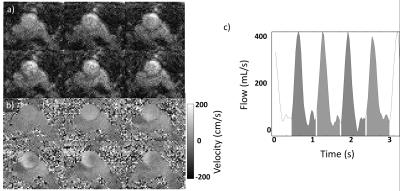
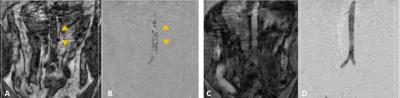
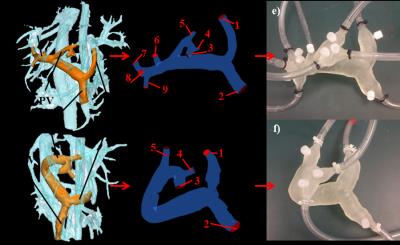
Myocardial Tissue Characterization
Traditional Poster
Cardiovascular
Thursday, 27 April 2017
| Exhibition Hall |
08:15 - 10:15 |
|
2719.
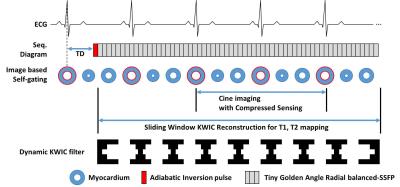 |
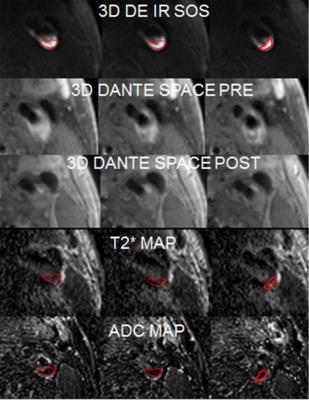
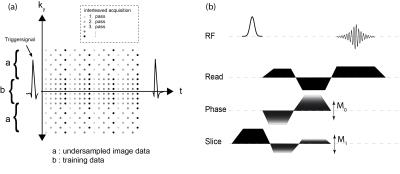
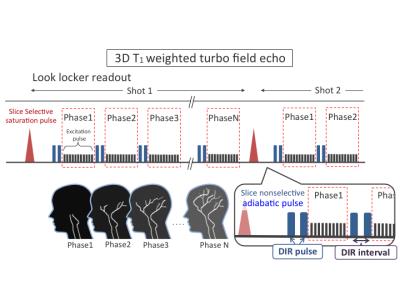
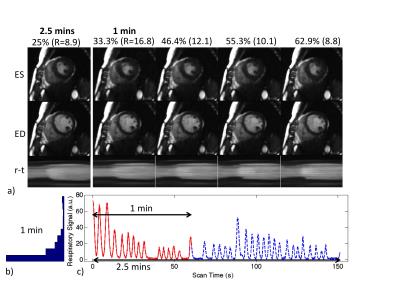
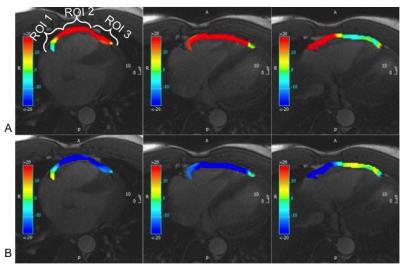
Simultaneous measurements of myocardium T1, T2 map, Cine and synthetic LGE using Inversion Recovery tiny golden angle radial balanced-SSFP within 6 second
Panki Kim, Byoung Wook Choi
In the cardiac MRI study, the quantification of T1, T2 relaxation time has become an important indication as well as the cine and the late gadolinium enhancement. In this work, we presented a novel method for simultaneous acquisition of T1, T2 map and Cine image of the myocardium based on the transient phase of inversion recovery balanced-SSFP imaging, and was proven potential both phantom and in vivo on a healthy volunteer.
|
|
2720. 
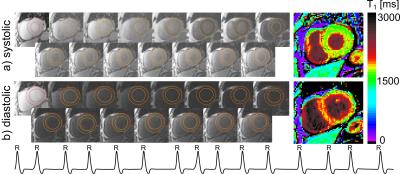 |
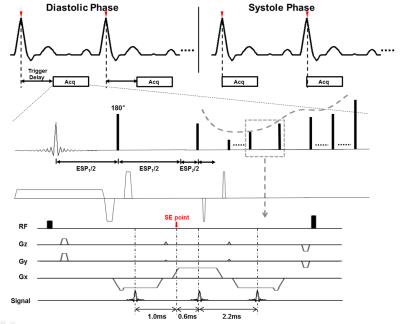
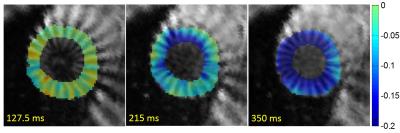
Accurate Myocardial T1-Mapping in Arrhythmia using Saturation-Recovery during Systole at 3T
Nadja Meßner, Sebastian Weingärtner, Johannes Budjan, Dirk Loßnitzer, Theano Papavassiliu, Lothar Schad, Frank Zöllner
In arrhythmic patients, ECG mis-triggering frequently leads to T 1-quantification inaccuracy. In this study, a heart-rate independent saturation-recovery T1-mapping method was adapted for systolic imaging at 3T by performing magnetization saturation right after the systolic imaging window and prior to R-wave detection. Estimated T1- and ECV- values during systole were (1557±53ms/ 0.21±0.03) compared to (1585±58ms/0.21±0.03) at diastole.
Our results show that SR T1-mapping might be an advantageous alternative to yield accurate T1- and ECV-values in patients with arrhythmia or reduced myocardial wall-thickness.
|
|
2727. 
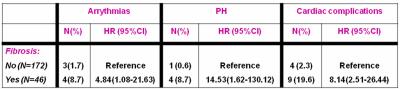 |
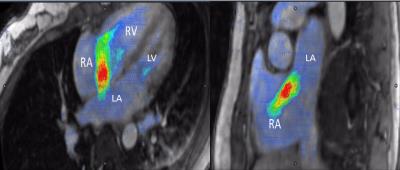
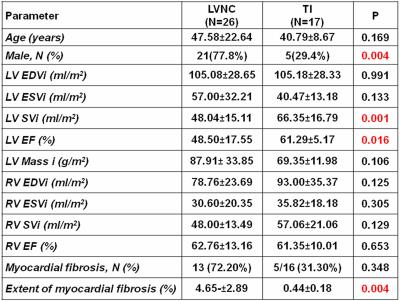
Myocardial fibrosis is a predictor of adverse outcomes in thalassemia intermedia patients
Antonella Meloni, Nicola Giunta, Pietro Giuliano, Stefania Renne, Laura Pistoia, Vincenzo Positano, Calogera Gerardi, Vincenzo Spadola, Petra Keilberg, Alessia Pepe
Myocardial fibrosis detected by LGE has been confirmed as an independent predictor of CV complications in thalassemia intermedia patients. Our finding is consistent with a growing evidence that LGE has a strong prognostic impact in thalassemic patients, warranting a close clinical and instrumental follow-up.
|
|
2721.
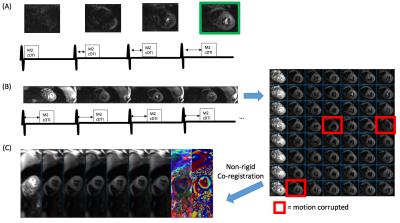 |
Towards High Success Rate in vivo Cardiac DTI on a Clinical 3T Scanner: Considerations on Heart Rate, Body-to-Mass Index, and Free Breathing
Christopher Nguyen, Sen Ma, Xiaoming Bi, Debiao Li
Clinical translation of cardiac diffusion tensor MRI has been challenging because of the sensitivity to bulk motion and thus, low success rates of scans. Current techniques require either high gradient systems (>40 mT/m) or excess breath holding ( >10 breath holds / slice) to acquire motion free cardiac DT-MRI. We propose a cardiac DT-MRI technique optimized for clinical translation and aimed at achieving high success rates in subjects with high and variable heart rate and high bold-to-mass index under free breathing conditions. Results in subjects with high BMI and variable HR yielded success rates > 90%.
|
|
2722. 
