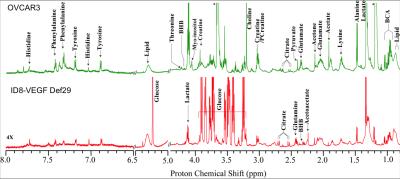
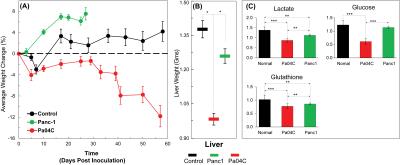
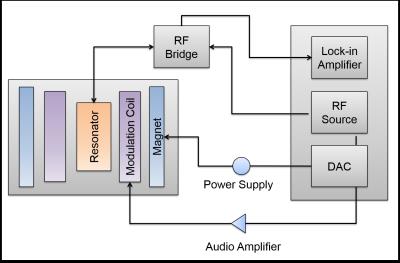
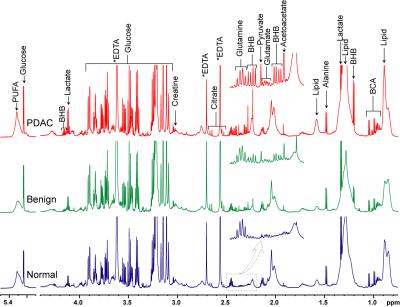
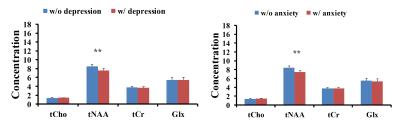
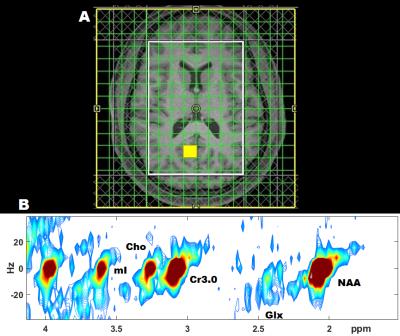
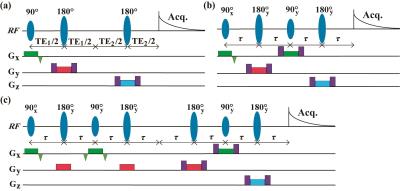
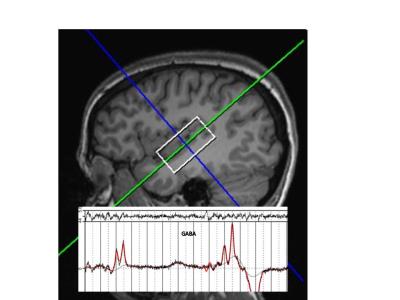
Non-Proton MRI & MRS
Electronic Poster
MR Spectroscopy
Thursday, 27 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
14:00 - 15:00 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
5616.
 |
56 |
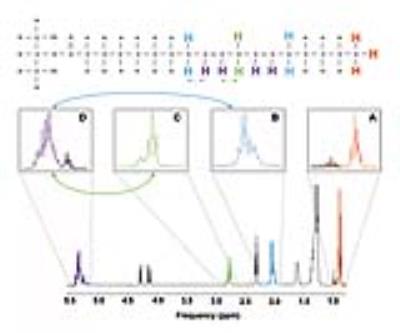
Short TE PRESS-based proton observed carbon edited (POCE) 13C Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy with a volumetric 1H transmitter for in vivo rat brain imaging at 7T 
Chathura Kumaragamage, Dan Madularu, Axel Mathieu, Henk De Feyter, Natasha Rajah, Jamie Near
Carbon-13 (13C) magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) remains to be the only noninvasive method capable of measuring neuroenergetics and neurotransmitter cycling in the brain in vivo [1]. However, 13C MRS is a challenging technique to implement, and suffers from low sensitivity. In this study we investigated a short TE (12.6 ms) PRESS localized proton observed carbon edited 13C MRS utilizing a volumetric resonator for proton excitation. The designed platform demonstrates high sensitivity to 1H signals, provides excellent localization, and high resolution 1H and 1H-[13C] spectra for in vivo rat brain imaging.
|
|
5629.
