Post-Processing & Analysis
Traditional Poster
Acquisition, Reconstruction & Analysis
Monday, 24 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
08:15 - 10:15 |
|
1430.
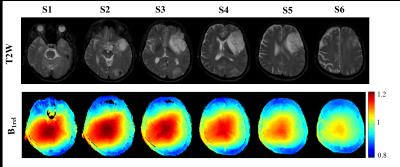 |
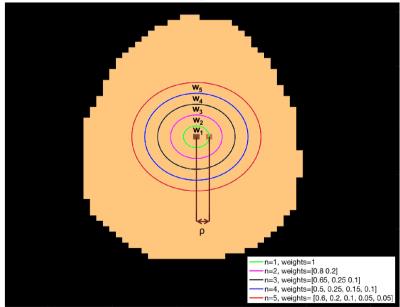
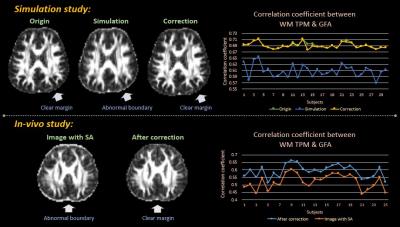
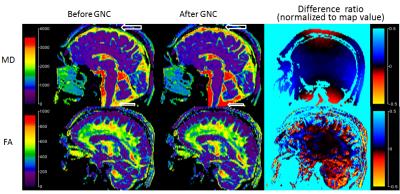
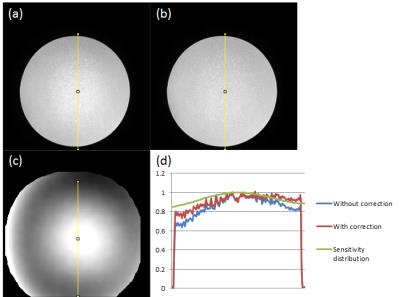
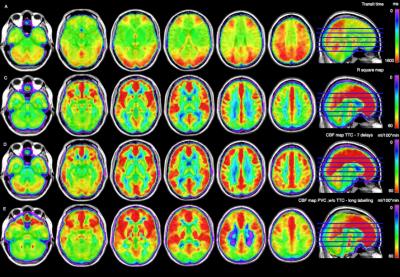
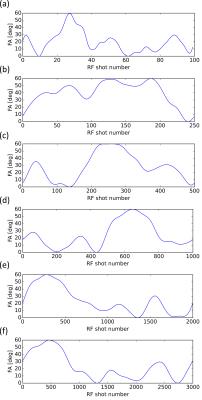
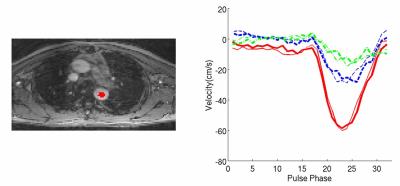
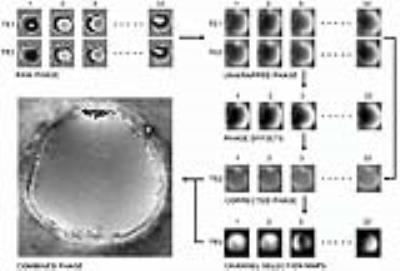
Evaluating effect of B1 field Inhomogeneity on DCE-MRI Data Analysis of Brain Tumor Patients at 3T
ANIRBAN SENGUPTA, RAKSHIT DADARWAL , RAKESH GUPTA, ANUP SINGH
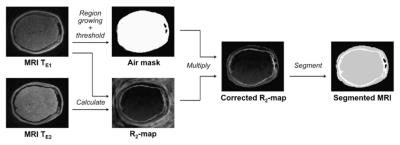
In the current study, transmit B1 field inhomogeneity(B1FI) distribution and propagation of flip-angle(FA) related errors to Dynamic-contrast-enhanced(DCE) MRI data analysis in brain tumors of human subjects at 3T MRI were studied. Experimental and simulation studies were performed to evaluate the propagation of these errors to DCE-MRI data analysis and its correction were performed during signal intensity(S(t)) to concentration-time-curve(C(t)) conversion. This study show that B1FI introduced substantial errors in DCE-MRI data analysis(tracer-kinetic and hemodynamic parameters) and these errors were mitigated by correcting FA using B1 map. B1FI related error also showed dependence on concentration of contrast agent and length of concentration-time-curve.
|
|
1431. 
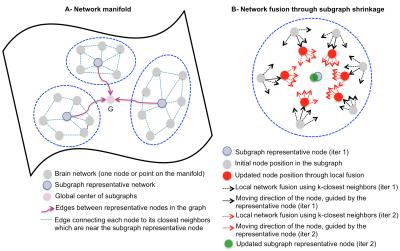 |
Brain Network Atlas Estimation using Centered Graph Shrinkage with Application to Developing and Aging Brains
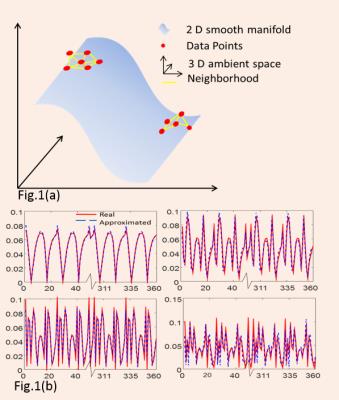
Islem Rekik, Gang Li, Minjeong Kim, Weili Lin, Dinggang Shen
Learning how to average brain networks (i.e., build a brain network atlas) constitutes a key step in creating a reliable ‘mean’ representation of a set of normal brains, which can be used to spot deviations from the normal network atlas (i.e., abnormal cases). However, this topic remains largely unexplored in neuroimaging field. In this work, we propose a network atlas estimation framework through a non-linear diffusion along the local neighbors of each node (network) in a graph. Our evaluation on both developing and aging datasets showed a better ‘centeredness’ of our atlas in comparison with the state-of-the-art network fusion method.
|
|
1432.
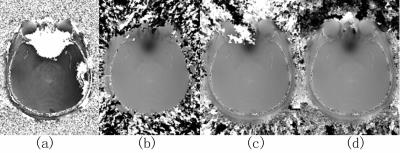 |
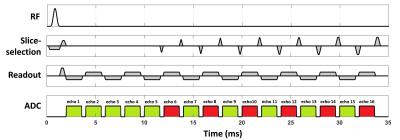
Robust and fast phase unwrapping strategy to improve SWI quality
Yongquan Ye, Jinguang Zong, Weiguo Zhang
A robust and fast phase unwrapping strategy was developed for multi-echo SWI, to improve image quality where classic SWI fails, such as cavity vicinity regions, as well as to provide pristine field map for subsequent QSM applications. A smoothing and a seed prioritizing method were proposed, which was demonstrated to provide very robust unwrapping on phase difference map between neighboring echoes. And with a high quality unwrapped phase difference map, the phase of all echoes can be robustly unwrapped in seconds.
|
|
1433.
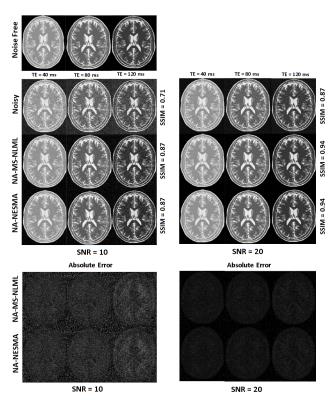 |
A Fast Adaptive Multispectral Nonlocal Denoising Filter
Michael Maring, Mustapha Bouhrara, Richard Spencer
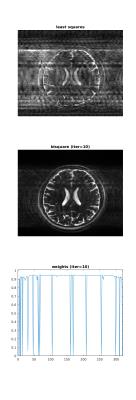
We introduce a new high-performance nonlocal filter, NESMA, for noise reduction in multispectral (MS) MR imaging. Through extensive analysis, we show that the NESMA filter demonstrates a high degree of overall image denoising while preserving edges and small structures. We compared the performance of the NESMA filter to the multispectral nonlocal maximum likelihood (MS-NLML) filter. Although the MS-NLML filter is highly efficient, it requires extensive computational time. NESMA markedly decreases computation time while maintaining comparable levels of noise reduction and feature preservation. Finally, we show that adaptive selection of similar voxels further improves filtering quality.
|
|
1434.
