Muscle & Bone
Traditional Poster
Musculoskeletal
Monday, 24 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
16:15 - 18:15 |
|
1563.
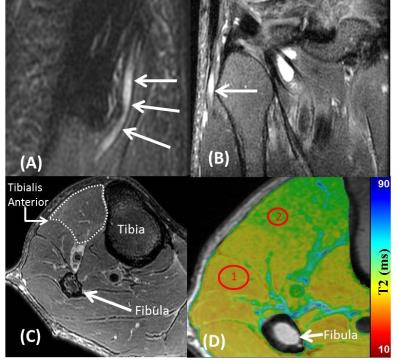 |
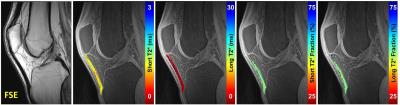
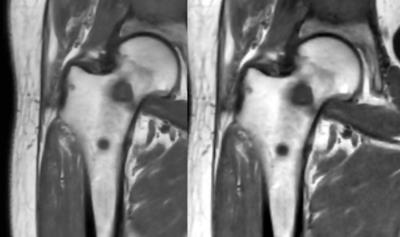
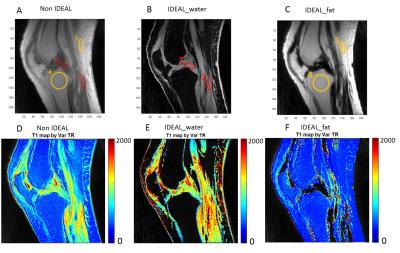
Quantitative Evaluation of T2 Signal Intensity for the Assessment of Muscle Denervation
Parina Shah, Erin Argentieri, Matthew Koff, Darryl Sneag
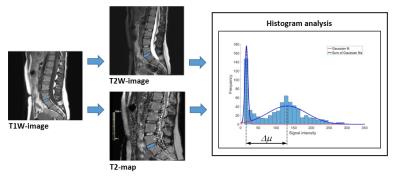
Presence and severity of muscle denervation due to peripheral neuropathy are conventionally evaluated using needle electromyography (EMG); the results of which are critical in the diagnosis of nerve injury and prognosticating nerve recovery. Routine MRI can confirm the presence of denervation but is unable to quantify severity and relies on qualitative detection of diffuse T2-weighted signal hyperintensity of the muscle and fatty infiltration (if chronic). This pilot study explores the role of T2 mapping in the diagnosis denervation and for quantification of severity. T2 mapping may be an important complement to EMG results, particularly given the drawbacks associated with EMG.
|
|
1564.
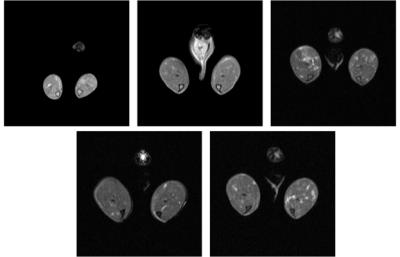 |
Noninvasive MRI Biomarkers for Muscular Dystrophy Progression in Young Muscle
Joshua Park, Ravneet Vohra, Thomas Klussmann, Niclas Bengtsson, Jeffrey Chamberlain, Donghoon Lee
Muscular dystrophy is a family of inherited diseases characterized by progressive muscle weakness that leads to muscle damage and wasting, and in the case of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), is fatal. Clinical measures of muscular dystrophy rely on surgical biopsy, which is invasive and provides a limited overview of the disease’s progression. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may provide valuable information pertaining to tissue characteristics of this disease. We performed multi-parametric MRI to assess the changes in young dystrophic mice. The changes observed in skeletal muscles demonstrate MRI parameters may be used to track disease progression and future treatment options.
|
|
1565.
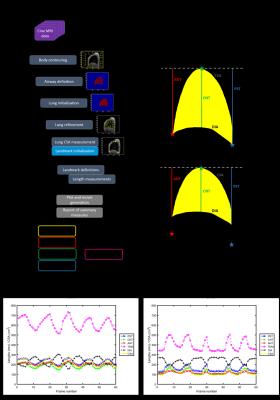 |
Semi-automated analysis of diaphragmatic motion with cine MRI in controls and non-ambulant Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patients
Courtney Bishop, Rexford Newbould, Valeria Ricotti, Christopher Sinclair, Jordan Butler, RB Matt Evans, Jasper Morrow, Mike Hanna, Paul Matthews, Tarek Yousry, John Thornton, Francesco Muntoni, Robert Janiczek
This study presents both an analysis pipeline for measuring diaphragmatic motion from cine MRI data, and the application of this image processing technique to investigate exploratory MRI endpoints of respiratory function in both healthy controls and non-ambulant DMD boys. Cine-derived metrics of diaphragm motility and contractility correlated with sitting spirometry-derived forced vital capacity, and showed relationships with disease progression surrogates of age and months non-ambulatory, as well as a longitudinal change over 12 months. Longitudinal changes were not seen in spirometry measures.
|
|
1566.
