Other
Traditional Poster
Diffusion
Tuesday, 25 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
13:45 - 15:45 |
|
1815.
 |
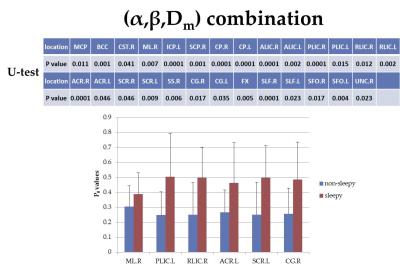
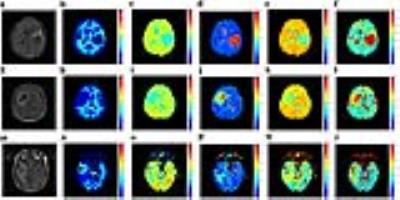
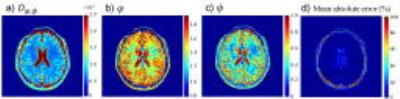
Towards interpretation of 3-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution results in pathology
Thijs Dhollander, David Raffelt, Alan Connelly
Multi-shell multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution (MSMT-CSD) and single-shell 3-tissue CSD (SS3T-CSD) resolve WM fibre orientation distributions and GM and CSF tissue compartments by deconvolving WM, GM and CSF response functions from the diffusion MRI data. We aim for more general interpretation of the “WM/GM/CSF” compartments obtained from 3-tissue CSD methods, specifically in the presence of pathology. We demonstrate their potential in this context and provide a simple framework that aids interpretation, with healthy tissues as a frame of reference. “CSF-like” partial volume is related to interstitial fluid, while “GM-like” partial volume may indicate gliosis, given an appropriate context.
|
|
1816.
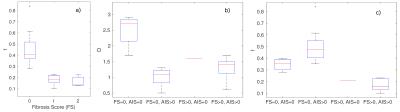 |
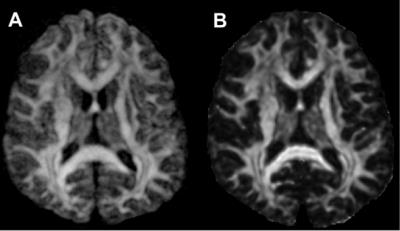
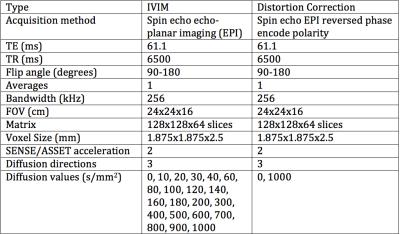
Evaluation of Motion-Compensated Spatially-Constrained IVIM (MC-SCIM) Model of Diffusion-weighted MRI for Assessment of Fibrosis in Crohn’s Disease using Surgical Histopathology Scores
Sila Kurugol, Moti Freiman, Jeffrey Goldsmith, Ryne Didier, Onur Afacan, Jeanette Perez-Rossello, Michael Callahan, Athos Bousvaros, Simon Warfield
Distinguishing bowel regions with fibrosis and regions with active inflammation would be clinically useful in Crohn’s disease to determine best therapy. Commonly used ADC model of DW-MRI, which encapsulates multiple diffusion components into a single parameter, may not suffice to fully describe tissue microenvironments. IVIM model, which describes fast and slow diffusion components, is not commonly used in clinic because of challenges of reliably estimating its parameters due to noise and physiological motion. We recently introduced a motion-compensated spatially-constrained incoherent motion model (MC-SCIM) for reliable parameter estimation. Here we compared MC-SCIM parameters to scores of inflammation and fibrosis from histopathology.
|
|
1817.
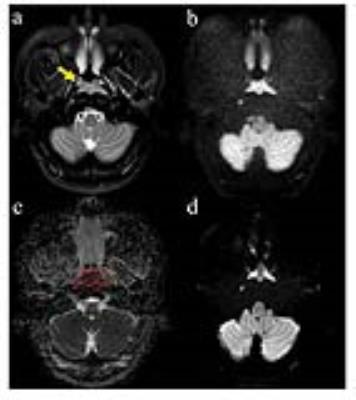 |
Potential value of turbo-spin echo diffusion-weighted imaging in nasopharynx: primary study for differential diagnosis between recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma and post-chemoradiation fibrosis
Shui Zhang
In our study, we found significantly higher image quality, lesion conspicuity and less distortion of TSE-DWI based on Alsop method compared with SS-EPI according to image quality scores. Frustratingly, the SNR for TSE-DWI was lower than for SS-EPI and the result was consistent with other non EPI-DWI sequences in previous studies. Clinically, the low SNR of TSE-DWI remains a major concern. May be it is contributed to the long reception time and higher actual resolution of TSE images compared with SS-EPI and the more efficient k-space coverage of SS-EPI. The CNR of nasopharynx lesions on DW images was significantly better for TSE-DWI imaging than for SS-EPI imaging, which enables a better visual discrimination of nasopharynx lesions with TSE-DWI imaging. In conclusion, TSE-DWI with fewer artifacts and much higher resolutions, which was near impossible before, will make up for the slightly poorer SNR. The ADC values of the brainstem, which was less affected by the susceptibility artifacts and ghosts, showed no significant differences between the two DWI techniques. However, the ADC values of the lesions on TSE were significantly different than those on SS-EPI. This result is obtained coincide with the previous result.These differences may be primarily attributed to susceptibility artifacts and ghost that also resulted in inhomogeneous ADC maps because nasopharyngeal DWI is vulnerable to these artifacts. Therefore, the ADC measurements from TSE-DWI might be more accurate than those from SS-EPI.
|
|
1818.
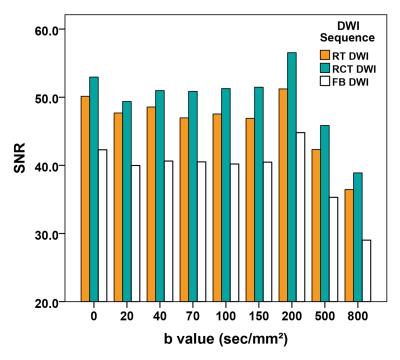 |
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of the Liver: Influence of Combined Respiratory-cardiac Triggering Method on Signal-to-noise Ratio and Repeatability of Quantitative Parameters
Jinning Li, Caiyuan Zhang, Yanfen Cui, Huanhuan Liu, Weibo Chen, Dengbin Wang
As extremely susceptible to various kinds of motions, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging always leads to insufficient image quality and poor reproducibility of quantitative measurements, especially for the liver. However, the use of combined respiratory-cardiac triggering, sychronizing data acquisitions with respiratory and cardiac cycles, could effective improve the signal-to-noise ratio and the repeatability of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters in the liver compared with respiratory triggering and free breathing without triggering method.
|
|
1819.
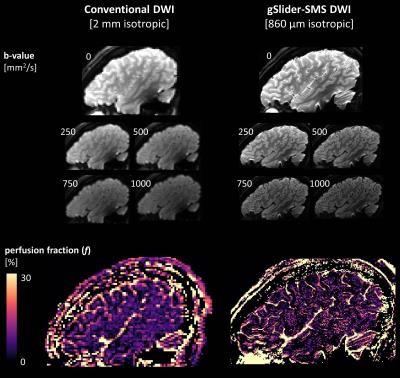 |
High-Resolution Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) with Generalized SLIce Dithered Enhanced Resolution Simultaneous MultiSlice (gSlider-SMS): Effect on CSF Partial Volume Contamination
John Conklin, Thomas Witzel, Kawin Setsompop
In this work, we introduce a high-resolution acquisition strategy for IVIM brain imaging using generalized Slider Simultaneous MultiSlice (gSlider-SMS) diffusion MRI. An SNR efficient multi b-value 10 simultaneous slice acquisition was used to obtain IVIM parameter maps with submillimeter isotropic resolution. Compared to a conventional acquisition (2 mm isotropic), high resolution IVIM provided improved delineation of the cortex and reduced partial volume contamination with CSF. Cortical perfusion measurements using the standard acquisition were falsely elevated by approximately 40% compared to gSlider-SMS IVIM. High resolution IVIM may provide more reliable perfusion information for evaluation of cortically based pathology.
|
|
1820.
