Preclinical CV Imaging
Electronic Poster
Cardiovascular
Wednesday, 26 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
14:45 - 15:45 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4872.
 |
1 |
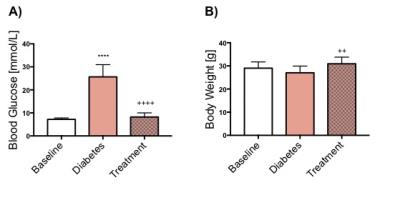
Reversible Changes in Cardiac Function and Metabolism in an Inducible Mouse Model of Type 1 Diabetes 
Dragana Savic, Maria Rohm, Vicky Ball, Mary Curtis, Lisa Heather, Frances Ashcroft, Damian Tyler
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in Type 1 diabetic patients, however the mechanistic link has not been fully established. In this study an inducible and reversible mouse model of Type 1 diabetes was used. Depression of cardiac function and the increase in blood glucose occur in combination with suppression of pyruvate to bicarbonate conversion. By reversing diabetes with Glibenclamide, cardiac function and blood glucose concentration was restored. This study demonstrated changes that occur alongside the development of a reversible model of Type 1 diabetes and how the action of Glibenclamide can affect metabolism and function of the heart.
|
|
4874.
 |
3 |
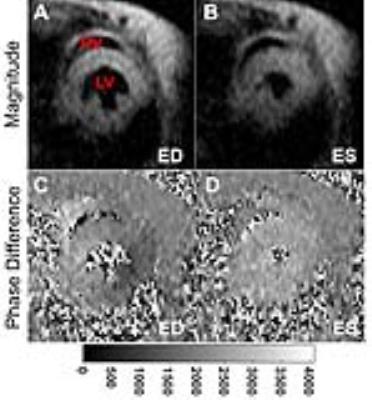
Repeatability and User Variability of Myocardial Tissue Phase Mapping in Mice 
Nivedita Naresh, Cynthia Yang, Sol Misener, Bradley Allen, Michael Markl, James Carr, Daniele Procissi
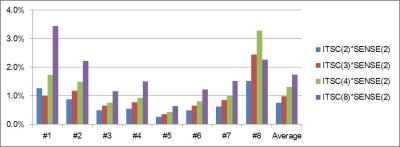
Mouse models can help investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying complex cardiovascular diseases. Assessment of myocardial regional wall motion plays a very important role in the diagnosis and management of several cardiovascular diseases and can be linked to many underlying biological processes. In this study, we evaluated the repeatability and inter-user variability of the myocardial tissue phase mapping method in mice. We found that myocardial tissue phase mapping can be performed with good repeatability and little user variability in mice to reliably quantify both global and regional myocardial velocities.
|
|
4875.
 |
4 |
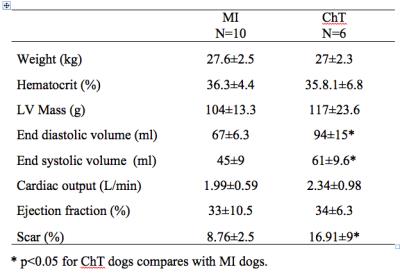
MRI/PET of Myocardial Extracellular Volume in a Canine model of Chemotherapy 
Chia-Ying Liu, Cynthia Davies-Venn, Comfort Elumogo, Rolf Symons, Victoria Hoffmann, Kelly Rice, Roberto Maass-Moreno, Veit Sandfort, Stefan Zimmermann, Amir Pourmorteza, Mark Ahlman, David Bluemke
We used simultaneous MR/FDG PET to measure the myocardial extracellular volume (ECV) and glucose metabolism (estimated by standard uptake value, SUV) in a canine model of chemotherapy (ChT); comparison was made to ECV in relationship to a myocardial infarct (MI) models. MRI ECV in the ChT group was elevated by 16% and 23% compared to the MI group in the remote and adjacent myocardial segments, respectively. PET SUV in the ChT group was reduced by 49% and 41% compared to the MI group in the remote and adjacent myocardial segments, respectively. Difference was also observed in the MRI partition coefficient but not in the native T1.
|
|
4873.
 |
2 |
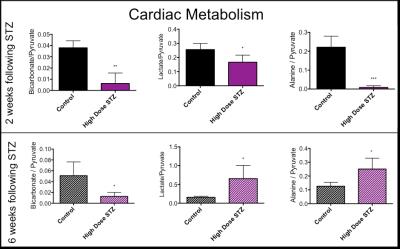
Type 1 Diabetic Hearts show Unexpected Biphasic Metabolic and Functional Progression as Evaluated with Hyperpolarised [1-13C]Pyruvate and CINE MR. 
