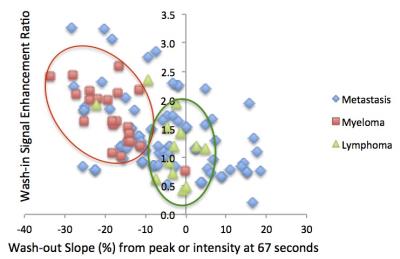
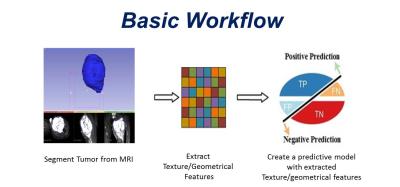
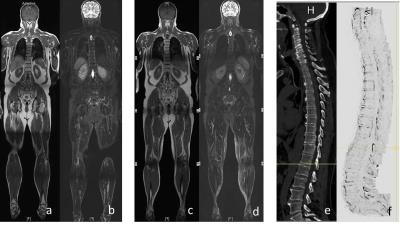
Muscle
Electronic Poster
Musculoskeletal
Wednesday, 26 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
16:15 - 17:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
4990.
 |
25 |
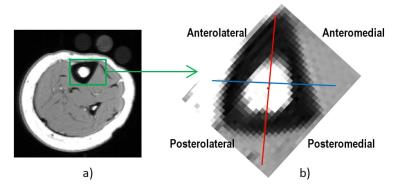
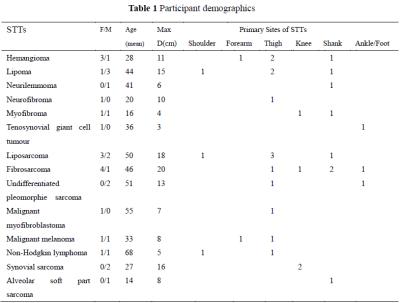
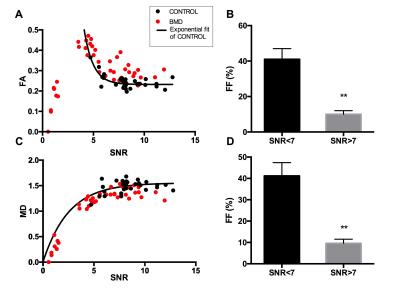
A quantitative relationship between R2* and deoxyhemoglobin levels in calf muscle 
Kexin Hao, Gwenael Layec, Corey Hart, Christopher Conlin, Kristi Carlston, Vivian Lee, Jeff Zhang
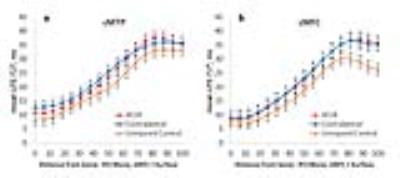
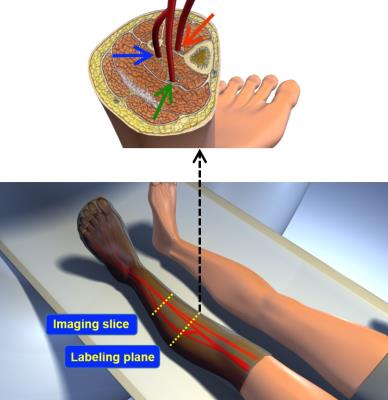
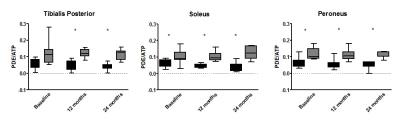
This study examined the relationship between R2* measurements from BOLD MRI and deoxyhemoglobin (HHb) measurements from near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) in calf muscle of subjects with varying degrees of peripheral artery disease (PAD). Following plantar-flexion exercise, the time required for R2* and HHb to recover to resting-state values was recorded. Linear regression was used to relate recovery time between R2* and HHb. This quantitative relationship enables estimation of HHb from MRI-measured R2*, which can help to improve the assessment of PAD since MRI can easily be performed for muscle tissue that is too deep for NIRS evaluation.
|
|
4991.
 |
26 |
Noninvasive Measurement of Calf Muscle Perfusion Immediately after Plantar Flexion Exercise in Elderly Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction - video not available
Robert Kraft, Craig Hamilton, Peter Brubaker, W. Scott Hoge, M. Constance Linville, J. Thomas Becton, Richard Thompson, Mark Haykowsky, Dalane Kitzman
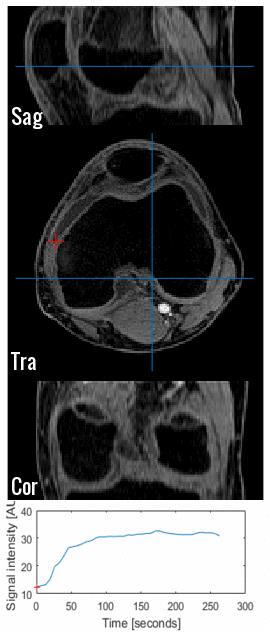
The pathophysiology of Heart Failure Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction is poorly understood but there is increasing evidence that skeletal muscle blood flow and metabolism play important roles in this disease. Accurately and non-invasively measuring skeletal muscle blood flow with sufficient temporal resolution to measure skeletal muscle blood flow dynamics in individual muscles is challenging. We present a optimized version of pseudo-Continuous ASL capable of measuring blood flow map of the calf every 16 seconds. Data from two healthy adults is presented.