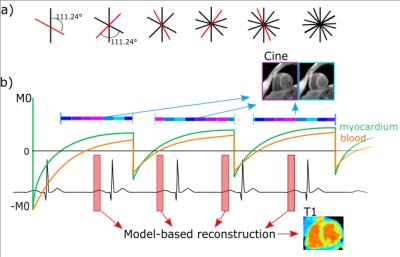 |
Multi-parametric cardiac MRI for T1 mapping and cine imaging using iterative model-based image reconstruction
Kirsten Becker, Jeanette Schulz-Menger, Tobias Schaeffter, Christoph Kolbitsch
In cardiac MRI, different diagnostic parameters are obtained in separate scans, leading to long examination times. In this work, we present an iterative model-based reconstruction approach for continuously acquired data, which provides native T1 maps and functional cine images within a single breath hold. The continuous acquisition allows for T1 reconstruction for different cardiac phases. Evaluation in a phantom demonstrated accurate T1 values (R²>0.99) and insensitivity to heart rates, with T1 variations of less than 5% (50 to 90 bpm). In three healthy volunteers T1 maps were assessed for diastole and systole and cine images had a consistent dark-blood contrast.
|
|
2723.
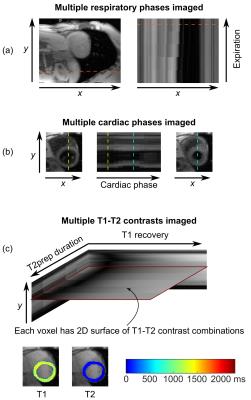 |
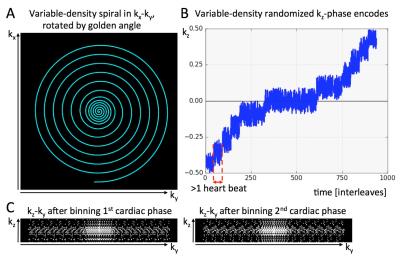
Non-ECG, Free-breathing Joint T1-T2 Mapping in the Myocardium with CMR Multitasking
Anthony Christodoulou, Christopher Nguyen, Jaime Shaw, Yibin Xie, Nan Wang, Debiao Li
Myocardial tissue characterization via quantitative T1 and T2 mapping is typically accomplished using ECG-triggering and breath-holding. Here we describe a novel method for non-ECG, free-breathing joint T1-T2 mapping using the cardiovascular low-rank tensor imaging framework for CMR multitasking. This method achieves joint T1-T2 mapping in the myocardium at multiple cardiac and respiratory phases within 1.5 min for one slice. Measurements were within the range reported in the literature, and were repeatable to 3.9% for T1 and 6.1% for T2.
|
|
2724.
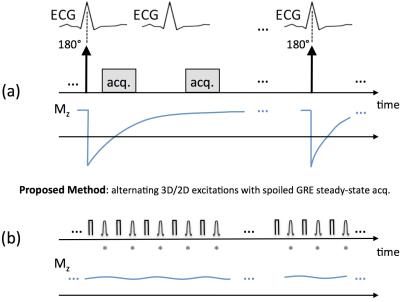 |
End-systolic myocardial T1 mapping using a spoiled steady-state approach: Towards reducing the confounding effect of intra-myocardial blood on native T1
Zulma Sandoval, Daniel Berman, Noel Bairey Merz, Behzad Sharif
Recent results in myocardial tissue characterization using cardiac MRI have shown that native myocardial T1 values are confounded by intra-myocardial water content, mainly driven by intra-myocardial blood volume. We developed and tested a free-breathing T1 mapping method that, in contrast to MOLLI-based methods, avoids any magnetization preparation and therefore can achieve significantly higher temporal resolution, thereby enabling it to capture purely-systolic or purely-diastolic T1 maps. End-systolic T1 mapping using the proposed steady-state approach has the potential to generate native T1 maps with minimal confounding effect from intra-myocardial blood.
|
|
2725. 
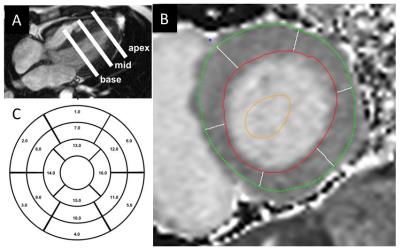 |
Left Ventricle Remodeling in Bicuspid Aortic Valve Evaluated by ECG, Echocardiography, and Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Kenichiro Suwa, Amir Rahsepar, Ahmadreza Ghasemiesfe, Julia Geiger, Alex Barker, Jeremy Collins, Micahel Markl, James Carr
The relationship between ECG characteristics, left ventricular (LV) diastolic function by echocardiography and Gadolinium extracellular volume fraction (ECV) in bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) are unknown. We aimed to test the hypothesis that BAV has an association with LV hypertrophy, myocardial fibrosis, and diastolic dysfunction. Cardiac magnetic resonance, ECG, and echocardiography were performed in 80 patients with BAV and 34 patients with trileaflet aortic valve (TAV). ECV was significantly higher in BAV than TAV. ECV, Sokolow-Lyon voltage, Cornell product, and e’ demonstrated significant relationships with LV end-diastolic volume index. ECV can be a useful predictor of LV remodeling in BAV.
|
|
2726.
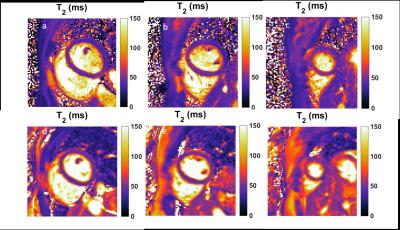 |
Simultaneous T1 and T2 mapping of the myocardium in normal volunteers using Cardiac MR Fingerprinting
Shivani Pahwa, Jesse Hamilton, Joseph Adedigba, Samuel Frankel, Gregory O'Connor, Ozden Kilinc, Wei-Ching Lo, Joshua Batesole, Seunghee Margevicius, Pingfu Fu, Mark Griswold, Nicole Sieberlich, Vikas Gulani
This study reports normative cardiac T1 and T2 values generated in a single cardiac MRF scan in a cohort of normal volunteers. These values were compared against MOLLI (for T1) and bSSFP (for T2). Our results show that cardiac relaxometry values obtained with MRF at 1.5 T are comparable to values previously reported in the literature and those obtained using MOLLI and bSSFP.
|
|
2728. 
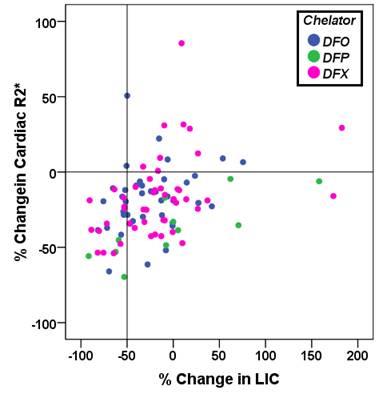 |
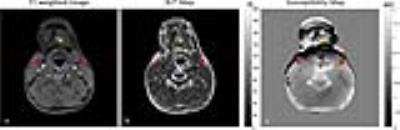
Association between cardiac iron clereance and hepatic siderosis by T2* MRI in thalassemia major patients
Antonella Meloni, Laura Pistoia, Nicolò Schicchi, Gennaro Restaino, Paolo Preziosi, Vincenzo Positano, Monica Benni, Maria Paola Smacchia, Daniele De Marchi, Alessia Pepe
We evaluated in thalassemia major (TM) if the cardiac efficacy of the three iron chelators (Desferrioxamine, Deferiprone, and Deferasirox) was influenced by hepatic iron levels over a follow up of 18 months. In patients treated with Deferasirox and Deferiprone percentage changes in cardiac R2* over 18 months were associated with final liver iron concentration (LIC) and percentage LIC changes. In no chelation group percentage changes in cardiac R2* were influenced by initial LIC or initial cardiac R2*.
