nodes harvested from transversely whole-mount specimens were compared with in vivo and ex vivo images to obtain MR characteristics including CSE, as well as other predictors of 255 benign and 35 metastatic nodes. Our results revealed that CSE is a reliable predictor for differentiating benign from metastatic lymph nodes. Other predictors of nodal location, border, signal intensity and minimum distance to rectal wall were also proved to be useful for the diagnosis.
|
|