|
|
4992.
 |
27 |
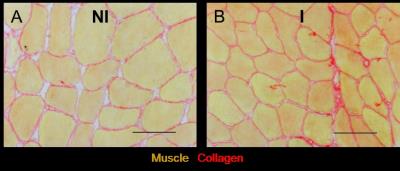
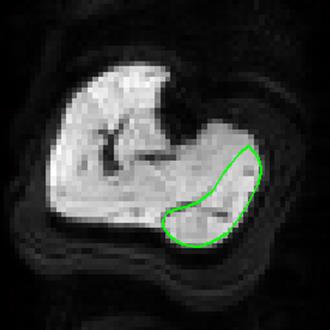
Stimulated Echo DTI in skeletal muscle of patients with Becker Muscular Dystrophy 
Celine Baligand, Jedrzej Burakiewicz, Melissa Hooijmans, Olivier Scheidegger, Matt Hall, Paola Porcari, Erik Niks, Pierre Carlier, Christopher Clark, Andrew Blamire, Jan Verschuuren, Hermien Kan
Cellular sizes in skeletal muscle are significantly larger than in the brain. Therefore standard spin-echo (SE)-DTI with inherently short diffusion times may lack sensitivity for the study skeletal muscle of neuromuscular disorders (NMDs). Alternatively, stimulated-echo (STE-)DTI allows for much longer diffusion times, increasing sensitivity to cell size. Due to the challenges presented by fat replacement STE-DTI has not been previously applied in NMDs. Here, we show that STE-DTI is feasible in Becker Muscular Dystrophy patients, and can detect FA differences compared to healthy controls in mildly affected muscles.
|
|
4993.
 |
28 |
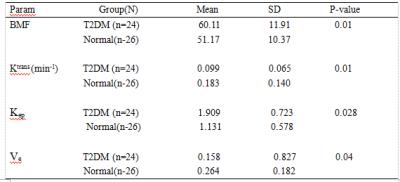
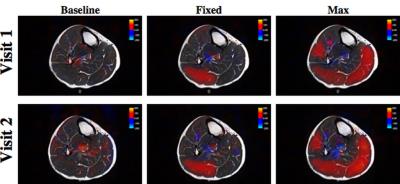
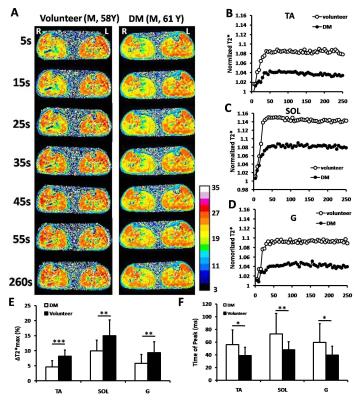
T1? and Dynamic BOLD MR imaging to evaluate the change of skeletal muscles of lower extremity in diabetes patients 
Xingui Peng, Shenghong Ju
This study aimed to measure the BOLD response in the calf muscle in T2DM patients during post-occlusive reactive hyperemia and to study whether T1ρ MR Imaging of calf muscle could differentiate T2DM patients from normal subjects. Twenty-two T2DM patients and twenty age-matched healthy volunteers were performed MR scanning. T1ρ relaxation time and maximal ΔT2* change (ΔT2*max) and time to peak (TTP) were measured. Our results showed that the lower degree of the increase (ΔT2*max and TTP) in calf muscles of DM patients. In addition, T1ρ relaxation time in TA muscle was significant higher in DM patient than in healthy subjects.
|
|
4994.
 |
29 |
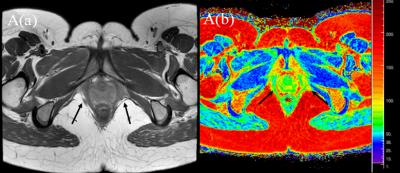
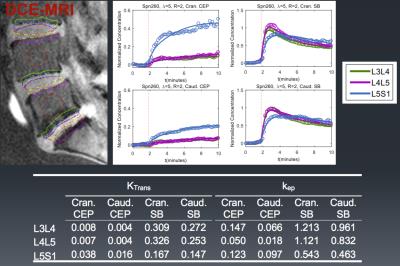
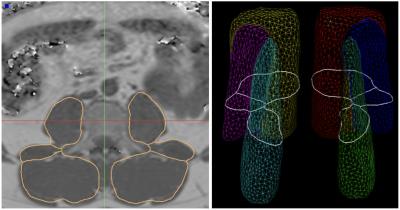
Automated assessment of paraspinal muscles fat composition based on the segmentation of chemical shift encoding-based water/fat-separated images 
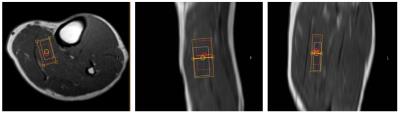
Friedemann Freitag, Thomas Baum, Michael Dieckmeyer, Jan Kirschke, Holger Eggers, Christian Buerger, Cristian Lorenz, Dimitrios Karampinos
Chemical shift encoding-based water-fat MRI derived proton density fat fraction (PDFF) of the paraspinal muscles has been emerging as important surrogate marker in subjects with intervertebral disc disease, osteoporosis, sarcopenia, and neuromuscular disorders. However, measurements of paraspinal muscle PDFF are currently limited in clinical routine due to the required time-consuming manual segmentation procedure. The present study aimed to develop an automatic segmentation algorithm of the paraspinal muscles at the lumbar spine based on water-fat MRI and compared the performance of this algorithm to ground truth data based on manual segmentation.