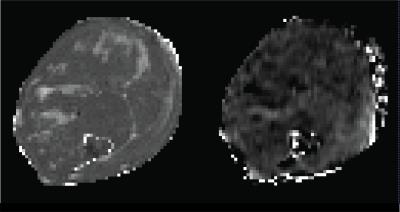 |
Potential of Stimulated Echo Diffusion-weighted Imaging as Disease Marker in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Bauke Kogelman, Maaike Putten, Matt Hall, Chris Clark, Andrew Blamire, Paola Porcari, Louise Weerd
We used stimulated echo diffusion weighted imaging (STE-DWI) in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (mdx). From the data in mdx or wild type animals we observe that although muscle fibre size is smaller in the mdx mouse, the diffusion data show increased diffusibility – opposite to the hypothesised effect if fibre size is the main determinant of restricted water diffusion. Muscle fibre permeability is significantly greater in the mdx mouse, suggesting that the overall system permeability has a countering effect on diffusion restriction. Additional modelling is required to capture these two opposing effects.
|
|
1567.
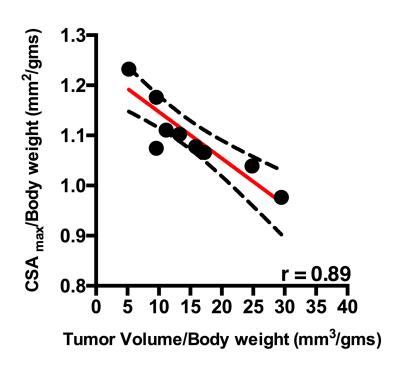 |
Magnetic resonance biomarkers for cachexia in a mouse model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Ravneet Vohra, Matthew Campbell, Joshua Park, Kayla Gravelle, Stella wHang, Yak-Nam Wang, Joo-Ha Hwang, David Marcinek, Donghoon Lee
Cancer induced cachexia is prevalent with many cancers and is characterized by loss of muscle and fat mass. In pancreatic cancer the syndrome affects approximately 80% of patients. Non-invasive multi-parametric MRI was used to monitor the progression of cachexia in a genetically engineered mouse model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Using pixel-by-pixel comparison, we demonstrate a significant decrease in skeletal muscle T2 and increase in magnetization transfer ratio (MTR). Additionally, we found significant difference in diffusion parameters.
|
|
1568.
 |
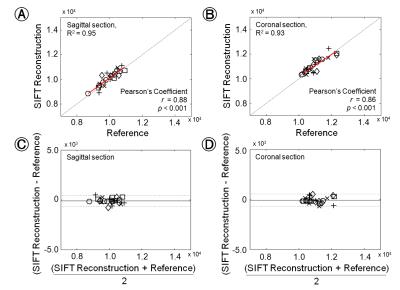
Fast delineation of calf muscles for quantitative MRI applications
Pierre-Yves Baudin, Morin Beyeler, Pierre Carlier, Olivier Scheidegger
One typical obstacle in quantitative MRI lies in the delineation of the regions of interest. When not absolutely necessary, per-muscle analyses are often abandoned, resulting in the loss of a wealth information. A software dedicated to accelerated segmentation of muscle images was recently introduced. It was tested here on the calf muscles of healthy volunteers and Duchenne patients. Results showed an important gain in average speed and were close to the manual segmentation used as reference. Thus, the tested software proved to be a valuable tool for quantitative analysis of skeletal muscle NMR images.
|
|
1569.
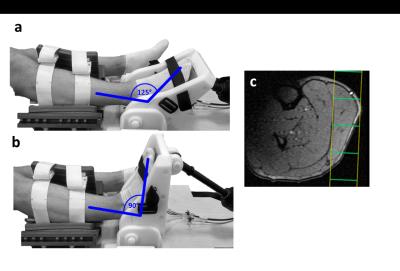 |
Influence of muscle fiber tension on 31P MRS recovery parameter after intense exercise
Kevin Moll, Alexander Gussew, Jürgen Reichenbach
When performing exercise induced 31P MRS motion and activities from the everyday life and the positioning of the investigated extremities within the MR scanner should be considered, since this could induce partial ischemia effects like muscular cramps. The aim of this study was to prove the effect of muscle tension on metabolic parameter measured by 31P MRS after an intense exercise. PCr recovery as well as pH kinetic was significantly slowed by a partial ischemia preventing a quantitative evaluation.
|
|
1570.
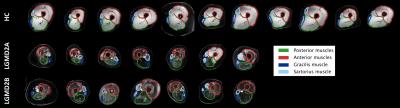 |
Multi-parametric characterization of highly fat infiltrated muscular dystrophy patients: results of a multi-variate analysis.