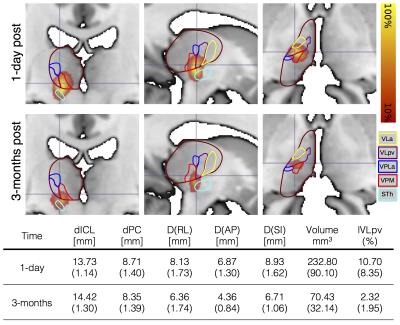 |
Diffusion weighted imaging of the cerebello-thalamic pathway after MR guided high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) thalamotomy
José A. Pineda-Pardo, Raul Martínez-Fernández, Rafael Rodríguez-Rojas, Marta Del-Alamo, Frida Hernández, Lydia Vela, José A. Obeso
In here we aimed at characterizing the impact of the HIFU thalamotomy over the cerebello-thalamic pathway. We used probabilistic tractography to map the subject-specific anatomy of this pathway, we defined a set of regions along a group average pathway, and we extracted DTI based average values in these regions. We found local and distant alterations along the pathway 3-months post-treatment. These changes were strongly correlated with the clinical improvement of the patients. These findings serve to strengthen DWI, as a tool to aid in the targeting of HIFU in the treatment of essential tremor.
|
|
1821.
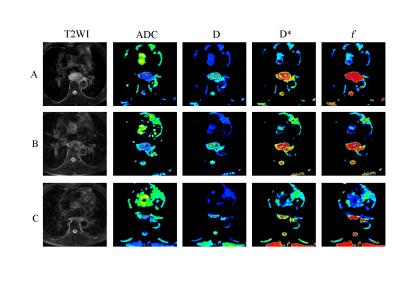 |
Value of the Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI in Pretreatment Predicting and Monitoring the Early Response to Chemoradiotherapy in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
fei ping li, zhongping zhang, Xiaoping Yu
Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) was considered to be a very effective treatment regimen for locally advanced or unresectable esophageal cancer (EC). Usually the therapy-induced early changes of tumor microenvironment were prior to morphological changes, which cannot be detected by traditional imaging techniques. This study used intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI) to investigate the early response to CRT in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). It was found that the IVIM-DWI parameters (ADC and D) might be valuable in pretreatment predicting and monitoring the early treatment response to CRT in ESCC.
|
|
1873.
|
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) diffusion-weighted imaging for response evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma after resin- and glass-based radioembolization
Claus Pieper, Alois Sprinkart, Carsten Meyer, Hans Schild, Guido Kukuk, Petra Mürtz
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model-based analysis of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is increasingly employed in oncologic imaging. Although first experiences with IVIM DWI for response analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after embolization therapies in general have recently been reported, response characteristics of specific treatment options are so far unknown. We describe differences in treatment response parameters of HCCs obtained by IVIM DWI in resin-radioembolization and glass-radioembolization.
|
|
1822.
 |
Rectal Adenocarcinoma: Diagnostic Accuracy of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging (DKI) and its Correlation with Prognostic Factors
Lan Zhu, Xu Yan, Cai xia Fu, Huan Zhang, Zilai Pan, Fuhua Yan
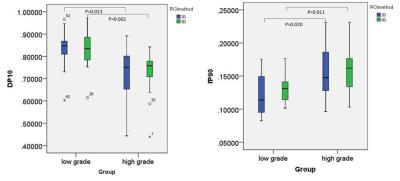
The high resolution MRI and conventional DWI suffers from unsatisfying accuracy in assessment of some prognostic factors of rectal adenocarcinoma. We employed DKI, a protocol mainly for evaluating the complexity of biologic tissues, to explore its diagnostic accuracy and correlation with prognostic factors. The kurtosis of DKI exhibited highest correlation with histologic grades especially the new grading criterion and higher potential in differentiation of high- and low grade tumors, and also in predicting nodal status, with higher specificity than or equivalent sensitivity to diffusivity and ADC. In conclusion, DKI could be a promising tool in predicting prognosis of rectal adenocarcinoma.
|
|
1823.
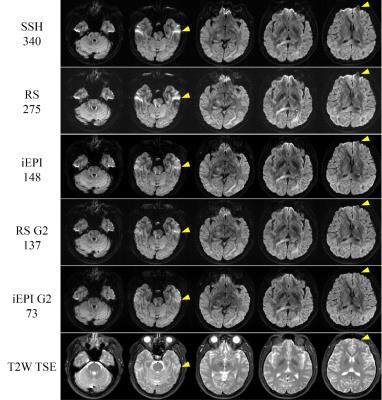 |
A Comparison of Readout Segmented EPI and Interleaved EPI in High Resolution Diffusion Weighted Imaging
Yishi Wang, Xiaodong Ma, Zhe Zhang, Erpeng Dai, Ha-Kyu Jeong, Bin Xie, Chun Yuan, Hua Guo
Multi-shot interleaved EPI (iEPI) and readout segmented EPI (RS-EPI) are two alternative strategies for high resolution diffusion imaging. This study made a comparison of the two methods in different aspects. Our comparison showed that the iEPI had the advantage of largely reducing the geometric distortion. Both RS-EPI and iEPI could achieve high resolution diffusion tensor imaging.
|
|
1824.
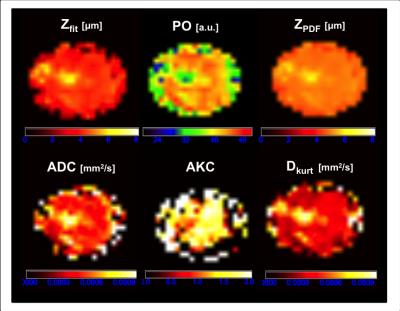 |
Evaluation of diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), kurtosis imaging (DKI) and q-space imaging (QSI) for profiling whole human breast tumour tissue microstructure
Nicholas Senn, Yazan Masannat, Ehab Husain, Bernard Siow, Steven Heys, Jiabao He
We investigated a clinically viable QSI protocol in whole breast tumours excised from patients on a clinical scanner within a clinically feasible time frame. QSI has been largely limited to the preclinical setting, requiring strong gradients and a long acquisition time. We compared QSI against conventional DWI and DKI and found that diffusion indices across these techniques were consistent. Previous studies have shown that QSI provides a comprehensive characterisation of tissue microstructure, particularly in the presence of restricted diffusion. These results provide pivotal foundation for the clinical translation of QSI in breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
|
|
1825.
 |
Effect of hyperglycemia on deep nucleus microstructure and iron deposition in people with type 2 diabetes: a DKI and SWI study
Junyi Dong, Chengcheng Zheng, Qingwei Song, Qiang Wei, Weiwei Wang, Yanwei Miao, Bing Wu
In this paper,the experimental group and the control group were respectively used as the people with type 2 diabetes and the health people ,the effect of high blood glucose on the microstructure and iron deposition in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus was studied used DKI and SWI study,and it is concluded that the high blood glucose level may have certain damage to the microstructure of the deep core.Furthermore,iron deposition may exacerbate the damage of microstructure.In conclusion,DKI and SWI study can evaluate secondary brain microstructure changes from hyperglycemia in T2DM patients.
|
|
1826. 
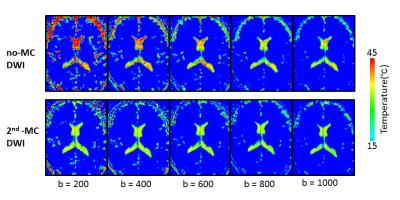 |
Optimal strategy for measuring intraventricular temperature using second-order motion compensation DWI
Shuhei Shibukawa, Tetsu Niwa, Naoki Ohno, Toshiaki Miyati, Tomohiko Horie, Susumu Takano, Nao Kajihara, Toshiki Saito, Tetsuo Ogino, Yutaka Imai
A method for monitoring the intraventricular cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) temperature calculated from the DWI is affected by the CSF pulsation. Moreover, DWI should be obtained by optimal b value according to the diffusion coefficient of the measuring tissues. We investigated the second-order motion compensation DWI (2nd-MC DWI) to the determination of the intraventricular temperature to improve that accuracy with optimal b value. In the case of using the optimal b value based on the literature (ie., approximately 400 s/mm2), the intraventricular temperature can be more accurately estimated with 2nd-MC DWI than conventional no-motion compensation DWI.
|
|
1827. 
 |
Estimation of a novel set of intra and extracellular diffusivity parameters from modern DW-MRI
Mario Ocampo-Pineda, Alessandro Daducci, Alonso Ramirez-Manzanares
We present a novel framework to estimate on in-vivo data a) independent intra and extracellular axial-diffusivities, b) extracellular radial-diffusivity, c) non-parametric bundle dispersion, d) axonal diameter indexes, and e) intracellular volume fractions. Our methodology does not fix a priori the value of any of these parameters or uses tortuosity models on the extracellular radial diffusivity. The proposal is an extension of the ED^3 method, which provided the best solution on the signal prediction on the White Matter Modelling Challenge 2015. We perform a comprehensive set of synthetic experiments under realistic conditions to validate the capabilities of the proposal.
|
|
1828.