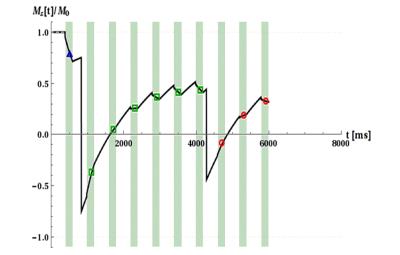 |
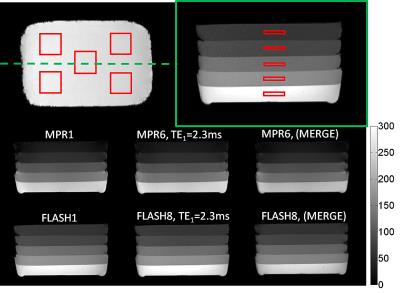
Inversion quality independent robust $$$T_1$$$-quantification of MOLLI sequence data
Thomas Kampf, Theresa Reiter, Wolfgang Bauer
Quantitative mapping of the longitudinal relaxation time has gained increasing interest as it allows monitoring of important structural and functional information of the myocardium. The MOLLI sequence commonly used in clinical research requires a high quality of the inversion pulses for unbiased quantification which is non-trivial especially at high fields. In this work we present a simple modification of the MOLLI sequence which in combination with the recently introduced IGF post processing solves the problem of insufficient inversion quality as demonstrated in phantom experiments.
|
|
1435. 
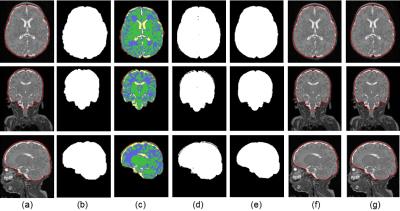 |
Improved Infant MRI Brain Extraction utilizing Clustering and Morphological Approaches
Yao Wu, Sonia Dahdouh, Marine Bouyssi-Kobar, Manoj Kumar, Josepheen Cruz, Wonsang You, Catherine Limperopoulos
Accurate brain extraction is a key procedure in neuroimage analyses. This paper aims to solve the intracranial cavity overestimation issue inherent to existing brain extraction methods when applied to infant brains. We applied k-means clustering method and morphological approaches to improve the accuracy of previously published brain extraction techniques. Evaluation of our proposed method on 28 preterm MR images showed more robust and effective infant brain extraction compared to previous methods.
|
|
1436.
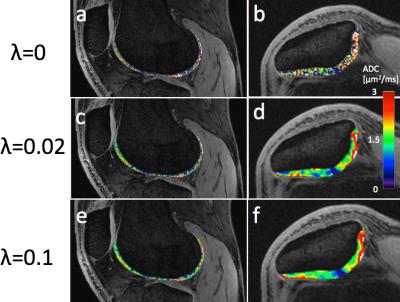 |
SNR-Weighted Regularization of ADC Estimates using Double-Echo in Steady-State
Bragi Sveinsson, Garry Gold, Brian Hargreaves, Daehyun Yoon
Double-echo in steady-state (DESS) is a 3D sequence which offers both morphological images and quantitative parameter maps (SNR-efficient 3D maps of T2 and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC)) in various applications, such as breast imaging or knee cartilage imaging. The sequence has less sensitivity to ADC than to T2, sometimes leading to noisy ADC maps. Here, we investigate the effects of using regularized fitting of the signals, with a penalty in ADC variability, to produce less noisy ADC maps. The method is designed to apply less regularization to regions with high SNR. The approach makes use of a recent analytical expression for a ratio between DESS signals.
|
|
1437.
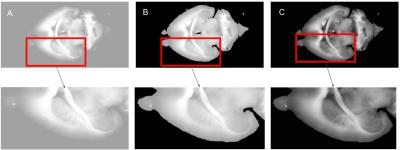 |
Optimal contrast enhancement of blockface images for MRI guided reconstruction of mouse brain volumes
Christoffer Gothgen, Catharina Holland, Christos Zoupis Schoinas, Karine Mardon, Maciej Plocharski, Lasse Østergaard, Andrew Janke
Blockface imaging can improve atlases of the rodent brain by supplying high resolution images. This study compares three different contrast stretching methods for enhancing the information in blockface images together with a registration to a 16.4 T atlas of the mouse brain. Contrast enhancement technique used was histogram equalization, adjusting the image intensity values by stretching them between the bottom 1% and the top 1% and CLAHE with a clip limit of 0.01 and a uniform histogram. Registrations was rigid, affine and SyN. By using CLAHE as contrast stretching method a high similarity to the MRI was found.
|
|
1438. 
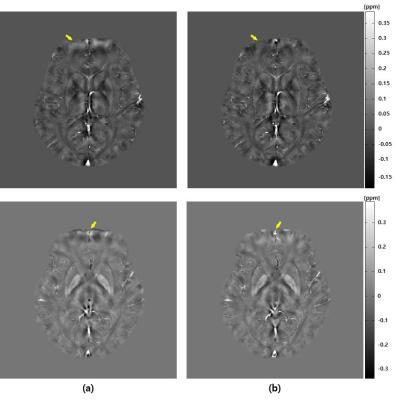 |
B0 Field Inhomogeneity Corrected Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping
Young-joong Yang, Jong-Hyun Yoon, Hyeon-Man Baek, Chang-Beom Ahn
QSM is a method that generates internal susceptibility distribution of subject using material’s intrinsic magnetic susceptibility property. Bo inhomogeneity affects magnitude and phase images. In this study, QSM with B0 field inhomogeneity correction is proposed. Using numerical simulation and in-vivo experiment, proposed method is verified. In simulation, improved susceptibility map is obtained with less root mean square error. In in-vivo experiment, signal loss and non-uniformity at frontal lobe are reduced. As field inhomogeneity increases according to the increase of main field strength, this method would be a more important element for QSM.
|
|
1439. 
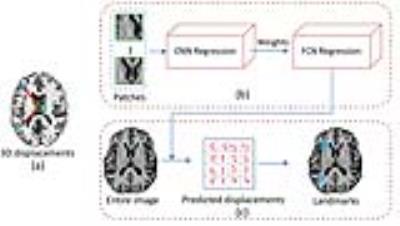 |
Real-time large-scale anatomical landmark detection with limited medical images
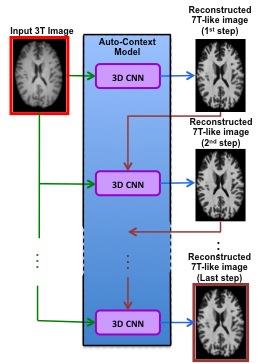
Jun Zhang, Mingxia Liu, Dinggang Shen
Landmark detection based on deep neural networks has achieved state-of-the-art performance in natural image analysis. However, it is challenging to detect anatomical landmarks from medical images, due to limited data. Here, we propose a real-time large-scale landmark detection method with limited training data. We train our model with image patches and test it with the entire image, inspired by fully convolutional networks. Also, we develop a weighted loss function in our model to increase the correlations between image patches and their nearby landmarks. The experimental results of detecting 1741 landmarks from brain MR images demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
|
|
1440.
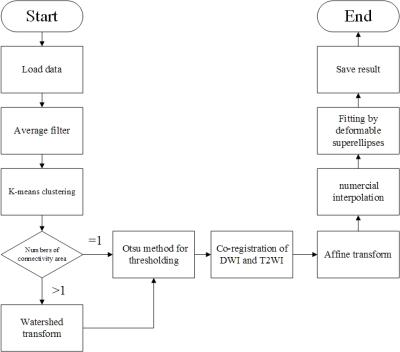 |
A fully automatic prostate segmentation method for both DWI and T2WI
Yi Zhu, Rong Wei, Ge Gao, Yajing Zhang, Xiaoying Wang, Jue Zhang, Jing Fang
Automatic prostate segmentation in MR images is a meaningful work, not only can be used in the first step of the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System, but also helps to predict pathologic stage of disease by determining the prostate volume. Here we show a novel new method can get the prostate contour for both T2WI and DWI fast and accurately without any manual intervention. The segmentation accuracies for 60 images are 83.7% (T2WI) and 87.1% (DWI). Even in some cases, such as prostate hyperplasia, our method shows good robustness.
|
|
1441.
