|
Electronic Poster Session
General Cancer Imaging |
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
Electronic PosterGeneral Cancer Imaging
3792 -3815 Radiation Treatment Planning
3816 -3839 Endogenous Contrast Mechanisms in Cancer Imaging
3912 -3935 Predictive Cancer Imaging
3936 -3958 Exogenous Contrast Mechanisms in Cancer Imaging |
| |
Radiation Treatment Planning
Electronic Poster
General Cancer Imaging
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
08:15 - 09:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
 |
3792.
 |
1 |
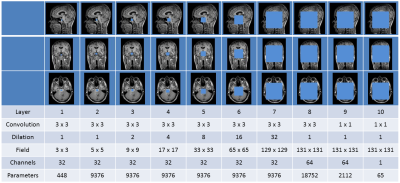
 CT synthesis for MR-only brain radiotherapy treatment planning using convolutional neural networks CT synthesis for MR-only brain radiotherapy treatment planning using convolutional neural networks
Anna Dinkla, Jelmer Wolterink, Matteo Maspero, Mark Savenije, Joost Verhoeff, Ivana Isgum, Peter Seevinck, Jan Lagendijk, Cornelis van den Berg
In MR-only radiotherapy, a synthetic CT (sCT) needs to be generated from MR to allow radiation dose planning without CT acquisition. We aim for such an MR-only workflow to decrease radiotherapy preparation time. If we can plan and deliver the dose in a single day, in a ‘one stop shop’ procedure, we prevent treatment delay which is of high importance for patients with fast growing brain metastases. In this study sCTs of the head were generated in a short amount of time, that highly resemble the original CTs and that enable accurate dose calculation.
|
|
3793.
 |
2 |
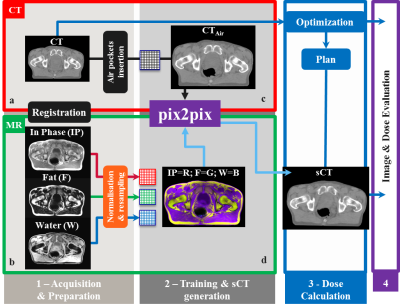
 Fast synthetic CT generation using a conditional Generative Adversarial Network and Dixon imaging for general pelvis MR-based Radiotherapy planning Fast synthetic CT generation using a conditional Generative Adversarial Network and Dixon imaging for general pelvis MR-based Radiotherapy planning
Mark Savenije, Matteo Maspero, Anna Dinkla, Peter Seevinck, Cornelis van den Berg
To enable MR-only radiotherapy planning and accurate MR-based dose calculations, substitutes of CT images, so-called synthetic CT (sCT) images, need to be generated. In this work, we assessed whether sCT images generated by a 2D conditional Generative Adversarial Network (cGAN) using a 3D dual echo SPGR MR sequence were suited for radiation treatment planning for general pelvis cancer patients. Image evaluation showed comparable performance among prostate, rectum and cervix patients. Dose planning calculations demonstrated that accurate MR-based dose calculation on sCT images generated by the cGAN after training is feasible for treatment planning in prostate cancer patients. In addition, the generation of the sCT is fast (< 6 s) and ideally suited for applications where time duration is essential, e.g. MR-guided radiotherapy planning.
|
|
3794.
 |
3 |
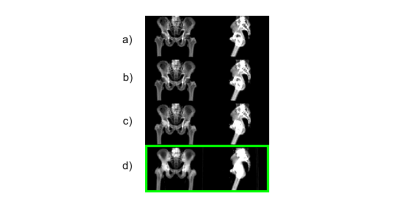
 MR-only Radiation Therapy Planning in the pelvis using Zero TE and LAVA-Flex based pseudo CT conversion. MR-only Radiation Therapy Planning in the pelvis using Zero TE and LAVA-Flex based pseudo CT conversion.
Cristina Cozzini, Mikael Bylund, Joakim Jonsson, Josef Lundman, Fredrik Illerstam, Mathias Engstrom, Tufve Nyholm, Florian Wiesinger
In this study, we demonstrate Zero TE (ZTE) and LAVA-Flex based pseudo CT conversion suitable for dose calculation for MR-only Radiation Therapy Planning (RTP) in the Pelvis. The dose planning performance of this method was evaluated in N=11 patients and compared to corresponding CT dose plans.
|
|
3795.
 |
4 |
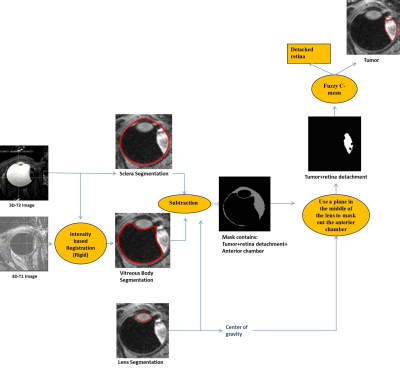
 Automated analysis of eye tumor MR-images for an improved treatment determination Automated analysis of eye tumor MR-images for an improved treatment determination
Mohamed Hassan, Denis Shamonin, Rahil Shahzad, Andrew Webb, Berend Stoel, Jan-Willem Beenakker
The optimal treatment for uveal melanoma, the most common primary malignant eye tumor, depends on tumor thickness. Conventionally tumor thickness is determined with 2D ultrasound, but MRI allows for a full 3D analysis. It is, however, often difficult to determine the maximum tumor thickness due to its complex 3D shape. We propose a fully automatic framework to segment these MR-images to measure the tumor thickness accurately and evaluate it in four patients. The proposed method has a direct impact on the clinical practice, as a more accurate 3D assessment of the tumor dimensions directly influences therapy determination.