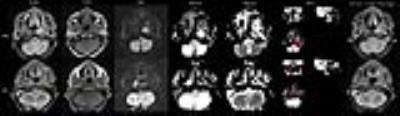 |
Prediction of Radiotherapy Response in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients Using Diffusion-Kurtosis Imaging
Weiyuan Huang, Jiianjun Li, Feng Chen, Yingman Zhao, Xiaolei Zhu
The first row: A 62-year-old man with NPC who was a nonresponder. The lesions located at the left nasopharyngeal wall and cavum. Manual draw an ROI within the boundaries of the NPC on Kmean map. The tumor’s maximum diameter was 3.5 before radiotherapy. Residual tumor was detected after radiotherapy. Mean Dmean and Kmean values were 1.48 10-3 mm2/s and 0.72 before treatment. The second row: A 63–year-old man with NPC who was a responder. The lesion affect the bilateral mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. The tumor’s maximum diameter was 3.09 before radiotherapy. No residual tumor was detected after radiotherapy. Mean Dmean and Kmean values were 1.22 10-3 mm2/s and 0.83 before treatment. NRG: non response group RG: reponse group
|
|
1829.
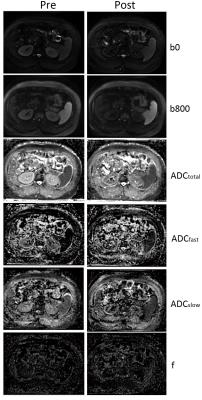 |
Effect of gadolinium contrast agent on IVIM derived parameters of abdominal organs
Yukun Chen, Chao Ma, Aiguo Jin, Li Wang, Minjie Wang, Luguang Chen, Caixia Fu, Xu Yan, Jianping Lu
This study investigated potential effects of gadolinium contrast agent on the IVIM derived parameters such as Dfast (blood microcirculation), Dslow (pure extravascular water diffusion), f (perfusion fraction) and the commonly used DWI-derived ADC of abdominal organs. The result shows that gadolinium administration does not make statistically significant differences in Dslow, Dfast, f or ADC of the liver, spleen, or pancreas. In the kidney, however, ADC values are significantly lower with post-contrast than pre-contrast.
|
|
1830. 
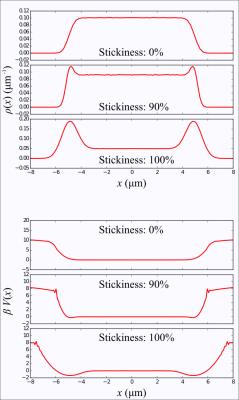 |
Imaging energy landscapes
Evren Özarslan, Kadir Simsek, Cem Yolcu, Carl-Fredrik Westin
We discuss the usage of a recently-proposed diffusion-sensitising gradient waveform for the purpose of imaging the potential energy landscape in which water molecules diffuse. The energy landscape encodes information about bulk heterogeneities of the medium as well as effects such as adsorption at the boundaries.
|
|
1831.
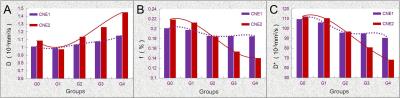 |
IVIM-derived parameters in evaluating the pathological features and hypoxia of nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts
Youping Xiao, Yunbin Chen, Xiang Zheng, Ying Chen, Li Peng, Jianji Pan, Weibo Chen
Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging was conducted on different radio-sensitive human NPC xenografts (CNE-1 and CNE-2) in order to investigate its application value in assessing the pathological features and tumor’s hypoxia of xenografts. CNE-2 xenografts of higher radio-sensitivity behaved greater changes on IVIM-parameters than CNE-1 xenografts of lower radio-sensitivity after fractional radiations. D and f values correlated significantly with the pathological features and tumor’s hypoxia of xenografts. Thus, IVIM-parameters is potentially valuable in evaluating the effect of radiotherapy in NPC.
|
|
1832. 
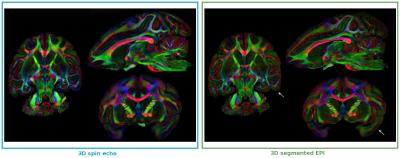 |
High-resolution diffusion imaging of post-mortem monkey brain: comparison of 3D Spin Echo and 3D segmented EPI sequence at 11.7T
Sophie Sébille, Anne-Sophie Rolland, Carine Karachi, Marie-Laure Welter, Eric Bardinet, Mathieu Santin
Diffusion-weighted spin echo (SE) acquisition is the golden-standard of diffusion imaging, yet it is limited by a very long acquisition time. This work present the optimization of a 3D segmented Echo Planar Imaging (EPI) sequence with the goal of reducing acquisition time and be able to perform tractography and to promote further analysis such as microstructure or histology correlation.
|
|
1834.
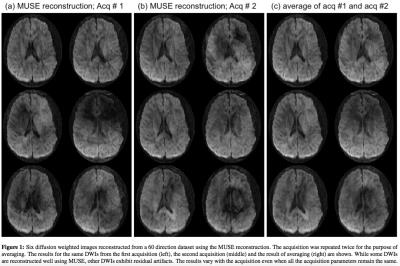 |
Comparison of MUSSELS vs MUSE for Multi-Shot Diffusion Imaging
Merry Mani, Mathews Jacob, Baolian Yang, Vincent Magnotta
Multi-shot diffusion weighted (MS-DW) imaging can offer reduced echo-time (TE) and improved SNR to enable high spatial resolution applications. However, the reconstruction of the high resolution diffusion weighted images (DWI) from the multiple shots is challenging because of the presence of motion-induced phase variations between shots. Recently, two methods were proposed to reconstruct the phase-compensated DWIs. In this work, we compare the performance of the methods, MUSE and MUSSELS, to reconstruct the DWIs from a MS-DW acquisition.
|
|
1835.
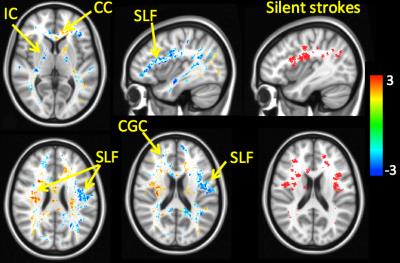 |
Fiber connection density differences detected in patients with sickle cell disease
Julie Coloigner, Jacob Antony, Roza Vlosova, Adam Bush, Soyoung Choi, Maxime Descoteaux, Jean-Christophe Houde, Thomas Coates, Natasha Lepore, John Wood
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a chronic disorder characterize by progressive cerebrovascular damage. We hypothesized that subtle cerebral injury might be visible with diffusion imaging data in these patients. Tractography based on the fiber orientation distribution function (ODF) was applied in order to investigate the character and severity of white matter injury in patients with SCD. We found both decreased and increased fiber density in patients, compared to control subjects that co-localized with silent cerebral infarctions. These data suggest progressive white matter injury and compensatory mechanisms in SCD patients.
|
|
1836. 
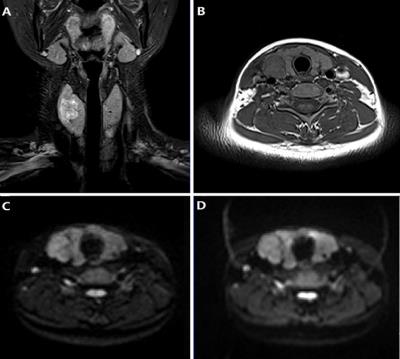 |
Diffusion weighted imaging in thyroid nodule: comparison of readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI Techniques
Luguang Chen, Peipei Sun, Bin Xu, Qiang Hao, Caixia Fu, Minjie Wang, Jianping Lu
Diffusion weighted imaging showed the potential to evaluate thyroid disease. This study aimed to evaluate whether readout-segmented EPI (RS-EPI) can provide better image quality in imaging thyroid gland in comparison with single-shot EPI (SS-EPI), and to compare ADC values, acquired from RS-EPI with those of SS-EPI. Sixteen patients were examined using both techniques. There were significant differences in susceptibility, motion artifacts, except for detectability of thyroid nodules and ADC measurements between RS-EPI and SS-EPI. The present study found that the RS-EPI technique provides significant image quality improvement compared with SS-EPI in imaging thyroid gland at 3 Tesla.
|
|
1837. 
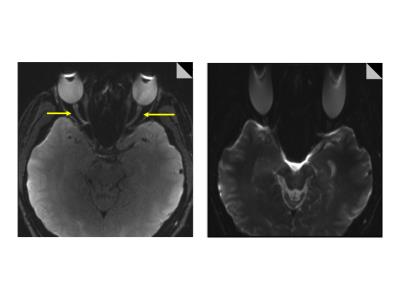 |
Towards a practical protocol for accurate and reliable MR-derived diffusion changes of the optic nerve in optic neuritis
Weiling Lee, Soo Lee Lim, Ling Ling Chan, Winston Lim, Helmut Rumpel
Optic neuritis is a demyelinating inflammation of the optic nerve that often occurs in association with multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), especially diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) is highly sensitive for inflammatory changes in the optic nerves. We propose a DTI protocol which balances susceptibility artefacts, scan time, and resolution for better image quality and clinical practicality. It allows a 1 mm in-plane resolution in order to avoid partial volume averaging with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounding the optic nerve in examining fractional anisotropy (FA) values and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) for severity of optic neuritis.
|
|
1838.