Dragana Savic, Vicky Ball, Carolyn Carr, Lisa Heather, Damian Tyler
Type 1 diabetes patients are insulin deficient resulting in hyperglycaemia. Diabetic patients have a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases. In this study the progression of cardiac metabolic and functional decline was followed in a streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type 1 diabetic model. Flux through pyruvate dehydrogenase was significantly decreased at 2 and 6 weeks post STZ injection. Interestingly, the incorporation of the 13C-label from pyruvate into lactate and alanine was decreased at 2 weeks, but significantly increased at 6 weeks. Cardiac output was normalized after 6 weeks. Such studies will allow a better understanding of the interactions between metabolism and function in the diabetic heart.
|
|
4876.
 |
5 |
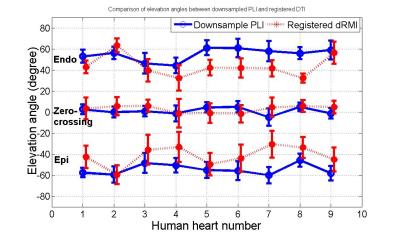
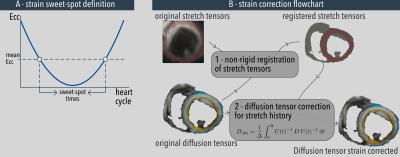
Evaluation of the impact of strain correction on the secondary eigenvector of diffusion with in vivo and ex vivo porcine hearts 
Pedro Ferreira, Sonia Nielles-Vallespin, Ranil de Silva, Andrew Scott, Daniel Ennis, Daniel Auger, Jonathan Suever, Xiaodong Zhong, Bruce Spottiswoode, Dudley Pennell, Andrew Arai, David Firmin
Myocytes have a laminar organization, where sheets of myocytes interleave with collagen-lined shear layers. Cardiac diffusion tensor imaging is capable of probing sheet dynamics with secondary diffusion directions, although questions remain about cardiac strain being a possible confounder. Here we study the validity of strain-correcting cardiac diffusion tensor data by directly comparing in vivo DTI data without and with strain correction, to ex vivo DTI data of the same porcine hearts arrested in a diastolic or systolic conformation. Results show that the current strain correction model exaggerates the contribution of microscopic strain to diffusion resulting in an over-correction.
|
|
4877.
 |
6 |
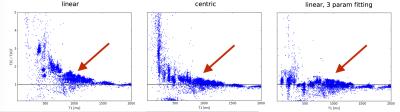
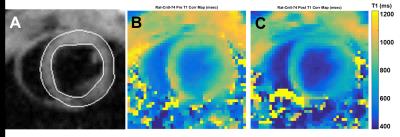
Simultaneous Cardiac and Renal oblique-slice T1-Mapping Differentiates Contrast Agent Activity in Normal and Doxorubicin-treated Rats 
Ronald Beyers, Dean Schwartz, Tessa Hutchinson, Meghan Ward, Nouha Salibi, Christian Goldsmith, Thomas Denney
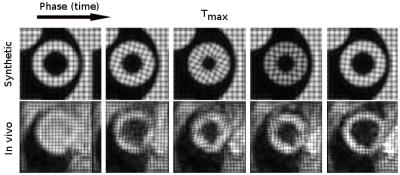
We developed a cardiac multi-oblique-slice T1-mapping sequence, called Tmax, for simultaneous in vivo cardiac and multi-region T1-mapping in rats. We validated Tmax with gadolinium contrast agent (CA) scans then applied it to support our concurrent development of a reactive oxygen species activated T1-shortening agent, called H4qtp2, in doxorubicin-treated (Dox) rats. The new Tmax sequence performed excellent at simultaneously quantifying gadolinium T1 effects in cardiac and renal regions. However, application of Tmax with low dose levels of H4qtp2 CA in Dox rats gave marginal results from too low dose of H4qtp2 to sufficiently affect the T1 and quantify Dox-induced pathology
|
|
4878.
