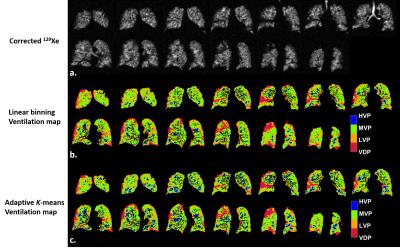
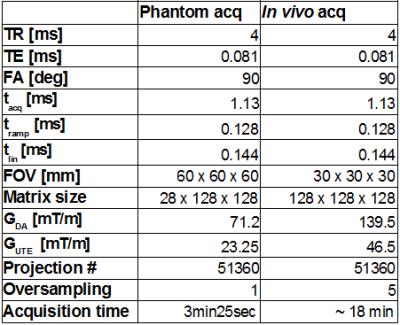
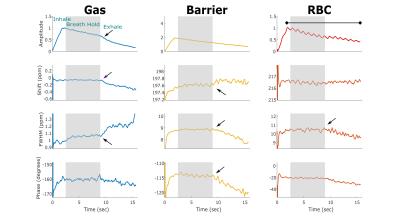
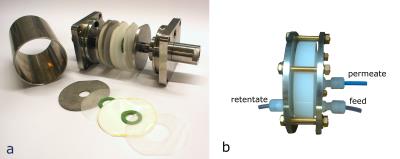
Hepatopancreaticobiliary
Traditional Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Wednesday, 26 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
08:15 - 10:15 |
|
1990. 
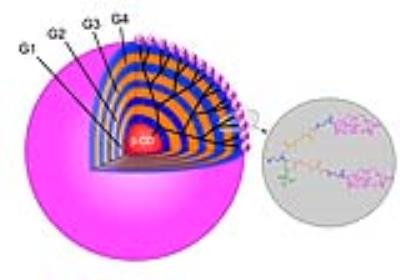 |
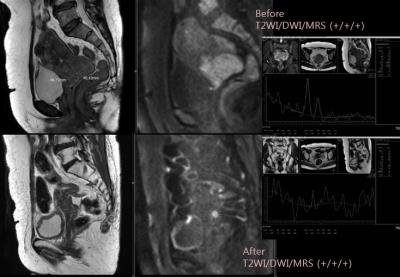
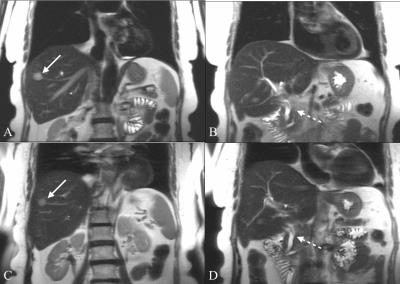
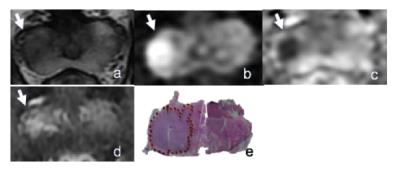
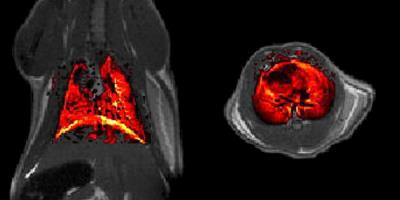
A biodegradable macromolecular MRI contrast agent for enhanced liver metastasis
Xiaoxuan Zhou, Hongjie Hu, Yue Qian, Yuxin Han, Mingzhou Ye, Jianbin Tang, Peipei Pang, Jun Yang
Tumor metastasis accounts for the related mortality, and precise diagnostic imaging of distant metastasis plays a significant role in clinical administration and treatment plan. Enhanced MRI with small-molecule contrast agent (CA) is a favorite imaging modality. However, small-molecule CA has some unsatisfied flaws such as short blood circulation time, low relaxivity and non-specificity. In this study, we synthesized a macromolecular CA with high relaxivity and long blood circulation time, and assessed early liver metastasis with enhanced MRI using this macromolecular CA.
|
|
1991. 
 |
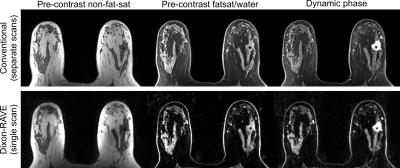
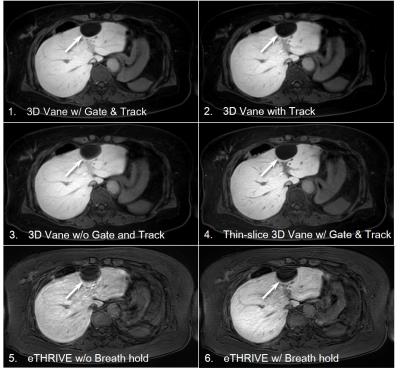
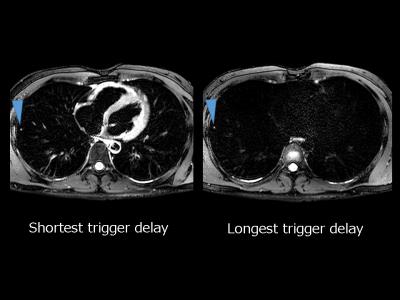
3D contrast enhanced high definition, free-breathing Dixon imaging using radial stack of stars and respiratory gating and tracking: Clinical comparison to state of the art breath hold Dixon imaging
Gabriele Beck, Michael Wyss, Rene Patzwahl, Joachim Hohmann, Christoph Andreas Binkert, Lars van Loon, Hans Peeters
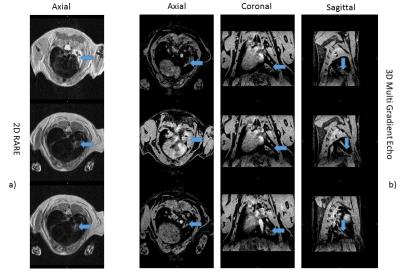
We investigated a motion immune Dixon TFE approach incorporating a 3D radial stack-of-stars acquisition module interleaved with a spiral excitation navigator to gate and track the acquisition. Image quality, sharpness and streaking artifact level and its variability over different patient breathing patterns is efficiently improved to an extent where it is preferred over the state-of-the art breath hold (BH) Dixon scans. Next to that, it allowed scan time reductions of 30% in average. This technique provides motion-free, high resolution hepatic imaging with the benefits of Dixon providing consistent good fat suppression over a large FOV with water, fat, IP and OP diagnostic information all-in-one scan.
|
|
1992.
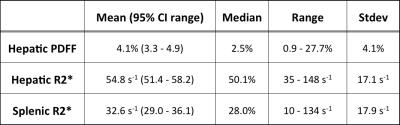 |
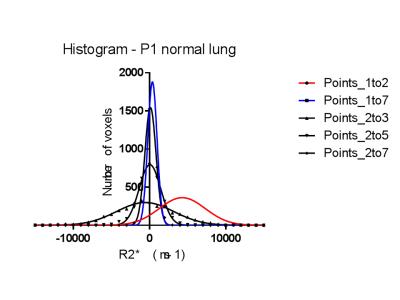
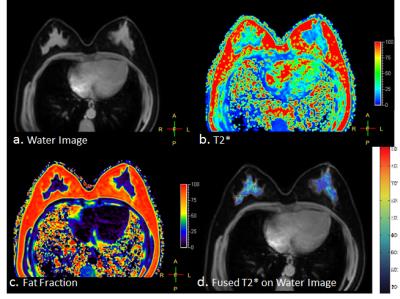
Quantification of Hepatic Fat Fraction and Liver/Spleen R2* in a Healthy Cohort at 3 Tesla
Rosalind Gerson, Chris Bowen, Manjari Murthy, Sharon Clarke
Non-invasive quantification of hepatic fat and iron with MRI has generated increasing clinical interest, particularly given the prevalence of chronic liver disease. Elevated R2* is a biomarker of iron deposition in the liver and spleen. The normative distribution of R2* in these organs at 3T is not well described, but is necessary for confident diagnosis of mild to moderate levels of iron deposition. Based on measurements in 97 adults selected from the general population, we confirm that ~20% have fatty liver and suggest that a hepatic R2* > 89 s-1 and splenic R2* > 69 s-1 can be considered abnormal.
|
|
2009.