|
|
2731.
 |
Improved Myocardial T1 mapping using a Novel Motion-Insensitive Reconstruction
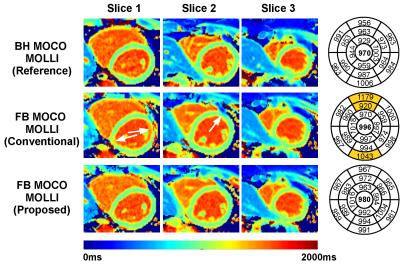
Céline Smekens, Radhouene Neji, Reza Razavi, René Botnar, Sébastien Roujol
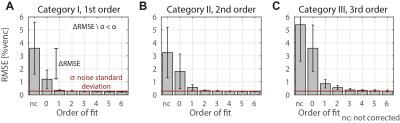
Myocardial T1 mapping sequences are commonly performed under breath-hold conditions. However, motion between T1-weighted images can be observed in ~50% of acquisitions. Image registration algorithms can be used for motion correction but are not available on all scanners, can occasionally fail and remain challenging using low contrast sequences such as saturation-based T1 mapping techniques. In this study we sought to develop and evaluate a novel motion-insensitive T1 mapping reconstruction approach which automatically discards misaligned/artefact T1-weighted images.
|
|
2732.
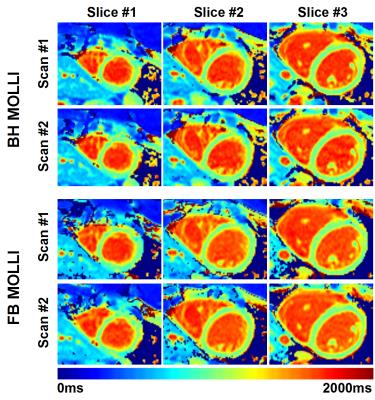 |
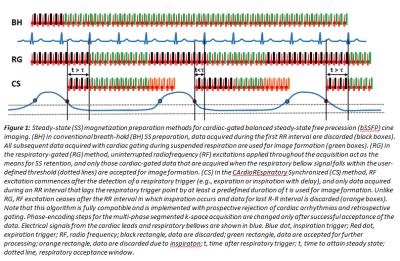
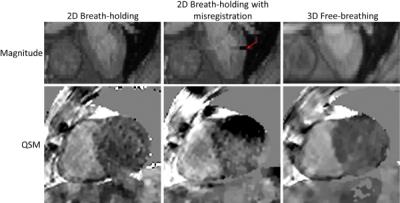
Free Breathing Myocardial MOLLI T1 Mapping using Real-time Slice Tracking and Non-Rigid Image Registration
Céline Smekens, Radhouene Neji, Reza Razavi, René Botnar, Sébastien Roujol
The modified Look Locker (MOLLI) sequence is the most widely used myocardial T1 mapping approach. In this 2D sequence, several T1-weighted images are acquired within a breath hold and used to create a T1 map. However, some patients are unable to sustain stable breath-holds which generates 3D motion between the T1-weighted images. While image registration can potentially be used to correct for in-plane motion, through-plane motion cannot be corrected and may introduce bias in T1 estimates. In this study, we sought to develop and assess a free breathing MOLLI sequence with real-time slice tracking and non-rigid image registration to reduce in-plane and through-plane motion effects.
|
|
2733. 
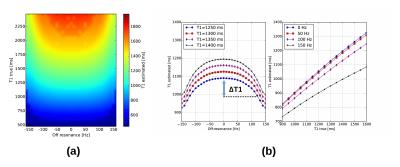 |
Off-resonance correction in myocardial T1-mapping using Bloch simulations of the MOLLI sequence
Nicola Martini, Andrea Barison, Maria Santarelli, Daniele Della Latta, Francesco Avogliero, Vincenzo Positano, Luigi Landini, Dante Chiappino
Myocardial T1 mapping using MOLLI is influenced by off-resonance effects that lead to underestimation of T1. In this study a method for the correction of the off-resonance influence on T1 mapping, based on the Bloch simulations of the MOLLI sequence, is proposed. In vivo results on a healthy population (N=67) showed that the regional variation of T1 is highly correlated with the distribution of the off-resonance. The proposed method effectively reduced the artifactual T1 underestimation due to off-resonance, especially in myocardial segments that exhibited elevated B0 inhomogeneities.
|
|
2734.
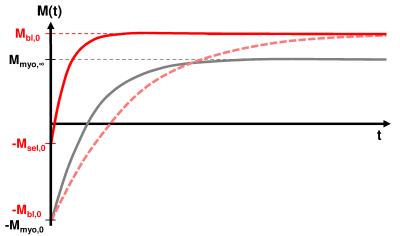 |
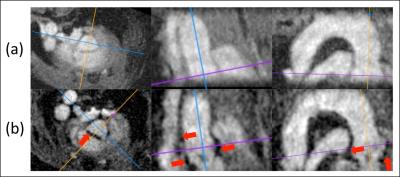
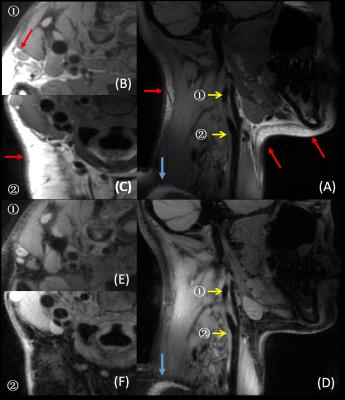
Quasi black blood T1-mapping using slice-selective TRASSI for improved visualization of the myocardium
Daniel Gensler, Tim Salinger, Georg Ertl, Peter Jakob, Peter Nordbeck
Currently available T1 mapping techniques have only restricted capabilities for the visualization of the right myocardium and they have the limitation that after contrast agent application the T1-contrast between blood pool and fibrotic myocardium is partially very low. The quasi black blood TRASSI sequence shows improved abilities for the visualization and T1-quantification of myocardial structures. So it might be suited in clinical routine for a clear visualization of the right myocardium or for the detection of slight endocardial infarctions, because it is an ultra-fast and robust cardiac T1-mapping method with a total acquisition time of less than 7s.
|
|
2735. 
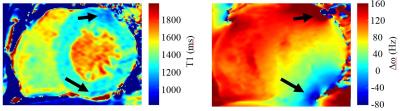 |
T1 Errors from Off-Resonance Effects for MOLLI at 3T: Experience in a Clinical Study
Justin Grenier, Natasha Wiebe, Stephanie Thompson, Scott Klarenbach, Marcello Tonelli, Paolo Raggi, Richard Thompson
The widely used MOLLI (MOdified Look-Locker Inversion recovery) T1 mapping approach underestimates T1 values as a function of several factors, including off-resonance frequency. Native T1 and matched off-resonance frequency (Δω) maps were acquired in 24 subjects as part of a study of patients with kidney disease (3T field strength). Δω within individuals had an average range 133±43Hz, and Δω was significantly correlated with underestimation of native T1, in good agreement with Bloch equation simulations. ~50% of slices had relatively large (75-150 Hz) off-resonance frequencies, for which T1 errors ranged from -25ms to -150ms.
|
|
2729. 