 |
69 |
Improving Sodium Concentration Measurements using sub-sampled Non-Cartesian Trajectories and Non-Linear Iterative Reconstruction algorithm 
Arthur Coste, Nicolas Chauffert, Fawzi Boumezbeur, Alexandre Vignaud, Philippe Ciuciu, Guillaume Madelin, Kathrin Reetz, Denis Le Bihan, Cécile Rabrait-Lerman, Sandro Romanzetti
In this work we explored different aspects that could benefit to in vivo Sodium concentration measurements in order to reduce Acquisition Time to improve patient comfort and an reduce risk of motion artifacts. We studied two Non Cartesian image reconstruction methods and explored subsampling.
|
|
5615.
 |
55 |
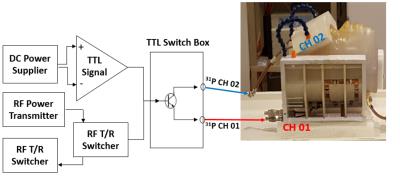
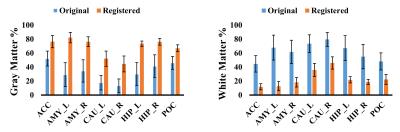
Improvement in 31P CSI voxel tissue segmentation 
Xian-Feng Shi, Young-Hoon Sung, Douglas Kondo, Colin Riley, Perry Renshaw
The aim of the present study was to test a novel method for improving the subcortical tissue segmentation results, of the anatomical brain images acquired using a 31P/1H dual-tuned coil. When a dual-tuned 31P/1H coil is utilized to perform phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of subcortical brain regions, the resulting anatomical images suffer from both low signal-to-noise ratio, and from reduced image contrast. By registering this volume image on a second anatomical image acquired using a single-tuned, 12 channel 1H head coil, we found that the subcortical tissue segmentation accuracy was significantly improved.
|
|
5621.
 |
61 |
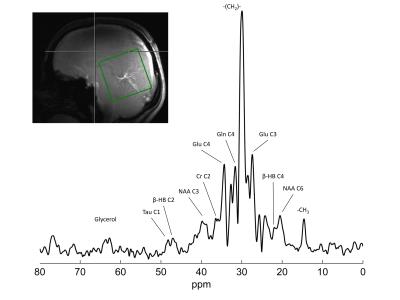
Feasibility of localized, 1H decoupled natural abundance 13C-MRS of human brain at 7T using double tuned array coils and polarization transfer 
Guillaume Donati, Rolf Gruetter
The inherent low sensitivity of 13C-MRS makes detection of natural abundance metabolites in human brain challenging. We aimed to demonstrate that double-tuned array coils are particularly well-suited for 13C-MRS studies in vivo, as they provide high sensitivity and high transmit efficiency over a large FOV. To further enhance the SNR, DEPT sequence was used to transfer polarization from 1H to 13C, as well as WALTZ-16 1H-decoupling, all within FDA guidelines. Natural abundance metabolites such as glutamate, glutamine, NAA and creatine were successfully detected and decoupled in 30 minutes acquisition time, showing strong efficiency and sensitivity of our measurement setup.
|
|
5622.
 |
62 |
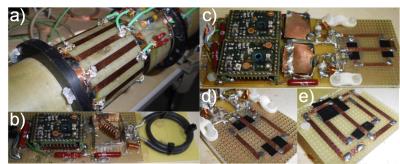
A 35Cl ToRo Resonator System for Preclinical MRI/MRS at 9.4T 
Matthias Malzacher, Ruomin Hu, Jorge Chacon-Caldera, Andreas Neubauer, Lothar Schad
Chloride (Cl-) is next to the cations Na+ and K+ the most abundant non-organic anion in the mammals. Assessment of chlorine’s (35Cl) concentration in tissue could provide further insights into tissue viability in addition to tissue sodium concentration. Yet, low Signal-to-Noise ratio (SNR) is challenging for the RF hardware components. To overcome these challenges, a Transmit-only-Receive-only (ToRo) system for 35Cl MRI/MRS at 9.4T was developed comprised of an actively-decoupled linearly-driven 16 leg low-pass Birdcage transmitter coil combined with two different receiver coils. Substantial SNR gain was reached using receive-only elements compared to the Birdcage coil in TxRx mode.
|
|
5618.