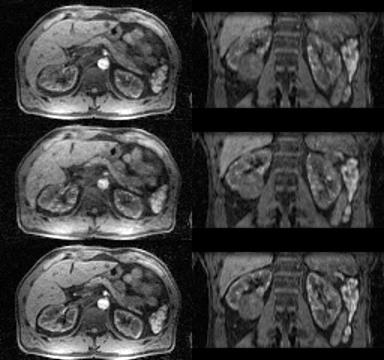 |
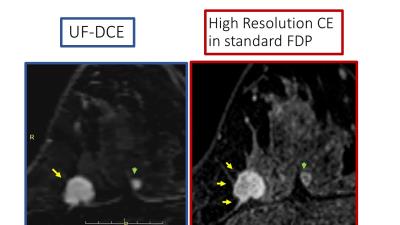
GRASP with Motion Compensation for DCE-MRI of the Abdomen
Koji Fujimoto, Li Feng, Rocardo Otazo, Kai Block, Henry Rusinek, Nicole Wake, Hersh Chandarana
A method to combine information of respiratory states with a non-rigid motion model is proposed to reconstruct motion-compensated 4D images of dynamic-contrast enhanced MRI with high temporal resolution. Abdominal DCE-GRASP MRI was reconstructed by grouping 4 consecutive spokes as one dynamic frame (0.6sec/frame). Respiratory motion was obtained from central k-space data (as in XD-GRASP). A temporal TV constraint was applied separately for each respiratory state. By using an optical-flow algorithm, four sets of motion vectors were obtained. Motion-compensated GRASP reconstruction was performed by including the motion vectors and showed improved image quality and reduced motion blurring.
|
|
1994.
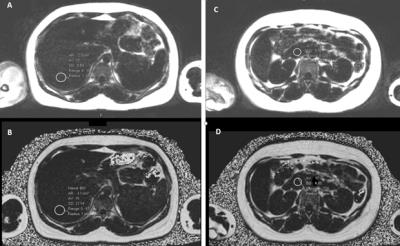 |
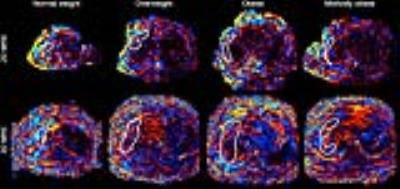
Correlation between incidental fat deposition in the liver and pancreas in asymptomatic patients
Mounes Aliyari Ghasabeh, Manijeh Zarghampour, Li pan, Pegah Khoshpouri, Farnaz Najmi Varzaneh, Nannan Shao, Ankur Pandy, Pallavi Pandy, Danial Fouladi, Ihab R Kamel
Liver steatosis is the most common parenchymal liver disease in Western Countries and it may progress to steatohepatis, fibrosis and cirrhosis. Also, fat deposition in liver and pancreas can cause diabetes by increasing resistance to insulin. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) has been shown to strongly correlate with histology in liver fat quantification. However, MRS has some limitations such as breathing artifact and difficulties in avoiding vessels or bile ducts within the voxel. So, it is desirable to utilize a novel and robust imaging technique that can screen for the presence of fat in the liver and pancreas.
|
|
1999. 
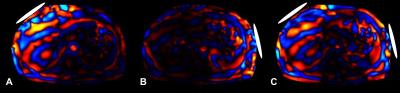 |
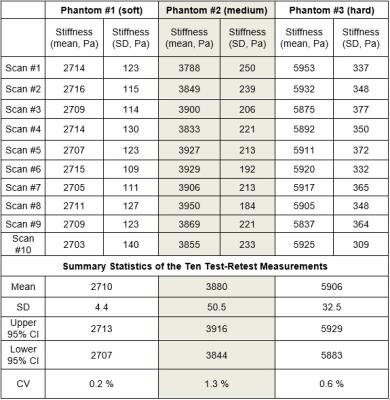
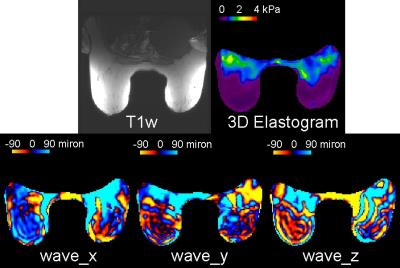
Simultaneous liver and spleen 2D MRE and 3D MRE acquisitions: Preliminary results
Paul Kennedy , Kevin Glaser, Curtis Johnson, Bradley Bolster Jr. , Jalpan Jani, Kashif Khokhar, Richard Ehman, Bachir Taouli
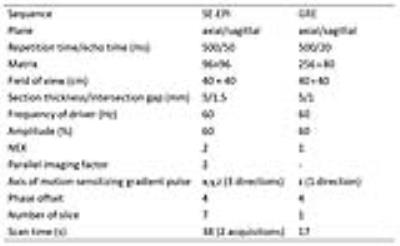
We present initial results of 2D MR elastography (MRE) and 3D MRE acquired in liver and spleen using a dual driver configuration in 13 subjects, 5 healthy and 8 with liver disease. 2D MRE showed a trend to higher stiffness in healthy subjects however in cirrhotic subjects liver stiffness was generally higher with 3D MRE. 3D MRE showed significantly higher liver stiffness in cirrhotic subjects compared to healthy subjects, with spleen stiffness also increased but not reaching significance. Coefficient of variation with single and dual drivers was 5% for liver and spleen in 2D and 3D MRE.
|
|
1995. 
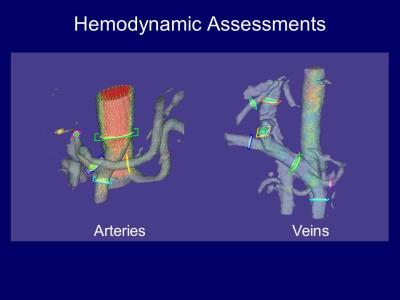 |
Hemodynamic Assessments of Hepatic Vasculatures using 4D-PCA and MRFD
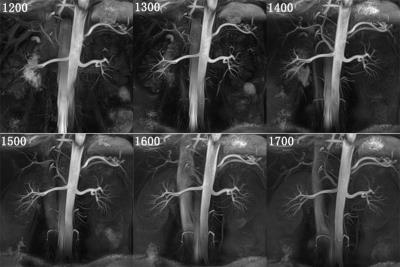
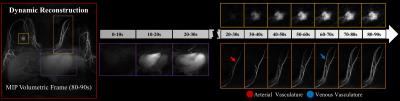
Takeshi Yoshikawa, Yoshiharu Ohno, Katsusuke Kyotani, Kouya Nishiyama, Shinichiro Seki, Yuji Kishida
We introduced new assessment method of liver hemodynamics using 4D-PCA and new flow analytic technique including wall shear stresses. We found 4D-PCA and MRFD enables detailed hemodynamic assessment and has the potential to be used for liver disease assessments.
|
|
1996. 