|
|
4995.
 |
30 |
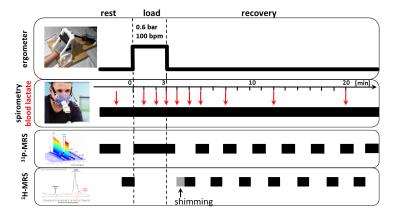
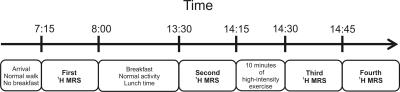
Diurnal changes of Acetylcarnitine in human vastus lateralis muscle and response to exercise: a 7T 1H MRS study 
Radka Klepochová, Ladislav Valkovic, Martin Gajdošík, Thomas Hochwartner, Norbert Bachl , Harald Tschan, Michael Krebs, Siegfried Trattnig, Martin Krššák
Carnitine plays an important role in fat metabolism. A long-echo time proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy protocol was implemented for detection of skeletal muscle acetylcarnitine during the day and after exercise on a clinical 7T scanner in the thigh (vastus lateralis) muscle. Our observation point towards diurnal changes of acetylcarnitine concentration which tended to be higher in the morning than after lunch. Moreover, following 10 minutes of high-intensity exercise the concentration significantly increased and again significantly decreased 15 minutes after cessation of the exercise. Our data emphasize the need for strict standardization,physical activity and dietary conditions for the measurement of the acetylcarnitine/carnitine.
|
|
4996.
 |
31 |
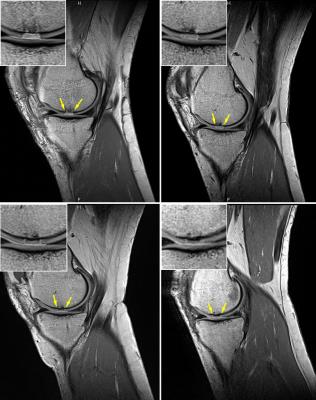
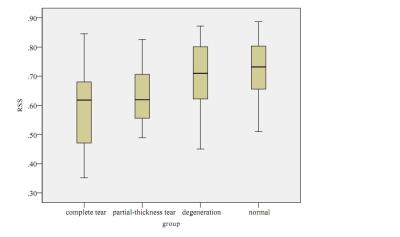
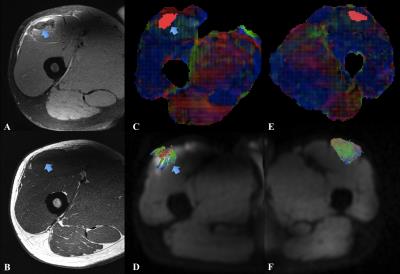
Normalized STEAM-based DTI parameters allow robust assessment of muscle tears in football players. 
Chiara Giraudo, Stanislav Motyka, Michael Weber, Manuela Karner, Christoph Resinger, Siegfried Trattnig, Wolfgang Bogner
STEAM-based DTI was applied to investigate lower limbs’ muscle tears in athletes using the contralateral muscles as reference.To account for possible physiological differences in DTI metrics between right and left limb, a ratio between two ROIs on the injured side (i.e.,one on the tear and one on a healthy area) and two ROIs on the contralateral limb (i.e.,both on healthy areas) was used. The ratio showed that structural changes, expressed by modifications in MD, FA, RD, fibers’ number and length, occur in muscle tears and are quantifiable by DTI.These findings are expected to improve the therapeutic management of muscle injuries.
|
|
4997.