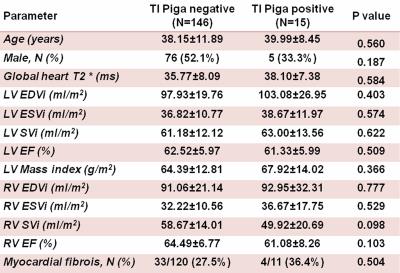 |
The prognostic role of hypertrabeculation by cardiac magnetic resonance in thalassemia intermedia patients
Antonella Meloni, Francesca Macaione, Vincenzo Positano, Andrea Barison, Laura Pistoia, Salvatore Novo, Pasquale Assennato, Alessia Pepe
We prospectively assessed whether the Piga’s criterion for left ventricle non-compaction (LVNC) (NC/C ratio threshold of >2.5) had a prognostic role for adverse cardiovascular outcomes in thalassemia intermedia patients. We found out that patients with Piga’s positive criterion had a significant higher risk of developing cardiac complications globally considered and arrhythmias.
|
|
2736.
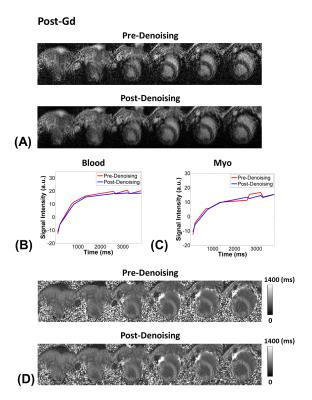 |
Multi-Slice GRE-MOLLI at 3T using Denoising with Low-Rank and Sparsity Constraints
Paul Han, Chao Ma, Nicolas Guehl, Nathaniel Alpert, Marc Normandin, Georges El Fakhri
Modified Look-Locker inversion recovery (MOLLI) uses bSSFP readout due to its high SNR, however, bSSFP is sensitive to off-resonance effects which result in banding artifacts. Recently, GRE has been proposed as an alternative readout for MOLLI, however, the low SNR efficiency of GRE-MOLLI is still a major problem. In this work, we propose to use a denoising reconstruction framework with low-rank and sparsity constraints to improve the low SNR of GRE-MOLLI. The proposed denoising method improved the low SNR of GRE-MOLLI, and multi-slice GRE-MOLLI is feasible for artifact-free T1 mapping with wider spatial coverage at high magnetic fields ($$$\geq 3T$$$).
|
|
2737.
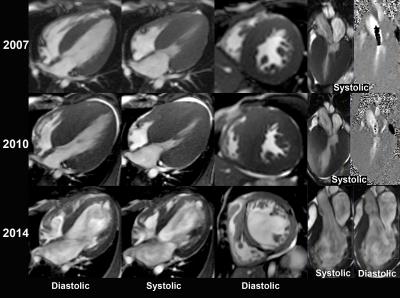 |
Prognostic value of cardiac MR imaging for end-stage phase of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients with or without adverse ventricular remodeling
Sainan Cheng, Chen Cui, Gang Yin, Lu Li, Shihua Zhao
Cardiac morphology as well as LGE extent proved to be particularly heterogeneous in ES phase of HCM patients. For ES phase of HCM patients with adverse ventricular remodeling, LGE was a significant predictor of poor outcomes. But for ES phase of HCM patients without ventricular dilatation, biatrial enlargement, extremely diastolic dysfunction and higher incidences of AF may contribute more to adverse prognosis.
|
|
2730. 
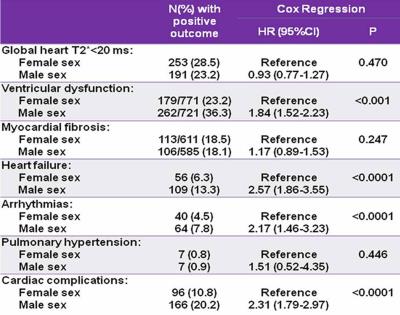 |
Gender-based optimization of cardiac follow up in thalassemia major patients
Antonella Meloni, Laura Pistoia, Silvia Maffei, Giuseppe Peritore, Valentina Vinci, Massimiliano Missere, Vincenzo Positano, Massimo Allò, Antonella Massa, Alessia Pepe
Females seem to tolerate iron toxicity better, possibly as an effect of reduced sensitivity to chronic oxidative stress. Based on our data about the significantly different risk in developing cardiac complications, in females older than 20 years the FU may be performed every 24 months, thus optimizing health care costs.
|
|
2738. 
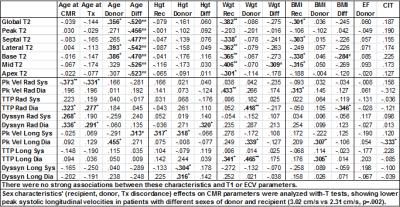 |
CMR-Derived Regional T2, T1/ECV, Myocardial Velocities, and Dyssynchrony Influenced by Donor and Recipient Characteristics after Heart Transplantation
Ryan Dolan, Amir Rahsepar, Julie Blaisdell, Allen Anderson, Kambiz Ghafourian, Esther Vorovich, Jonathan Rich, Jane Wilcox, Clyde Yancy, Jeremy Collins, Michael Markl, James Carr
Cardiac MRI is increasingly being used for cardiac allograft surveillance following transplantation, so it is important to investigate which recipient and donor characteristics influence several CMR parameters: global ventricular function, myocardial velocities, dyssynchrony, T2, native T1, and ECV. Notable associations with T2 included donor age, normalized recipient-donor age difference, and recipient weight. Peak diastolic longitudinal velocity was associated with donor age and cold ischemic time.
|
|
2739. 
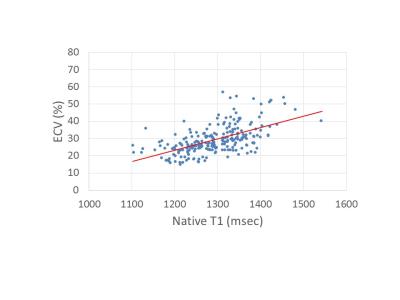 |
Non-contrast T1 mapping can detect myocardial fibrosis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy without gadolinium. Is native T1 a superior alternative to late gadolinium enhancement?
Yoshiaki Morita, Naoaki Yamada, Teruo Noguchi, Yoshiaki Watanabe, Tatsuya Nishii, Atsushi Kono, Tetsuya Fukuda
Native T1 mapping is a novel cardiac magnetic resonance technique for myocardial tissue characterization without contrast administration. Native T1-mapping in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy was correlated with T1 map-based extracellular volume fraction, and native T1 of apparently late gadolinium enhancement (LGE)-negative segments were significantly longer than normal myocardium. Therefore, native T1 mapping has the potential to quantify the volume of interstitial space without gadolinium, which would be useful particularly in patients who are limited in use of gadolinium. Furthermore, native T1 would be a useful biomarker for the detection of diffuse myocardial damage difficult to evaluate using conventional LGE alone.
|
|
2743. 
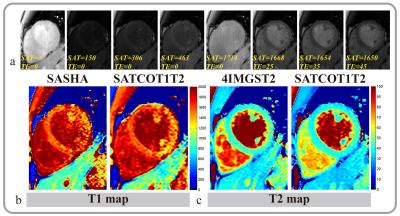 |
A 2D combined myocardium T1 and T2 mapping
Rui Guo, Zhensen Chen, Jianfeng zhang, Jianwen Luo, Haiyan Ding
In this study, we developed a 2D combined myocardial T1 and T2 mapping sequence that uses a combination of saturation pulse and T2 preparation pulse and allows simultaneously obtaining T1 and T2 map with acceptable breath holding time (12 heartbeats). High quality multiple T1 and T2 weighted images were obtained in the other cardiac cycle between the saturation pulse and T2 preparation pulse. Phantom experiment showed that T1 and T2 measured by proposed method highly correlated with reference methods. In vivo experiment showed that the proposed sequence can yield comparable myocardium T1 and T2 values with the conventional separated T1 and T2 mapping sequences.
|
|
2744.