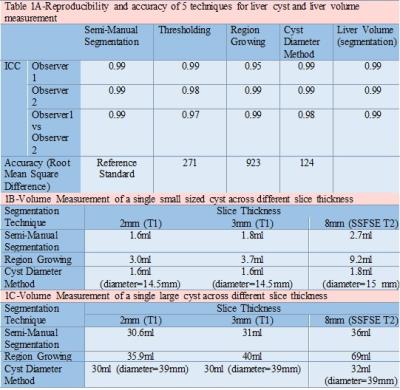 |
MRI of Liver Cysts in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Effect of Genotype
Zerwa Farooq, Ashkan Heshmatzadeh Behzadi, Jon Blumenfeld, Martin Prince
ADPKD patients (n=25) undergoing abdominal MRI were analyzed 2 times each by 2 separate reviewers using a) thresholding; b) region growing c) cyst diameter d) semi-manual segmentation to determine liver cyst volume. Using the most reproducible technique, 75 additional ADPKD patients were studied correlating their liver parameters with genotype, gender and age. Semi-manual segmentation was the best technique for measuring cyst volume with intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.99. PKD1 mutation was found to be associated with higher total liver volume and liver cyst volume across different age groups and gender compared to PKD2 mutation, suggesting greater hepatic involvement with PKD1.
|
|
1997.
 |
Feasibility and grading performance of Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping for Hepatic Iron quantification
Huimin Lin, Hongjiang Wei, Xu Yan, Caixia Fu, Stephan Kannengiesse, Chunlei Liu, Fuhua Yan
This study aimed to evaluate the performance of Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) on estimating and grading the liver iron concentration (LIC), using Ferriscan-R2 values as reference. Thirty-three patients suspected of hepatic iron overload were included in this study. The results showed a significant positive correlation between QSM and Ferriscan-based LIC (r=0.924). ROC analysis revealed that QSM could accurately grade LIC for low and moderate iron overload patients, indicating that high-quality QSM maps may allow to reliably estimate and grade iron deposition in the liver.
|
|
1998. 
 |
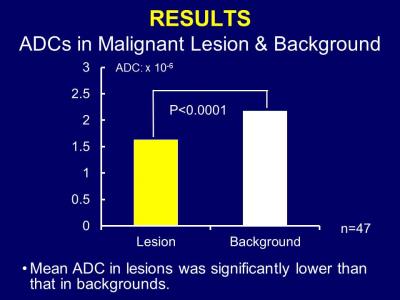
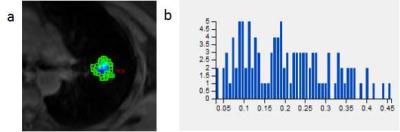
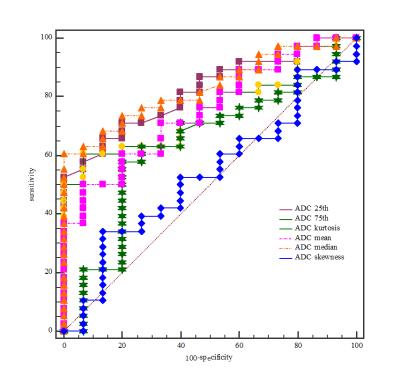
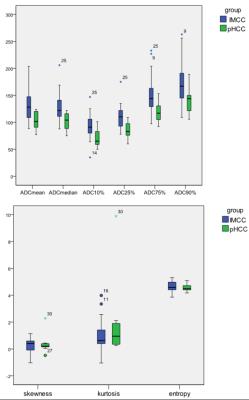
Characterization of Primary Liver Cancers with DWI Histogram Analysis
Sara Lewis, Steven Peti, Stefanie Hectors, Michael King, Juan Putra, Swan Thung, Bachir Taouli
ADC measurement using DWI have shown promise for characterizing focal liver lesions. In this study, we assessed the ability of advanced ADC histogram parameters to distinguish the histological diagnosis and the grade of primary malignant liver cancers. We found that both ADC mean and ADC percentiles could distinguish between tumor types; ADC percentiles were also predictive of tumor grade for HCC and ICC. Advanced ADC histogram analysis may be useful for accurate tumor diagnosis and prediction of tumor grade.
|
|
2000.
 |
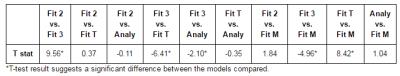
Liver quantification with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for evaluation in hepatic function and staging of post-hepatitic liver cirrhosis
Zhang Lan
To evaluate the value of DCE-MR for hepatic reserve function assessment and staging in post-hepatitic liver cirrhosis (PHLC). 10 patients with compensatory PHLC, 10 with decompensatory PHLC and 10 healthy volunteers were performed DCE-MRI scanning. All data were calculated by Extended Tofts model fitting with pharmacokinetic curve and the permeability and perfusion parameters were measured in quantification. The new method validated the feasibility of using quantitative parameters of DCE-MRI with pharmacokinetic model to assess liver cirrhosis. In conclusion, DCE-MRI quantitative parameters can be used for diagnosing and staging liver cirrhosis.
|
|
1993. 
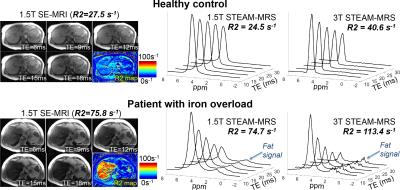 |
Spectroscopy-Based R2 Relaxometry for Liver Iron Quantification at 1.5T and 3.0T
Diego Hernando, Changqing Wang, Ryan Mattison, Takeshi Yokoo, Scott Reeder
R2-based techniques for liver iron quantification using Spin-Echo (SE) imaging require long acquisitions. In contrast, single-voxel Stimulated-Echo Acquisition Mode (STEAM)-MR spectroscopy enables liver R2 measurements in a single breath-hold. However, the accuracy and field strength dependence of STEAM-MRS R2 quantification are unknown. This study evaluated the accuracy and field strength dependence of STEAM-MRS for R2 quantification in healthy controls and patients with liver iron overload. At 1.5T, STEAM-MRS R2 was in close agreement with SE-MRI-based R2. Further, STEAM-MRS R2 measurements were highly correlated across field strengths. Finally, STEAM-MRS R2 measurements at 1.5T and 3.0T were calibrated to liver iron concentration.
|
|
2001.
 |
Assessment of the Hepatocyte Fraction for Estimation of Liver Function Based on a Simple Pharmacokinetic Model
Ruo-kun Li, Fu-hua Yan, Jin-wei Qiang, Hui-min Lin, Weibo Chen, Tomoyuki Okuaki, Eunju Kim
There were 16 consecutive patients (12 men, 5 women; mean age, 45.7 years; range, 33–65 years). Imaging was performed on clinical 3T scanner (Philips Ingenia) using 32ch body/cardiac coil. A hepatocyte fraction (HF) map and K map were derived. The HF and K values for Gd-EOB-DTPA were correlated with Child-Pugh scores. Patients with Child-Pugh class B disease showed significantly lower liver FA value and K value. HF value and K value were positively correlated with the Child–Pugh scores (r=0.752 to 0.855, p<0.05). HF value and K value had the largest AUC of 0.975 and 0.78 for distinguishing the Child–Pugh class A of cirrhosis from class B. K value had the most area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.99 for identifying the presence of liver cirrhosis.The study suggested that hepatocyte fraction and hepatic uptake derived from Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI can quantify liver function.
|
|
2003.