 |
7 |
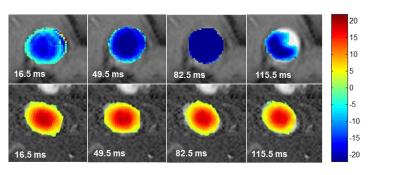
TWO-DIMENSIONAL PHASE-CONRAST MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AS TOOL TO DETERMINE HEPATIC HEMODYNAMICS IN RATS WITH A HEALTHY, FIBROTIC OR CIRRHOTIC LIVER 
Denise Schaffner, Dominik von Elverfeldt, Peter Deibert, Irmgard Merfort, Adhara Lazaro, Lisa Lutz, Manfred Baumstark, Wolfgang Kreisel, Wilfried Reichardt
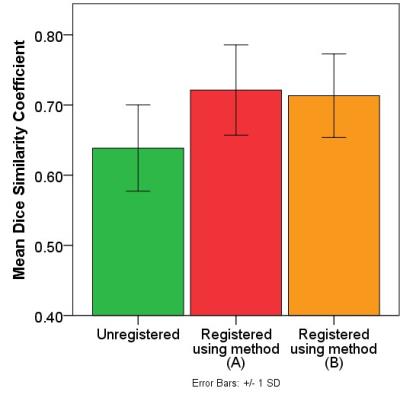
In this work we wanted to test a Magnetic Resonance (MR) scanning protocol as a non-invasive tool to determine hepatic hemodynamics and to assess the liver fibrosis degree in an animal model of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. MR rat liver images provided a good discrimination of healthy from diseased liver, but for the assessment of liver fibrosis degree histology is indispensable. The results show that portal and aortal flow patterns for a cardiac cycle could be measured with high reliability in Conclusion, this MR scanning protocol presents a reliable non-invasive tool to determine hepatic hemodynamics in healthy and diseased rats
|
|
4879.
 |
8 |
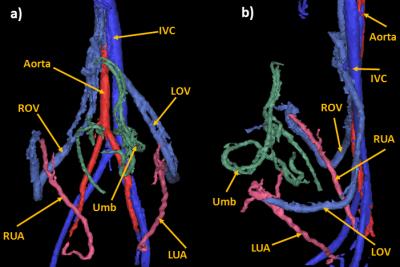
Feasibility of 4D-Flow Imaging of Uterine Blood Flow in the Pregnant Rhesus Macaque 
Philip Corrado, Jacob Macdonald, Sydney Nguyen, Kevin Johnson, Chris Francois, Ronald Magness, Scott Reeder, Ian Bird, Dinesh Shah, Thaddeus Golos, Oliver Wieben
4D-Flow MRI is introduced as an alternative to Doppler velocimetry in monitoring blood flow to the placenta in pregnancy. Our 3D radially undersampled PC-VIPR technique provided volumetric coverage of uterus and relevant vasculature with a 10-minute scan. Uterine arteries and ovarian veins were visualized in a 0.83mm isotropic resolution angiogram and flow rates and vessel sizes were measured retrospectively. Repeated scans of four rhesus macaques on subsequent days showed reproducibility of flow rate and cross sectional area measurements in vessels of interest, demonstrating the potential for 4D-Flow MRI for assessing utero-placental vascular health.
|
|
4880.
 |
9 |
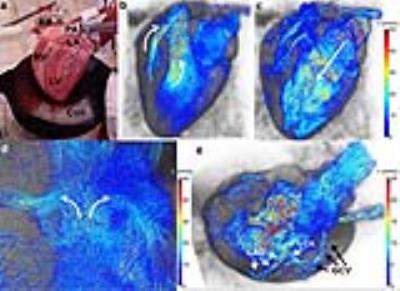
4D flow MRI measurements in ex vivo beating pig hearts as a testing platform for transcathether aortic valve implantation 
Eva Peper, Alberto Leopaldi, Sjoerd van Tuijl, Nicky de Jonge, Gustav Strijkers, Arend de Weger, Aart Nederveen, Henk Marquering, Pim van Ooij
In this 4D flow MRI study, ex vivo beating pig heart models in an MR-compatible setup mimicking human physiological conditions were used to investigate flow alterations after implantation of artificial valves designed for transcathether aortic valve implantations (TAVI). Two pig hearts had implanted TAVI valves (one with and one without attachment to the aortic sinuses) and were compared to five pig hearts without valve implantation. For both pig hearts with implanted valves, substantial aortic backflow, and thus paravalvular leakage, was observed. The ex vivo set-up presented is thus suitable for cardiac flow experiments.