Alberto De Luca, Alessandra Bertoldo, Denis Peruzzo, Maria Grazia D'Angelo, Martijn Froeling, Filippo Arrigoni
Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophies (LGMD) are a family of myopathies characterized by progressive degeneration and fat infiltration of muscular tissue. In the context of a study that includes Dixon, T2quantification and diffusion MRI (dMRI), we investigated a multi-variate analysis to remove the effect of fat from concurrent measures and correlate them with clinical indexes of strength. In our dataset of highly infiltrated patients, T2 and dMRI metrics were strongly biased by fat. Our results show that it is possible to mitigate the bias by multi-variate modeling of the FF effect while retaining disease specific effects.
|
|
1571.
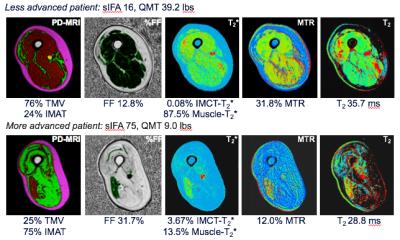 |
Changes in muscle morphometry, composition and performance in patients with sporadic inclusion body myositis
Didier Laurent, Jonathan Riek, Christopher DJ Sinclair, John S. Thornton, Ronenn Roubenoff, Dimitris A. Papanicolaou, Parul Houston, Tarek Yousry, Pedro M. Machado, Michael G. Hanna
A comprehensive MRI approach was used to characterize changes in muscle structure and composition in patients with sporadic inclusion body myositis (sIBM) over 1-year. Results showed progressive deterioration in muscle quality, e.g. increased connective tissue volume in the most affected muscles, and this appeared to be associated with a functional impact.
|
|
1572.
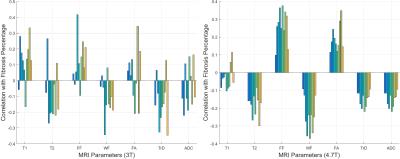 |
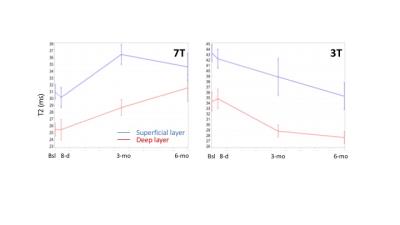
Correlating MRI and Histological Parameters in GRMD Muscles: A Comparison Between 3T and 4.7T Acquisitions
Aydin Eresen, Stephen McConnell, Sharla Birch, Wade Friedeck, Jay Griffin, Joe Kornegay, Jim Ji
The relationship between localized histological truth and various MRI quantitative measures were investigated using canine models. In this study, GRMD pectineus muscle samples were imaged on a 3T clinical scanner and a 4.7T small-bore scanner. Trichrome stained histology slice was registered to the 3D MRI volume. Localized quantitative MRI parameters are correlated with histology analysis (muscle, fibrosis and interstitial tissue percentage). Parameters derived from the 4.7T MRI data show consistent correlations, while those from 3T MRI data do not show consistent correlation.
|
|
1573.
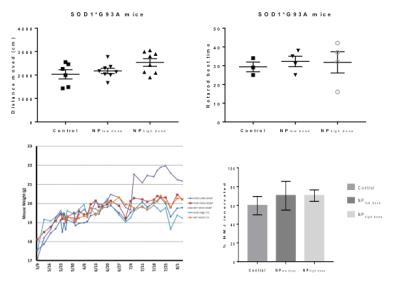 |
Targeted modulation of retinoid signaling using polymeric nanoparticles in a mouse model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
David Medina, Eugene Chung, Ricki Ceton, Robert Bowser, Rachael Sirianni, Gregory Turner
Retinoid signaling activity in the CNS, mediated by RARβ, directly influences ALS pathology development and progression in vivo and CNS targeted delivery of RARβ agonists can reduce ALS pathology in vivo when delivered systemically via polymeric nanoparticles. In this study the therapeutic affect of adapalene, a RARβ agonist, loaded nanoparticles were examined by measuring quadriceps volume in a SOD1G93A mouse model of ALS.
|
|
1574. 
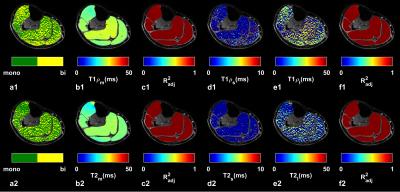 |
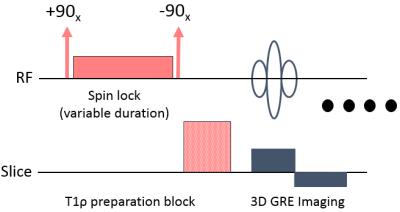
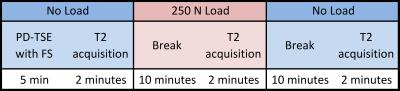
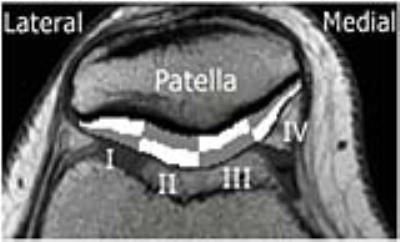
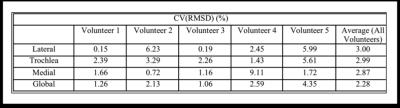
Multicomponent 3D-T1? and T2 Relaxation Mapping of Skeletal Muscle: In-vivo Feasibility
Azadeh Sharafi, Gregory Chang , Ravinder Regatte
In this study, we investigated the in-vivo feasibility of multicomponent 3D-T1ρ and T2 relaxation mapping in calf muscle using 3T MRI in clinically feasible scan times on eight healthy volunteers. Our preliminary results demonstrate that the biexponential model better characterized the relaxation behavior in calf muscle and can be used to differentiate between different water compartments associated with macromolecules (collagen and contractile proteins) and extracellular/vascular water in calf muscle.