 |
58 |
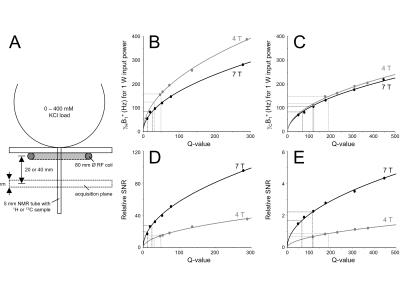
Comparison of direct 13C and indirect 1H-[13C] MR detection methods for the study of dynamic metabolic turnover in the human brain 
Hao Chen, Henk De Feyter, Peter Brown, Douglas Rothman, Robin de Graaf
A wide range a direct 13C and indirect 1H-[13C] MR detection methods exist to probe dynamic metabolic pathways in the human brain. Choosing an optimal detection method is difficult as sequence-specific features regarding spectral resolution, power requirements and sensitivity complicate a straightforward comparison. Here we combine density matrix simulations with experimentally determined values for intrinsic 1H and 13C sensitivity, T1 and T2 relaxation and transmit efficiency to allow selection of an optimal 13C MR detection method for a given application and magnetic field.
|
|
5623.
 |
63 |
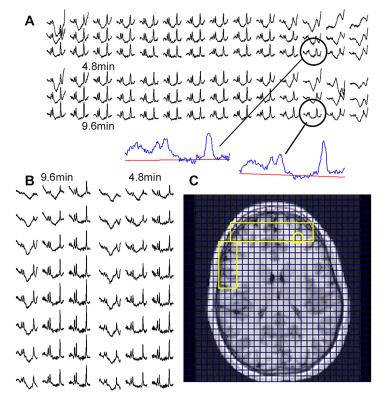
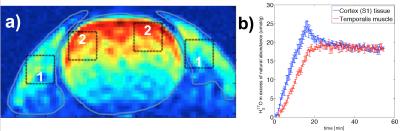
Simultaneous measurement of metabolic rates of oxygen via 17O NMR imaging in brain and muscle tissue of rat at 16.4T 
Hannes Wiesner, Dávid Balla, Klaus Scheffler, Kamil Ugurbil, Xiao-Hong Zhu, Wei Chen, Kamil Uludag, Rolf Pohmann
In this study, we exploit the feasibility of the 17O MRSI technique for simultaneous measurement of the metabolic rates of oxygen in brain and surrounding muscle based on ROI analysis of dynamics of tissue H217O time courses acquired at 16.4T with 3D 17O MRSI. An established three-phase model originally developed for brain application was extended with certain assumptions applied to the resting temporalis muscle of rats.
|
|
5620.
 |
60 |
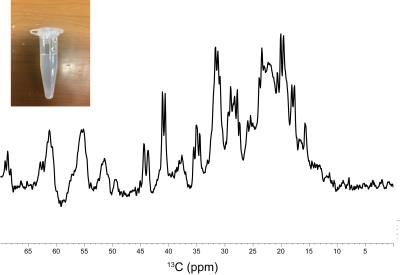
NMR and MRS studies of the neurotoxic oligomer of a-Synuclein toward investigating its in vivo structure 
Keika Saito, Mitsuhiro Takeda, Sosuke Yoshinaga, Hiroaki Terasawa
α-Synuclein (α-Syn) is an abundant protein in neurons, and changes to a neurotoxic α-helical oligomer in vitro. The goal of our study is to investigate the structure of the α-Syn oligomer in vivo, by delivering 13C-labeled α-Syn into mouse brains and performing a 13C CEST experiment. We report the MRS detection of the 13C signals of the α-Syn monomer in an agarose gel phantom, mimicking a physiological environment. We also report that the in vitro oligomerization rate of α-Syn varies, depending on buffer conditions. We envisage that the CEST effect will be detected by adjusting the oligomerization kinetics of α-Syn.
|
|
5613.