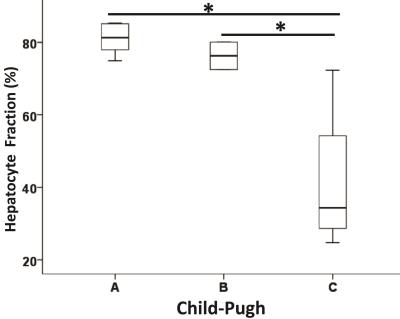 |
Quantitative Assessment of Hepatic function with Hepatocyte Fraction
Mengqi He, Yingjie Mei, Jing Zhang, Zeyu Zheng, Hongxiang Li, Tomoyuki Okuaki, Eunju Kim, Yikai Xu
Gadoxetic acid has been shown to evaluate liver function as it is known to be actively taken up by hepatocytes via organic anion transporters (OATPs). The measurement of hepatic parenchymal enhancement during the hepatobiliary phase (HBP) may accurately reflect liver function. This study evaluated the liver function of the subject in the Child-Pugh classification method which is still the most commonly applied method for evaluating liver function in clinical. The hepatocyte fractions were significantly different among groups classified according to Child–Pugh scores between A and C, B and C. The hepatocyte fraction could be considered as a promising method for the quantitative assessment of liver function.
|
|
2020. 
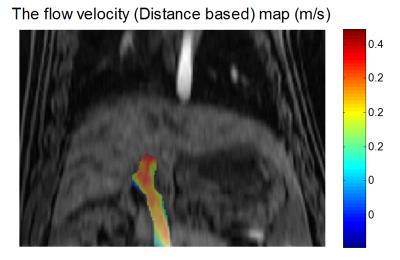 |
Vascular Input Function Correction with Inflow Relative Enhancement Quantification in Liver DCE-MRI
Jia Ning, Tilman Schubert, Huijun Chen, Chun Yuan, Scott Reeder
Dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) with pharmacokinetic modeling can help to quantify the perfusion and function of liver. The accurate pharmacokinetic modeling relies on the accurately and reliably captured vascular input function (VIF)s. However, due to the fast blood velocity, the blood in the large vessels including abdominal aorta and the main branch of the portal vein experiences only a limited number of excitations and hasn’t reached a steady state. This introduces bias in the VIFs, and consecutively bias in pharmacokinetic parameters. In this study, we sought to correct the inflow effect on VIF acquisition in liver DCE-MRI.
|
|
2004.
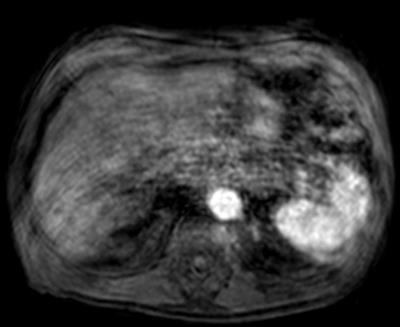 |
Assessment of interrater agreement and reliability for characterization of respiratory motion related artifacts at gadoxetate disodium-enhanced liver MRI
Kristina Ringe, Julian Luetkens, Rolf Fimmers, Renate Hammerstingl, Guenter Layer, Martin Maurer, Claas Naehle, Sabine Michalik, Peter Reimer, Christina Schraml, Andreas Schreyer, Patrick Stumpp, Thomas Vogl, Frank Wacker, Winfried Willinek, Guido Kukuk
In this prospective multicenter study, interrater agreement and reliability for characterization and grading of respiratory motion artifacts related to the injection of gadoxetate disodium were evaluated. Interrater agreement and reliability for scoring of motion artifacts in the arterial phase was excellent among experienced abdominal radiologists from different European tertiary referral centers with an intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.983 and 0.985, respectively. Characterization and grading of respiratory motion artifacts can thus be performed with a high level of confidence, which is a prerequisite for assessing the incidence of this phenomenon in larger multicenter studies.
|
|
2005.
 |
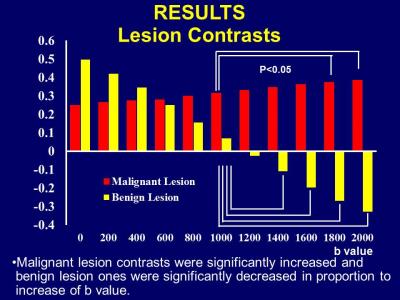
The predictive value of diffusion-weighted imaging on radiation-induced liver injury of hepatic malignancies
Xiaohong Ma, Shuang Wang, Yongjian Zhu, Han Ouyang, Chunwu Zhou, Xinming Zhao
Radiation-induced liver injury (RILI) is one of the most dreaded complications of radiation therapy (RT),which prevents radiation dose escalation and limits the effectiveness of the treatment . Therefore, it was important to predict and evaluate the RILI on hepatic malignancy using the RT in the early term. In this study, the ADCmid-RT value was significantly highest, and had negative correlation with the radiation dose. As the ADCmid-RT value was less than 1.29 x10-3mm2/s, the RILI could possibly occur. Therefore, the ADCmid-RT value may serve as a biomarker for predicting RILI in patients with hepatic malignancies treated with RT.
|
|
2018. 
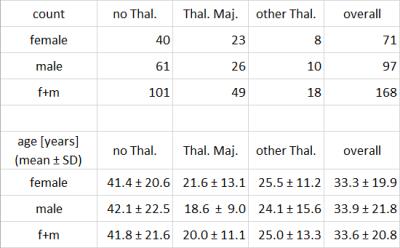 |
Liver Iron Concentration determined with Gradient Echo MRI by Signal Intensity Ratio: Effects of Patient Characteristics
Arthur Wunderlich, Holger Cario, Isabelle Tomczak, Meinrad Beer, Stefan Schmidt
To investigate the relation between signal intensity ratios gained from gradient echo (GRE) MRI and liver iron concentration (LIC), we studied the influence of patient characteristics. 168 patients (71 f, 97 m; 49 with Thalassemia major, 101 without Thalassemia) suspected for liver iron overload were scanned according to Ferriscan® with spin echo MRI to obtain reference LIC values, and GRE protocols suitable for LIC determination. GRE analysis by manually drawn liver and muscle ROIs yielded liver-to-muscle signal intensity ratios (SIR). Correlation analysis of ln (SIR) to reference LIC revealed differences between patient subgroups concerning disease, gender and age.
|
|
2007.
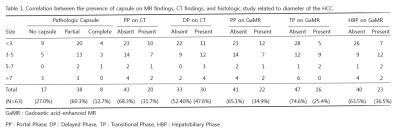 |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Capsule Appearance in Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR Images : Correlation with Dynamic CT and Pathologic Fibrous Capsule
Jei Hee Lee, Bohyun Kim, Young Bae Kim
For visualization of capsule appearance on HCC, GaMR is comparable with dynamic CT. And pathologic fibrous capsule can be seen as hypointense rim in HBP. Lower visualization of capsule appearance in TP on GaMR seem to be parenchymal enhancement during the transitional phases. Hyperintensity rim in T2 weighted images with hopointense rim on HBP shows disruption of fibrous capsule with extension of tumor cells across the fibrous capsule in pathology. Hypointense rim on the HBP in the 2014 version of LI-RADS should not be considered as capsule appearance, and further study is also needed.
|
|
2010.