|
|
1575.
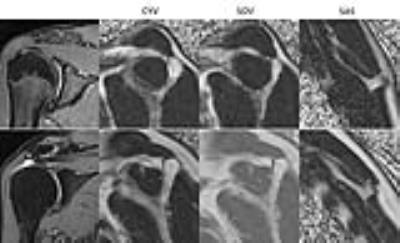 |
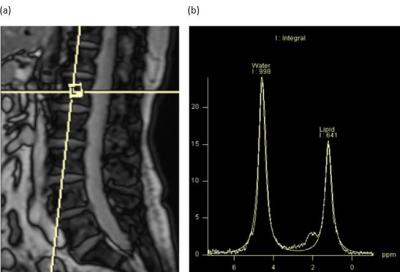
Fat fraction and muscular volume of entire supraspinatus muscle with/without tendon tear using IDEAL-IQ sequence
Taiki Nozaki, Yasuyo Teramura, Takeshi Hara, Saya Horiuchi, Atsushi Tasaki, Yasuyuki Kurihara, Hiroshi Yoshioka
Muscular atrophy and fatty degeneration of the supraspinatus muscle occurs after rotator cuff tear. It is often necessary to evaluate for these muscle abnormalities following tears to determine surgical candidacy. We usually evaluate this on a single slice. However, it is not well known whether this slice is representative of fatty degeneration and muscular atrophy overall. Furthermore, it is also not known how fatty degeneration and muscular atrophy will progress after tear. The purpose of this study was to make a standardized fat fraction and muscular volume model in patients with or without supraspinatus tendon tear using IDEAL-IQ sequence.
|
|
1576.
 |
Perturbed muscle mitochondrial function in Sarcopenia
Jamie Ho, Stacey Tay, Subhasis Banerji , Mary Stephenson
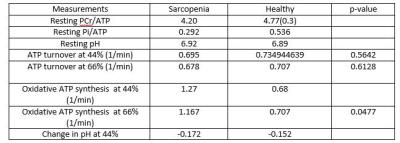
In this study we use 31P MRS in combination with Near Infra-red Spectroscopy to assess muscle mitochondrial function and changes in oxygenation in patients with Sarcopenia as to date, the etiology and molecular mechanisms of sarcopenia remain poorly understood. 10 males diagnosed with sarcopenia and 10 healthy controls were scanned where 31P MRS: A fully relaxed 31P MR spectrum data and exercise paradigm were acquired. MVC were significantly different between the sarcopenic and healthy groups (p=0.0044). Despite this, there was a tendency for increased ATP turnover in patients compared with healthy controls (44% and 66% MVC (ATP turnover p= 0.5642 44%MVC, p= 0.6128 66%MVC). Patients with sarcopenia showed significantly higher oxidative ATP synthesis ATP at 66%MVC where p= 0.0477. These results indicate that at least some of this increased requirement can be met oxidatively, with no contribution from breakdown of PCr at the end of exercise.
|
|
1577.
 |
Disease progression in skeletal muscles of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 evaluated using quantitative MRI
Linda Heskamp, Marlies van Nimwegen, Guillaume Bassez, Marieke Ploegmakers, Jean-Francois Deux, Baziel van Engelen, Arend Heerschap
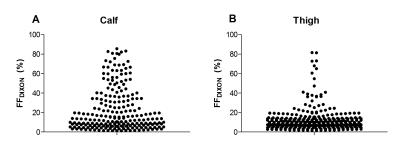
We studied the occurrence and progression of fatty infiltration, atrophy and edema-like processes in calf and thigh muscles of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1) patients. Fat fraction (FF) and muscle volume (MV) were obtained by a DIXON-sequence and T2 of muscle water (T2water) was calculated by a bi-component extended-phase-graph model. Calf and thigh muscles show fatty infiltration and increased T2water in non-fat infiltrated and fat infiltrated muscles. Atrophy is observed in four calf muscles and one thigh muscles. FF significantly increases in 10 months in fat infiltrated and non-fat infiltrated muscles, but MV only decreases in fat infiltrated thigh muscles.