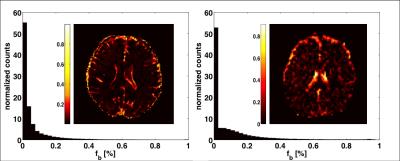 |
Joint estimation of free water and perfusion fraction in human brain
Anna Scherman Rydhög, André Ahlgren, Filip Szczepankiewicz, Ronnie Wirestam, Carl-Fredrik Westin, Linda Knutsson, Ofer Pasternak
The perfusion of blood affects the estimation of diffusivities, especially fast components such as free water. Here, we acquired human data to demonstrate the applicability of a three-compartment model for the joint estimation of tissue diffusivities, free water, and the perfusion fraction. We evaluated the feasibility of the model by comparing a multiple b-value approach with a shorter, clinically feasible approach. The conclusion is that the two-compartment free-water estimation is affected by both water and blood. The three-compartment model disentangles these effects, useful in distinguishing between changes originating from capillary blood from those originating from the extracellular space.
|
|
1839.
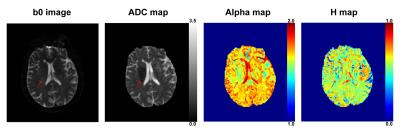 |
Fractional motion related diffusion MRI in the detection of acute ischemic stroke
Yang Fan, Boyan Xu, Lu Su, Bing Wu, Zhenyu Zhou, Peiyi Gao, Jia-Hong Gao
The use of FM model has been demonstrated in distinguishing low- and high-grade pediatric brain tumors. However, its feasibility in detecting acute stroke has not yet been investigated. In this work, FM model was applied in patients with acute ischemic stroke and compared with traditional ADC to investigate its clinical potential.
|
|
1840.
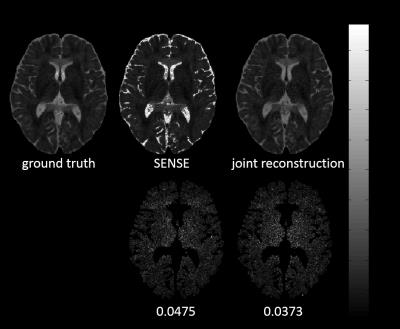 |
Model-Based Joint Reconstruction for Multi b-Value Diffusion-Weighted Imaging
Zhongbiao Xu, Li Guo, Wenxing Fang, Chenguang Zhao, Yingjie Mei, Zhifeng Chen, Wufan Chen, Ed X. Wu, Feng Huang, Yanqiu Feng
In current multi b-value DWI, each b-value image is usually reconstructed independently by using parallel MRI techniques. In this work, we propose a model-based joint reconstruction method for the reconstruction of under-sampled multi b-value DWI data. The proposed method can directly estimate quantitative parameters form k-space data, and exploit inter-image constraint to improve the quality of reconstructed image.
|
|
1841.
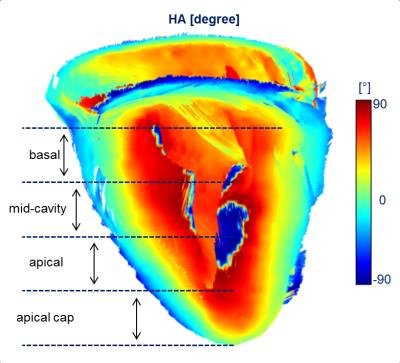 |
High Resolution Cardiac DTI - Fiber Tractography Statistics of the ex Vivo pig Heart
David Lohr, Maxim Terekhov, Andreas Weng, Anja Schroeder, Heike Walles, Laura Schreiber
A whole heart, high resolution diffusion tensor data set with 1.3 mm isotropic voxels was acquired in 15 ex vivo pig hearts using a Stejskal-Tanner sequence at 3T. ADC, FA and HA values were calculated and analyzed for the whole heart. Purpose was to create a reliable statistical reference of diffusion parameters. Sharp modes for median and interquartile range of the ADC and median and mean values of the helix angle indicate similar distributions of those values for the individual hearts. This provides a statistically compelling reference for future cardiac DTI pig studies in vivo and at higher field strengths.
|
|
1842. 
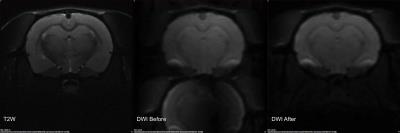 |
In Vivo 3D Single-Shot Echo-Planar DWI at 7T for Mapping Tissue Microstructure using Mean Apparent Propagator (MAP) MRI
Alexandru Korotcov, Asamoah Bosomtwi, Elizabeth Hutchinson, Michal Komlosh, Carlo Pierpaoli, Peter Basser, Andrew Hoy, Bernard Dardzinski
A number of advanced diffusion models have demonstrated great promise for mapping tissue microstructure in ex vivo studies with high resolution and fidelity using a wide range of diffusion weightings, but the increased acquisition time (days) is not feasible in vivo. In this study we have addressed some basic DWI acquisition pitfalls by using 3D single-shot EPI on a high-field (7 Tesla) pre-clinical MRI system, and adapted one of the most promising diffusion modeling techniques, mean apparent propagator (MAP) MRI in vivo to derive information about rat brain microstructure within a reasonable time frame.
|
|
1843. 
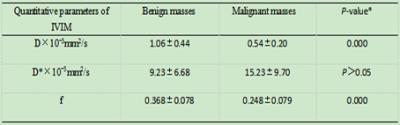 |
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) in Evaluation of Orbital Masses
Ya-wen AO, Jun Chen , Liang Zhang, Fei Sang, Hong-yan Nie, Dong-jie Huang, Hui Lin, Bing Wu
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has been proven that malignant orbital masses demonstrate significantly and visually appreciable lower apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) than benign orbital masses[1-2]. Nevertheless, ADC cannot separate the pure molecular diffusion from the motion of water molecules in the capillary network; thus, perfusion contamination would increase the ADC value. According to the IVIM DWI model[3], both microscopic perfusion and diffusivity can be separated using a biexponential decay function, providing additional parameters for tissue characterization. From the result we can see that it is feasible that quantitative parameters of orbital masses can be derived from IVIM DWI.
|
|
1844.
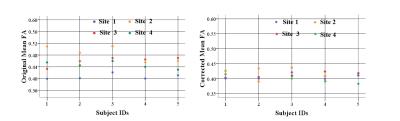 |
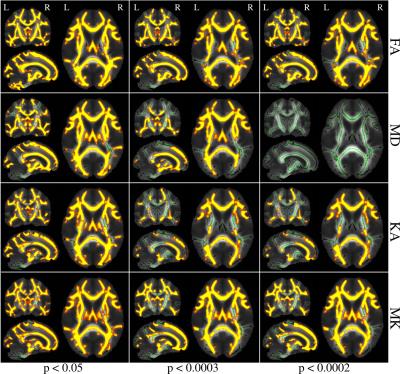
Harmonization for DTI measurements mapping across sites in multi-center MRI study
Chuanzhu Sun, Lijun Bai, Hao Yan, Shan Wang, Xiaocui Wang, Xianjun Li, Chao Jin, Xiaocheng Wei, Hong Yin, Zengjun Zhang, Xiaoqun Yao, Xiaoling Zhang, Jian Yang, Jian Yang, Jian Yang
Despite the fact that multi-site diffusion imaging studies are increasingly used to study brain disorders, but it is noteworthy that there are large differences among diffusion measurements from different sites. The current study aimed to confirm the variability and to harmonize data across sites. Our results indicated that not only DTI metrics in human brain within inter-site but also within inter-site changed obviously. Furthermore, a brain voxel-based model was developed to harmonize the DTI metrics and to reduce the deviation compared with reference site data and thus improve the reliability of group analysis in multi-center study.
|
|
1845. 
 |
Benefits of flow, eddy current and concomitant field compensation in diffusion weighted MRI
Lars Mueller, Andreas Wetscherek, Tristan Kuder, Frederik Laun
Diffusion-weighted MRI suffers from artifacts due to flow, concomitant fields and eddy currents. Different combinations of compensation for these effects were examined in phantom measurements as well as in vivo in the brain and in the prostate. The signal variations in the phantom measurements indicate that it could be advantageous to simultaneously compensate of all three effects over only flow and concomitant field compensation. This could not be seen in the in vivo results, where flow and concomitant field compensation proved to be as good as the full compensation.
|
|
1846. 