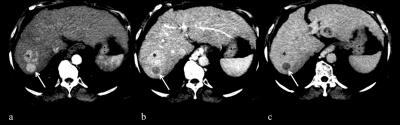 |
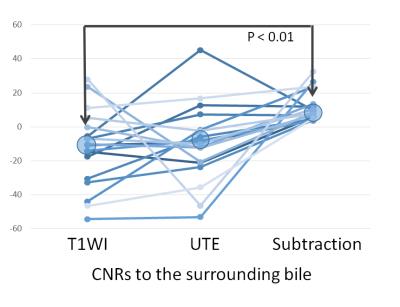
HCC detection in pre-transplant patients: A comparative retrospective study between multiphasic CT, gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI and extracellular gadolinium based contrast-enhanced MRI
Sahar Semaan, Christopher Song, Sara Lewis, Manjil Chatterji, M. Isabel Fiel, Cecilia Besa, Bachir Taouli
In this study, we present preliminary data comparing the diagnostic performance of multiphasic contrast-enhanced CT with contrast enhanced MRI using a liver specific gadolinium based contrast agent (GBCA), gadoxetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA) and extracellular (EC) GBCAs, using explant pathologic data as the reference. We also assessed the added value of delayed hepatobiliary phase (HBP) imaging and DWI in HCC detection. Our data suggests that CT and MRI have similar overall sensitivities for HCC detection and that the addition of DWI and HBP improved HCC detection when using Gd-EOB-DTPA.
|
|
2011. 
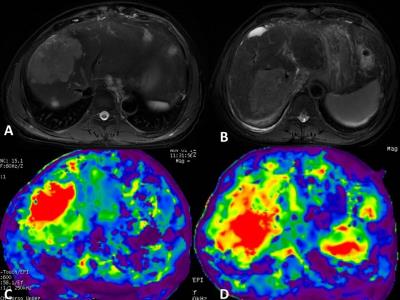 |
The value of magnetic resonance elastography in differential diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
kan liu, qi zhang, hong mei zhang, han ouyang, xinming zhao
To determine the value of MRE in the differential diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with 3.0-T MR scanner . The MRE were performed in 36 patients(26 hepatocellular carcinomas and 11 intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas) by using 60-Hz mechanical waves and Spin echo echo planar sequence.Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas had significantly greater mean shear stiffness than hepatocellular carcinoma (9.08 ±2.13kPa vs 6.54 ±1.84kPa). They have statistically significant differences(p<0.01).MRE can help the differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
|
|
2012.
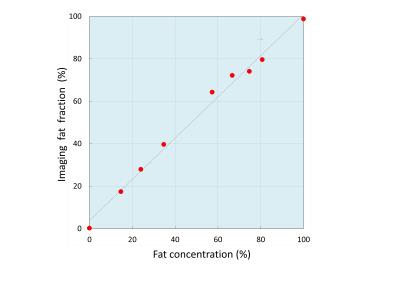 |
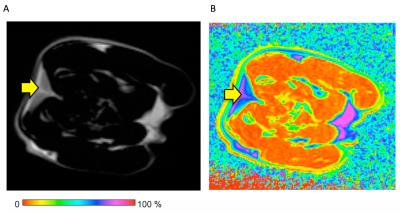
Hepatic fat quantification using automated six-point Dixon methods: comparison with conventional chemical shift based gradient-echo sequences and computed tomography.
Tomohiro Namimoto, Masataka Nakagawa, Kie Shimizu, Takeshi Nakaura, Kosuke Morita, Yasuyuki Yamashita
To compare automated six-point-Dixon(6-p-Dixon) with dual-echo GRE chemical shift imaging(CSI) for quantification of hepatic fat fraction(FF) with CT. In a phantom study, various FF vials were performed to validate the accuracy. In clinical study, fifty-nine patients were examined both 3.0T MRI and CT. Quantitative measurements were calculated SI-index of CSI and imaging-FF of 3D-6-p-Dixon. In phantom study, linear regression between FF and imaging-FF/SI-index showed good agreement(imaging-FF R2=0.992:0-100%FF;SI-index R2=0.978:0-34.7%FF). In clinical study, linear regression between imaging-FF and SI-index showed good agreement(R2=0.890). CT attenuation value was strongly correlated with imaging-FF(R2=0.852) and SI-index(R2=0.812). Imaging-FF of 6-p-Dixon has potential for automated hepatic fat quantification.
|
|
2013. 
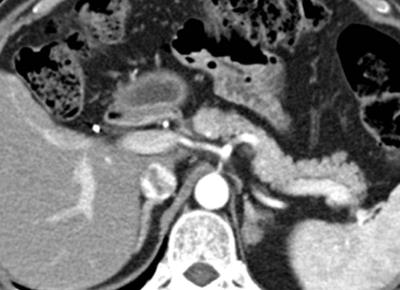 |
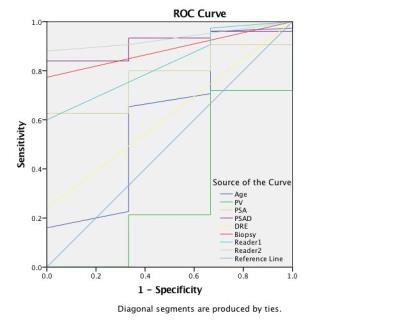
Value of Noncontrast MR Imaging with Diffusion-weighted Imaging for Detection of Primary Small (= 20mm) Solid Pancreatic Tumors and Prediction of Pancreas Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Hyun Jeong Park, Kyung Mi Jang
With recent advances of MRI in abdominal imaging, improved performances on T2-weighted image and diffusion- weighted imaging (DWI) are achieved for pancreatic tumors. We hypothesized that diagnostic performance for detection of primary solid tumors of pancreas on noncontrast MRI with DWI could be sufficiently high and noncontrast MRI with DWI would be useful for pancreas screening. We conducted this study to determine the diagnostic performance of noncontrast MRI with DWI for detection of primary small (≤20mm) pancreatic solid tumors and prediction of ductal adenocarcinoma in comparison with pancreas CT and pancreas MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography.
|
|
2006. 
 |
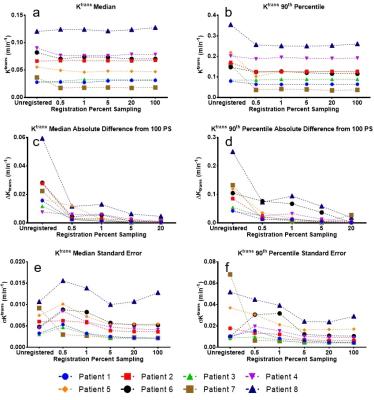
Inter- and intra-reviewer agreement of region-of-interest-based quantification of liver R2* in patients with iron overload
Camilo Campo, Diego Hernando, Tilman Schubert, Andrew Van Pay, Scott Reeder
This study evaluated the inter- and intra-reviewer agreement of different region-of-interest (ROI) sampling methods for the quantification of liver R2* (1/T2*) in patients with iron overload. 37 MRI datasets from patients suspected of having liver iron overload were retrospectively analyzed using ROI sampling methods that have been previously reported. Our results demonstrate that the inter- and intra-reviewer agreement of liver R2* quantification improve when using ROIs that are large in size and number. We conclude that researchers and clinicians should strive to sample as much area of the liver by using multiple large ROIs.
|
|
2014.