 |
32 |
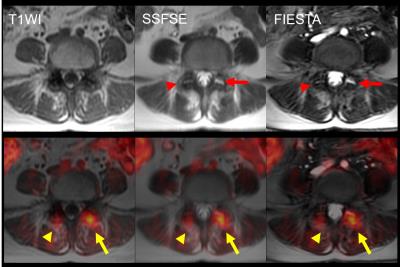
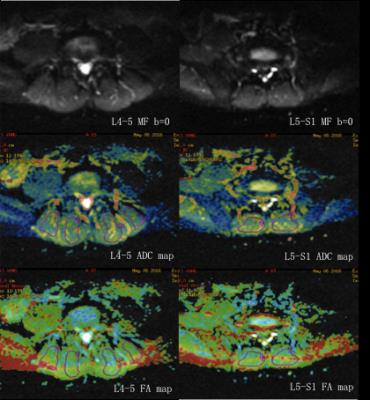
Paraspinal Muscle Changes with Chronic Low Back Pain by Using 3.0T MR Diffusion Tensor Imaging Technology - video not available
Li Yiwen, Yuan Huishu, Xie Lizhi
The purpose of the current study is to assess the potential difference of multifidus muscle between non-specific chronic low back pain patients and the healthy individuals using DTI and to compare the sensitivity of DTI to conventional lumbar MRI in detecting muscle pathological changes. DTI and conventional MRI parameters were obtained including FA, ADC, MD and tCSA, fCSA, fCSA/tCSA ratio. Compared to the healthy individuals, NCLBP patients demonstrated differences in DTI parameters of bilateral multifidus muscles. We conclude that DTI is more sensitive in detecting paraspinal muscle pathological changes in the early stage of lumbar degeneration than conventional lumbar MRI.
|
|
4998.
 |
33 |
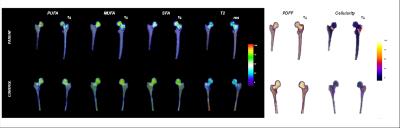
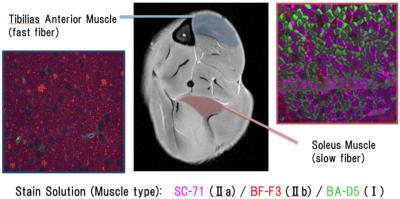
Validity of skeletal muscle fiber type distinguished using q-space imaging 
Junichi Hata, Kanehiro Fujiyoshi, Osahiko Tsuji, Yuji Komaki, Keigo Hikishima, Masaya Nakamura, Hideyuki Okano
We developed a technology that the muscle composition ratio can be non-invasively visualize at q-space imaging. And, these MR image confirmed validation by comparison to the skeletal muscle histology. We scanned diffusion data using 7T MRI scanner and performed analysis to calculate QSI index. The mice lower leg was stained by several solutions to enable muscle typing. As a result, the cell size by sections showing the correlation between the QSI indices. Moreover, the visualization in a staining compared, it is possible to obtain the same image. We confirmed validation by comparing the stained image to QSI.
|
|
5004.
 |
39 |
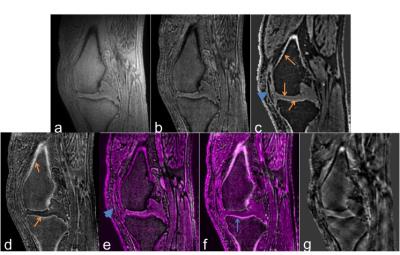
Assessment of Spontaneous Mechanical Activities in Musculature by Simultaneous Multi-Slice Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Fiber-Tractography Data Validation 
Martin Schwartz, Petros Martirosian, Guenter Steidle, Michael Erb, Bin Yang, Fritz Schick
Simultaneous multi-slice diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) was applied on human right calf for imaging Spontaneous Mechanical Activity in Musculature (SMAM) in multiple slices in order to improve assessment of the spatial extension of these spontaneous activities. For data validation, diffusion-tensor images (DTI) were acquired with subsequent fiber tractography to fuse anatomical fiber orientation to spontaneous events in DWI. High accordance between both modalities and reliable application of simultaneous multi-slice diffusion-weighted imaging is demonstrated.
|
|
4999.
 |
34 |
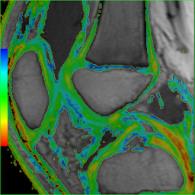
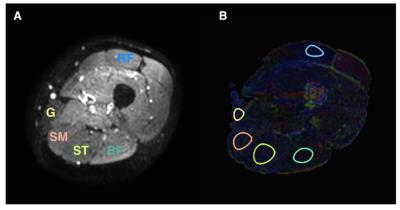
ROI-based Evaluation of Diffusion Tensor Metric of Skeleton Muscles 
Sarah Keller, Jin Yamamura, Shaheen Ahmed, Gerhard Adam, Nancy Rollins, Zhiyue Wang
This study evaluates and compares a pixel-based and ROI-based quantification of DTI-metrics for skeleton muscles in healthy subjects. Besides SNR, an “intra-ROI diffusion direction dispersion angle" is evaluated as a quantitative metric to assess reliability of ROI-based DTI-metrics
|
|
5000.