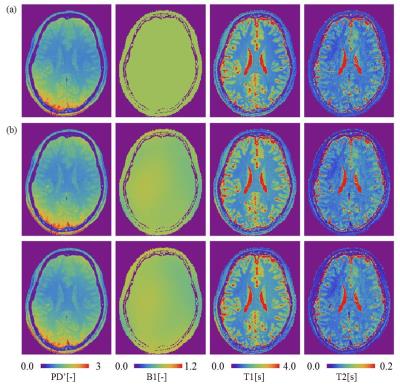 |
Fast fitting method for simultaneously quantifying multiple MR parameters using local optimization method with predetermined initial values
Suguru Yokosawa, Yo Taniguchi, Tomoki Amemiya, Toru Shirai, Ryota Sato, Yoshihisa Soutome, Hisaaki Ochi
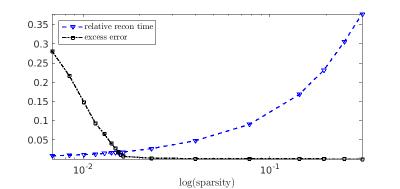
A fast fitting method for quantifying multiple MR parameters using local optimization method with predetermined initial values is proposed. In the proposed method, an optimal neighborhood solution is extracted as predetermined initial values. A difference in MR parameters between the proposed method and the conventional method was less than 5 %. On the other hand, a computing time of the proposed method was approximately 15 times faster compared with the conventional method. We concluded that the proposed method can provide fast fitting process while maintaining calculation accuracy.
|
|
1442. 
 |
Improved image texture features by Gaussian mixture models of grey-level co-occurrence matrices
Tommy Löfstedt, Patrik Brynolfsson, Tufve Nyholm, Anders Garpebring
Image texture features based on gray-level co-occurence matrices (GLCMs) are useful in e.g. the analysis of MR images of tumours. However, the features can be quite sensitive to the number of grey-levels in the analysed image, in particular if the region of interest is small. In this work we propose a new method for computing the GLCM, based on Gaussian mixture models. The results show that the new method improves the estimation of the GLCM and at the same time eliminates the difficult task of selecting the number of grey-levels.
|
|
1443.
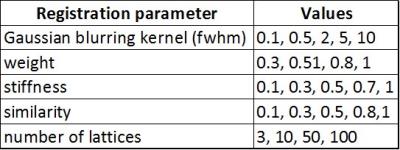 |
Optimization of 2D registration using minctracc on myelin stained brain slices
Max Prihoda, Simon Hametner, Andreas Deistung, Verena Endmayr, Andrew Janke, Claude Lepage, Thomas Haider, Simon Robinson, Xiang Feng, Hans Lassmann, Jürgen Reichenbach, Evelin Haimburger, Christian Menard, Hannes Traxler, Siegfried Trattnig, Günther Grabner
Histological analyses are important for a wide spectrum of in vivo and in vitro imaging projects. But unlike MRI or CT, histological analyses are typically performed in two dimensions. Nonlinear tissue deformation and ruptures of brain tissue are often common, making analysis in slice direction more difficult. In this work, we optimized a hierarchical, nonlinear fitting pipeline on the basis of two high resolution, myelin stained brain sections using mintracc.
|
|
1444. 
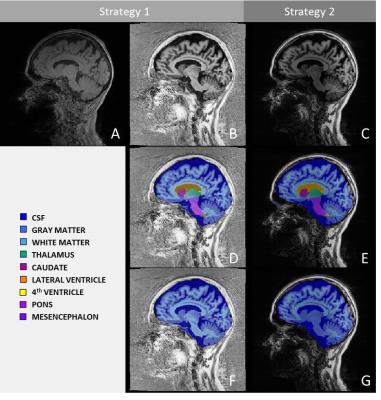 |
Comparison of MP2RAGE-based morphometry methods for anorexia nervosa
Bénédicte Maréchal, José Baiao Boto, Gkinis Georgios, Nadia Ortiz, Karl-Olof Lövblad, François Lazeyras, Maria Isabel Vargas, Alexis Roche, Tobias Kober
We explore the sensitivity of a morphometry tool to detect anorexia-related brain atrophy in MP2RAGE images. We compare volumetry resulting from two previously reported morphometry strategies on 16 patients with clinical suspicion of anorexia and identify both similarities and differences in brain atrophy evaluation.
|
|
1445.
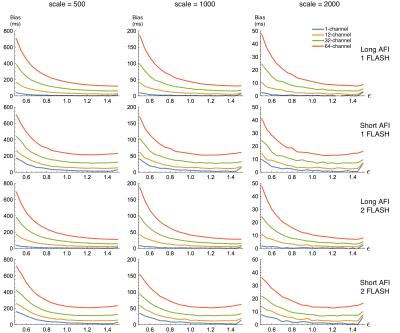 |
Bias and SNR of $$$T_1$$$ estimates derived from joint fitting of actual flip-angle and FLASH imaging data with variable flip angles
M. Dylan Tisdall
Previous work has suggested fitting joint AFI/FLASH data for T1 and B1+ by minimizing the 2-norm of the difference between the signal model and measurements will produce unbiased estimates of T1. We demonstrate that, contrary to previous results, the estimator has a substantial bias that varies with both the true T1 and B1+, and the receive channel count. We also demonstrate that the correct ML estimator removes the effect of channel count, and that the choice of AFI protocol has a larger impact of the quality of estimates than the addition of an extra FLASH scan.
|
|
1446.
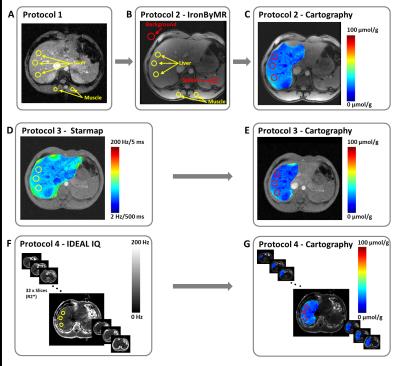 |
Quantification of iron liver with clinical MRI protocols
Redouane Ternifi, Philippe Pouletaut, Magalie Sasso, Véronique Miette, Fabrice Charleux, Sabine Bensamoun
Iron quantification has been assessed through the development of magnetic resonance sequences. The purpose is to improve the existing MRI iron protocols to better diagnose the degree of hemochromatosis. Five volunteers with healthy livers underwent four protocols for the quantification of iron overloads concentration (IOC). The results have demonstrated that existing clinical protocols could be improved to provide spatial distribution of iron within one slice and all over the entire liver volume. IDEAL-IQ® could be the best protocol to have IOC volume representation with a short time of acquisition and standard deviation values associated to mean IOC data.
|
|
1447.
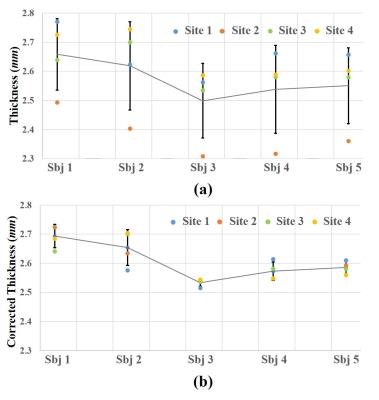 |
Harmonization for cortical thickness across sites in multi-center MRI study
Lin Zhao, Tuo Zhang, Xianjun Li, Chao Jin, Miaomiao Wang, Xiaocheng Wei, Hong Yin, Zengjun Zhang, Xiaoqun Yao, Xiaoling Zhang, Jian Yang
Cerebral cortex encodes crucial information of brain development, cytoarchitecture and function. However, varying data acquisition conditions at different centers could hamper group-wisely statistical analysis. This study aims to test the consistency of cortical thickness in the human brain across four sites and harmonize the deviations. Our results showed that variation of cortical thickness across sites were regionally independent, and deviation across centers could be reduced by linear regression method at a global scale, while the variations across subjects were well preserved. Those results suggest that our method has the promise in harmonizing cortical thickness measures in multi-center study.
|
|
1448.