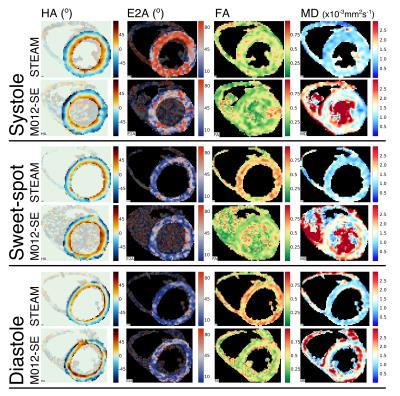 |
An in-vivo comparison of STEAM and 2nd order motion compensated spin-echo imaging in multi-phase cardiac DTI at 3T
Andrew Scott, Sonia Nielles-Vallespin, Pedro Ferreira, Zohya Khalique, Dudley Pennell, David Firmin
Cardiac diffusion tensor imaging (cDTI) is a novel non-invasive method of interrogating myocardial microstructure that has seen a recent surge in interest. Many of the most interesting clinical results were obtained using stimulated echo acquisition mode (STEAM) imaging at multiple cardiac phases. Recently however, spin-echo cDTI with second order motion compensated diffusion gradients (M012-SE) was proposed. In this study we report results of a comparison of M012-SE and STEAM imaging in multiple cardiac phases at 3T in 15 healthy subjects with matched sequence parameters. While M012-SE provides comparable quality data in systole, STEAM is the more reliable technique in diastole.
|
|
2745.
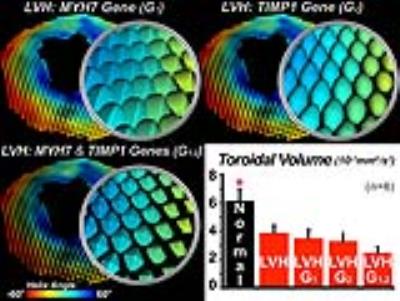 |
Integrated Analysis of Cardiac Genetic and Structural Alterations in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy using the Supertoroidal Model
Choukri Mekkaoui, Howard Chen, Iris Chen, Ronglih Liao, William Kostis, Timothy Reese, Marcel Jackowski, David Sosnovik
Response to disease occurs over many scales ranging from individual gene expression to whole organ physiology. We employed the supertoroidal model of the diffusion tensor to study the interaction between gene expression and microstructure of the heart. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) was induced in C57Bl6 mice through aortic banding, and characterization of the cardiac microstructure was performed in vivo with DTI. The supertoroidal model was constrained by both diffusion information and gene expression data related to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and myofiber orientation. Our model enabled further characterization of LVH by unifying information at different scales and across domains.
|
|
2746.
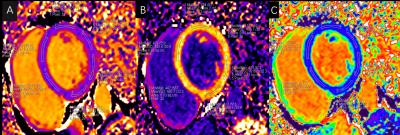 |
Segment and sexual variation of myocardium in T1 mapping and extracellular volume fraction with cardiovascular magnetic resonance in healthy volunteers
Yukun Cao, Yue Cui, Xiangchuang Kong, Shan Zhang, Xu Yan, Heshui Shi
This study aimed to evaluate sex and segment differences of myocardium in native T1 value and ECV in healthy volunteers. We measured native T1 value of 425 segments and ECV of 424 segments. The results showed that myocardial ECV of females was higher than that of males in basal, middle and apical segments. The ECV of the apical segments was higher than in the basal and middle segments. The mean native T1 value and ECV were not associated with age, ejection function(EF), end diastolic volume(EDV), end systolic volume(ESV), and stroke volume(SV).
|
|
2747.
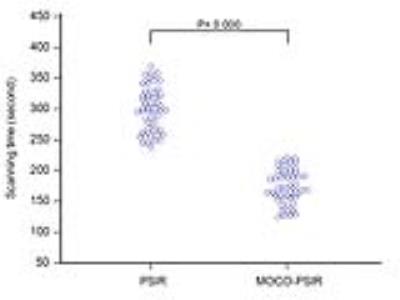 |
Role of free-breathing motion-corrected phase-sensitive inversion recovery (MOCO-PSIR) imaging technique for the assessment of late gadolinium enhancement
Yinyin Chen, Shan Yang, Hong Yun, Xiaoming Bi, Caixia Fu, Hang Jin, Mengsu Zeng
We aimed to investigate the role of motion-corrected phase-sensitive inversion recovery (MOCO-PSIR) technology for the evaluation of LGE. LGE imaging was conducted in 55 patients with MOCO-PSIR and conventional breath-hold PSIR sequences successively. Image quality was scored using a four-point scale. Compared with conventional PSIR, MOCO-PSIR showed better image quality and detected larger LGE volumes in nonischemic cardiomyopathy. Free-breathing motion-corrected PSIR method is a promising alternative to conventional PSIR sequence.
|
|
2748.
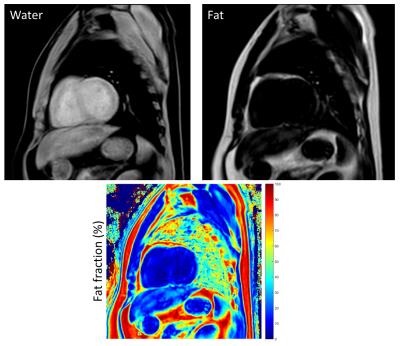 |
Myocardial fat quantification of normal subjects via 7-peaks mDixon model
Yu-Fen Huang, Feng Mao Chiu, Queenie Chan, Ya-Wen Shen, Chao-Jung Wei, Chih-Miang Chiang
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging provides a lot of physiological information about myocardial pathology, and the mDixon technique also has been developed on cardiac application recently. The fat deposition in myocardium is possibly related with cardiomyopathy, so it is important to determine the fat composition of myocardium. The mDixon provides an easy way to acquire such this information within one breath hold, and it has a consistent result with magnetic resonance spectroscopy from the previous study. Also it has been reported that multipeak fat spectrum model gives more robustness, and 7-peaks model is used in this study. The aim of this study is to evaluate fat fraction of myocardium with 7-peaks model.
|
|
2749.
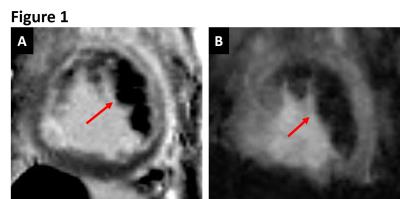 |
Reperfusion Hemorrhage Following Prolonged Myocardial Ischemia Leads to Fatty Degeneration of Myocardial Infarctions via Iron-Mediated, Self-Perpetuating Loop of Foam Cell and Ceroid Accumulation
Ivan Cokic, Avinash Kali, Hsin-Jung Yang, Richard Tang, Joseph Francis, Rohan Dharmakumar
Fatty infiltration within chronic myocardial infarctions (MI) is a common finding. It is typically observed in the peri-infarct border zone of old scars and has been linked to adverse outcomes in the chronic post-MI setting. To date, the trigger for fat deposition within old MI is unknown. Recent reports showed that iron deposits from hemorrhagic MI drive the recruitment of new monocytes/macrophages into the infarcted territory throughout the chronic phase after MI. Since iron-laden macrophages (siderophages) are prone to transforming into foam cells, we hypothesized that fatty degeneration of hemorrhagic myocardial infarctions has its origin in iron-driven foam cell formation.
|
|
2750.