|
|
1578.
 |
Body Composition Analysis Combined with Individual Muscle Measurements using Dixon-MRI
Janne West, Thobias Romu, Sofia Thorell, Hanna Lindblom, Emilia Berin, Anna-Clara Spetz Holm, Lotta Lindh Åstrand, Magnus Borga, Mats Hammar, Olof Dahlqvist Leinhard
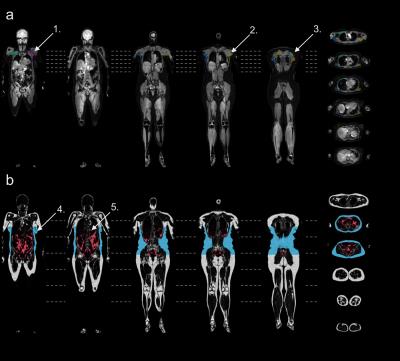
Body composition analysis is increasingly important for diagnosis and follow-up in many patient groups and medical conditions. The combined fat and muscle quantification on global and regional level is not commonly reported. In this study a Dixon-MRI based acquisition and body composition analysis was extended to quantify individual muscles. Test-retest reliability was established in a clinically relevant group of 36 postmenopausal women. This method enables advanced phenotyping combined with measurements of specific muscles to target clinical questions.
|
|
1579. 
 |
A Potential Pathophysiological Link Between Generalized and Localized Muscle Fat Infiltration in Chronic Whiplash Patients
Anette Karlsson, Anneli Peolsson, James Elliott, Thobias Romu, Helena Ljunggren, Olof Dahlqvist Leinhard
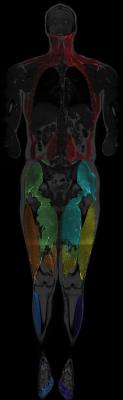
Muscle fat infiltration (MFI) in the cervical multifidi muscles and whole-body skeletal muscle tissue was measured in participants with chronic whiplash associated disorders (WAD) using whole-body fat-water separated MRI to investigate potential interaction between deep neck muscle and generalized MFI. Thirty participants with chronic WAD and 30 matched controls were included. MFI in multifidi was strongly associated to whole-body MFI as well as to severity of WAD. The strong association between Multifidi MFI and whole-body MFI indicates that both generalized factors and localized effects related to the trauma may be important for understanding the pathophysiology of chronic WAD.
|
|
1580. 
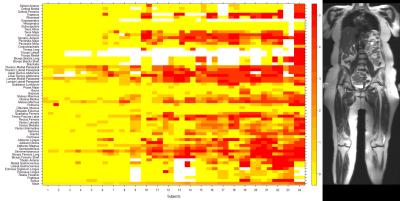 |
Whole-body MRI in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy: Preliminary results
Doris Leung, Li Pan, John Carrino, Kathryn Wagner, Michael Jacobs
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is a hereditary disorder that causes progressive muscle wasting. Whole-body MRI (WBMRI) was used to scan 24 adults with genetically-confirmed type 1 FSHD. Muscles were scored for fat infiltration and edema-like changes. Fat infiltration scores were compared to muscle strength and function measurements. Our analysis reveals a distinctive pattern of muscle involvement and sparing in FSHD. Averaged fat infiltration scores for muscle groups in the legs were statistically significantly associated with quantitative muscle strength and 10-meter walk time. We conclude that WBMRI offers a promising disease biomarker in FSHD and other muscular dystrophies.
|
|
1581. 
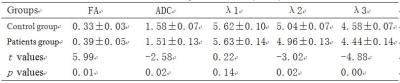 |
DTI imaging application of vastus medialis oblique muscle in recurrent patellar dislocation
Lisi Liu, Zhuozhao Zheng, Huishu Yuan, Lizhi Xie
The osseous-related factors that influence patellofemoral joint instability have been well-studied in plenty of the previous reported literatures. However, the muscle-related factors that affect patellofemoral joint instability have not been fully revealed. MRI is a noninvasive imaging method, including conventional MRI scans and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) sequence, which can respectively reflect the macroscopic and microscopic structures of the muscle fibers.1,2 In the current study, the cross-sectional area were measure with DTI parameters of FA, ADC, and λ1, λ2, λ3 of vastus medialis oblique (VMO). Thereafter, these parameters were compared between the recurrent patellar dislocation patients and the healthy volunteers.
|
|
1582. 