 |
53 |
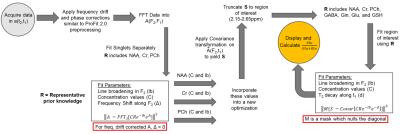
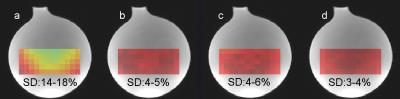
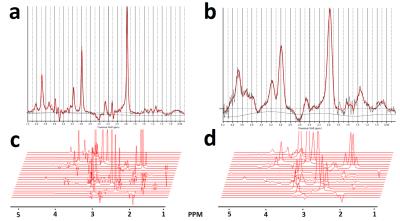
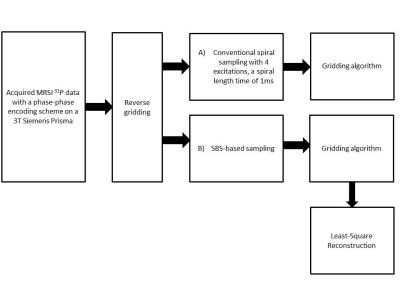
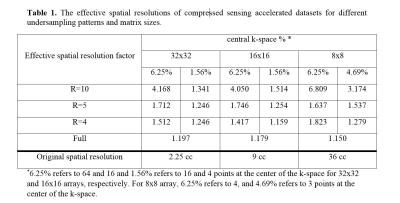
Optimization of Regularization Parameters of Compressed Sensing Reconstruction for Fast Phosphorus MR Spectroscopic Imaging of Human Brain. 
Gokce Hale Hatay, Muhammed Yildirim, Esin Ozturk-Isik
This study aims at investigating the effects of compressed sensing data acquisition and reconstruction factors for accelerated phosphorus MR spectroscopic imaging (31P-MRSI). Simulated 31P MRSI datasets containing healthy and tumor regions were created based on the metabolite information of brain tumor patient 31P-MRSI acquired at 3T. k-space data were randomly undersampled with three different reduction factors while preserving the central portion for different noise levels, reduced datasets were reconstructed using compressed sensing by combining eleven different total variation and L1-norm penalties. Findings showed that data acquisition pattern and reconstruction parameters have a significant effect on the resultant 31P-MRSI spectral quality.
|
|
5614.
 |
54 |
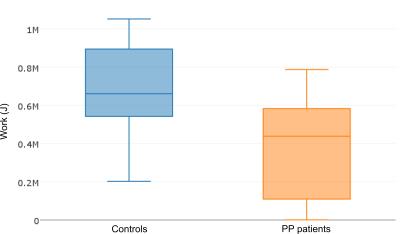
Dynamic 31P MR spectroscopy of fatigue in triceps surae muscles on post-poliomyelitis patients versus healthy age-matched volunteers at 3T 
Xeni Deligianni, Tanja Haas, Patricia Hafner, Simone Schmidt, Vanya Gocheva, Francesco Santini, Oliver Bieri, Dirk Fischer
This study was focused on comparing the metabolism of triceps surae muscles on postpoliomyelitis patients and age-matched healthy volunteers through dynamic 31P spectra acquisition at 3T magnetic field. It has been suggested previously that in postpolio patients, metabolic changes are secondary to neurogenic pathways, but may influence Pi/PCr ratios. Here, it was shown that baseline PDE/PCr ratios were higher in patients. During exercise, controls performed significantly higher work and the change of Pi/PCr ratios was lower than in patients. Investigation of the correlation of Pi/PCr with the degree of the disease could be a promising clinical direction.
|
|
5609.
 |
49 |
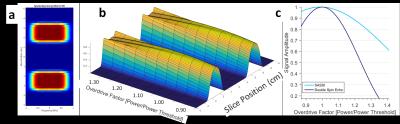
The feasibility of absolute quantification for 31P MRS at 7T 
Lucian Purvis, Ladislav Valkovic, Matthew Robson, Christopher Rodgers
Calculation of in vivo concentrations requires knowledge of the B1 field. A common solution to this problem has been to use field maps measured in phantoms, but this becomes increasingly difficult at high field. The size of the effect of material and B0 field strength determining B1 in the liver using phosphorus (31P) phantoms was investigated at 1.5, 3, and 7T using CST simulations. The effect of concentration differences at 7T was demonstrated using 15 and 30mM phosphate phantoms. At 1.5T, using phosphate phantoms with concentrations between 5-40mM give an error of less than 3%. This increases to 10% at 3T, and 20-114% at 7T.
|
|
5628.