 |
35 |
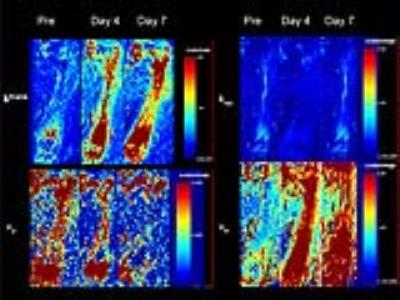
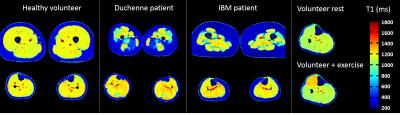
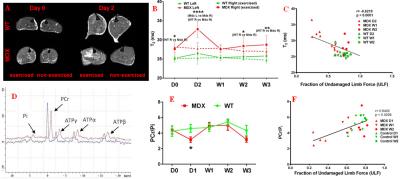
MRI/S Assessment of Skeletal Muscle Morphology and Energetics in Mdx Muscle Injured Mouse as a Model for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy 
HASAN ALSAID, Mary Rambo, Tinamarie Skedzielewski, Alan McDougal, Fritz Kramer, Beat Jucker
The purpose of this study was to longitudinally and non-invasively assess the effect of eccentric contraction induced muscle damage in the Mdx mouse as a model for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy using non invasive MRI and MRS. Mdx mice showed a significant increase in absolute T2 value at baseline and a severe increase in the exercised leg at Day 2 following injury compared to the Wild type group. PCr/Pi ratios decreased in the Mdx group acutely upon exercise induced damage and resolved by day 7. The fraction of Undamaged Limb Force is correlated negatively with T2 and positevely with the PCr/Pi ratios.
|
|
5001.
 |
36 |
Development of an MR-Compatible Ergometer for Use in Quantifying Human Skeletal Muscle Bioenergetics During Supine Dynamic Contractions of the Knee Extensors - permission withheld
Rajakumar Nagarajan, Youssef Jaber, Miles Bartlett, Liam Fitzgerald, Julia Miehm, Frank Sup IV, Jane Kent
The goal of this project was to develop an MR-compatible, multi-modal ergometer for the reliable measurement of human skeletal muscle torque, velocity, power and joint angle during 31P MRS studies of knee extensor muscle energetics. Intracellular [PCr], [Pi] and pH were determined in the vastus lateralis with 4-s time resolution during 4 min of maximal voluntary isokinetic contractions at 240 degrees per second, with a 30 degree range of motion. High S/N for both the MRS and power data indicate that this tool will be useful in future studies of in vivo muscle bioenergetics.
|
|
5002.
 |
37 |
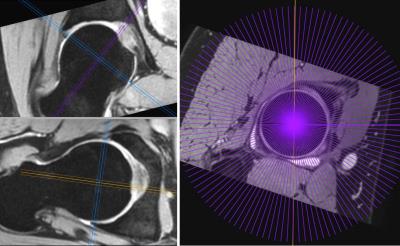
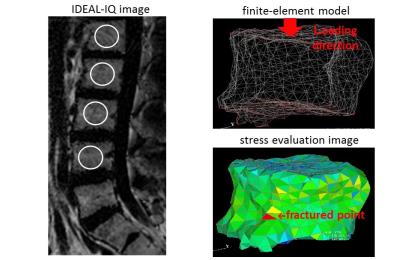
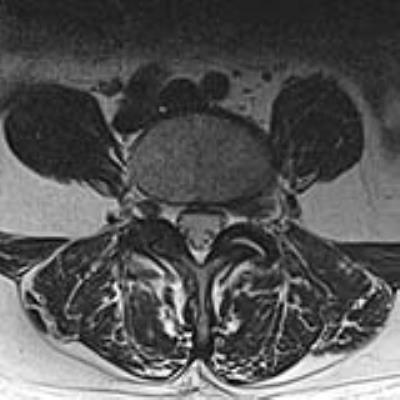
Study of correlation between multifidus muscles atrophy and degenerative diseases of lumbar spine in patients with low back pain using MRI 
Jiufa Cui, Mingqian Huang, Mark Schweitzer
Multifidus muscles (MF) atrophy are common in patients with Low back pain (LBP). Degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine, such as disc herniation, disc degeneration and facet joint osteoarthritis, are leading cause of LBP. Various studies have previously focused on the relationship between MF atrophy and disc degeneration, disc herniation. However, the results are inconsistent. Besides, no study for the correlation between MF atrophy and facet joint osteoarthritis has previously been conducted. This study will investigate the correlation between MF atrophy and disc degeneration, disc herniation, facet joint osteoarthritis using MRI.
|
|
5003.