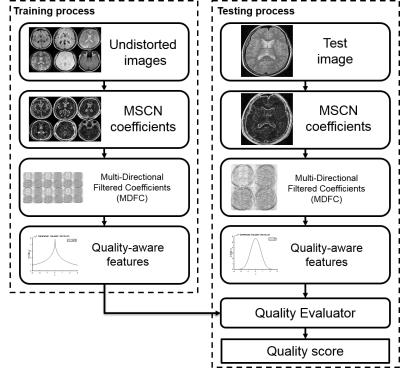 |
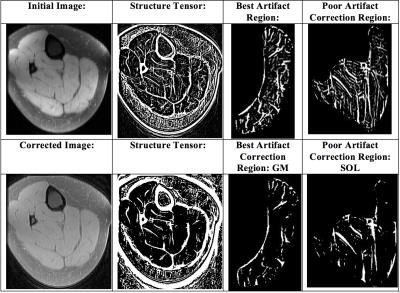
QEMDIM : Quality Evaluation using Multi-DIrectional Filter for no-reference MR image
Jinseong Jang, Kihun Bang, Hanbyeol Jang, Dosik Hwang
This paper proposes a new image quality assessment (IQA) for no-reference MRI, Quality Evaluation using Multi-DIrectional filters for MRI (QEMDIM), that is obtained from difference of statistical features between test images and numerous pre-scanned images in Mean Subtracted Contrast Normalization (MSCN) coefficient and Multi-Directional Filtered Coefficients (MDFC). the proposed method is capable of detecting various types of artifact and can be applied to clinical applications as well as being used to evaluate the performance of MRI hardware and software
|
|
1449.
 |
Diagnostic performance of texture analysis on MRI in differentiated degree of head and neck carcinoma
Yu Chen, Yuan Li, Yuanli Zhu, Huadan Xue, Zhuhua Zhang, Hailong Zhou, Zhengyu Jin
The aim of this study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of pathological differentiated degree of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) using MRI texture analysis. The following texture analysis parameters were derived from the T1WI, T2WI , T2fs and Post-Gad T1WI based on different scale: entropy , mean pixel intensity, standard deviation(SD), skewness, and kurtosis. ROC curves and AUC of each parameter was determined, respectively. We conclude that the entropy at fine texture scale on Post-Gad T1WI had the best ability .
|
|
1450. 
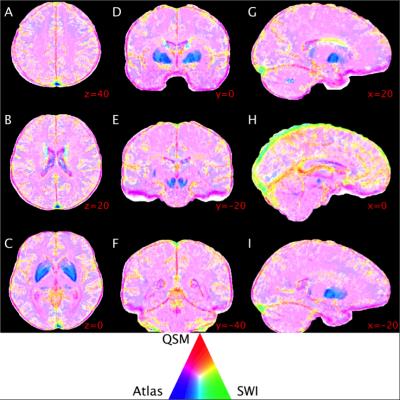 |
Regional variations in cerebral venous contrast using susceptibility-based MRI
Phillip Ward, Nicholas Ferris, Parnesh Raniga, Amanda Ng, David Dowe, David Barnes, Gary Egan
In this study we compared the image contrast properties of susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) and quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) for cerebral venous identification and visualisation. SWI and QSM are minimally invasive techniques to image cerebral veins with distinct contrast properties. We hypothesised that these techniques would provide complementary vein contrast in different brain regions. Contrast was measured using 1072 manually traced vein images from ten volunteers. We found regional variations in the predictive power of vein contrast and computed maps of contrast profiles that may inform which technique is best for a given application.
|
|
1451.
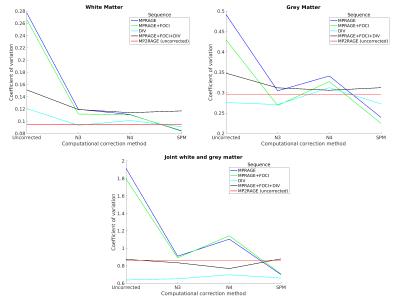 |
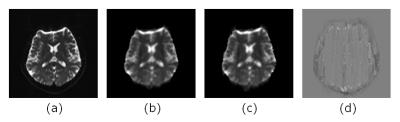
Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of bias field correction methods
Falk Luesebrink, Hendrik Mattern, Alessandro Sciarra, Oliver Speck
Bias field correction is an essential prerequisite for image analysis, especially at high field strength. In this study multiple correction methods, based on acquisition of a reference image and computational approaches with varied input parameters, are compared. The results indicate that acquisition of a conventional MPRAGE corrected by SPM yields quantitatively and qualitatively comparable results to acquiring a reference image (e.g. MP2RAGE), however, scan time is up to halfed.
|
|
1452. 
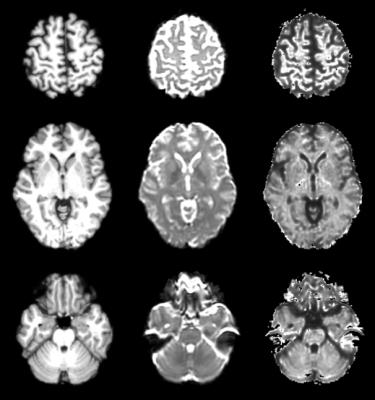 |
Rapid registration of EPI to high-resolution structural images
David Manners, Claudia Testa, Stefania Evangelisti, Stefano Zanigni, Caterina Tonon, Raffaele Lodi
Post-processing methods that can non-linearly register diffusion-weighted EPI data to high-resolution images are useful in the context of clinical protocols. The current research attempts to apply currently available registration methods to rapidly perform such registration. Investigations on healthy subjects show that an appropriately generated target image allows good quality registration to be performed even with freely available software. This is useful for example to provide cortical seeds for diffusion tractography.
|
|
1453.
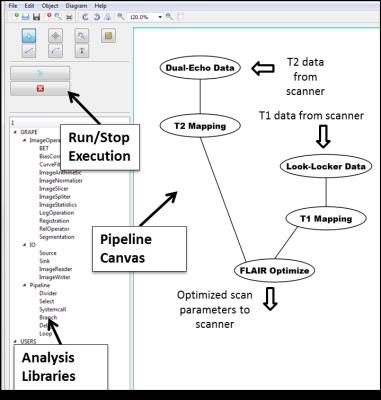 |
A graphical programming environment for creating and executing adaptive MRI protocols
Refaat Gabr, Getaneh Tefera, William Allen, Amol Pednekar, Ponnada Narayana
Inline processing of magnetic resonance images allows fast feedback of analysis and immediate access to quantitative information. It further allows the development of adaptive MRI protocols. Here, we present GRAPE, a development platform for graphical programming to facilitate the development of adaptive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocols. This platform provides tools to enable graphical creation, execution, and debugging of image analysis algorithms integrated with the MRI scanner, all within a graphical environment. GRAPE is demonstrated with the implementation of patient-specific optimization of the scan parameters of 3D fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) protocol to enhance the contrast of brain lesions in multiple sclerosis, performed on a 3.0 Tesla MRI scanner.
|
|
1454.
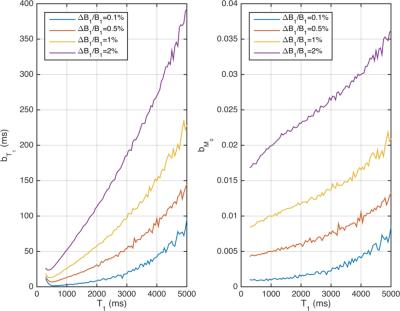 |
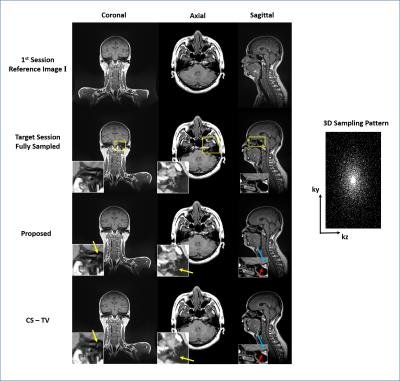
Validation of CSF based calibration for accurate and robust quantification of water content.