|
|
4881.
 |
10 |
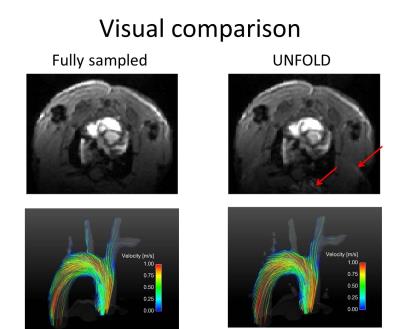
Evaluation of accelerated preclinical 4D-flow imaging with UNFOLD 
Moritz Braig, Axel Krafft, Jochen Leupold, Juergen Hennig, Marius Menza, Dominik von Elverfeldt
There is growing interest in preclinical imaging and analysis of complex flow patterns. For example, 4D flow imaging of mouse models with vascular plaques or aortic constriction could provide insights into the development and pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. Unfortunately, 4D-flow MRI is often compromised by a trade-off of reasonable acquisition durations and achievable spatial resolution. Our work evaluates an undersampling strategy, namely UNFOLD, for preclinical 4D flow MRI, which has the potential to decrease measurement time by 50%. Artifacts emerging from the undersampling are removed by unaliasing in the temporal domain using a lowpass filter after fourier transformation.
|
|
4882.
 |
11 |
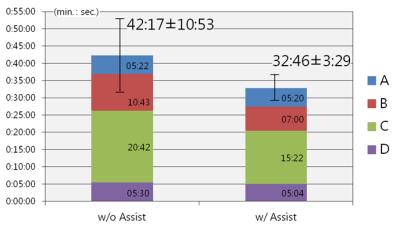
Quantitative gated and non-gated rat phase contrast MRI: optimized analysis of blood flow and wall shear stress. 
Chen-You Huang, Chiun-Wei Huang, Shao-Chieh Chiu, Wu-Chung Shen, Shin-Lei Peng
Goals of this study are to test effects of gated/non-gated, velocity encoding (VENC) and spatial resolution on blood flow, wall shear stress (WSS) and artery area when performing phase-contrast (PC) MRI for rat common carotid artery (CCA). Results show the usage of gated instrument can provide more reproducible results. VENC has insignificant influences on flow, WSS and artery area. To compromise the trade-off between accuracy and time-consuming, the resolution of 0.21 mm is suggested for extracting hemodynamic information about rat CCA.
|
|
4883.
 |
12 |
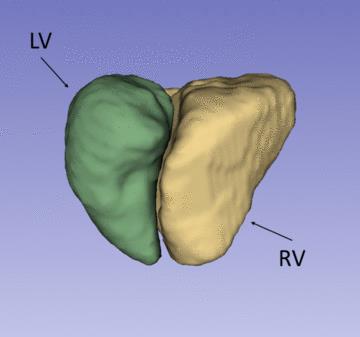
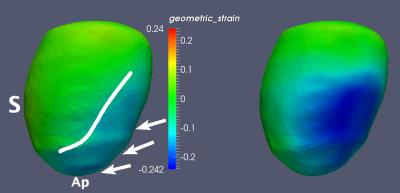
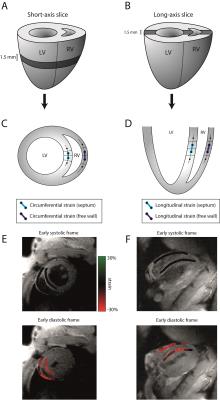
Right ventricular myocardial strain in rats 
Emil Espe, Jan Magnus Aronsen, Lili Zhang, Ivar Sjaastad
The function of the right ventricle (RV) is closely linked to clinical outcome in many cardiovascular diseases. Experimental heart disease in rodents play an irreplaceable role in modern cardiovascular research, but no in vivo method exists offering robust measurements of RV myocardial function in small animals. We used phase-contrast MRI to measure RV strain in rats. We found that RV strain and ejection fraction were closely related, and confirmed that high RV afterload is linked to reduced RV strain.