 |
38 |
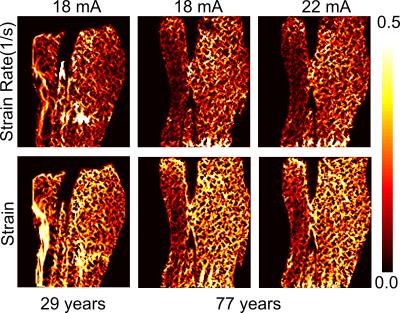
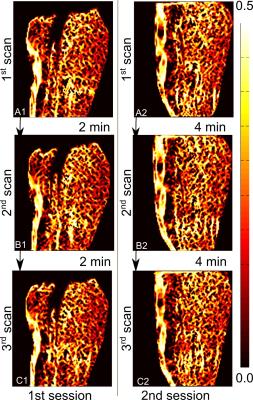
Repeatability of quantitative muscle strain and strain rate measurements by means of synchronous dynamic muscle MRI during electrical muscle stimulation 
Xeni Deligianni, Michele Pansini, Meritxell Garcia, Anna Hirschmann, Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, Oliver Bieri, Francesco Santini
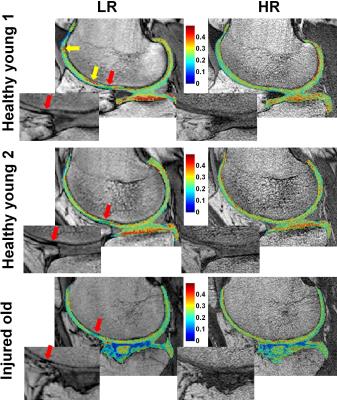
Stimulation of the quadriceps muscle group of the thigh and synchronous phase contrast imaging at a 3T MRI scanner were applied to six healthy volunteers, to assess repeatability of the dynamic strain and strain rate maps. The repeatability was higher for strain (ICC=0.665-0.751) than for strain rate (ICC=0.242-0.571) and the correlation of the results increased with longer intra-scan rest periods. In conclusion, strain and strain rate measured with synchronous MRI of EMS-controlled muscle contraction are repeatable, though attention should be paid to intra-stimulation rest periods.
|
|
5005.
 |
40 |
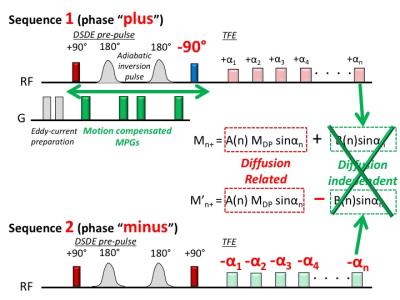
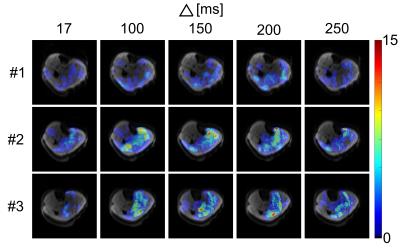
Estimation of the Sensitivity Characteristics and Detection Capability of Diffusion-Weighted MR Sequences in Imaging Spontaneous Mechanical Activity in Musculature 
Martin Schwartz, Guenter Steidle, Petros Martirosian, Ander Ramos-Murguialday, Alto Stemmer, Bin Yang, Fritz Schick
Spontaneous mechanical activity in musculature (SMAM) can be observed from time to time in diffusion-weighted images (DWI) of the human lower leg. In DWI, motion sensitivity is usually restricted to a time window between diffusion-sensitizing dephasing and rephrasing gradients. Capabilities to detect SMAM occurring outside this time window by DWI are expected to be clearly reduced. The temporal sensitivity of diffusion-weighted sequences to SMAM is evaluated by varying diffusion-sensitizing time. In addition, concurrent surface electromyography (sEMG) measurements were performed in order to reveal the temporal correlation of the events in both modalities.
|
|
5006.
 |
41 |
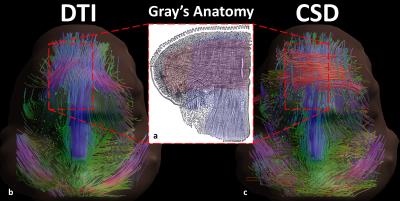
Crossing muscle fibres in the tongue resolved using constrained spherical deconvolution 
Luuk Voskuilen, Valentina Mazzoli, Jos Oudeman, Ludi Smeele, Alfons Balm, Ferdi van der Heijden, Martijn Froeling, Gustav Strijkers, Aart Nederveen
Tongue muscle architecture is suspected to be important in the prediction of speech and swallowing complications after surgery. The tongue contains areas of crossing muscle fibres unable to be resolved by diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). We show that constrained spherical deconvolution (CSD) is able to distinguish these crossing fibres ex vivo and in vivo using a clinically acceptable scan time of 10 min. Also, we show improved tractography in CSD compared to DTI, allowing segmentation of different tongue muscles which conforms to known anatomy.
|
|
5007.