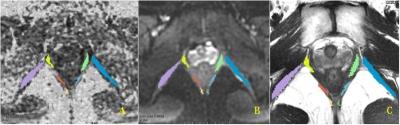 |
Diffusion Tensor imaging in the Injuries of the Levator Ani Muscle in Female Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
Huici Zhu, Jianyu Liu, Yan Zhou, Lizhi Xie
To find the most vulnerable component of levator muscle, this research compared the levator ani muscle which contains pubovisceral, puborectal and iliococcygeal muscles between the control group and the patient group by using DTI. 49 female PFD (pelvic floor dysfunction) patients and 51 female healthy subjects underwent DTI imaging on a 3.0T MR system. A significant difference was found in the FA value of the right pubovisceral muscle between the two groups, and therefore, this part are more likely to be damaged comparing with other compartments of levator ani muscle. DTI with fiber tractography permits the evaluation of the injuries of levator ani muscle, which has a certain effect in revealing the pathogenesis of the female pelvic floor dysfunction.
|
|
1583.
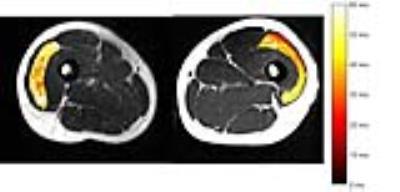 |
Analysis of T2 Relaxation Times in Vastus Lateralis Muscle after Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
Richard Lawless, Peter Hardy, Anders Andersen, Brian Noehren
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries are associated with a persistent decrease in quadriceps muscle strength despite rehabilitation. Previous studies have shown that ACL injury results in muscle disorganization, which could account for the loss in strength. We sought to use dual-spin echo and multi-spin echo sequences to estimate T2 of the vastus lateralis in injured and uninjured limbs of twenty-two ACL injured subjects. T2 of the injured limb was significantly longer than the uninjured limb for both pulse sequences. Our results suggest that T2 relaxation may provide clinicians a means to quantitatively monitor muscle recovery after ACL injury.
|
|
1584.
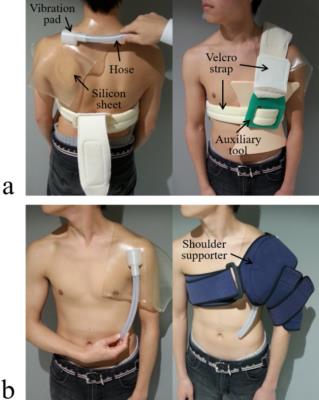 |
Optimal excitation location for magnetic resonance elastography of the supraspinatus muscle
Daiki Ito, Tomokazu Numano, Kazuyuki Mizuhara, Koichi Takamoto, Takaaki Onishi, Hisao Nishijo
It is difficult to palpate the supraspinatus muscle since it is difficult to determine their anatomic location superficially. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) can measure tissue stiffness quantitatively only if vibrations reach these tissues. To vibrate the tissues efficiently, it is necessary to determine the best excitation location. We investigated the excitation location suitable for MRE of the supraspinatus muscle. When the excitation location was placed on the trapezius muscle, the wave images represented clear wave propagation compared with those on the head of humerus. Therefore, optimal excitation location may be the trapezius muscle in the MRE of the supraspinatus muscle.
|
|
1585.
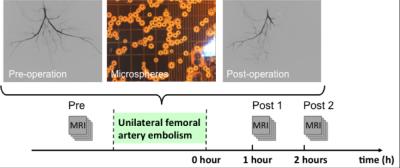 |
Simultaneous measurement of muscle transverse relaxation rates of R2, R2' and R2*: application in unilateral femoral artery embolization
Chengyan Wang, Rui Zhang, Bihui Zhang, Haochen Wang, Xiaodong Zhang, Min Yang, Jue Zhang, Xiaoying Wang, Jing Fang
Diagnosis of the ischemic lesion is challenging and often requires the use of pharmaco-mechanical methods. This study demonstrates the feasibility of using a susceptibility-based MRI technique with the multi-echo gradient and spin echo (MEGSE) sequence to assess the skeletal muscle oxygenation alternations in animal model of unilateral femoral artery embolization. The results shown that the skeletal muscle R2 decreases obviously from after femoral artery embolization, while R2’ increases correspondingly. MEGSE seems to be an appropriate method for the evaluation of skeletal muscle ischemia after embolization.
|
|
1586. 
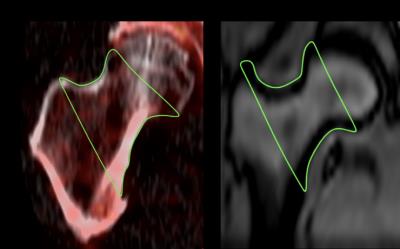 |
Feasibility of Quantifying Bone Metabolism in the Femoral Neck in Human Subjects using Multi-Modality Imaging
Christian McHugh, William Raynor, Tom Werner, Abass Alavi, Chamith Rajapakse
18F-sodium fluoride (NaF) is a readily available radiotracer that has shown great potential to study bone metabolism associated with osseous diseases such as osteoporosis. We analyzed PET/CT and MRI data to study the effects of bone volume fraction and marrow distribution on the uptake of NaF in the proximal femur. Our data showed that the mean standardized uptake (SUVmean) decreased with age and became more significant when local adjustments for bone and bone marrow were taken into account. We foresee the importance of high-resolution microstructural bone MRI for the partial volume correction of PET data for accurate quantification bone metabolism.
|
|
1587. 