 |
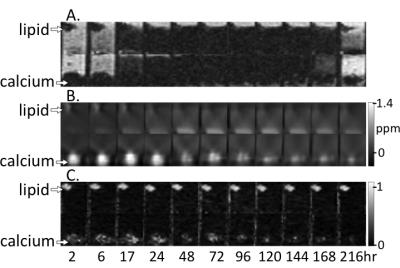
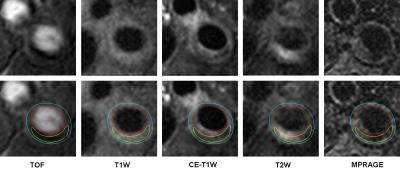
Cardiomyopathy in later-onset Fabry disease: a correlative study of T1 mapping on MR and histology
Jian-Ling Chen, Liang-Wei Chen, Sheng-Che Hung, Hsien-Tzu Liu, Mei-Han Wu, Fu-Pang Chang, An-Hung Yang, Ting-Rong Hsu, Dau-Ming Niu, Ming-Ting Wu, Chui-Mei Tiu, Chien-Yuan Lin
Fabry disease is a rare and X-linked disorder characterized by accumulation of glycosphingolipid within lysosomes and resultant multiple organ damage including heart. Since lipid is known to shorten the MRI parameter T1, non-contrast T1 mapping has emerged as key imaging modality to assess Fabry cardiomyopathy and early detection of lipid deposition. This study provides a histologic validation of 7 male patients of untreated later-onset Fabry disease to demonstrate the negative correlation between native myocardial T1 value and severity of lipid deposition (correlation coefficient, -0.771; p, 0.042) and justifies the application of T1 mapping as a noninvasive predictor of surveillance strategy.
|
|
2751. 
 |
Cardiac MR Derived Extracellular Volume Measurements Using Different Contrast Agents
Amir Ali Rahsepar, Ahmadreza Ghasemiesfe, Monica Korell, Jeremy Collins, James Carr
T1 and ECV values calculated from gadoterate meglumine enhanced CMR are comparable to more routinely used gadopentetate dimeglumine and gadobutrol CMR measurements.
|
|
2752. 
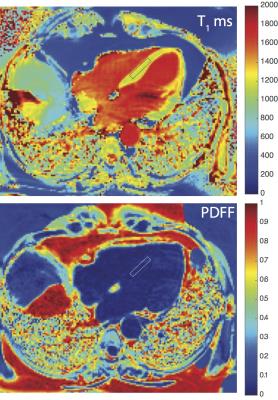 |
Single Breath-hold Measurement of T2 Corrected Myocardial Proton Density Fat Fraction in Humans at 3T
Ronald Ouwerkerk, Ranganath Muniyappa, Monica Skarulis, Ahmed Gharib
Localized 1H-MRS was used to determine T2s for water and lipid signals in the human heart in a single breath hold and derive relaxation corrected proton density fat fractions.
|
|
2740. 
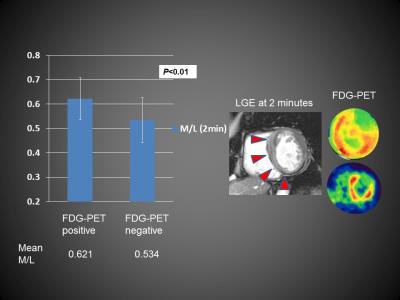 |
Assessment of myocardial inflammation in cardiac sarcoidosis using early gadolinium enhancement
Yoshiaki Morita, Naoaki Yamada, Teruo Noguchi, Yoshiaki Watanabe, Tatsuya Nishii, Atsushi Kono, Tetsuya Fukuda
In patients with cardiac sarcoidosis, assessment of the activity of myocardial inflammation is as crucial as the choice of therapeutic strategy and monitoring of therapeutic effects. It is known that early gadolinium enhancement (at 2–5 minutes after gadolinium administration) can visualize myocardial inflammation and/or edema such as in acute myocarditis and acute myocardial infarction. In this study, images of gadolinium enhancement at 2 minutes delay were significantly associated with findings regarding active inflammation, suggesting that early gadolinium enhancement has the potential to act as a marker of inflammation activity in cardiac sarcoidosis.
|
|
2753.
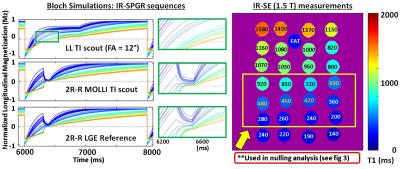 |
A Versatile MOLLI-based Inversion Time (TI) scout sequence for Myocardial Nulling Determination in emerging Late Gadolinium Enhanced CMR Variants: A Phantom Study
Keigo Kawaji, Adam Hasse, Amita Singh, Akhil Narang, Hui Wang, Timothy Carroll, Amit Patel
A Look-Locker scout is used for optimal inversion time (TI) determination of myocardial nulling in Late Gadolinium Enhancement (LGE) Cardiac Magnetic Resonance. Recently, novel LGE technique variants such as the Wideband approach have been proposed, and these approaches can lead to variability in the signal evolution between the Look-Locker TI-scout and LGE. In this study, we propose a Modified Look-Locker Inversion (MOLLI)-based TI-scout that closely matches its signal evolution to that of any LGE variant. Bloch simulation and phantom evaluation are performed to compare the null-times from the conventional LL-based and proposed MOLLI-based approaches against the LGE protocol over a range of clinically relevant T1 values observed in viability imaging.
|
|
2741. 
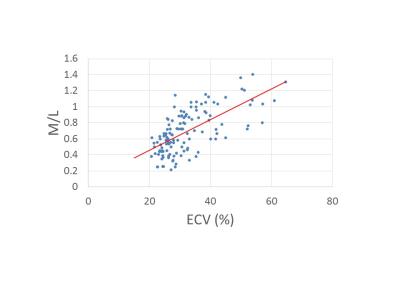 |
Simple quantification using the myocardium-to-lumen signal ratio in diffuse myocardial fibrosis of non-ischemic cardiomyopathies: Correlation with T1 mapping derived ECV
Yoshiaki Morita, Naoaki Yamada, Teruo Noguchi, Yoshiaki Watanabe, Tatsuya Nishii, Atsushi Kono, Tetsuya Fukuda
Myocardial T1 mapping has recently been applied to the quantification of extracellular volume fraction (ECV) and has shown potential for the detection of myocardial fibrosis. However, for the measurement of ECV, additional scans of pre- and post-contrast T1 mapping are necessary, and the post-processing procedure is time consuming. In this study, the myocardium-to-lumen signal ratio (M/L) in conventional late gadolinium enhancement images with fixed inversion time showed acceptable levels of correlation with ECV obtained by the T1 mapping in non-ischemic cardiomyopathy, suggesting that M/L has the potential to allow for simple quantification of the fibrotic change in non-ischemic cardiomyopathies.
|
|
2754. 
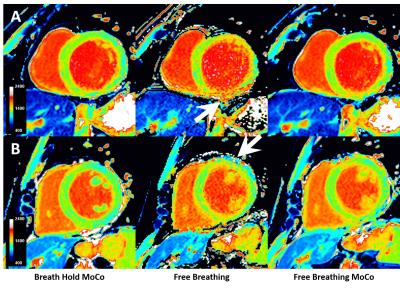 |
Free-breathing native cardiac T1 and T2 mapping with flexible elastic image registration: Preliminary Clinical Result
Shuo Zhang, Tomoyuki Okuaki, Sven Kabus, Bao Ru Leong, Yiying Han, Yi Hui Hung, Ping Wang, Ru San Tan
Current myocardial T1 and T2 mapping based on inversion-recovery and single-shot readout techniques require generally at least 7 to 10 seconds breath hold. Improper and difficulties of breath hold is one of the main sources of error and reduced reproducibility. To mitigate the dependence of mapping on breath holds and also to increase patient comfort, we report free-breathing T1 and T2 mapping using different acquisition schemes using flexible elastic image registration. We demonstrate the feasibility of this approach with motion correction for increased image quality and quantification accuracy.
|
|
2755.