 |
68 |
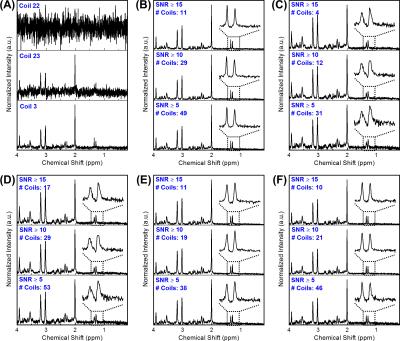
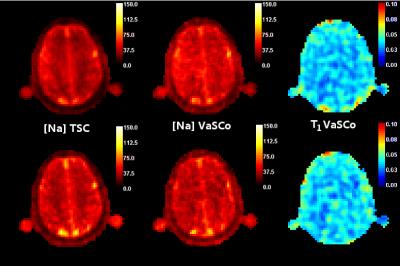
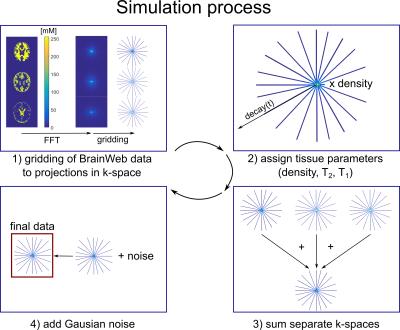
Realistic simulation of 23Na brain data: Understanding the influence of acquisition parameters on the accuracy of 23Na concentration measurement 
Jonathan Lommen, Nicolas Behl, Peter Bachert, Mark Ladd, Armin Nagel
Sodium (23Na) is connected to tissue physiology and can be spatially resolved by MRI. Low in-vivo concentrations and short relaxation times render a quantitative determination challenging. We present a simulation method which allows synthesizing realistic 23Na MRI raw data. Thereby, most effects in typical quantification experiments on the basis of an external concentration reference can be studied. To establish a reference accuracy level, we investigate the influence of T2* decay, undersampling, TE, and TR on 23Na quantification. The presented simulations can be used for the testing and evaluation of quantitative reconstruction methods as well as to test significance in clinical studies.
|
|
5631.
 |
71 |
Sodium short and long T2* components in the normal human brain: a multi-TE 23Na MRI study at 7T 
Mark Bydder, Armin Nagel, Adil Maarouf, Jeremy Verneuil, Patrick Viout, Maxime Guye, Jean-Philippe Ranjeva, Wafaa Zaaraoui
The study aimed to provide values of the short and long T2* sodium components of the human brain at 7T using a multi-echoes 23Na MRI approach (n=24 TE). These results may help improving sodium quantification at 7T.
|
|
5617.
 |
57 |
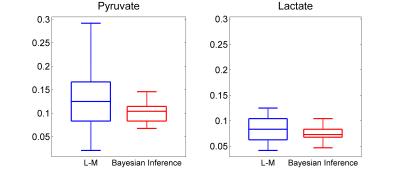
Quantitative analysis of hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate metabolic kinetics using Bayesian Inference algorithms 
Nikolaos Dikaios, Charlie Daniels, Ferdia Gallagher, James O’Callaghan, David Atkinson, Shonit Punwani
Metabolic processes monitored by MRS precede the micro-structural changes visualised by MRI. It is well-recognised that cancer cells reprogram their metabolic pathways to meet their energy demands for abnormal proliferation. Pyruvate is produced through the breakdown of glucose in glycolysis, and is essential for providing cellular energy. Histological studies have shown increased exchange of pyruvate to lactate in prostate cancer, demonstrating a positive correlation with more aggressive disease. In regions of up-regulation of glucose metabolism, [1-13C]pyruvate is more readily converted to [1-13C]lactate, providing added value for diagnostic imaging. This work aims to robustly quantify the exchange rates between pyruvate and lactate using Bayesian Inference algorithms.
|
|
5630.
 |
70 |
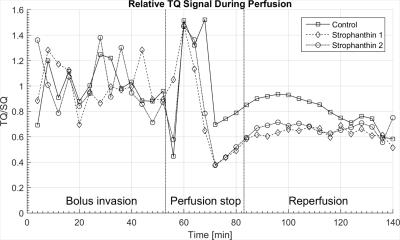
Investigation of Strophanthin Induced Na-/K-ATPase Blockage by Means of 23Na Multi Quantum Spectroscopy in a High Density Cell Culture on Chip 
Andreas Neubauer, Matthias Malzacher, Victor Schepkin, Jorge Chacon-Caldera, Ruomin Hu, Eric Gottwald, Cordula Nies, David Thiele, Lothar Schad
Sodium multi quantum (MQ) spectroscopy was used to record single (SQ) and triple quantum (TQ) resonances from a 3D cell culture implanted in a MRI compatible bioreactor under the strophanthin induced inhibition of the sodium-potassium pump (Na-/K-ATPase) at 9.4T. The results show a clear alteration in the ratio TQ/SQ under strophanthin influence. Due to the high control of physiological parameters the bioreactor provides, this alteration can be directly linked to the inhibition of the Na-/K-ATPase.