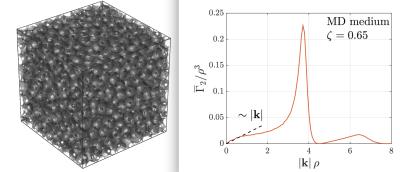 |
Diffusion Diffraction Inside Out
Valerij Kiselev, Alexander Ruh, Bibek Dhital
Diffusion diffraction, a famous result on NMR in porous media founds little application to in-vivo MRI. Beyond the high technical requirements, the reason can be seen in the principal limitations of this technique. It probes the shape of identical closed pores, which are not typical in-vivo. In this work, we generalize diffusion diffraction for an infinite connected compartment outside impermeable inclusions such as space external to biological cells with low membrane permeability. The signal at high diffusion weighting is expressed in terms of the inclusions' correlation function. The developed theory is supported by experiments in aqueous suspension of polystyrene microbeads.
|
|
1847.
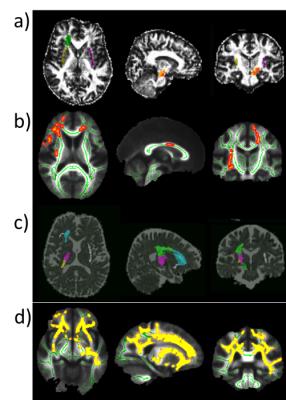 |
Investigation of Diffusion Tensor Indices by ROI analysis and TBSS of Patients with Depressive Symptoms in the Elderly with Dementia
Tsung-Yuan Li, Ni-Jung Chang, Clayton Chi-Chang Chen, Jyh-Wen Chai
The differences of indices in diffusion tensor images (DTI) of patients with dementia are well-discussed in recent years. However, the comorbidity of dementia and depression was observed. In this study, we focused on the white matter changes associated with depressive symptoms in dementia and the relationship between DTI indices and cognitive functions in depressed and non-depressed patients. By an ROI-based analysis of the indices and TBSS analysis in DTI, we investigated the differences between patients of dementia with depression and without depression. Furthermore, we correlate the differences with the score of some clinical cognitive test to figure out the subtle differences.
|
|
1848.
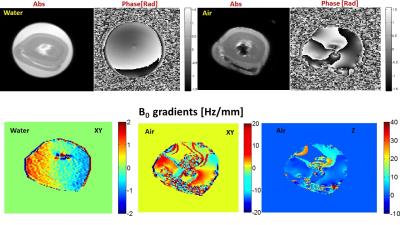 |
Myocardium Tissue DTI with Stimulated Echo at Large Susceptibility Induced B0 gradients: Examination of the Shimming Strategies Efficiency and Errors.
Maxim Terekhov, David Lohr, Laura Schreiber
In this paper, we investigated experimentally and statistically the effect of distortions of myocardium DTI with STEAM-EPI due to susceptibility induced gradients varied in a range of factor 10 to 20 to the reference. The special focus was given to examining the effect of prolonged EPI-readout, B0-shimming effect and motion-induced shimming errors relevant for high-resolution DTI in-vivo. Fresh ex-vivo pig hearts were used for DTI measurements with an in-house developed STEAM-EPI sequence. The distribution of diffusion directions components was found well preserved for prolonged readout even at high internal gradient.
|
|
1849.
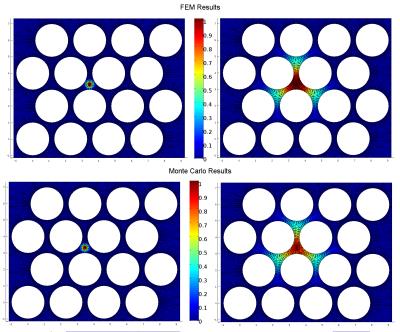 |
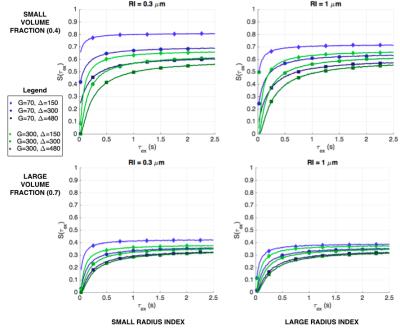
Validating Particle Dynamics in Monte Carlo Diffusion Simulation using the Finite Element Method
Jonathan Rafael-Patiño, Alonso Ramirez-Manzanares, Joaquin Peña, Hui Zhang
Monte-Carlo Diffusion Simulation (MCDS) is commonly used to develop and validate analytical models for quantifying tissue microstructure using diffusion MRI. However, the validation of the tools implementing MCDS has been limited, especially for complex domains, such as the extra-cellular space of brain tissue. To address this challenge, we propose a novel framework using the Finite Element Method (FEM), an established method for solving the diffusion equation with complex domains, to provide the ground-truth to assess MCDS. We demonstrate the framework by assessing how the accuracy of MCDS is influenced by the number of particles and the number of diffusion steps.
|
|
1850.
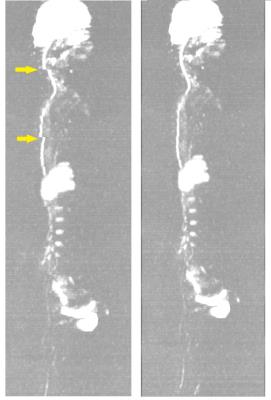 |
Distortion free whole-body diffusion weighted imaging using a self-adaptive post deformation algorithm
Lizhi Xie, Bo Hou, Zhenyu Zhou
Conventional Whole-Body DWI that consists of several sequential stations often troubled geometric distortions and signal drops in areas with strong susceptibility, such as the neck and lumbar vertebra. The aim of this study was to propose a new WBDWI protocol and post process deformation algorithm to get distortion free whole body images. Consistently good results were received and in helps to diagnose several cases of tumors that were previously unclear to the volunteers and patients.
|
|
1851.
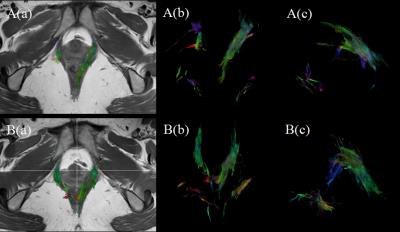 |
A longitudinal follow-up study of levator ani muscle injury during vaginal delivery using diffusion tensor imaging
yujiao zhao, zhizheng zhuo, wen shen
Levator ani muscle (LAM) injury has been known to be highly associated with vaginal delivery, the natural recovery course of injured LAM is unclear recurrently. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) with fiber tracking is a useful noninvasive MRI technique, which can be used to assess pelvic floor muscles injury and recovery quantitatively, and the fiber tract can display the direction and thickness of LAM fibers. In this study, we tried to apply DTI imaging to explore the natural recovery course of LAM injury during vaginal delivery. And the results showed that the injured LAM during vaginal delivery has some degree of repair as time goes on.
|
|
1852. 
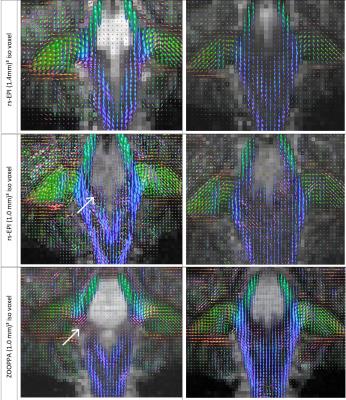 |
Shortening acquisition time and increasing resolution to (1 mm)³ isotropic in 7T diffusion MRI (dMRI) still allows resolving fiber orientations and fiber crossings: a step towards clinical applications?
Ralf Lützkendorf, Robin Heidemann, Sebastian Baecke, Michael Luchtmann, Jörg Stadler, Thorsten Feiweier, Jörn Kaufmann, Johannes Bernarding
Prior results in single-shot diffusion weighted EPI indicated that voxel sizes below (1.4mm)3 prohibit reliable resolution of fiber orientations and fiber crossings. Here we compare zoomed single-shot EPI with (1mm)³ isotropic resolution with readout-segmented EPI with (1.4mm)³ and (1.0mm)³ isotropic at ultra-high field strength of 7 Tesla. In all cases, fiber density orientation maps could be determined reliably thus enabling a resolution of main fiber directions and crossings even at (1mm)³ resolution.
|
|
1853.
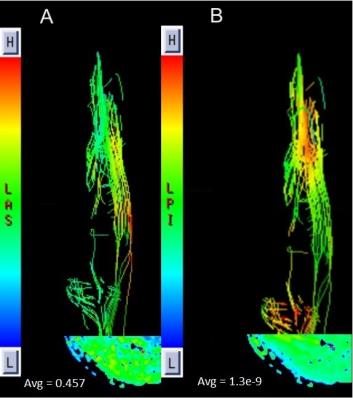 |
Applied Research of Diffusion Tensor Imaging in traumatic tibial nerve injury
Xiaojuan Wang, Chen Zhao, Kening Xu, Lizhi Xie
DTI plays an important role in detecting nerve injury. It offers a great opportunity for imaging the tibial nerve injury follow trauma.In this work, we demonstrated DTI combined with DTT can clearly review the morphological transformation of Nerve fiber after tibial nerve injured; quantitatively analyze the damage degree,which can provide detailed information for clinical treatment.
|
|
1833. 