Zaheer Abbas, Dominik Ridder, Krzysztof Dzieciol, Nadim Jon Shah
Estimating tissue water content is challenging. Reliable quantification of the water content requires significant number of corrections and calibration to a reference. In this work, we proposed to use a region in cerebrospinal fluid for robust calibration; this is further validated in a cohort of healthy volunteers and compared to existing methods.
|
|
1455.
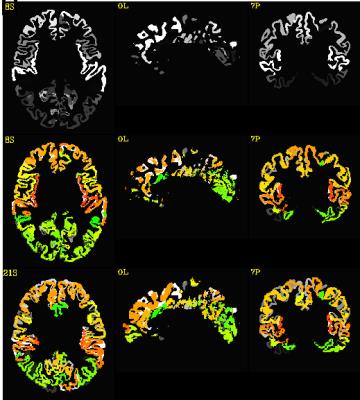 |
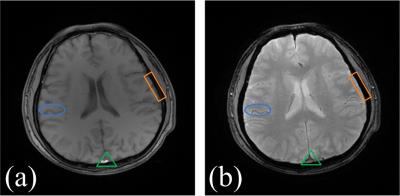
Automatic nonlinear transformation of 7T MRI brain image to Talairach stereotaxic space
Mingyi Li, Jian Lin, Katherine Koenig, Mark Lowe
Transforming MRI brain images into Talairach space will greatly facilitate the comparison of neuroimaging research results across subjects and applications of atlas to research subjects and clinical patients. We developed an automatic processing pipeline based on nonlinear registration to transform 7T MRI brain images to Talairach space. The pipeline utilized matching scores derived from brain parcellation for quality assurance (QA). The pipeline was tested on subjects including five controls, three MS patients and three ALS patients. The results showed that the method generated better results than the automatic Talairach transformation provided by AFNI. The QA scores were also comparable to those computed from 3T MRI brain images in our previous study.
|
|
1456. 
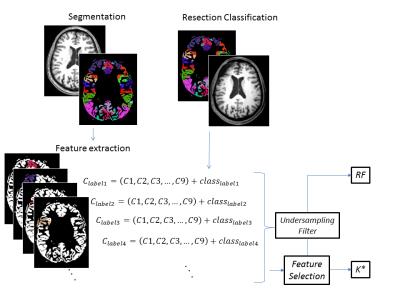 |
Epilepsy Surgery Followup: Resected Tissue Analysis and Classification
Fabrício Simozo, Tonicarlo Velasco, Luiz Murta Jr.
Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) is one of the main causes of refractory epilepsy. There is no self-sufficient method in order to evidence the presence and location of FCD, making complete diagnosis very difficult. Although some studies have addressed FCD identification, image texture is poorly explored. This study evaluated pre and post-surgical magnetic resonance images (MRI) of epilepsy patients in order to test Machine Learning classifiers and their ability to identify dysplasia using texture features and cortical thickness. Precision and recall scores suggest the capabilities of the proposed methodology in responding to the presence of FCD tissue.
|
|
1457. 
 |
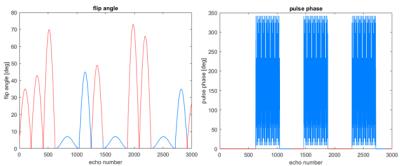
Optimization of multiple orientation QSM for building a clinically feasible protocol
Harshan Ravi, Wen-Tung Wang, Dzung Pham, John Butman
Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) offers unique, quantitative information about tissue magnetic susceptibility. A multi-orientation method, calculation of susceptibility through multi-orientation sampling (COSMOS), enables the dipole inversion by acquiring data at multiple orientations. In practical imaging settings, however, it is a challenge to image the subject multiple orientations. Although small angle COSMOS has been shown to generate reasonable QSM images, the selection of orientations within a practical acquisition protocol remains an open question. In this work, we investigated the influence of the number and direction of orientations on the outcome of small angle COSMOS for in vivo imaging.
|
|
1458. 
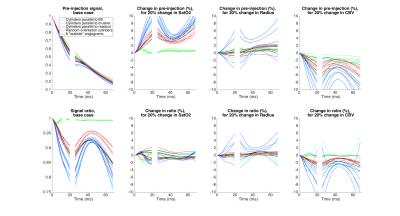 |
Differences in parameter sensitivities of GESFIDE MR signals generated on realistic angiograms and on idealized cylinders
Philippe Pouliot, Louis Gagnon, David Boas, Frederic Lesage
Idealized models of cylinders for the vasculature are used in several quantitative MRI techniques such as for perfusion, CBV, vessel size and vascular MR fingerprinting. While limitations of these models are recognized, a direct comparison of the predicted MR signal between different cylinder models and those using a real vasculature as substrate has not been done to our knowledge. Here we compare the sensitivity of the MR signal for the GESFIDE sequence for 4 sets of , models of cylinders and 6 realistic angiograms from mouse somatosensory cortex. In general, simulation results are all different between the different angiograms and the different models of cylinders. This suggests that much care should be used in interpreting literature results based on models of cylinders, or as well with models on angiograms, to account for the possibility of biases in the absolute results. Correlations and differences in absolute values, for some parameters, may perhaps be less subject to bias.
|
|
1459. 
 |
Adaptive Magnetic Resonance Image signal enhancement using squared eigenfunctions of the Schrodinger operator
Abderrazak Chahid, Hacene Serrai, Eric Achten, Taous-Meriem Laleg-Kirati
The main of challenge of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is dealing with high levels of noise which may corrupt the image especially since the noise is almost correlated with the image details. In this regard, we propose a new MRI enhancement method to overcome this limitation. The proposed MRI enhancement method relies on square sub-images enhancement depending on the noise level in each position using spatial adaptation of the Semi-Classical Signal Analysis (SCSA) method, where an enhancement parameter h is subject to a Gaussian distribution. The results show significant improvement in noise removal and preserving small details in the image.
|
|
1460. 
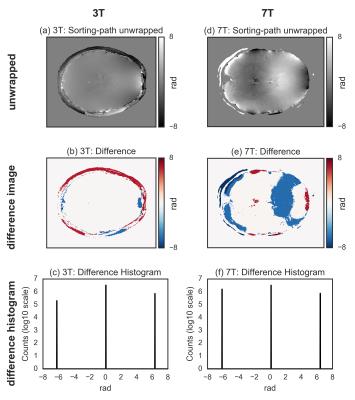 |
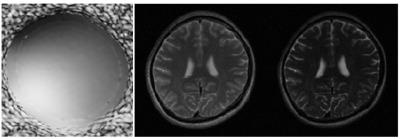
Obtaining accurate and fast unwrapped phase images
Riccardo Metere, Harald Möller
The unwrapping of phase data is a common problem in MRI. However, its solution is non-trivial for 2D or 3D images, and there has been some general research in this direction, notably in the field of optics. The two most pupular algorithms for MRI applications are: (i) a Laplacian-based method that is fast but inaccurate; (ii) a region-merging optimization method that is accurate but very slow. Here, we propose the adoption of a recently developed and freely available unwrap algorithm that significantly outperforms the other considered methods, allowing for both fast and accurate calculation of unwrapped phase images.
|
|
1461. 
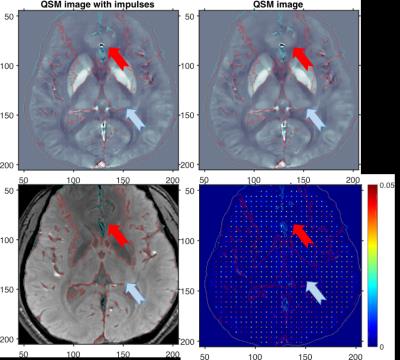 |
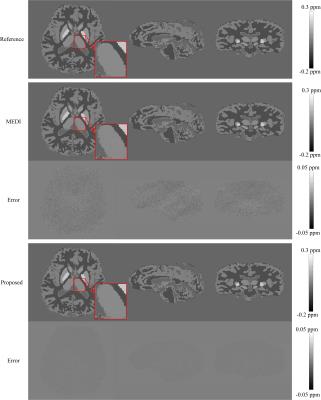
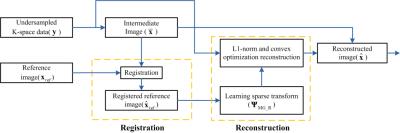
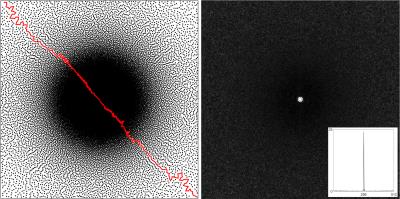
Spatial resolution properties of QSM images using MEDI algorithm
Se Young Chun
We investigated the spatial resolution of the MEDI reconstructed QSM images by deriving an analytical expression of the estimator in terms of the true QSM image. The implication of this expression is that no regularization will be applied to some part of the QSM images if the corresponding magnitude image area contains strong edges and relatively strong regularization will be applied to some part of the QSM images if the corresponding magnitude image area contains low magnitude values. Our simulations with a phantom and a in-vivo QSM image confirm this analysis; Impulse perturbations were suppressed on the area where the magnitude image has low contrasts and impulses were preserved on the area where the magnitude image has high contrast or edges.
|
|
1462. 