|
|
5612.
 |
52 |
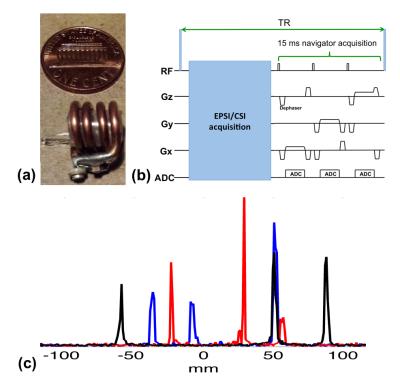
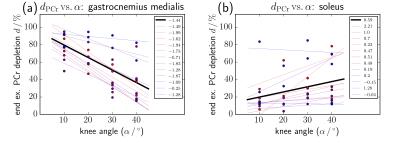
Different activated calf muscle groups measured simultaneously during plantar flexion exercise with multiple knee angles using multivoxel 31P-MRS. 
Fabian Niess, Georg Fiedler, Albrecht Schmid, Sigrun Goluch, Roberta Frass-Kriegl, Michael Wolzt, Ewald Moser, Martin Meyerspeer
The distribution of workload between GM and SOL during plantar flexion exercise is strongly linked to the knee angle. This work investigates the differences in muscle activation of GM and SOL during plantar flexion with multiple knee angles. Time series spectra of both muscle groups were acquired simultaneously with high time resolution using dynamic multi-voxel 31P MRS. A linear correlation was found between knee angle and 31P MRS parameters related to muscle activation (PCr depletion, pH, PCr recovery time), confirming predominant involvement of GM with a straight knee, and increasing contributions of SOL with a bent knee.
|
|
5619.
 |
59 |
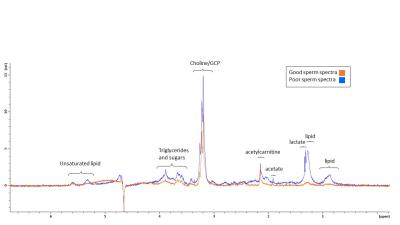
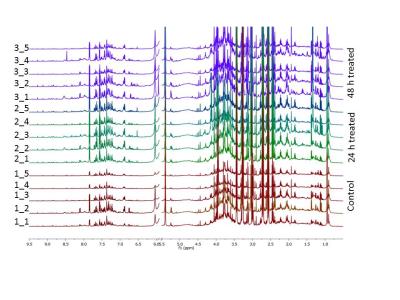
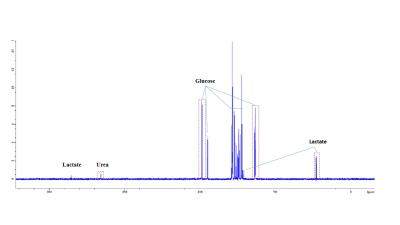
The effect of malonate, succinate, oxaloacetate and 2-deoxy-D-glucose on boar sperm metabolism using 13C MRS 
Nurul Fadhlina Ismail, Steven Reynolds, Sarah Calvert, Allan Pacey, Martyn Paley
One in five young men has poor semen quality, including low motility. Studying energy metabolism may provide better understanding of sperm motility. We acquired 13C Magnetic Resonance spectra of sperm incubated with 13C-glucose with different concentrations of inhibitors: malonate, oxaloacetate, succinate, and 2-deoxy-D-glucose. This study examined the effect of these inhibitors on sperm lactate production and vitality, with a secondary aim to observe Krebs cycle intermediates in the MR spectrum. Glucose signal significantly decreased with increasing oxaloacetate concentration. Malonate and oxaloacetate and 2DG significantly decreased in lactate production. These inhibitors did not lead to observable 13C labelled Krebs cycle intermediates.
|
|
5610.