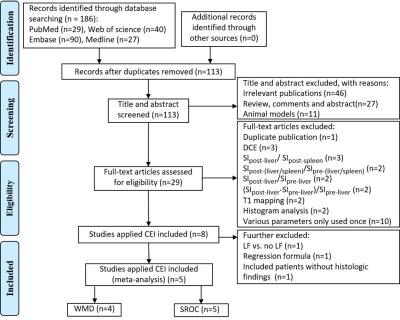 |
Gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis
Yuelang Zhang, Xiang Li, Haitian Liu, Chenxia Li, Jian Yang
To collect and summarize parameters used by gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging (GD-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI) for staging of liver fibrosis (LF) and evaluate diagnostic performance. A systematic literature search was performed in PubMed, Web of science, Embase and Medline database. Studies used frequently-used parameter were included. Pooled weighted mean difference (WMD) was applied to determine the clinical significance. Pooled sensitivity, specificity, and summary receiver operating characteristics (SROC) curve were calculated to evaluate diagnostic performance. Finally, 5 studies were included, and contrast enhancement index (CEI) was the most frequently-used parameter, which was considered to be an efficient biomarker in the staging of LF.
|
|
2015.
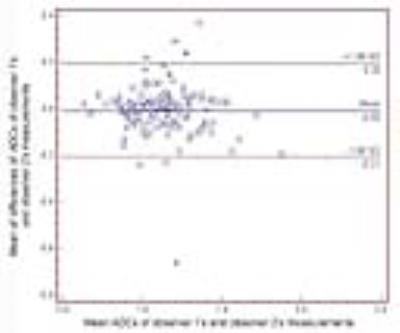 |
Apparent Diffusion Coefficient of Hepatocellular Carcinomas on Diffusion-Weighted Imaging: Correlation with Histopathologic Tumor Grade versus Arterial Vascularity during the Dynamic MRI
In Kyung Park, Jeong-Sik Yu, Eun-Suk Cho, Joo Hee Kim, Jae Joon Chung
Depending on the difference of cellular densities related to the histopathologic grades of HCCs, some investigators have recently suggested apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) as an effective biomarker for the prediction of the patients’ prognosis before the treatment of HCC. In the present study, ADCs of well- or poorly differentiated HCCs were lower than moderately differentiated HCCs; meanwhile the degree of arterial phase enhancement during the dynamic imaging rather well stratified the ADCs of the lesions. We concluded that ADC could not be independently used to estimate the histopathologic grades of HCCs.
|
|
2016.
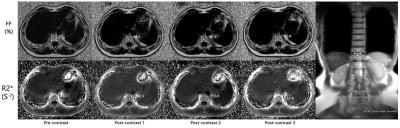 |
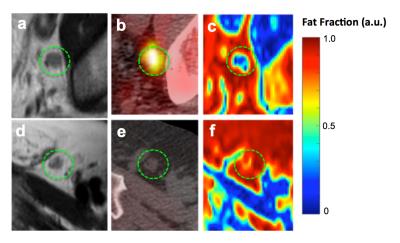
Quantification of liver fat after Gd-EOB-DTPA injection: a IDEAL-IQ feasibility study
Yuan Tian, Pengfei Liu, Lizhi Xie
This article is to explore the feasibility of liver fat quantification via dynamic liver enhancement scanning after injection of Gd-EOB-DTPA. IDEAL-IQ was used to quantify liver fat in 65 patients who were injected with contrast. IDEAL-IQ was performed four times to determine the fat fraction (FF) and R2*. One-way repeated-measures analysis was conducted to evaluate the difference between the four time points of the FF. The assessment of FF at four time points in liver, spleen and spine showed no significant differences. However, after injection of contrast agent, R2* was increased, and the IDEAL-IQ result was relatively stable.
|
|
2017.
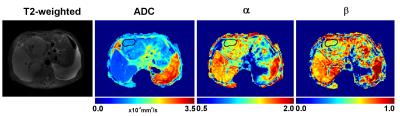 |
A Preliminary Study of the Clinical Value of FM Model in Malignant Tumor of Liver
huang can
Several models have been proposed to explain the anomalous diffusion in biological tissues. Among them, the fractional motion (FM) model was considered more appropriate. In this study, the FM model was applied to assess its feasibility for diagnosing malignant tumors of liver. It was found that the FM model could improve the diagnostic accuracy in differentiation normal liver tissue and tumor lesion, indicating the potential of the FM model to facilitate future studies of pathological changes in clinical populations.
|
|
2019. 
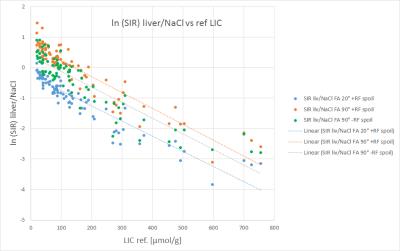 |
Liver Iron Concentration determined by Gradient Echo MRI using Signal Intensity Ratios: Impact of Acquisition Parameters and Image Quality
Arthur Wunderlich, Holger Cario, Isabelle Tomczak, Meinrad Beer, Stefan Schmidt
Tissue signal intensity ratio (SIR) has been used for a long time to determine liver iron concentration (LIC) based on gradient echo MRI. We studied the influence of acquisition parameters FA, RF spoiling and saturation regions, as well as image quality score, on the correlation of natural logarithm of SIR values to reference LIC obtained with spin echo. In our cohort of 85 patients, no significant influence on the slope of linear regression line was found, neither of acquisition protocol settings nor image quality, whereas the intercept was dependent on parameters influencing T1 sensitivity, namely FA and RF spoiling.
|
|
2021.
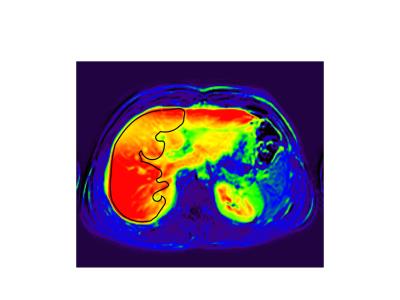 |
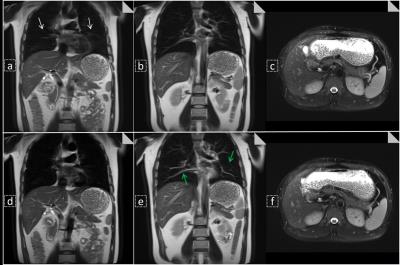
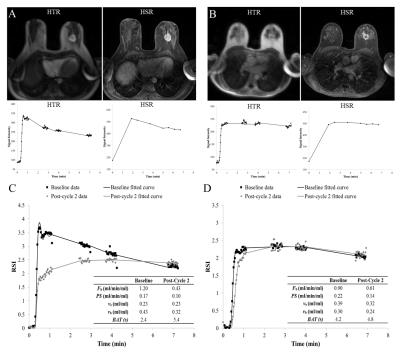
Gadoxetate disodium (Gd-EOB-DTPA) DCE-MRI of the Liver for the Assessment of Parenchymal Alterations in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Sarah Keller, Jan Sedlacik, Fabian Kording, Gerhard Adam, Christoph Schramm, Jin Yamamura
This study evaluates the feasibility of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) with Gd-EOB-DTPA for detection of hepatic inflammation/fibrosis in comparison to Ultrasound elastography in primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC).
|
|
2022.