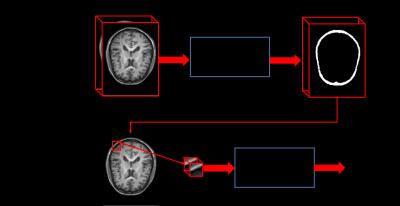 |
Segmentation of CMF Bones from MRI with A Cascade Deep Learning Framework
Dong Nie, Li Wang, Jianfu Li, Daeseung Kim, James Xia, Dinggang Shen
Accurate segmentation of CMF bones from MRI is one of the most important fundamental steps in clinical applications, and it can also be used in other areas, such as character animation and assistive robotics. In this paper, we propose a cascade framework based on the recently well-received and prominent deep learning methods. Specifically, we first propose a 3D fully convolutional network architecture for a coarse segmentation of the bone tissue. Further, we propose to utilize CNN for fine-grained level segmentation around the predicted bone tissue area. The conducted experiments show that our proposed 3D deep learning model could achieve good performance in terms of segmentation accuracy.
|
|
1588.
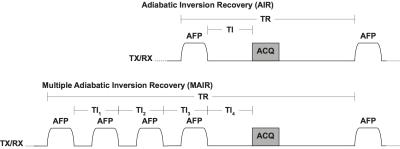 |
Robust Pore Water Suppression in Cortical Bone with Multiple Adiabatic Inversion Recovery
Kevin Harkins, Sasidhar Uppuganti, Jeffry Nyman, Mark Does
Measurement of bound water concentration in cortical bone with MRI is a promising method for evaluating bone fracture risk. One approach to measure bound water involves suppression of pore water signal with an adiabatic inversion-recovery pulse sequence. However, this approach requires a priori knowledge of pore water T1 which itself is expected to vary with bone porosity. We propose to minimize the effect of subject-dependent pore water T1 variation by in bound water imaging using a multiple adiabatic inversion recovery preparation optimized to suppress pore water over a broad T1 domain.
|
|
1589. 
 |
MRI Assessment of the Effect of Low-Magnitude Mechanical Stimulation on Postmenopausal Bone Loss
Chamith Rajapakse, Wenli Sun, Christian McHugh, Ben Newman, Mona Al Mukaddam, Peter Snyder, Felix Wehrli
Low-magnitude mechanical stimulation (LMMS) has shown great potential as a non-pharmacological intervention for improving bone quality in animal models. However, human trials have yielded less compelling evidence, possibly related to difficulties in maintaining adherence and use of conventional imaging techniques not being able to detect subtle longitudinal changes. Here we investigated the use of high-resolution structural bone MRI in monitoring treatment efficacy of LMMS in postmenopausal women. The data show that baseline bone volume fraction at the distal tibia is associated with the changes observed over one year of active LMMS or placebo treatment.
|
|
1590.
 |
Potential of High Resolution Isotropic Microstructural MRI of the Proximal Femur
Austin Alecxih, Elizabeth Kobe, Alyssa Johncola, Marissa Evans, Shivali Patel, Sun Kim, Benjamin Newman, Gregory Chang, Christian McHugh, Chamith Rajapakse
Microstructural MRI based finite element modelling is an area of current research in regards to the role that this technology can play as an efficient and affordable metric for quantifying bone integrity and for identifying fracture risk. This study was conducted in an attempt to unveil the extent to which MRI resolution impacts the quantitative output generated by finite element models pertaining to the parameter of bone stiffness of the proximal femur in vitro. Conclusions reveal a statistically significant variance relative to the values generated for two differing MRI resolution classes.
|
|
1591.
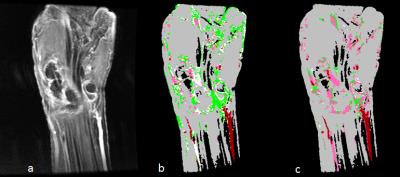 |
Simplified approach to quantification for hand synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis using dynamic contrast enhanced MRI: pixel-by-pixel time intensity curve shape analysis
Yuto Kobayashi, Tamotsu Kamishima, Taro Sakashita, Hiroyuki Sugimori, Shota Ichikawa, Atsushi Noguchi, Michihito Kono, Toshitake Iiyama, Tatsuya Atsumi
Quantification for synovitis using time intensity curve (TIC) shape analysis of rheumatoid arthritis has been believed to require long acquisition time up to 6-7 minutes to observe washout phase. In this study, we found that wash out phase does not contribute to accurate depiction of synovitis in the hand and simplified TIC shape analysis could significantly decrease acquisition time from about 6 minutes to 3 minutes.
|
|
1592.