 |
50 |
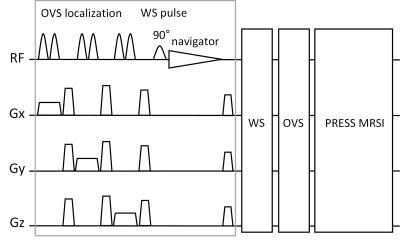
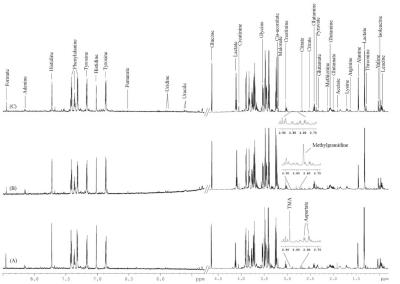
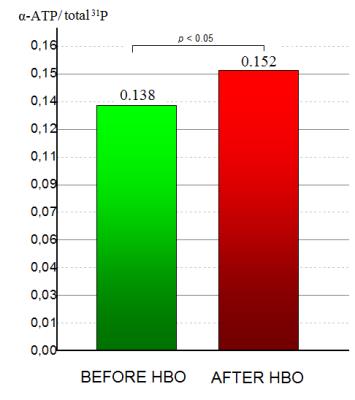
Effect of hyperbaric oxygenation on human brain phosphate metabolites at 3 Tesla. In vivo 31P MRS study 
Andrei Manzhurtsev, Olga Vasyukova, Victoria Sergeeva, Tolibjon Akhadov, Ilia Mel'nikov, Olga Bozhko, Natalia Semenova
This study is aimed to reveal the effects of hyperbaric oxygenation on human brain phosphate metabolites using 31P MRS. At first, 31P MRS study was conducted, after that the subjects took a session in hyperbaric chamber (1.2 atmosphere, 100% O2) and then 31P MRS study was repeated. The increase of α-ATP peak intensity was revealed after hyperbaric oxygenation, while other peak intensities and pH remained unchanged. This phenomenon is likely to happen because of [NAD(H)] increase, that might confirm the positive effect of hyperbaric oxygenation on human brain metabolism.
|
|
5624.
 |
64 |
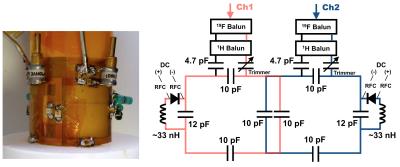
Design and construction of a novel double-tuned 1H/19F coil using PIN-diode switches at 9.4T 
Chang-Hoon Choi, Suk-Min Hong, YongHyun Ha, N. Jon Shah
A double-tuned 1H/19F coil using PIN-diode switches was developed and evaluated its performance on a 9.4T preclinical MRI scanner. This proposed design uses an inductor rather than a capacitor in series with the PIN-diode so that the resonance frequency is shifted in the opposite direction compared to the conventional method. This is a key difference from the previous developments and in this way we can maintain the SNR or image quality of the X-nuclei (therefore 19F); the SNR is nearly as good as a single-tuned 19F coil.
|
|
5611.
 |
51 |
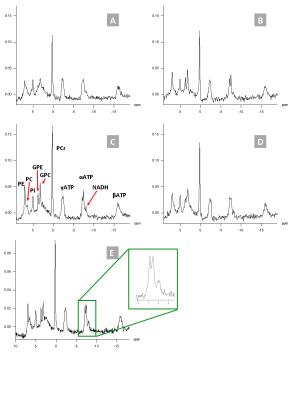
31P spectroscopic imaging of the human brain at 3T: effect of NOE and 1H-decoupling 
Mark J. van Uden, Tom H. Peeters, Tom W.J. Scheenen, Arend Heerschap
31P MRS of the brain can reveal changes in energy and lipid metabolism in healthy and diseased brain. In this abstract we compare 31P MRS measurements with and without NOE and/or 1H-decoupling. Adding nuclear Overhauser enhancement (NOE) and 1H-decoupling to a 31P MRS measurement at 3T increases spectral resolution to that at 7T and improves sensitivity so that the theoretical difference with 7T is partly compensated for. At relatively short repetition times both 1H-decoupling and NOE have to be taken into account for proper quantification.
|
|
5625.