 |
42 |
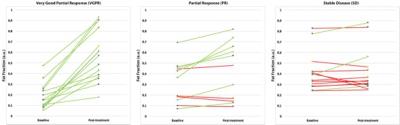
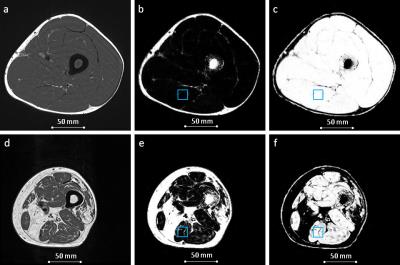
Magnetic Resonance Methods for Quantitative Evaluation of Intramuscular Adipose Tissue 
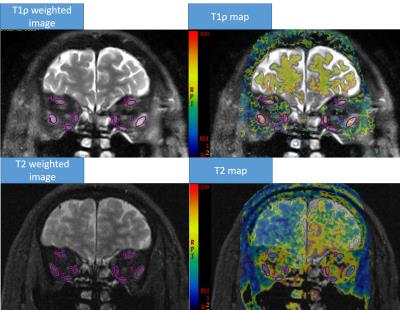
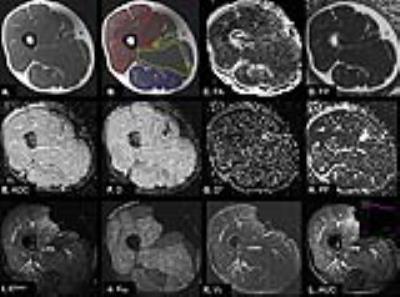
Alexandra Grimm, Heiko Meyer, Mathias Nittka, Esther Raithel, Oliver Chaudry, Andreas Friedberger, Michael Uder, Wolfgang Kemmler, Klaus Engelke, Harald Quick
Intramuscular adipose tissue directly affects physical performance. 56 subjects (80 ± 5 yrs) with sarcopenia and 23 physically well-trained subjects (28 ± 4 yrs), all male, were examined at the thigh on a 3T MR system using quantitative MRI and MRS sequences. The results show that the use of spectroscopy involves challenges with regard to representative assessment of the entire muscle and might overestimate fat in low-fat tissues as muscle tissue. Furthermore, 2pt in comparison to 6pt Dixon sequences should be used with caution for quantitative evaluation, while multi-echo Dixon sequences are capable of quantifying intramuscular adipose tissue.
|
|
5008.
 |
43 |
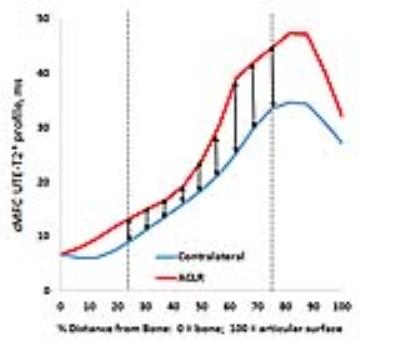
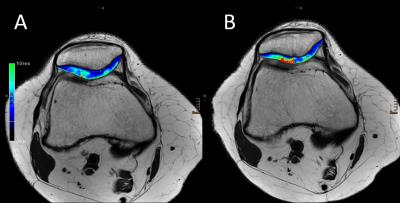
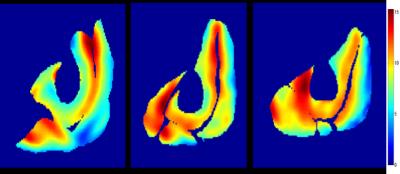
Heterogeneity of Quadriceps Muscle Activation during Isometric Contractions as revealed by Velocity Encoded Phase Contrast (VE-PC) Imaging. 
Toshiaki Oda, Vadim Malis, Taija Finni, Shantanu Sinha
The relative contributions of the four compartments of the quadriceps to force production are clinically very important information. The spatial and temporal heterogeneity of velocity and strain, (surrogate biomarkers of neural activation) was determined, within and between different compartments of normal quadriceps and along the proximo-distal (Z) axis, during isometric contraction using gated VE-PC imaging. Statistically significant differences were determined, within the same muscle compartment, across compartments and between different Z axis positions. Determining how these change in the diseased state e.g. post-ACL tear will be important in tailoring rehabilitative strategies, with particular relevance to preventing early onset of osteoarthritis.
|
|
5009.
 |
44 |
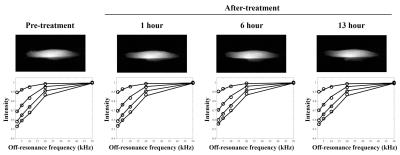
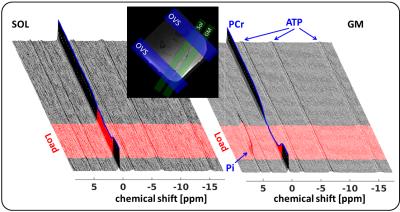
MUSCLE: MUlti SliCe Localized Excitation 31P-MRS 
Alexander Gussew, Martin Krämer, Kevin Moll, Jürgen Reichenbach
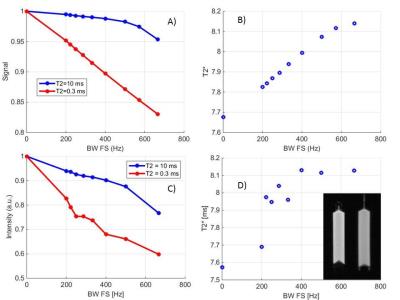
We present a new 31P-MR spectroscopy pulse sequence, the so called Multi-SliCe-Localized-Excitation approach (MUSCLE), which enables time resolved, interleaved non-spin-echo acquisitions of spectra in multiple muscle slabs. The accuracy of slab selection was successfully verified at 3 T by in vitro measurements in a multiple compartment phantom as well as by in vivo measurements of moderately loaded human calf muscles.
|
|
5010.