We show, for the first time, that it is possible to accurately measure myocardial function in the RV in rodents.
|
|
4884.
 |
13 |
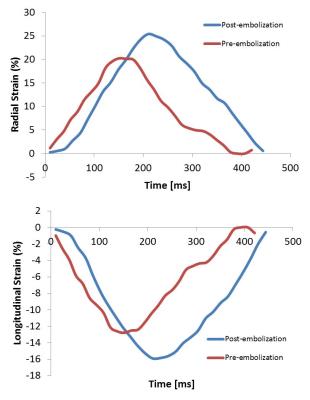
Cardiac MRI measurement of right ventricular strain using feature tracking in a model of embolic pulmonary hypertension. 
Zachary Borden, Donald Benson, Alejandro Roldan, Heidi Kellihan, Ashley Mulchrone, Naomi Chesler, Christopher Francois
Right ventricular strain was assessed using an MRI tissue tracking algorithm on bSSFP axial sequences in both acute and chronic embolic pulmonary hypertension canine models. Strain values were heterogeneous in the acute population with statistically significant decreases in acute radial and longitudinal strain rate and chronic radial and longitudinal strain and strain rate values. Findings suggest MRI cardiac strain measurement is a promising technique in the clinical evaluation of post embolic pulmonary hypertension patients.
|
|
4885.
 |
14 |
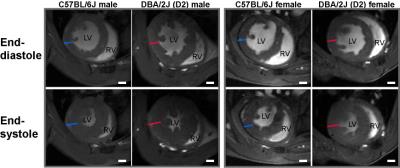
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance for Characterizing a Spontaneous Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Mouse Model 
Min-Chi Ku, Till Huelnhagen, Andreas Pohlmann, Thoralf Niendorf
HCM is the most common inherited heart disease. The two most frequently seen mutated genes are MYH7 and MYBPC3 which account for nearly 80% of familiar HCM. In this study we hypothesized that these gene variants will affect both LV and RV function. By in-vivo CMR we detected LV hypertrophy in a mouse strain DBA/2J bearing the two gene variants. Interestingly there is no defected LV function found but changes in RV function as both male and female DBA/2J mice had declined RVEF. Our results provide new insights into the correlation of genetic alteration and HCM phenotype.
|
|
4886.
 |
15 |
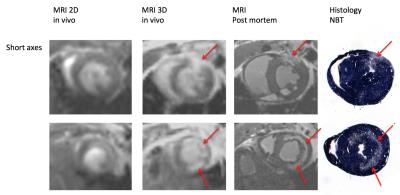
4D Cine Strategy for Assessment of Mouse Cardiac Function and Infarct Size in a Single Acquisition Optimized for a Clinical 3T MR System 
Lindsey Crowe, Fabrizo Montecucco, Federico Carbone, Iris Friedli, Anne-Lise Hachulla, Vincent Braunersreuther, Francois Mach, Jean-Paul Vallée
Small cardiac imaging on clinical 3T machines is an important, cost effective translational step for new contrast media and sequence validation. We developed for the first time a new 4D strategy tailored for 3T to simultaneously assess function and infarct in mice, validated against 2D cine, post mortem and histology. Isotropic 3D cardiac cine of mice on a clinical 3T system improved coverage and reduced flow artifacts with higher spatial and temporal resolution for more accurate quantification of cardiac function. Infarct volume enhancement was quantifiable from the same 3D cine acquisition.
|
|
4887.