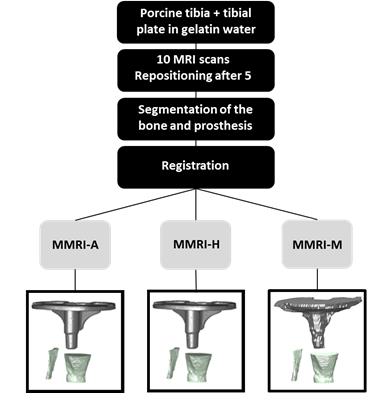 |
A novel approach to measure tibial component migration by low field markerless magnetic resonance imaging
Femke Schroder, Frank Simonis, Dean Pakvis, Rianne Huis in't Veld, Bennie ten Haken
This study evaluated if low field MRI is a practical alternative for Roentgen stereophotogrammetric-analysis (RSA) to measure prosthetic migration. This also included determining the optimal registration method for this purpose. The detection of migration on low field MRI was sufficient for clinical use in two of the translation directions and all three rotational directions. Manual registration proved to be the most accurate method for markerless MRI (MMRI) estimation of the migration.
|
|
1593. 
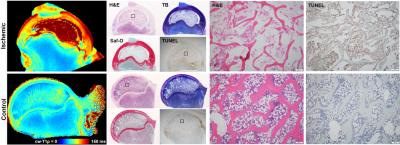 |
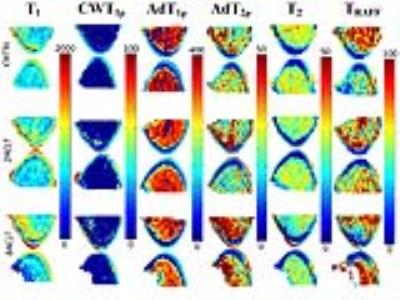
Quantitative Mapping of the Ischemic Femoral Head in a Piglet Model of Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
Casey Johnson, Luning Wang, Ferenc Toth, Cathy Carlson, Harry Kim, Jutta Ellermann
This study investigated the sensitivities of T1, T2, continuous-wave T1ρ, adiabatic T1ρ, and RAFF relaxation times to ischemia-induced necrosis and subsequent repair of the developing femoral head in a piglet model of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease (LCPD), a disabling childhood hip disorder. Quantitative maps of ischemic and control femoral heads acquired ex vivo at 9.4T MRI were compared numerically and validated with histology. Our findings reveal that the relaxation times provide complementary information on the status of the pathological hip, which can potentially address a clinical need for diagnostic imaging tools to assess the early stages of LCPD.
|
|
1594. 
 |
Age estimation using MR imaging of the third molar teeth and the medial clavicular epiphysis: Validation of a multifactorial approach
Thomas Widek, Pia Baumann, Heiko Merkens, Thomas Ehammer, Andreas Petrovic, Isabella Klasinc, Martin Urschler, Eva Scheurer
High migration rates in the last years put forensic age estimation of living people at the forefront of forensic research. The established standard for age estimation uses images acquired with ionizing radiation, therefore radiation-free alternatives such as MRI are currently of high interest. In this study a CT based multifactorial approach that combines wisdom teeth and clavicles was validated with MRI data. The sensitivity to estimate subjects under 18 years of age as minors with MRI lies above 93%. Our results showed that MR could replace the CT based multifactorial Approach.
|
|
1595.
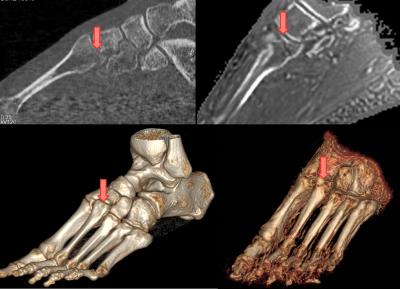 |
Three-dimensional fracture visualization with Zero Echo Time MRI
Gaspar Delso, Geoffrey Warnock, Caroline Zellweger, Felipe de Galiza, Irene Burger, Martin Huellner, Patrick Veit-Haibach
The present study is aimed at assessing the performance of proton density-weighted zero-echo time (ZTE) acquisition for the visualization of bone fractures.
|
|
1596.
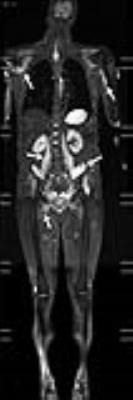 |
An Efficacy Analysis of Whole-Body Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis
Zhen-guo Huang, Min-xing Yang, Bao-xiang Gao, Xiao-liang Chen, He Chen, Kai-ning Shi
To evaluate the value of whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WBMRI) in diagnosing muscular and extramuscular lesions in patients with polymyositis (PM) and dermatomyositis (DM). A retrospective analysis of WBMRI data was performed on PM / DM patients who met the Bohan and Peter diagnostic criteria. WBMRI comprehensively displays the muscular involvement in PM / DM patients, and has the ability to diagnose other associated extramuscular diseases, such as ILD and systemic malignancy. WBMRI can also help screen for multifocal steroid-induced osteonecrosis.
|
|