 |
65 |
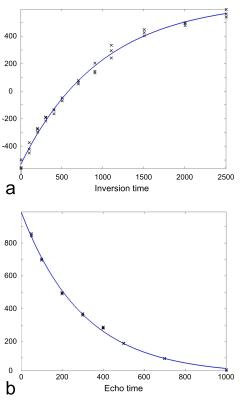
Study of MR characteristics of anti-psychotic drugs using fluorine (19F) MR spectroscopy at 9.4 T 
Chu-Yu Lee, In-Young Choi, Jean Dinh, William Brooks, J. Leeder, Phil Lee
19F MRS allows assessment of fluorine containing anti-psychotic drugs in the brain. However, the reliable quantification remains challenging due to low drug concentrations and MR characteristics of the drugs are not well understood. This study aimed to characterize MR properties of four anti-psychotic drugs: pimozide, paliperidone, risperidone, and racemic fluoxetine, in phantoms at 9.4 T. Our results demonstrated that pimozide, paliperidone and risperidone showed over 50 ppm differences in chemical shifts and over 200 ms differences in T1 and T2 relaxation times compared with racemic fluoxetine. These different MR characteristics may have important implications for the 19F MRS technique development.
|
|
5627.
 |
67 |
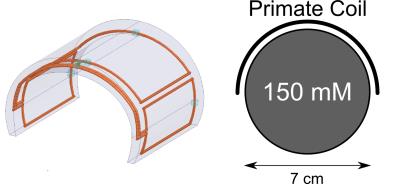
Simultaneous multi-parametric and quantitative estimation of 23Na physical properties at 7 Tesla using QuICS 
Lisa Leroi, Arthur Coste, Ludovic de Rochefort, Mathieu Santin, Romain Valabrègue, Franck Mauconduit, Marie-France Hang, Edouard Chazel, Jérémy Bernard, Michel Luong, Eric Giacomini, Denis Le Bihan, Cyril Poupon, Fawzi Boumezbeur, Cécile Rabrait-Lerman, Alexandre Vignaud
Quantifying physical properties of sodium could be of benefit to assess more specifically changes in cellular homeostasis accompanying neuroinflammatory or neurodegenerative diseases. This work aimed at adapting for 23Na MRI at 7 Tesla the Quantitative Imaging using Configuration States (QuICS) method, primarily developped for 1H MRI. We demonstrate the possibility to not only estimate accurately the T1, T2, FA, M0 and ADC simultaneously for 23Na at physiological concentration at UHF, but to acquire 3D maps for all of them.
|
|
5632.
 |
72 |
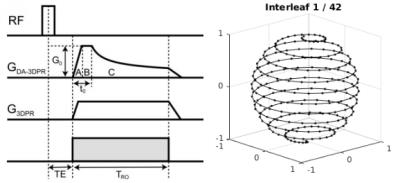
Validation and Initial Results from Dynamic 23Na fMRI - permission withheld
Mark Bydder, Wafaa Zaaraoui, Lothar Schad, Maxime Guye, Jean-Philippe Ranjeva
In this abstract we develop and validate an MRI acquisition/reconstruction method to derive the temporal dynamics of 23Na within a 20 min scan.
|
|
5626.
 |
66 |
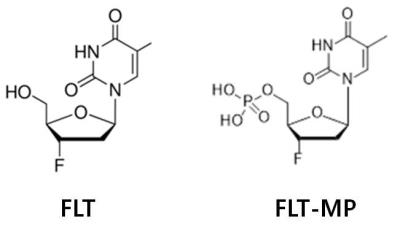
Monitoring of cell proliferation by 19F-MRS via quantitation of 3'-deoxy-3'-fluorothymidine (FLT) and its monophosphate metabolite (FLT-MP) in invivo 
Inok Ko, Ki-Hye Jung, Kyung Jun Kang, Kyo Chul Lee, Yong Jin Lee, Jung-Young Kim, Sang Moo Lim, Ji-Ae Park
Distinguishing between FLT(fluorothymidine) and FLT-MP(flruorothymidine - monophosphate) by imaging methods is important for evaluating the tumor cell proliferation rate. The aim of this study is to develop and validate a suitable 19F MR Spectroscopy for measuring TK1 activity via quantitation of FLT and FLT-MP in vivo. We observed the good correlations between SNR and FLT concentration (r2= 0.94). In phantom study, the locations of FLT and FLT-MP was -175.99, -175.24 ppm, respectively. In vivo study, FLT spectrum in mouse tumor was observed in 25 min after injection, whereas FLT-MP spectrum occurred in 90 min after injection. This result shows that 19F MR Spectroscopy is suitable for monitoring of FLT-MP generation in in vivo.
|
|