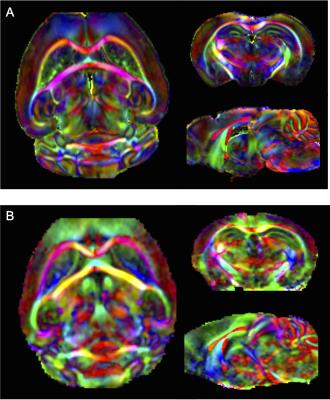 |
Comparaison of in vivo and ex vivo high resolution imaging of the mouse brain at 11.7T
Sophie Sébille, Isaac Adanyeguh, Elise Marsan, Sirenia Mondragon-Gonzalez, Fatma Gargouri, Mathieu Santin
This study compares high resolution in vivo and ex vivo diffusion imaging of mouse brain at 11.7T. The study shows that even with the advancement in image sequences and equipment, ex vivo imaging remains superior to in vivo imaging in terms of resolution with clear delineation of brain structures. However, fractional anisotropy values obtained from ex vivo imaging may not be a true representation of the in vivo condition. Nonetheless, the resolution obtained from in vivo imaging should allow for longitudinal studies.
|
|
1854. 
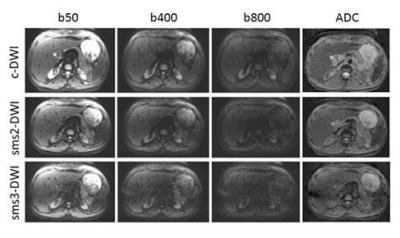 |
Scan time reduction in DWI of the pancreas using simultaneous multislice technique with different acceleration factors: how fast can we go?
Jana Taron, Petros Martirosian, Thomas Kuestner, Mike Notohamiprodjo, Jakob Weiss, Ahmed Othman, Konstantin Nikolaou, Christina Schraml
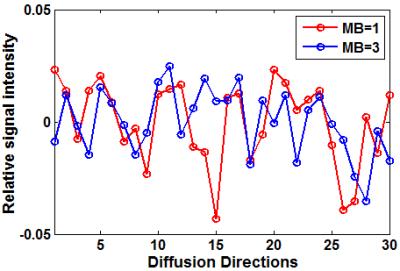
We investigated the feasibility of simultaneous multislice-accelerated diffusion-weighted imaging of the pancreas using an acceleration factor of 2 and 3 (sms2/sms3-DWI) and its influence on image quality, acquisition time and apparent diffusion coefficients in comparison to conventional sequences (c-DWI) in ten healthy volunteers and 20 patients at 1.5 T. Images recorded with sms2-DWI offered high quality with a scan time reduction to one third; sms3-DWI showed significantly poorer overall image quality. In conclusion, sms2-DWI is feasible in clinical routine providing high image quality and a substantial reduction of acquisition time, whereas the use of higher acceleration factors is currently not recommended.
|
|
1855.
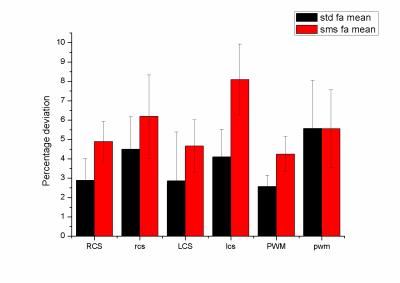 |
Robustness of kurtosis acquisition via simultaneous multi-slice EPI: a test-retest in children
Antonio Napolitano, Chiara Carducci, Laura Filograna, Vittorio Cannatà, Giovanna Stefania Colafati
Diffusion kurtosis imaging is an emerging technique based on non-gaussian diffusion of water in biologic systems and provides complementary information to the traditional diffusion. Although the method is very promising in identifying new biomarkers, it suffers from long time acquisition, which is very challenging in . However, a recent technique, named simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) acquisition, allows multiple slices acquisition thus drastically reducing the acquisition time. The purpose of this work is then to study the robustness of diffusion kurtosis in children when acquired via sms method.
|
|
1856.
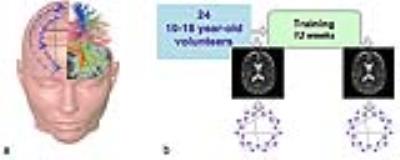 |
Mental training effects on adolescent brain networks
Olga Tymofiyeva, Eva Henje Blom, Justin Yuan, Colm Connolly, Tiffany Ho, Lisa Baldini, Trevor Flynn, Matthew Sacchet, Kaja LeWinn, Rebecca Dumont Walter, Tony Yang, Duan Xu
In this study we used diffusion MRI network analyses to examine the effects of a 12-week training of attention and emotion regulation. Our preliminary results in 24 healthy adolescents demonstrate an improvement of executive attention and an increase of the node strength of the left anterior cingulate cortex.
|
|
1857. 
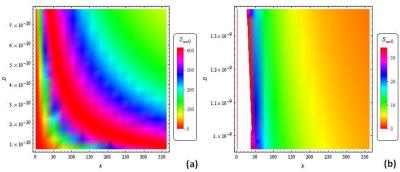 |
Analytical Solutions of Bloch NMR Flow Equations: Emerging and Future Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Bamidele Awojoyogbe, Michael Dada
Diffusion imaging has proved to be very important in clinical diagnosis and its exclusive application to numerous medical problems is currently plagued with some limitations which is most pronounced in heterogeneous voxels. In order to address this problem, we have presented an analytical method with which diffusion MR signals can be evaluated from point to point within a voxel of interest. The proposed method is shown to be useful in brain tumor diagnosis and general computational tissue imaging. The interesting part of this method is that only few data are required for image reconstruction.
|
|
1858.
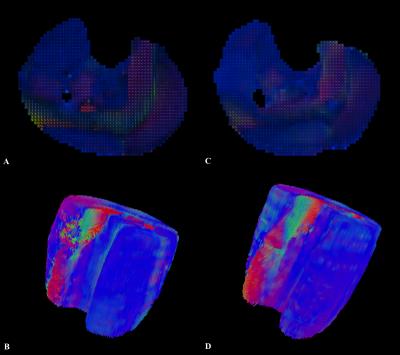 |
Diffusion Tensor Imaging of human muscle at ultra-high-field (7T) MR.
Chiara Giraudo, Stanislav Motyka, Christoph Resinger, Thorsten Feiweier, Siegfried Trattnig, Wolfgang Bogner
Ultra-high-field (7T) imaging already demonstrated to provide more robust DTI measurements in comparison to 1.5 and 3T in the brain but, to the best of our knowledge, it was not applied for DTI measurements on human muscles. Our results showed higher SNR as well as an overall improvement in DTI metrics for the entire calf muscle at 7T than at 3T. Single muscle analyses (gastrocnemii, tibialis anterior) demonstrated more heterogeneous results. Future studies including a larger population and considering technical challenges (e.g.,RF inhomogeneity, gradient performance) are necessary to assess if 7T may provide higher benefits in specific muscles.
|
|
1859.
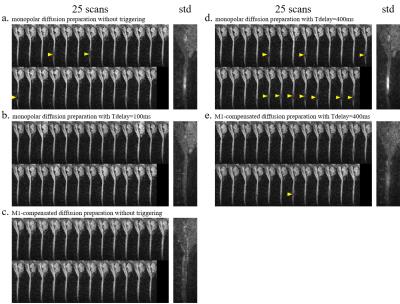 |
Effect of Velocity-compensated Diffusion Preparation for Spinal Cord Diffusion Imaging
Zhe Zhang, Xiaodong Ma, Chun Yuan, Hua Guo
The spinal cord and surrounding cerebrospinal fluid undergo significant cardiac pulsations, which can influence the microscopic motion-sensitive diffusion preparation and cause signal void in the diffusion images. In this work, velocity-compensated diffusion-encoding gradient waveform was implemented in spinal cord diffusion imaging and the images are compared with traditional monopolar preparation and cardiac gating approaches. Results show that with velocity-compensated diffusion preparation, the spinal cord diffusion imaging shows fewer signal voids compared to the traditional monopolar diffusion preparation. Using velocity-compensated diffusion preparation without cardiac triggering can provide a new approach for spinal cord diffusion imaging.
|
|
1860. 