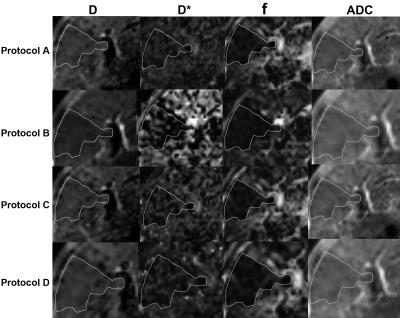 |
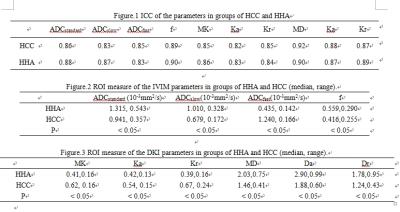
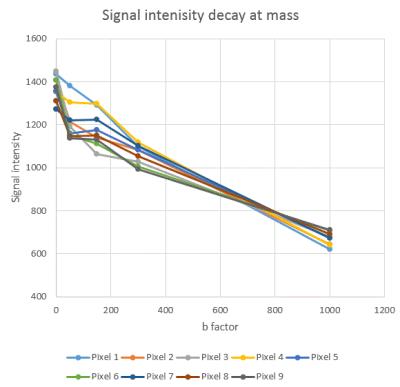
Evaluation of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion with Different b Values in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Li Yang, Mengsu Zeng, Xuhao Song, Caixia Fu, Xu Yan
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model provides both pure water motion and microcirculation by using multiple b values. IVIM imaging has been shown to be useful for assessment of liver diseases, including liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. However, the clinical implementation of IVIM imaging is limited by long acquisition time. We compared IVIM imaging with different b-values to determine the combination of b-values in IVIM imaging that allows the relatively short acquisition time to obtain reproducible values of the IVIM parameters in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Our results showed at least 10b-values should be used in IVIM imaging for the assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma, and 5b-values IVIM imaging might increase errors in the perfusion-related f and D* values.
|
|
2008.
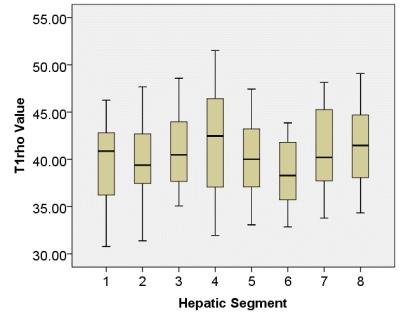 |
Liver T1rho Distribution across Eight Functionally Independent Segments
Weibo Chen, Xin Chen, Li Yang, Shanshan Wang, Queenie Chan, Guangbin Wang
ROI-based analysis may suffer from sampling errors due to the user-defined placement of the ROI and the choice of slice location. The aim of our study was to find an approach that allow the detection and measurement of the T1rho values of the hepatic segments.
|
|
2023. 
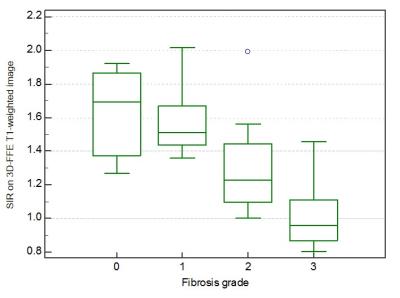 |
Pancreatic MRI associated with pancreatic fibrosis and postoperative fistula: comparison between pancreatic cancer and non-pancreatic cancer tissues
Yoshifumi Noda, Satoshi Goshima, Natsuko Suzui, Tatsuhiko Miyazaki, Kimihiro Kajita, Hiroshi Kawada, Nobuyuki Kawai, Hiromi Koyasu, Masayuki Matsuo
Pancreatic cancer (PC) occurs a histopathologically stronger pancreatic fibrosis compared to other non-PC. The risk factors of postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) were reported as soft or normal pancreatic parenchyma, and ampullary or duodenal disease. In this study, in patients with non-PC, frequency of POPF was greater due to lower grade of pancreatic fibrosis, and our results suggest that T1 signal and ADC value of the pancreas may link to the POPF. The T1 signal and ADC value of the pancreas may be a potentially useful imaging biomarker for the assessment of pancreatic fibrosis and POPF.
|
|
2025.
|
Pancreatic changes in patients with liver cirrhosis and diabetes: a 3-T MRI evaluation
Tomohiro Sato, Katsuyoshi Ito, Tsutomu Tamada , Akira Yamamoto, Akihiko Kanki
The liver plays a pivotal role in glucose metabolism, so 60-80% of patients with cirrhosis experience impaired glucose tolerance and hyperinsulinemia, and 10-50% develop diabetes. This study was intended to clarify the extent to which pancreatic MRI findings are affected by the presence of diabetes mellitus in patients with liver cirrhosis. On 3-T MRI, size of the pancreas was significantly increased, the grade of pancreatic lobulation was significantly reduced, and pancreatic SIRs on T2WI with fat suppression were significantly increased in cirrhotic patients complicated with diabetes as compared to cirrhotic patients without diabetes.
|
|
2026. 
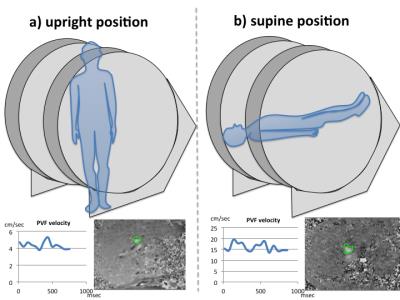 |
Evaluation of gravity effect on portal venous flow using multi-posture MRI
Yoshisuke Kadoya, Tosiaki Miyati, Naoki Ohno, Satoshi Kobayashi, Toshifumi Gabata
Portal venous flow (PVF) seems to be affected by gravity, ie., it depends on the body posture. We validated the effect of gravity on PVF in supine and upright positions using an original multi-posture MRI. We compared maximum PVF, PVF velocity, PVF volume, and cross-sectional area of portal vein between supine and upright positions. The mean PVF velocity, PVF volume, maximum PVF, and cross-sectional area in the upright position were significantly lower than those in the supine position. Gravity reduces PVF velocity and volume, and these differences between postures potentially provide new diagnostic information.
|
|
2024.
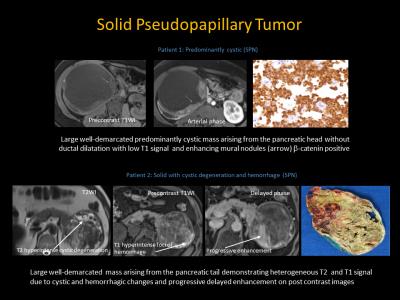 |
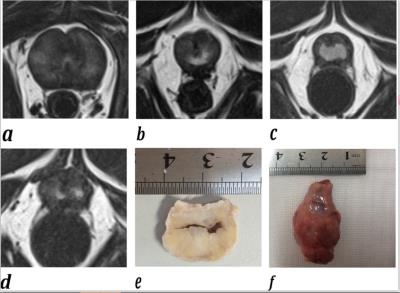
Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas, Mimics and Histopathological Correlation
Nikhar Kinger, Peter Harri, Lauren Alexander, Courtney Moreno, Pardeep Mittal
SPN is a rare epithelial neoplasm of low grade malignant potential for local and metastatic spread, occurring predominantly in young females. Differential diagnosis of SPN includes a wide spectrum of cystic and solid entities in the pancreas including pancreatic neuroendocrine, serous or mucinous cystadenoma or carcinoma, intrapancreatic splenules etc. Contrast enhanced MRI plays a key role in characterization of SPN and its mimics , helps to reach a specific diagnosis and narrows the differential, which is complimentary to EUS and biopsy when findings are equivocal to reach an accurate diagnosis which is of utmost importance for management and treatment planning
|
|
2027.