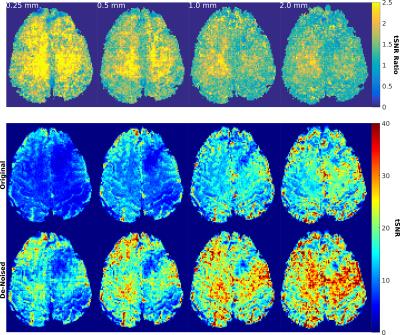 |
AWESOME-Based De-Noising of Complex-Valued fMRI Time Series
Henrik Marschner, Laurentius Huber, André Pampel, Harald Möller
In this study we investigate possible benefits of an application of ‘AWESOME’ de-noising on fMRI. The application in a high-SNR finger tapping experiment showed a reduction of the already low thermal noise contribution and therefore improvement of tSNR and reduction of false positives; no adverse effects in the form of smoothing or suppression of ‘true’ activation was observed. A second investigation of the scalability of tSNR improvement on a resting state experiment with variable slice thickness / SNR showed that thermal noise can be reliably reduced and the tSNR proportionally improved without visible reduction of detail sharpness / resolution.
|
|
1463. 
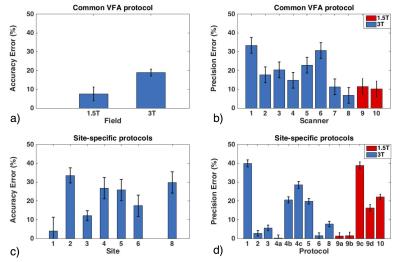 |
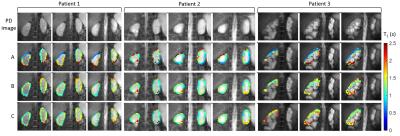
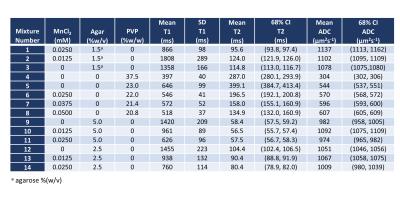
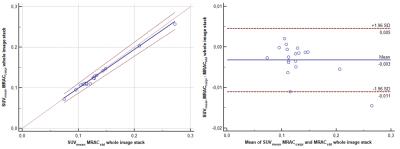
Assessment of interplatform reproducibility of T1 quantification methods used for DCE-MRI: results from a multicenter phantom study
Octavia Bane, Stefanie Hectors, Mathilde Wagner, Lori Arlinghaus, Madhava Aryal, Michael Boss, Yue Cao, Thomas Chenevert, Fiona Fennessy, Wei Huang, Nola Hylton, Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer, Kathryn Keenan, Dariya Malyarenko, Robert Mulkern, David Newitt, Karl Stupic, Lisa Wilmes, Thomas Yankeelov, Yi-Fen Yen, Stephen Russek, Bachir Taouli
Our multicenter study examined variability in T1 quantification by testing common inversion-recovery spin echo and variable flip angle (VFA) protocols, as well as T1 mapping methods used by participating sites, using a phantom with known T1 values. We found field strength dependence of the accuracy, and platform dependence of the repeatability of T1 measurements with the common VFA protocol. Accuracy for site-specific protocols was influenced by site, while repeatability, by type of protocol. Our findings suggest modified IR methods and VFA protocols with multiple flip angles and B1 correction as good methods for repeatable T1 measurement.
|
|
1464.
 |
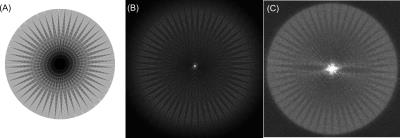
Bio-inspired optimization of technical fiber-reinforced ramifications using high-resolution MRI of Dracaena marginata branchings as concept generators
Linnea Hesse, Tom Masselter, Nils Spengler, Jan Gerrit Korvink, Jochen Leupold, Thomas Speck
MRT is still a little-known and highly underestimated imaging method within the field of functional morphology and biomechanics of plants and biomimetics. Its non-invasive and non-destructive character in combination with a large variety of applicable imaging sequences, gives this method a strong potential to shed light to various unanswered scientific questions concerning both the plant structure and function as well as on physiology. Using a Bruker Biospec 94/20 9.4T and a 3D FLASH sequence we could gain new insights into the biomechanics and development of dragon tree ramifications as a source of inspiration for the optimization of technical fiber-reinforced ramifications.
|
|
1465.
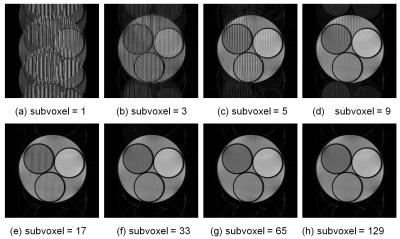 |
Fast Bloch-Torrey simulation of 3D RF spoiled gradient echo sequences using a number of subvoxels and molecular diffusion effect
Ryoichi Kose, Katsumi Kose
RF spoiled gradient echo sequences were studied both with experiments and Bloch-Torrey simulation. The Bloch simulation of the 256×256×32 voxel images clarified that adequate number of subvoxels were required for artifact-free images. The Bloch-Torrey simulation for one voxel magnetization clarified that adequate number of subvoxels were required for image intensity reproduction by diffusion effect. In conclusion, molecular diffusion effects are indispensable to reproduce the image contrast in SPGR.
|
|
1466.
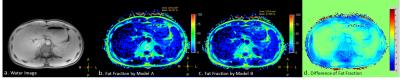 |
Analysis of error in Fat-Water Quantifications Originated from Models
Xiaoqi Wang, Xiaoguang Cheng, Li Xu, Li Baoqing
Fat-water separation imaging methods with multi-echo acquisition require specific fat spectrum model. The optimal spectrum model to be applied relies on the fat chemical properties as well as the acquisition scheme regarding to, for example, TR and TE. Herein we exam the consequence if inaccurate fat spectrum is used in the fat quantification processing, and analyze the related errors.
|
|
1467.
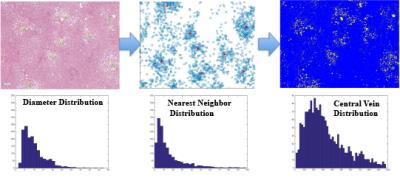 |
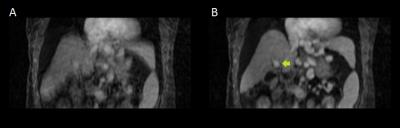
Liver Biopsy Analysis to Determine Fat Droplet Distribution
Benjamin Ratliff, Diego Hernando, Curtis Wiens, Changqing Wang, Rao Watson, Rashmi Agni, Claude Sirlin, Scott Reeder
The purpose of this work was to quantify the size and clustering of fat droplets using liver biopsy, as part of a long-term effort to characterize the relationship between tissue microstructure and quantitative MRI signals in fat-containing tissue. Three H&E stained liver core biopsies with varying fat-fractions were analyzed using segmentation software in order to generate probability density functions for fat droplet size and location. This work demonstrates that fat droplet distribution in the liver can be modeled statistically to determine the size and location distribution of fat droplets, potentially enabling characterization of the MR signal observed from fatty liver.
|
|
1468. 