 |
45 |
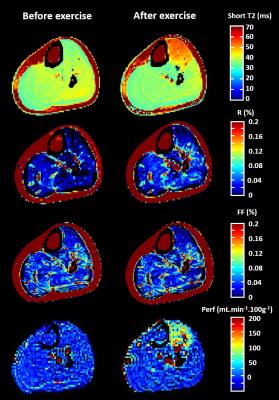
Quantitative NMR imaging of short and long T2 components in the SKM tissue by 1H T2- relaxometry study 
Teresa Gerhalter, Pierre-Yves Baudin, Noura Azzabou, Eriky Caldas, Harmen Reyngoudt, Pierre Carlier, Benjamin Marty
Muscle water T2 is currently being used to assess and monitor the pathology of neuromuscular disorders. The vascular signal of water T2 is close to the one of fat, which might have an impact on the fat fraction quantification using a 2-component fitting approach on MSME data. Here, we examined the impact of long water T2 variations during exercise on fat quantification using the 2-component extended phase graph (EPG) model. Exercise increased the short T2 and the ratio between the amplitudes of short and long T2 signals suggesting an impact of the vascular space on the fat fraction quantification.
|
|
5011.
 |
46 |
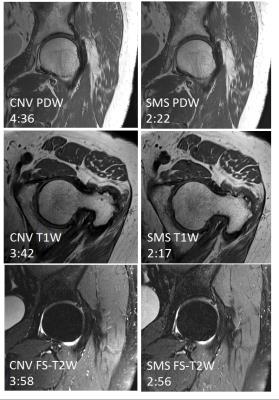
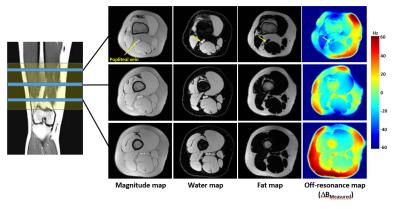
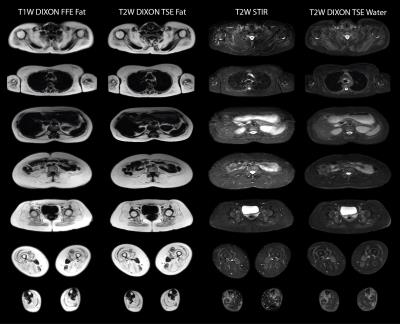
T2-weighted Dixon TSE for accelerated simultaneous grading of whole body skeletal muscle fat infiltration and edema in patients with neuromuscular diseases 
Sarah Schlaeger, Elisabeth Klupp, Dominik Weidlich, Barbara Cervantes, Marcus Deschauer, Benedikt Schoser, Sarah Bublitz, Federica Montagnese, Christoph Katemann, Hendrik Kooijman, Ernst Rummeny, Claus Zimmer, Jan Kirschke, Dimitrios Karampinos
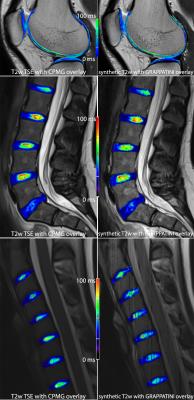
The assessment of fatty infiltration and edema in the whole body musculature of patients with neuromuscular diseases typically requires the separate performance of a T1-weighted sequence and a fat suppressed T2-weighted sequence. T2-weighted Dixon TSE enables the generation of T2-weighted fat-separated and water-separated images, which could be used to simultaneously assess fatty infiltration and edema and to reduce total scan time. The present study examines the diagnostic performance of whole body T2-weigthed Dixon TSE imaging in 10 patients with neuromuscular diseases.
|
|
5012.
 |
47 |
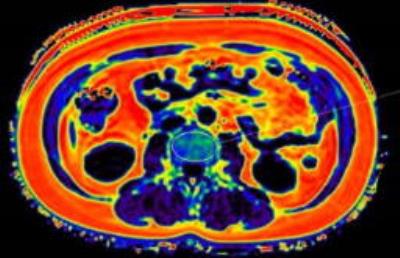
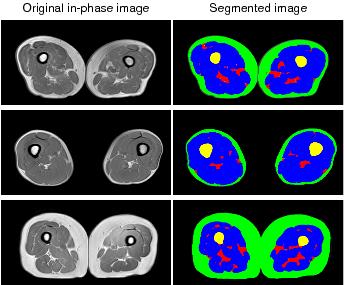
Magnetic resonance imaging estimates of intermuscular fat density in the thigh in sarcopenia population: correlation with physical performances 
Yu Xin Yang, Wee Shiong Lim, Mei Sian Chong, Laura Tay, Suzanne Yew, Audrey Yeo, Cher Heng Tan
Emerging evidence suggests that intermuscular fat (IMF) accumulation is associated with reduced muscle quality and increased risk of physical limitation. However, the impact and mechanism of IMF in sarcopenia or sarcopenic obesity (SO) are still unclear. MRI is a promising tool for early detection of sarcopenia and SO. This may translate to use in clinical trials and in future clinical practice, where quantitative assessment may become standard of care. . This study aims to study a new index that we term “IMF density”, shows promise as an important quantitative variable that reflects patients’ physical performances.
|
|