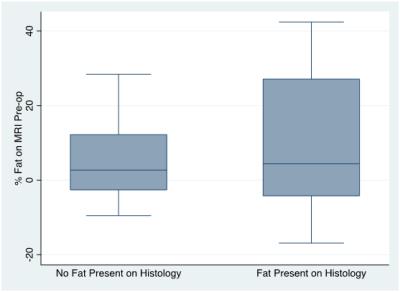 |
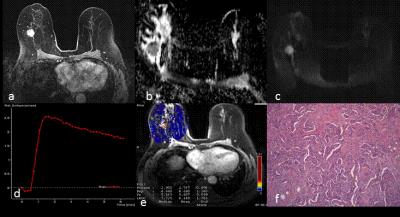
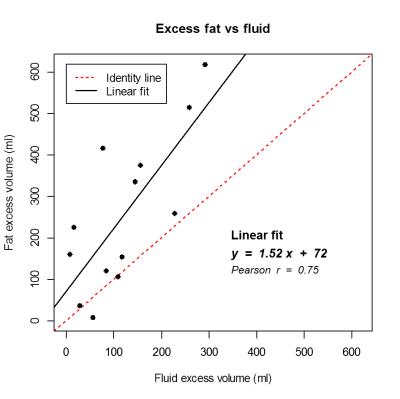
Pre-operative MRI quantification of hepatic fat and its correlation with histology, BMI and length of peri-operative stay following resection of liver metastases
Davinia Ryan, Alessandra Borgheresi, Simone Krebs, Sarah Eskreis-Winkler, Lorenzo Mannelli
We correlate pre-operative quantification of hepatic fat on MRI in patients with colorectal cancer metastatic to the liver with the presence of fat on histology of the resected specimen, patient BMI and hospital length of stay.
|
|
2002.
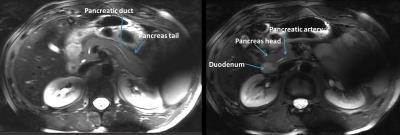 |
Quantitative T1 and T2 measurements of pancreas at 7 Tesla using a multi-transmit system
Mariska Damen, Quincy van Houtum, Maarten van Leeuwen, Peter Luijten, Andrew Webb, Dennis Klomp, Catalina Arteaga de Castro
Inversion recovery and echo time series were obtained at 7T with a multi-transmit system to determine the T1 and T2 relaxation times of the healthy pancreas. These parameters are crucial when optimizing MR protocols. The T1 and T2 values found were in average 921+/-98 ms and 57+/-12 ms respectively. Excellent T2 contrast is obtained for the pancreas at TE/TR=80ms/17s.
|
|
2028. 
 |
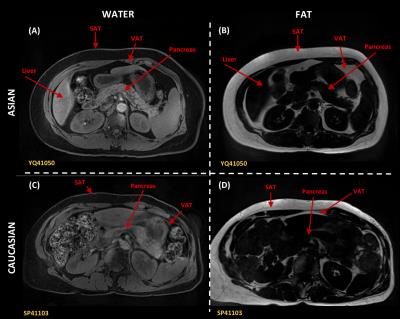
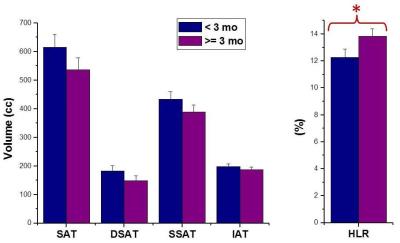
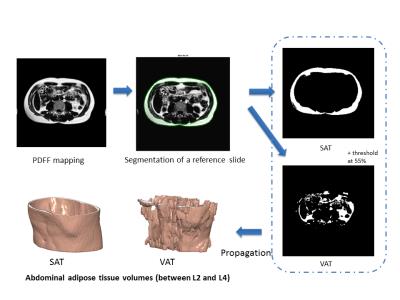
The effects of a 2 week hyperenergetic high carbohydrate or high fat diet on subcutaneous, visceral fat and metabolism
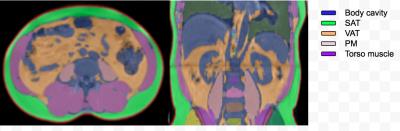
Mehri kaviani , Carolyn Chee, Caroline Hoad, Stephen Bawden, Peter Mansell, Sally Cordon, Aithal Guruprasad, Ian Macdonald, Penny Gowland
With the rise in obesity globally, there is great interest in quantifying body composition and in particular metabolically active visceral adipose tissue (VAT). Increased accumulation of VAT has been linked with an increase in risk factors for cerebrovascular disease and Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM) . We investigated the degree to which weight, subcutaneous fat visceral fat, liver and lipid markers are affected by 2 weeks of overfeeding at 25% excess energy given as either carbohydrate or fat. 2 weeks of 25% excess energy overfeeding of either carbohydrate of fat does not alter subcutaneous or visceral abdominal fat in line with no changes in weight. MRI measurements of SAT and VAT can be used in longitudinal studies of diet to ascertain any changes in abdominal body fat deposition.
|
|
2029.
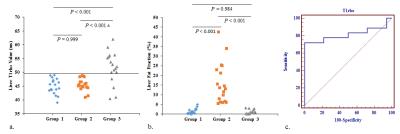 |
Liver T1rho detects liver fibrosis without impact of fatty liver in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a prospective study
shuangshuang xie, qing li, zhizheng zhuo, yu zhang, yue cheng, wen shen
This study investigated the merit of liver T1rho values for detecting fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B and the potential impact of fatty liver on T1rho measurements. Eighteen healthy control subjects, eighteen patients with clinically diagnosed simple fatty and eighteen with liver fibrosis were underwent T1rho MRI and mDIXON-Quant. Mean T1rho values and fat fraction (FF) were compared among the three groups. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to evaluate the merit of T1rho values for detecting liver fibrosis. T1rho values were correlated with FF and clinical data. Our results showed significant differences in T1rho values among the three groups and T1rho had moderate diagnostic efficacy to detect fibrosis. T1rho values were not correlated with FF, subject age, or body mass index. We conclude liver T1rho values can be used as a MR biomarker for liver fibrosis and are not influenced by fatty liver severity.
|
|
2030.
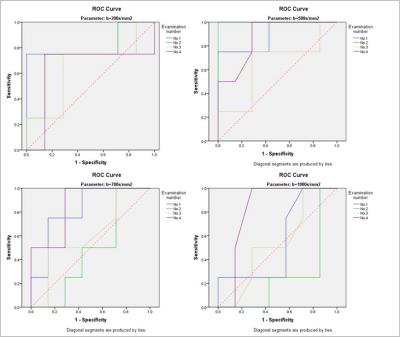 |
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Variable Flip Angle T1 Mapping in Progression Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Caused by Hepatitis B Virus Infection: A longitudinal study
Peng Hu, Jihong Sun, Fangfang Lv, Borui Pi, Fangping Xu, Guocan Han, Xi Hu, Yue Wang, Ning Huang, Xia Wu, Yong Zhang, Jun Yang, Peipei Pang, Xiaoming Yang
Liver fibrosis caused by Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a worldwide health problem. However, liver biopsy as the gold standard of diagnosing and evaluating therapy of liver fibrosis is an invasive examination with possible errors from sampling and intra- and inter-observer interpretation (1, 2). The non-invasive MRI may be a promising modality to evaluate the liver fibrosis. We used diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and variable flip angle (VFA) T1 mapping to explore the progression of liver fibrosis caused by HBV infection in a longitudinal study.
|
|