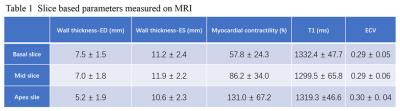 |
The Correlation of Clinical and Image of Acromegaly Patients Based on 3.0T Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Quantitative Analysis of Myocardial T1 and Extracellular Volume
Jian Cao, Peijun Liu, Lu Lin, Xiao Li, Xiaopeng Guo, Jing An, Bing Xing, Yining Wang
The aim of this study was to find out if there might be some correlation between clinical information and image measurements for acromegaly patients. And it found that for acromegaly patients, the basal slice of heart might be the most involvemented position, and its contractility had a positive correlation with GH burden, and both T1 and ECV had a negative correlation with IGF-1. And we need to enlarge the sample size and compare the changes before and after the surgery in order to give more informations to the clinicians.
|
|
2756. 
 |
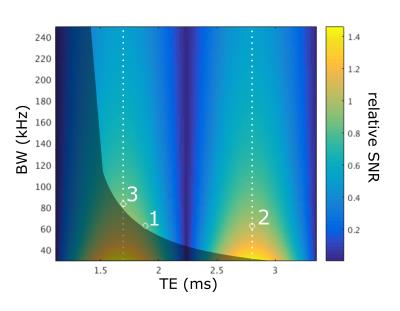
SMART1Map: Accuracy and Influencing Imaging Parameters For Cardiac T1 Mapping.
Malek MAKKI, Barbara Burkhardt, Emanuela Valsangiacomo
SMART1Map sequence was performed on 6 phantoms with different T1 values. Sixteen schemes were prescribed: 4 heart rates (60, 80, 100, 120 bpm), 2 spatial resolutions (FOV = 30 cm and FOV = 48 cm) and 2 cardiac phases (systole and diastole). The results show that SMART1Map underestimates long T1 (native T1 myocardium) at any scheme. We also found an increase in error with reduced FOV (all other parameters being identical), and an influence of the cardiac phases on T1 at the levels of native and post-contrast blood and myocardium
|
|
2757. 
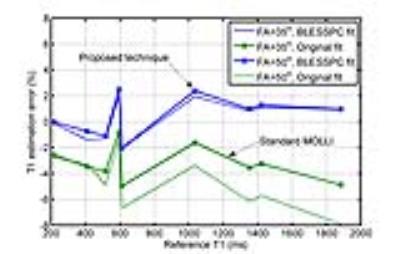 |
An alternative T1 estimation algorithm with a higher flip angle improves T1 mapping accuracy and precision of the MOLLI sequence
Jiaxin Shao, Kim-Lien Nguyen, Peng Hu
Good T1 estimation accuracy and precision is important for clinical application of the myocardial T1 mapping technique. Although the widely used T1 mapping technique, modified Look-Locker inversion-recovery (MOLLI), has good precision and reproducibility, it is not accurate. Several T1 estimation algorithms have been proposed to improve the accuracy for MOLLI. These algorithms however, often have reduced T1 estimation precision. We developed an improved MOLLI technique to achieve better accuracy and precision than the standard MOLLI sequence. Based on phantom and volunteer studies, a higher flip angle MOLLI with Bloch equation simulation and slice profile correction (BLESSPC) is used for T1 estimation.
|
|
2758.
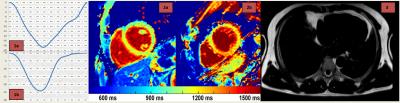 |
Coronary artery disease is not related to pathologic epicardial fat volumes, left ventricular strain or T1-relaxation times in hypertensive patients
Rami Homsi, Michael Meier-Schroers, Alois Sprinkart, Juergen Gieseke, Daniel Kuetting, Stefan Fischer, Darius Dabir, Julian Luetkens, Christian Marx, Hans Schild, Daniel Thomas
Hypertension is related to increased amounts of epicardial fat, to myocardial fibrosis and to left-ventricular contractility disturbances despite a normal systolic left-ventricular ejection fraction. However, the presence of stable coronary atherosclerotic disease in general - and with no cardiac damage due to prior coronary pathologies - does not additionally affect these parameters.
|
|
2759. 
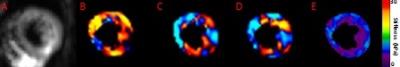 |
3D High Frequency Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Elastography Quantitatively Differentiates Myocardial Stiffness in Patients with HFPEF and Healthy Volunteers
Shivaram Poigai Arunachalam, Arvin Arani, Ian Chang, Yi Sui, Phillip Rossman, Kevin Glaser, Joshua Trzasko, Kiaran McGee, Armando Manduca, Barry Borlaug, Richard Ehman, Philip Araoz
Increased myocardial stiffness in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is known to affect diastolic filling. The purpose of this work was to determine if 3D high frequency cardiac MR elastography (MRE) can quantitatively differentiate increased myocardial stiffness in HFpEF patients compared to healthy volunteers. Two patients with clinical diagnosis for HFpEF and 47 healthy volunteers were studied. The myocardial stiffness of HFpEF patients (mean: 10.57 kPa) was found to be significantly stiffer (p < 0.05) than healthy controls (mean: 7.79 kPa). Recruitment of more HFpEF patients is underway for further validation of this finding.
|
|
2742. 
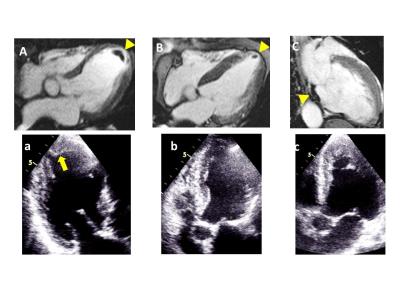 |
Assessment and detection of left ventricular thrombus in patients with acute ischemic stroke using cardiac MR (ADVENT study)
Yoshiaki Morita, Junji Takasugi, Naoaki Yamada, Teruo Noguchi, Yoshiaki Watanabe, Tatsuya Nishii, Atsushi Kono, Tetsuya Fukuda
In patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS), the assessment of left ventricular thrombus (LVT) is essential. In this study, we showed the utility of the early phase of gadolinium enhancement for detecting LVT in AIS patients, which conventional TTE hardly identified. CE-CMR, when using the early phase of gadolinium enhancement, should be performed on acute ischemic stroke patients, especially those with prior myocardial infarction or LV dysfunction and without definitive stroke etiologies.
|
|
2760. 
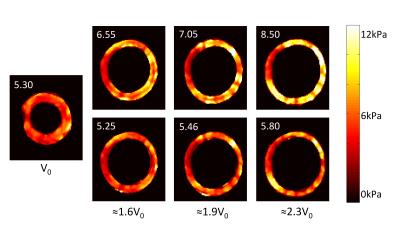 |
Reconstructing Inherent Stiffness in a Deforming Heart Phantom using MR Elastography
Myrianthi Hadjicharalambous, Adela Capilnasiu, Daniel Fovargue, Ayse Dokumaci, Stefan Hoelzl, Jack Lee, Ralph Sinkus, David Nordsletten
Cardiac MR-Elastography has significant potential to provide a non-invasive measure of myocardial tissue health. A core challenge in its application is the substantial motion of the heart over the cardiac cycle, which introduces a bias in the quantified apparent stiffness. In this work we apply a reconstruction technique for MRE designed to correct changes in apparent stiffness due to deformation. The reconstruction method is tested on anatomically accurate homogeneous and heterogeneous heart phantoms that are inflated to mimic diastolic function. The results demonstrate the ability of the reconstruction technique to retrieve intrinsic stiffness values, even under substantial inflation.
|
|
2761.
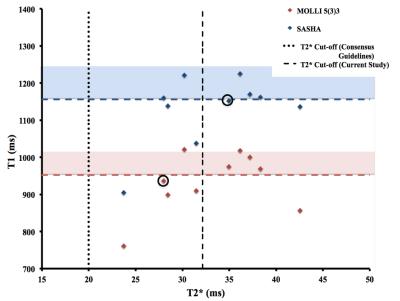 |
Comparison of SASHA and MOLLI sequences for Iron Quantification in the Myocardium.