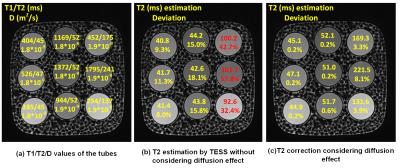 |
Diffusion effects on T2 relaxometry with triple echo steady-state free precession sequence
Yangzi Qiao, Chao Zou, Xin Liu, Hairong Zheng
In this study, the underestimation of T2 by TESS was revealed through simulation and phantom study. The bias becomes significant in high resolution TESS imaging with larger unbalanced gradient moment, as the diffusion effect can not be neglected. A possible correction scheme was also proposed, the results validated the diffusion effect on T2 estimation. However, the correction method relies on T1/T2/D as priori to calculate the signal change ratio through EPG algorithm. A possible solution might be simultaneous estimation on apparent diffusion coefficient and T2.
|
|
1469.
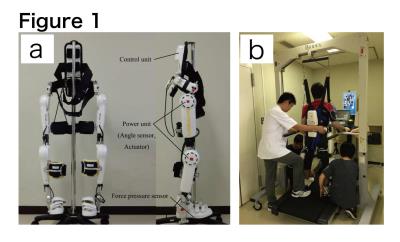 |
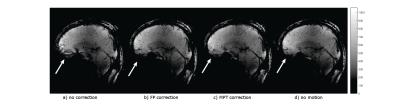
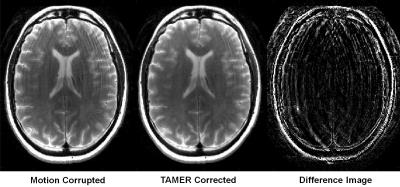
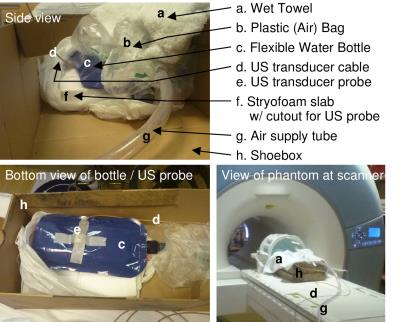
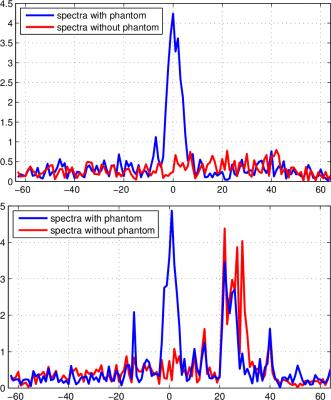
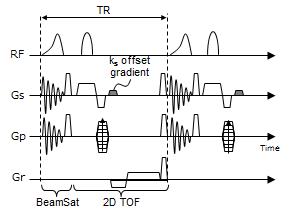
Brain activity alteration during the training period of the Hybrid Assistive Limb® (HAL) for chronic spinal cord injuries: a task-based fMRI case report
Kousaku Saotome, Akira Matsushita, Aiki Marushima, Hiroaki Kawamoto, Hideo Tsurushima, Tomohiko Masumoto, Masashi Yamazaki, Akira Matsumura, Yoshiyuki Sankai
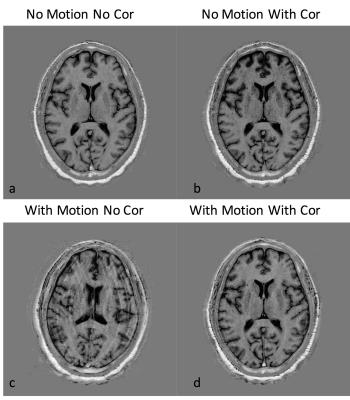
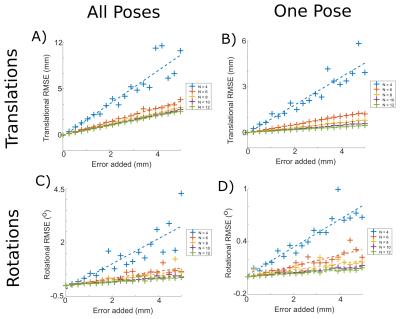
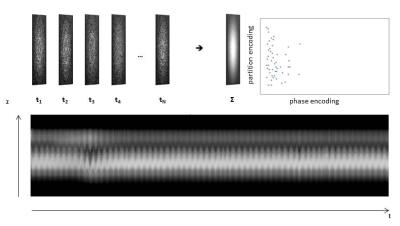
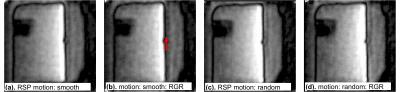
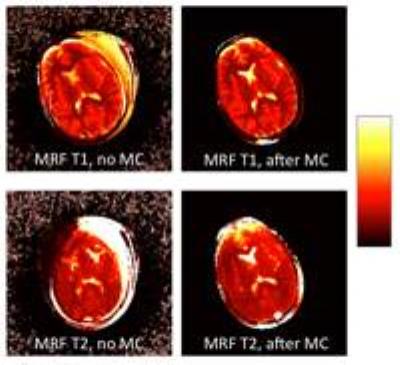
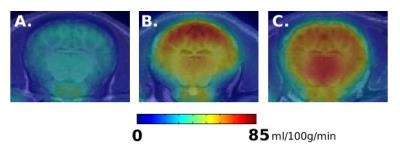
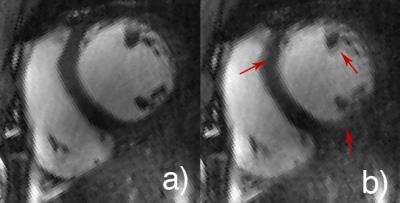
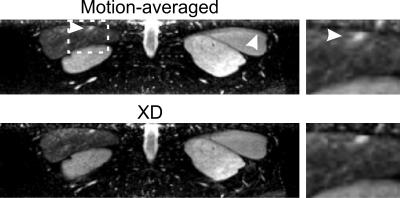
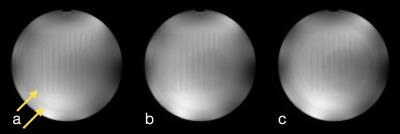
We previously developed the novel brain phantom showing image contrast and construction similar to those of in vivo MRI. This phantom has the potential to quantitatively assess the capability of the motion-corrected PROPELLER technique, which has been never approached. In the current study, we investigated the rotational frequency dependencies of the different two motion-corrected PROPELLER techniques by using our brain phantom. Our findings allow to quantitatively assess the capability of the Motion-Correction in PROPELLER.
|
|
1470.
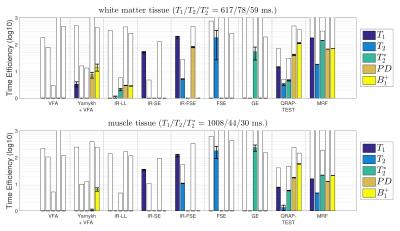 |
Determining the Time Efficiency of Quantitative MRI Methods using Bloch Simulations
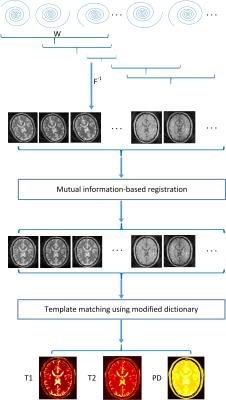
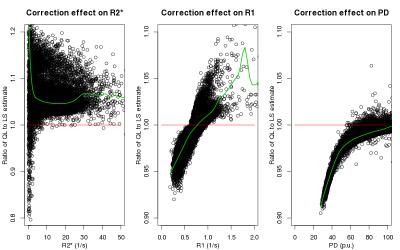
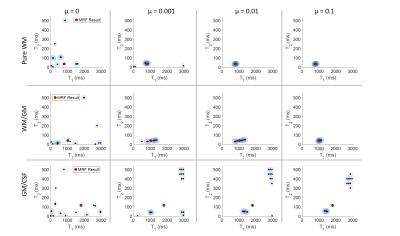
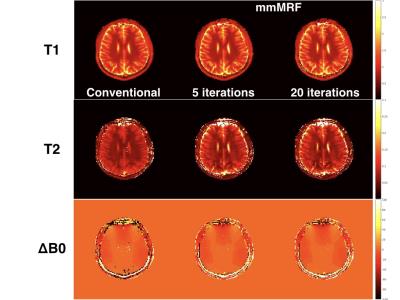
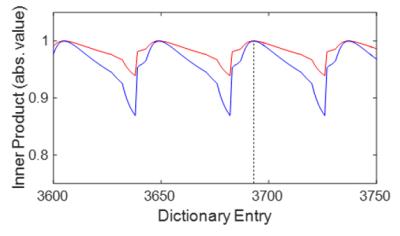
Willem van Valenberg, Frans Vos, Stefan Klein, Lucas van Vliet, Dirk Poot
When measuring $$$T_1, T_2, T_2^*, PD$$$, or $$$B_1^+$$$, we prefer the MRI sequence that provides the best precision in the allowed scan time (i.e. having optimal time efficiency). However, experimentally determining the time efficiency is impractical when comparing many sequences, each possibly with varying settings, and multiple tissue types of interest. Here, we derive time efficiency through Bloch simulations which is applicable to any MRI sequence and tissue type. A specific strength of our framework is that it does not require an explicit fitting procedure which may not yet exist when designing novel MR sequences.
|
|
1471. 