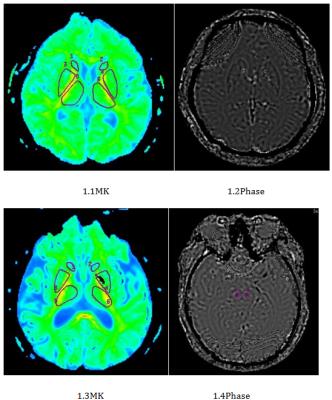
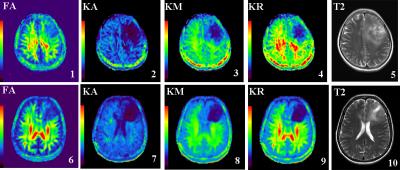 |
The diffusion kurtosis imaging findings of preoperative glioma-related epilepsy
Ankang GAO, Jingliang Cheng, Jie Bai, Yong Zhang, Shujian Li, Zanxia Zhang, Yijie Zhang, Xiao Cheng, Shaoyu Wang
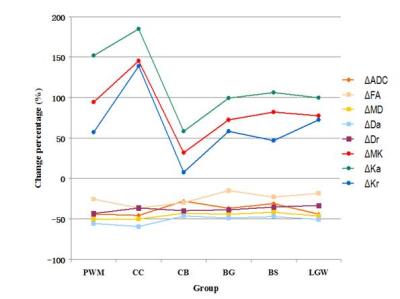
MK not only reflects the microstructure of the glioma, but also may reflect neurotransmitter metabolism microenvironment.
|
|
1861. 
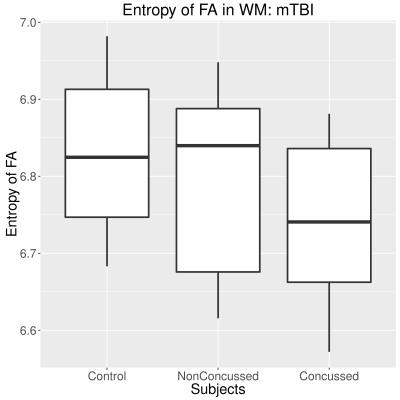 |
Diffusion Entropy of Fractional Anisotropy Values in White Matter in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
Alexander Weber, Michael Jarrett, Shiroy Dadachanji, David Li, Jack Taunton, Alexander Rauscher
A paper in Radiology by Delic et al. in 2016 looked at the Shannon entropy of fractional anisotropy values in white matter in the brains of people with mTBI and controls, and found significant differences between the two. We attempted to replicate their findings with retrospective mTBI data of our own. We did not find any significant differences with controls, and ice hockey athletes concussed after two weeks. We also did not find any changes in concussed athletes comparing data before injury with data after 3 days, 2 weeks, and 2 months.
|
|
1862. 
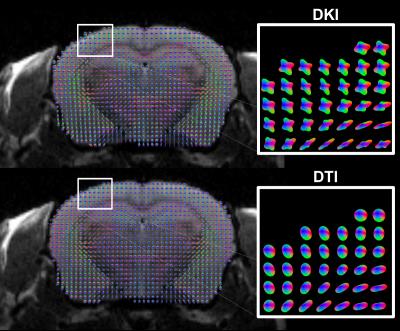 |
Exploring Cortical Fiber Crossings in Mice using Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging
Emilie McKinnon, Jens Jensen, G Glenn, Andy Shih, Joseph Helpern
The ability of diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) to detect multiple intravoxel fiber directions in vivo is demonstrated for mouse cortex, with two or more directions being detected in the majority of voxels. The distribution of angular differences between the different fiber directions for individual voxels peaked at near 90o, suggestive of a grid-like pattern of neurites. Our findings support the feasibility of DKI-based tractography in mouse cortex.
|
|
1863. 
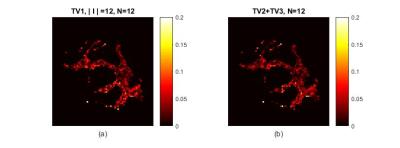 |
A Study on Total-Variation Regularization for Model-Based Reconstruction in DTI
Kazem Hashemizadeh, Samer Merchant, Dong Liang, Rong-Rong Chen, Edward Dibella, Edward Hsu, Leslie Ying
In this work, we study total-variation (TV) regularization for model-based reconstruction from undersampled DTI data. Various TV regularization methods are examined. Using ex-vivo brain DTI data, we show that imposing TV constraints on DWI provide more reliable quantitative estimates of diffusion than those imposing TV constraints directly on the tensor. A gradient descent algorithm with line backtracking is used for better convergence to optimal solution. For highly undersampled data of 12 diffusion encoding directions and a reduction factor of R=4, we show that good estimates of primary eigen-vector, fractional anisotropy, and mean diffusivity can still be obtained using TV-based regularization.
|
|
1864.
 |
Repeatability of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters at 3.0 Tesla in orbital masses.
Augustin Lecler, Julien Savatovsky, Laure Fournier
- IVIM technique is feasible in the orbit with a good to acceptable repeatability of ADC and D. (coefficient of variation range 12%-25%) - Interobserver repeatability agreement is excellent for all the IVIM parameters in the orbit. (intraclass correlation coefficient range 90-95%) - The use of PF or D* as biomarkers should be cautious because of high test-retest and interobserver variabilities.
|
|
1865. 
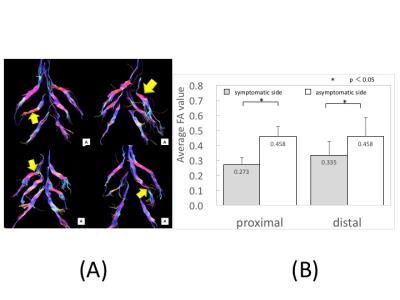 |
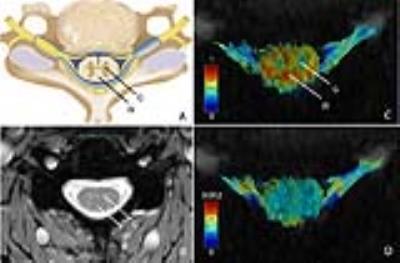
Functional Assessment of Lumbar Nerve Roots Using Direct Coronal Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo Diffusion Tensor Imaging - Application to Patients with Bilateral Spinal Canal Stenosis Showing Unilateral Neurological Symptom -
Takayuki Sakai, Masami Yoneyama, Yasuchika Aoki, Toshiaki Miyati, Noriyuki Yanagawa
Clinically, there are some patients with spinal canal stenosis who have unilateral neurological symptom despite the existence of bilateral nerve compression on the conventional MRI images. The purpose of this study was to investigate the availability of TSE-DTI for patients with bilateral spinal canal stenosis who have unilateral neurological symptom. At the level responsible for symptom, the average FA values of symptomatic side were significantly lower than those of asymptomatic side. FA values of TSE-DTI might be helpful in identification of responsible lumbar nerves roots for patients with bilateral spinal canal stenosis who have unilateral neurological symptom.
|
|
1866.
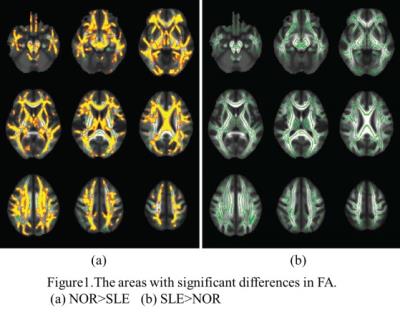 |
Investigation of Diffusion Tensor Indices by TBSS analysis and of Patients with symptoms of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus
YUNG CHIEH CHANG, YA PING CHEN, NI JUNG CHANG, KAO LUN WANG, CLAYTON CHI CHANG CHEN, JYH WEN CHAI
In this project, we attempted to study the NPSLE subjects without abnormal lesion in conventional MR imaging in order to investigate the effective imaging biomarkers in early detection of neurological degeneration. Brain diffusion-tensor imaging with TBSS analysis was performed for studying the micro-structural alternations in NPSLE patients. The preliminary results illustrated statistically significant differences of FA and MD in some important nerve tracts between NPSLE patients and normal volunteers. There also existed a significant difference between NPSLE patients with and without depression.
|
|
1867.
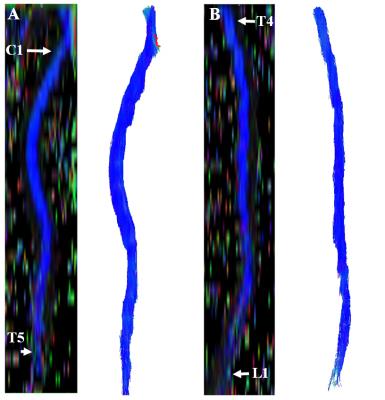 |
Age Related Diffusion and Tractography Changes in Typically Developing Pediatric Cervical and Thoracic Spinal Cord
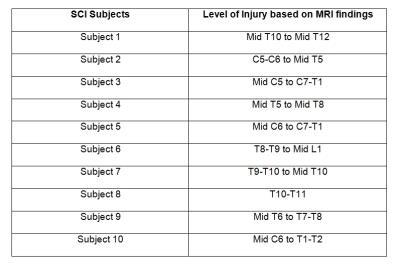
Mahdi Alizadeh, Yusra Sultan, Sona Saksena, Chris Conklin, Devon Middleton, Joshua Fisher, Laura Krisa, Scott Faro, MJ Mulcahey, Feroze Mohamed
This study investigates age related changes in diffusion tensor imaging and tractography parameters in pediatric spinal cord. This will help to understand maturation process in pediatric population and consequently will help for detection of diseased or injured spinal cord.
|
|
1868.