Sarah McElroy, Torben Schneider, Daniel Sado, Tarique Hussain, Amedeo Chiribiri, Sarah Peel
Development of T1 mapping in the myocardium in recent years has demonstrated that the technique can add information to inform the diagnosis or management of patients in a number of pathologies. Sequences have been developed to enable T1 mapping of the myocardium within a single breath-hold and the limitations of these sequences have been well characterized. Recent studies have investigated myocardial T1 mapping in iron overload patients using variants of the MOLLI sequence. These studies have concluded that T1 mapping could be more sensitive and reproducible than T2* mapping for the measurement of iron overload in the myocardium. The current study aims to determine the optimal T1 mapping sequence for iron overload. Simulations, phantom studies and in-vivo studies were carried out to investigate MOLLI and SASHA sequences used for T1 mapping of low T1 and T2 tissues (comparable to iron overload in the myocardium).
|
|
2762. 
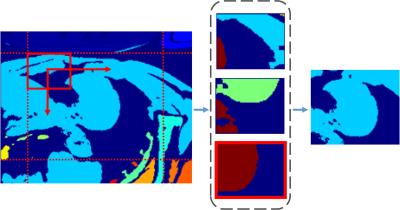 |
Optimization of MOLLI reconstruction for free-breathing myocardial T1 imaging
Yun-Wen Wang, Yi-Fu Tsai, Teng-Yi Huang
The free-breathing MOLLI (FB-MOLLI) presented in our previous study allowed T1 mapping in vivo without breath-hold. In this study, we attempted to implement unsupervised reconstruction for FB-MOLLI data sets and used a deformable method for image registration to improve the reliability of free-breathing T1 mapping. The results supported that the method improved the image alignments of the FB-MOLLI data sets and thus increased the quality of the T1 map. The variations of the repeated T1 measurements were significantly reduced in the anterolateral of the LV walls.
|
|
2763.
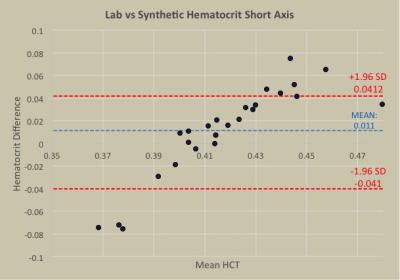 |
Derivation and Validation of Synthetic Hematocrit Calculation from Blood Pool T1 values at multiple different cardiac blood pools, in both high and low flow states on 3T MRI
Ozair Rahman, Kelvin Chow, James Carr, Jeremy Collins
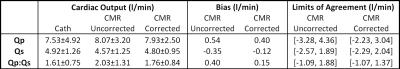
Comparison of the relationship between blood R1 and venous derived hematocrit in the left ventricle, left atrium, descending thoracic aorta, and short axis (apex, mid, and base) blood pools.
|
|
2764.
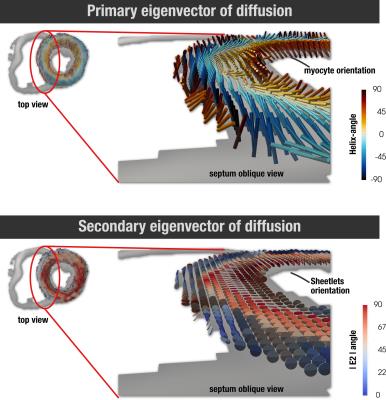 |
Dual identity of the interventricular septum with in vivo diffusion tensor imaging
Pedro Ferreira, Sonia Nielles-Vallespin, Andrew Scott, Zohya Khalique, Dudley Pennell, David Firmin
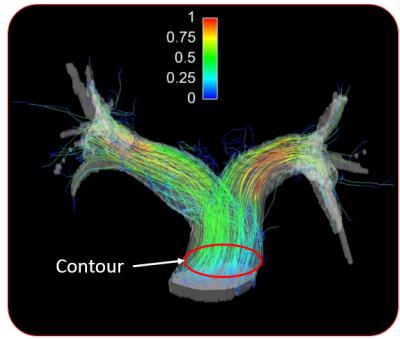
Heart muscle has a complex cellular helical arrangement, where bundles of myocytes, known as sheetlets interleave with collagen-lined shear layers. The right and left ventricle form separately in early stages of cardiogenesis, resulting in a dual inter-ventricular septum. In this work we compare the myocyte and sheetlet microstructure in the septum and LV free-wall in healthy and HCM hearts with in vivo diffusion tensor imaging. Results show that the right-side of the interventricular-septum has myocyte orientations not seen in the free-wall, and also lower sheetlet angles, which may indicate an RV identity in this region.
|
|
2765.
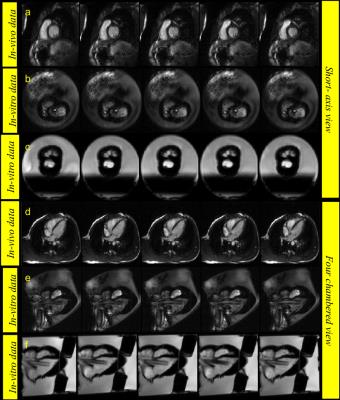 |
A Cost-effective 3D Printed Cardiac MR Phantom
Shivaprasad Chikop, Amaresh Konar, Nimitha Reddy, Nithin Vajuvalli, Darshan Keelara, Ashwini Kumnoor, Ramesh Venkatesan, Sairam Geethanath
Cardiac phantoms have been employed as testing and validating tools for newly developed techniques focused on sampling and reconstruction strategies. In this work, a 3D printed cardiac phantom was built to mimic the human heart. This was achieved through the integration of a peristaltic pump. Results depict the structural and functional behavior of the cardiac phantom, based on MR imaging on 1.5T scanners from 2 vendors. Ongoing work involves implementing the post-processing pipeline to correlate UI parameters with those derived from images. Future work focuses on employing PVA for preparing the heart model employing the 3D printing heart mold.
|
|
2766.
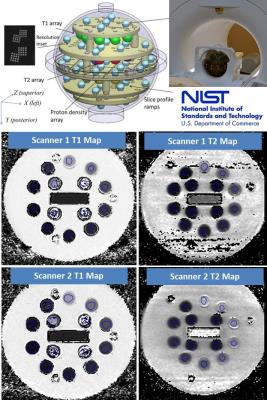 |
Inter-Scanner T1 and T2 Measurement Variability Evaluation on Two 3T Scanners with Identical Hardware and Software Configuration
Anshuman Panda, Clinton Jokerst, Kristopher Cummings, Prasad Panse
Inter-scanner T1 and T2 measurement variability was evaluated on two 3T scanners with identical hardware and software configuration to identify the most robust combination of sequence, parameters and post-processing that produces accurate measurement and to establish confidence intervals for T1 and T2 measurements for in-vivo studies by incorporating “native” inter-scanner variability.
|
|
2767.
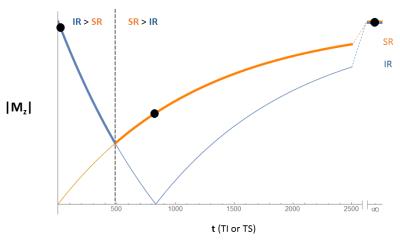 |
Cardiac T1 Mapping Using True Hybrid Inversion and Saturation Recovery
Glenn Slavin, Anne Menini, Haonan Wang, Anja Brau
Despite limited accuracy, MOLLI remains popular for T1 mapping due to high precision and visual quality of the maps. This is due primarily to the large dynamic range afforded by the inversion-recovery (IR) acquisition. Methods using saturation-recovery (SR) have better T1 accuracy but have relatively poor precision compared with MOLLI. This work presents a true hybrid IR/SR acquisition that targets the optimal regions of both the IR and SR relaxation curves, employs a novel method for maximizing dynamic range, and uses an improved sampling strategy. The proposed hybrid method combines the accuracy of single-point SR with the precision of IR.
|
|