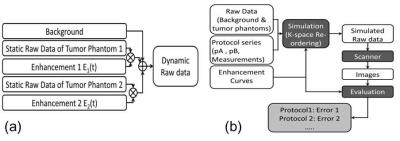 |
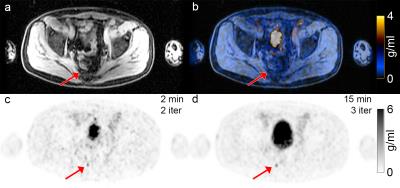
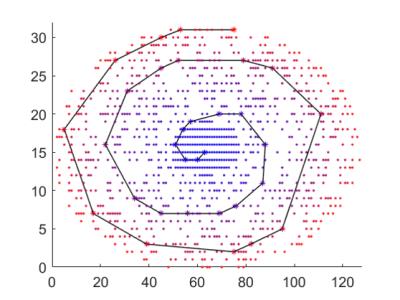
Quantitative DCE-MRI Accuracy Evaluation Using Dynamic Physical vs. Digital Phantom: a Cross-Validation
Yuan Le, Yuxiang Zhou, Eric Stinson, Stephen Riederer, Joel Felmlee
To study the image accuracy of quantitative DCE-MRI a digital phantom and computer simulation were usually used. To validate the digital phantom method, we conducted a cross-validation study comparing the image accuracy estimation from simulation with that from a dynamic physical phantom with contrast infusion. Results showed that the estimated errors were usually higher with the physical phantom, likely due to the difference in reproducibility. Consistency was found in the measurement error comparison between imaging techniques when the temporal resolution was high.
|
|
1472.
 |
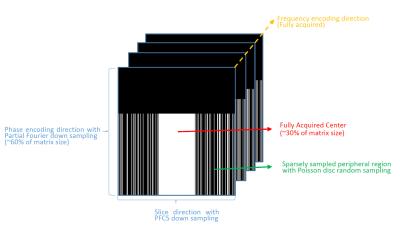
Early enhancement in breast DCE-MRI is sparse and can be imaged with a reduced FOV to increase temporal resolution
Federico Pineda, Ty Easley, Gregory Karczmar
Early enhancement in breast DCE-MRI is very sparse, if the FOV is reduced in these images and aliasing occurs, the likelihood that two significantly enhancing voxels overlap is low. We present a method for ‘unfolding’ of aliased DCE-MRI acquisitions that closely approximates fully-sampled acquisitions. This method could be used to increase the temporal resolution of DCE-MRI at very early times when enhancement is rapidly changing, allowing for the accurate measurement of early lesion kinetics.
|
|
1473.
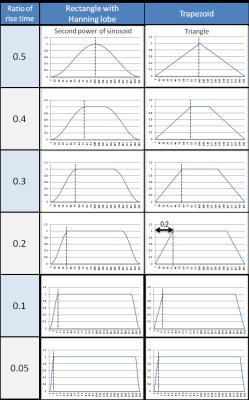 |
Simulation of Sound Pressure Level of MRI Scan Considering Eddy Currents
Yukari Yamamoto, Yo Taniguchi, Hisaaki Ochi, Yoshihisa Soutome
Since optimal waveforms should be chosen for each gradient pulse in order to reduce sound pressure levels (SPLs) in MRI scans, the simulation accuracy of the SPL must be improved. Assuming that the eddy current component is a cause of the disagreement between the measured and the simulated SPLs, we compared the simulation results with and without the eddy current component in this study. By including the eddy current component in the simulation, the magnitude of the SPL decreased, which reflects the decrease in the peak amplitude of the frequency component of the gradient waveform. However, the eddy current component did not affect the change trends of the SPLs depending on the change of waveforms. On the other hand, a slight change in the peak position of the frequency response functions appears to cause a significant change in the SPL, and the error of the FRF was also thought to cause disagreement between the measured and simulated SPLs.
|
|
1474.
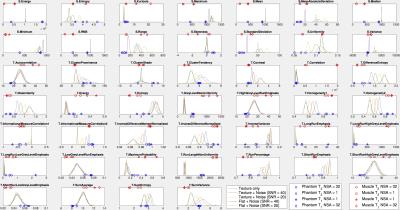 |
The effect of MR noise and resolution on textural features in simulated and real textures: implications for clinical practice.
Joshua Shur, Matthew Orton, Simon Doran, James D'Arcy, David Collins, Maria Bali, Martin Leach, Dow-Mu Koh
Sensitivity of textural features to acquisition parameters has important clinical implications. The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of noise and resolution on textural features. We compared textural features from a uniform and simulated texture, varied with noise, with experiment in a uniform phantom and organic texture.
Our data demonstrate that a uniform texture behaves as if it has inherent texture, due to presence of artefact, and this in turn will influence textural features as noise and acquisition parameters are varied.
We note that certain textural features used in clinical practice vary widely with image noise, whereas others appear to be robust.
|
|
1475.
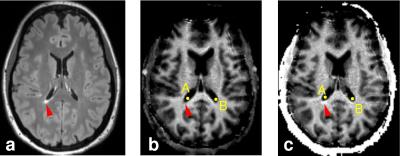 |
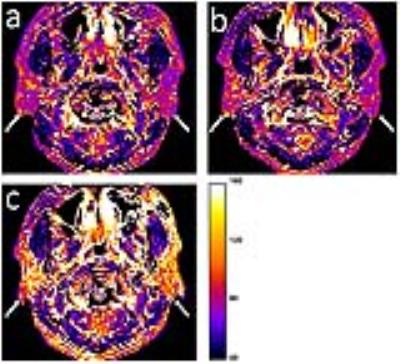
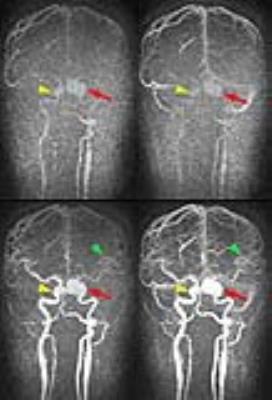
Quantification of contrast agent-induced enhancement of brain lesions in multiple sclerosis
Jung-Jiin Hsu, William Stern, Jung-Yu Hsu, Roland Henry
Contrast agents are routinely used in MRI to detect and evaluate tissue lesions. Conventional clinical protocols use T1-weighted sequences to visualize Gd contrast agent enhancement. Because T1-weighted MRI does not produce quantitative measurements, it is difficult to describe the lesion enhancement in quantitative terms and to infer the degree of the underlining disease activities of the lesions. A fast, whole-brain high-resolution T1 mapping method was developed to address this problem and applied to multiple sclerosis.
|
|
1476. 
 |
LEI-ALOHA – Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Tropical Island Setting
Christopher Wiggins, Benedikt Poser
While there are exceptions, most major MRI research centers are located in urban areas where a sizeable population is served by a large medical infrastructure and/or university. For researchers and technical staff alike, this often precludes the possibility of combining their research program with a remote, island-based lifestyle. Here we propose a set of theoretical techniques that form a framework for a purely philosophical research program.
|
|