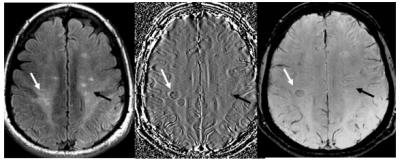 |
Observing the evolution of MS plaques using SWI and DCS-PWI
Liang Han, Lemei Tang, Weiwei Wang, Qingwei Song, Ailian Liu, Yanwei Miao, Bing Wu
In this study,we aim to study the morphologic and micro-hemodynamic changes of MS plaques using SWI and DSC-PWI. We selected twenty-one MS patients diagnosed by the McDonald criteria (Revised Edition 2010) underwent MR scans including SWI and dynamical susceptibility contrasted MR perfusion weighted imaging (DSC-PWI) at baseline. Then Results were obtained by follow-up and scan. The MS plaques shows decreased phase value and blood perfusion. The characteristic of MS plaque is hypointense foci with small veins and only “abnormal vessels” region predict early changes.
|
|
1869.
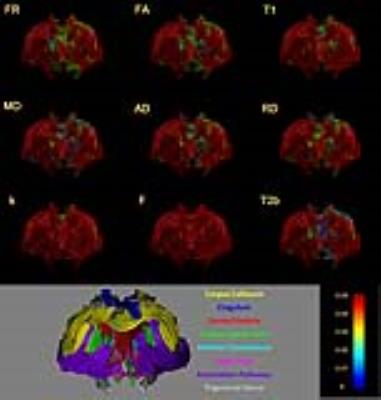 |
The influence of rat strain on multi-parametric white matter metrics – a Tractometry study
Daniel Barazany, Debbie Anaby, Derek Jones
White matter macrostructural organization and its microstructural composition are two complementary features that may help understand intact brain development, function and brain impairment. The Tractometry framework, which aims to characterise white matter by multi parametric MR metrics, was applied on 3 rat strains (Wistar, SD and Lewis). In this study we examined the impact of rat strain on microstructural features of white matter in the brain, which is suspected to origin from their genetics background.
|
|
1870.
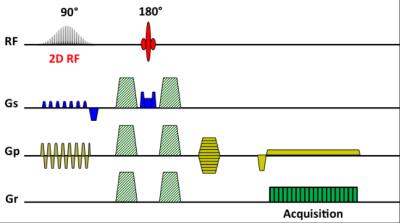 |
Targeted-FOV DWI can better depict the microemboli-induced renal lesions comparing to conventional full-FOV DWI
Chengyan Wang, Li Jiang, Hanjing Kong, Fei Gao, Wenjian Huang, Rui Wang, Lian Ding, Yan Jia, Hui Xu, He Wang, Xiaodong Zhang, Li Yang, Jue Zhang, Xiaoying Wang, Jing Fang
DWI suffers from problems of severe geometric distortion and artifacts due to the susceptibility gradients and long echo train length (ETL), and the spatial resolution is quite limited due to the single-shot EPI acquisition scheme. This study investigates the utility of a targeted-FOV (TFOV) DWI technique in characterizing acute renal injure caused by microemboli injection in animal models. Compared with full-FOV DWI, the TFOV DW images show apparently higher image quality and better depiction of renal lesions. The advantage of TFOV DWI technique in characterizing microemboli-induced acute renal injure in is quite obvious.
|
|
1871. 
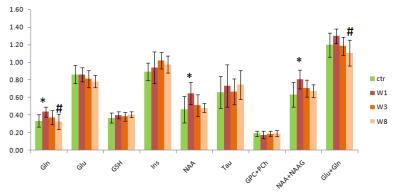 |
Diffusion MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveal microstructural and functional alteration in chronic mild stress exposed rat brains: A CMS recovery study
Ahmad Khan, Brian Hansen, Ove Wiborg, Christopher Kroenke, Sune Jespersen
Chronic mild stress (CMS) exposure leads to depression and other psychiatric disorder. Temporal changes post CMS exposure is still unclear. Present study employed CMS exposure on rats and utilised in-vivo longitudinal diffusion MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to reveal microstructural and functional alterations up to eight weeks post CMS exposure. Advanced diffusion kurtosis metrics have revealed significant alteration in stress sensitive regions, such as amygdala, hippocampus, prefrontal cortex and caudate putamen. MRS also showed significant metabolic alteration in ventral hippocampus, particularly on week1 post CMS exposure. Present finding could be useful in treatment of depression or similar disorders.
|
|
1872.
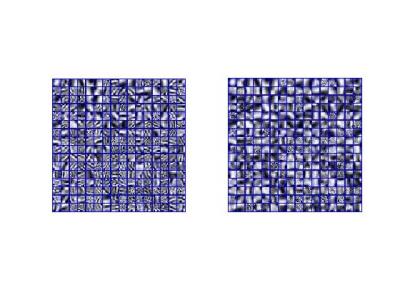 |
Diffusion-weighted images super resolution via external and internal patch-based regularization
ying fu, xi wu, yangzhi peng, jiliu zhou
Super-resolution (SR) of diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) data is an ill-posed problem, which can be regularized by exploiting diverse priors learned from image patches. In this work, based on patch-based strategy of SR, we propose a new regularization method to reconstruct DW images, which integrates the sparse representation prior with dictionary learned from external image patches and non-local self-similarity prior learned from internal image patches. Meanwhile, in dictionary learning part, nonparametric Bayesian method is adopted to infer dictionary learning variables such as the size of the dictionary from data automatically. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms current methods in DWI reconstruction.
|
|
1874.
|
Changes of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) diffusion-weighted imaging based parameters in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) creation – An initial analysis
Claus Pieper, Alois Sprinkart, Daniel Thomas, Carsten Meyer, Wolfgang Block, Hans Schild, Guido Kukuk, Petra Mürtz
The creation of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) influences hepatic blood flow dynamics. TIPS-related changes of diffusion-weighted imaging based intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) parameters at 1.5 T were investigated in liver parenchyma of cirrhotic patients. An increase of the IVIM perfusion fraction was found, indicating improved microvascular flow within the liver tissue after decompression of the portal vein. Diffusion parameters were not significantly influenced by TIPS-creation.
|
|
1875.
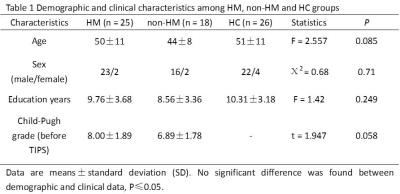 |
White matter abnormalities of brain and cervical spinal cord in Hepatic Myelopathy patients: a diffusion tensor imaging study
Liu-Xian Wang, Lin Liu, Kang Liu, Ning-Bo Fei, Long-Biao Cui, Yi-Bin Xi, Ting-Ting Liu, Wei Qin, Hong Yin
The prominent syndrome of HM such as spastic paraparesis is usually considered resulting from abnormal function of thoracic segments, nevertheless, the involvement of intracranial fibers and cervical spinal cord is not clear. In this study, we found a widespread and robust white matter tract abnormality in brain of HM and non-HM patients, without significant difference with cervical spinal cord. Our finding may help shedding light on the underlying pathological mechanism of HM.
|
|
1876.
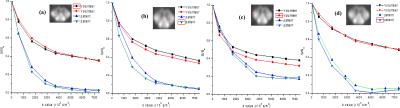 |
Signal behavior of Ultra-High-b radial DWI (UHb-rDWI) signal in different tract of the cervical spinal cord
Bijaya Thapa, Nabraj Sapkota, YouJung Lee, EunJu Kim, John Rose, Lubdha Shah, Eun-Kee Jeong
The ultrahigh-b radial DWI (UHb-rDWI) technique is used to study the white matter disease in the spinal cord. The diffusion signal from the extra axonal (EA) space drops to noise level while that from the intra axonal (IA) space is almost constant at UHb region for the myelinated axons where the myelin layers prohibit the exchange of water molecules between IA and EA spaces. However for partially or unmyelinated axons, the diffusion signal from IA space is no longer constant. The signal behavior at UHb region could be used as a biomarker for the demyelination and axonal loss.
|
|