 |
16 |
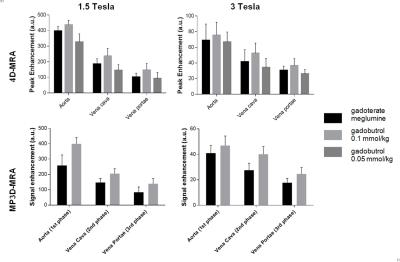
Gadobutrol- vs. gadoterate meglumine-enhanced multi-phase 3D-MRA and 4D-MRA at 1.5T and 3T: an intra-individual quantitative and qualitative comparison of macrocyclic contrast agents in minipigs - permission withheld
Dariusch Hadizadeh, Gregor Jost, Vera Keil, Christian Marx, Maximilian Rauch, Frederic Schmeel, Hubertus Pietsch, Hans Schild, Winfried Willinek
In an animal model bolus kinetics and image quality of the macrocyclic contrast agents (CA) gadobutrol (standard and half-dose) and gadoterate meglumine (standard-dose) were investigated intra-individually in multi-phase 3D- (MP3D) MRA and in 4D-MRA at 1.5T and 3T. Standard dose gadobutrol provided significantly higher signals in both MP3D- and 4D-MRA at both field strengths. Differences were most prominent in venous imaging phases. At 3T, arterial first pass peaks were truncated in 7/8 minipigs using standard dose CA. Image quality analysis of MP3D confirmed higher image quality in venous phases with standard-dose gadobutrol compared to gadoterate meglumine at both field strengths.
|
|
4888.
 |
17 |
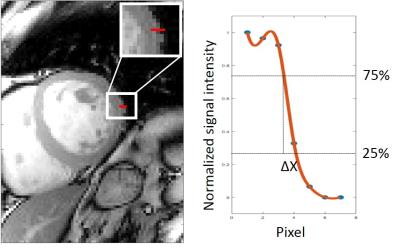
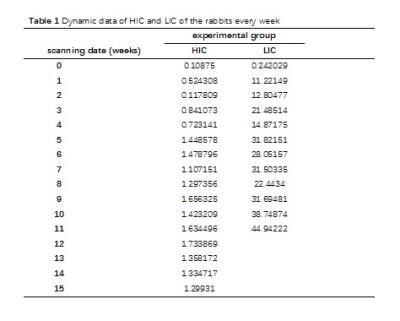
Histological validation of loading lag of heart iron with respect to liver iron in a rabbit model 
xiaodong chen, Zipan Chen, Heng Lv, Ziliang Cheng, Qihua Yang, Zuoquan Zhang, Zebin Luo, Jiaji Mao, Queenie Chan, Yingjie Mei, Jingwen Huang, Wubiao Chen, Biling Liang, Hua Guo
Whether there exists a lag in the iron loading between liver and heart in transfusion dependent patients has clinical significance in prevention and treatment of heart iron overload. We performed this study to verify this time lag on a rabbit model. The result shows that the iron loading, measured with pathology, MRI and atomic absorption spectrophotometer, was much faster and heavier in the liver than that in the heart. Therefore, there existed a time lag between heart and liver iron overload on the rabbit model. This may lead to improved clinical guidelines for cardioprotection.
|
|
4889.
 |
18 |
Multiparametric CMR protocol and analysis methods for the detection of early cardiotoxicity remodelling in the mini-swine. 
Delphine Perie, Clémence Balosetti, Hélène Héon, Nagib Dahdah, Farida Cheriet, Matthias Friedrich, Daniel Curnier
Some Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) studies investigated the long term effects of cancer treatments, but were never applied to the detection of early changes during cardiotoxicity remodelling. The CMR parameters we investigated in the miniature swine therapeutic model with doxorobucin was able discriminate treated animals from controls. Differences were detectible earlier than onset of classical echocardiographic changes. Translating these observations to personalized medicine approach could be the premise for the oncologist to know accurately when the treatment just starts to have deleterious effect on myocardium instead of just observing that the heart was damaged by doxorubicin.
|
|
4890.
 |
19 |
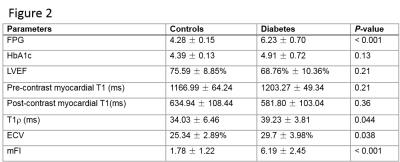
A spontaneous type 2 diabetic rhesus monkey model for cardiac MR study - permission withheld
Yu Zhang, Jie Zheng, Fabao Gao
The aim of this study was to provide a human-like diabetic monkey model for cardiovascular research. Myocardial function and tissue characterizations were measured by CMR in 14 diabetic and 5 control monkeys. In addition to diastolic dysfunction, minor and moderate diffuse fibrosis was shown in cardiac T1, T1r, ECV, and non-contrast fibrosis index images in all the hearts of all diabetic monkeys, confirmed by histopathology finding in one diabetic monkey.
|
|
4891.
 |
20 |
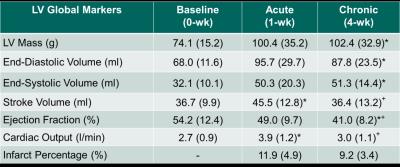
Early Prediction of Chronic Infarct Size by Acute Strain: A Cardiac MRI Study of Myocardial Infarction in Pigs 
Sarayu Parimal, Smita Sampath, Ibrahim Mazlan, Grace Croft, Teresa Totman, Yvonne Tay Wei Zheng, Elaine Manigbas, Michael Klimas, Jeffrey Evelhoch, Dominique Kleijn, Chih-Liang Chin
We characterized cardiac structure and function longitudinally in myocardial infarcted pigs, induced by permanent ligation of left circumflex artery of left ventricle (LV), to identify early strain biomarkers that are predictive of late stage remodeling. Pigs were imaged pre- and post-surgery at 1-wk and 4-wk. Reduction of percentage of infarct was observed at basal antero-lateral and mid infero-lateral regions at 4-wk post-surgery. Decreased peak circumferential strain was observed at infarcted areas showing compromised contractility. In addition, ROC analyses revealed that acute strain at 1-wk and early strain change from baseline can predict chronic infarct size suggesting that LV strain could potentially serve as early biomarker for novel therapies.
|
|
4892.
 |
21 |
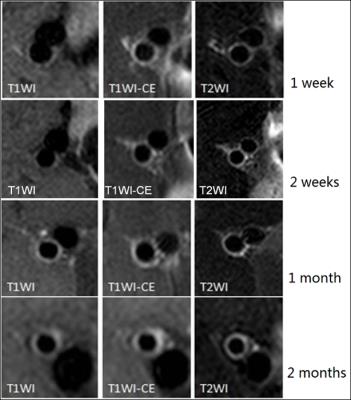
Aortic Wall MR Imaging for Assessing Rosuvastatin Therapy in Atherosclerotic Animal Model 
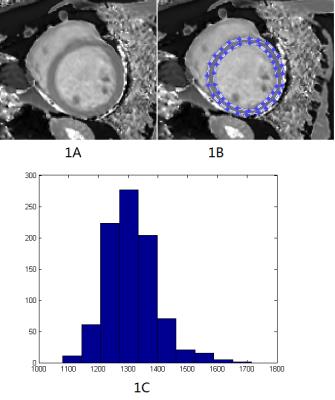
Juan Huang, Yan Song , Mingmei Li, Xiaotao Deng, Sheng Jiao, Jingying Yu, Min Chen, Xiaoqi Wang
Here we present the high-resolution MRI imaging for assessing therapy of titrated rosuvastatin for atherosclerosis in rabbit models. This study shows that abdominal aorta wall in both control and treated rabbits get thicker with prolonged continuous feeding of cholesterol, aortic plaques grows bigger with this progression. The MRI vascular wall imaging measured atherosclerotic plaques with well correlation of histological classifications. Statical regression showed that the group with rosuvastatin treatment reduced the aortic plaques comparing to the control rabbits.
|
 |
4893.
 |
22 |
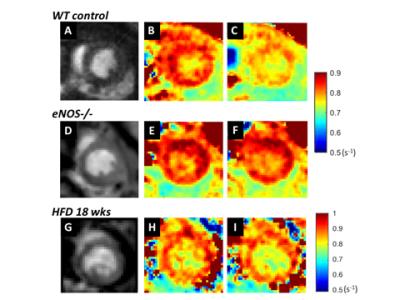
T1 Mapping with Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) Inhibition Detects Impaired Coronary Endothelial Function in Mice Fed a High Fat Diet 
Sophia Cui, Frederick Epstein
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)-mediated production of NO regulates the microvasculature, controlling both vessel diameter and permeability. We hypothesized that T1 mapping of the healthy heart during NOS inhibition would detect increased water content resulting from increased coronary microvascular permeability, while a blunted change in T1 between baseline and NOS inhibition would indicate coronary eNOS dysfunction. Using these methods, we detected an increase in myocardial T1 of 113±15 ms due to NOS inhibition in control mice, but no change in eNOS-/- or HFD mice, demonstrating the eNOS mechanism and detection of coronary endothelial dysfunction in a model of heart disease.
|
|