|
|
3796.
 |
5 |
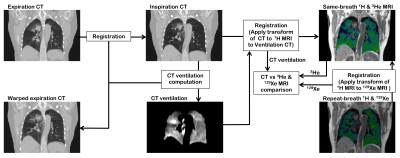
 CT-based surrogates of ventilation: A comparison with hyperpolarized Helium-3 and Xenon-129 MRI in lung cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy planning CT-based surrogates of ventilation: A comparison with hyperpolarized Helium-3 and Xenon-129 MRI in lung cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy planning
Bilal Tahir, Paul Hughes, Stephen Robinson, Helen Marshall, Alberto Biancardi, Neil Stewart, Graham Norquay, Ho-Fung Chan, Guilhem Collier, Kerry Hart, James Swinscoe, Matthew Hatton, Jim Wild, Rob Ireland
Image registration of lung CT images acquired at different inflation levels has been proposed as a surrogate method to map lung ‘ventilation’ and has notable applications in functionally guided radiotherapy planning. However, the technique requires validation against established ventilation modalities such as hyperpolarized gas MRI. Here, we develop an image acquisition and analysis strategy to facilitate direct spatial correlation of several CT ventilation techniques with both hyperpolarized 3He and 129Xe MRI and apply our method to a cohort of 11 lung cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy.
|
|
3797.
 |
6 |
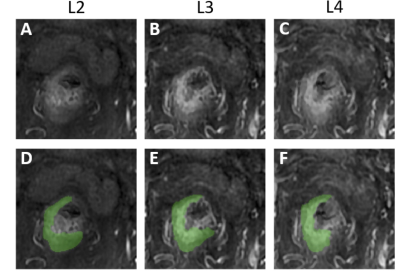
 Evaluation of MRI-Guided Radiotherapy Planning Target Volume Delineation for Colorectal Cancer Due to Variations in Image Contrast and Patient Motion Evaluation of MRI-Guided Radiotherapy Planning Target Volume Delineation for Colorectal Cancer Due to Variations in Image Contrast and Patient Motion
Yang Zhang, Liming Shi, Xiaonan Sun, Tianye Niu, Ning Yue, Jeon-Hor Chen, Tiffany Kwong, Min-Ying Su, Ke Nie
This study evaluates the difference in defining the target volume of rectal cancer with MRI-guided radiation treatment planning. Tumors show different appearances on different MR sequences, and also the motion of patients during the scan may affect defining planning target volume. A quantitative radial distance method was developed to evaluate variations coming from image contrast and patient motion. A total of 45 patients with pre- and post-radiation treatment MRI were analyzed. The mean difference in the radial distance between ROI’s drawn on different post-contrast images was 2-3 mm, and the difference in the 90th percentile tumor pixel was 6-8 mm.
|
|
3798.
 |
7 |
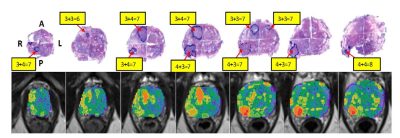
 An Automated Multiparametric MRI Quantitative Imaging Prostate Habitat Risk Scoring System for Defining External Beam Radiotherapy Boost Volumes An Automated Multiparametric MRI Quantitative Imaging Prostate Habitat Risk Scoring System for Defining External Beam Radiotherapy Boost Volumes
Radka Stoyanova, Matthew Abramowitz, Felix Chinea, Deukwoo Kwon, Isildinha Reis, Kyle Padgett, Sanoj Punnen, Oleksandr Kryvenko, Alan Pollack
The standard of clinical care, Prostate Imaging, Reporting and Diagnosis System (PI-RADS), does not tap into the wealth of quantitative imaging information contained in the multiple sequences of mpMRI, nor does it elucidate intralesional spatial heterogeneity. A habitat risk score (HRS) approach that combines the quantitative information from the diffusion and perfusion mpMRI sequences is developed. HRS was devised in ten subcategories with increasing levels associated with a greater risk of harboring higher Gleason Score's and depicted as a heat map. The automated method is used to define radiotherapy (RT) boost volumes in the background of a randomized Phase II clinical trial.
|
|
3799.
 |
8 |
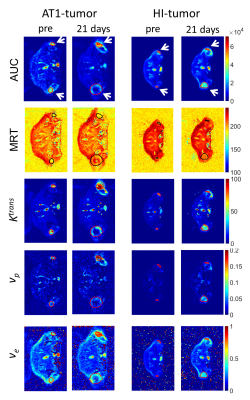
Longitudinal response monitoring in experimental prostate tumors by DCE-MRI after C-12 ion and photon radiotherapy
Video Permission Withheld
Alina Bendinger, Christian Karger, Charlotte Debus, Ralf Floca, Jürgen Debus, Jörg Peter, Christin Glowa
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI was used for the longitudinal monitoring of two well characterized experimental prostate tumors (Dunning R3327-AT1 and -HI) after isodose and isoeffective radiotherapy. The effect of carbon (12C)-ion irradition compared to photons on tumor vasculature was characterized by non-compartmental analysis and pharmacokinetic modelling employing the extended Tofts model. Isodose and isoeffective irradiation experiments indicated that the beam modality has a stronger effect on tumor perfusion and permeability than the dose. While changes in perfusion were identified for the highly undifferentiated AT1-tumor, the more differentiated HI-tumor showed only minor changes in perfusion upon irradiation.
|
|
3800.
 |
9 |
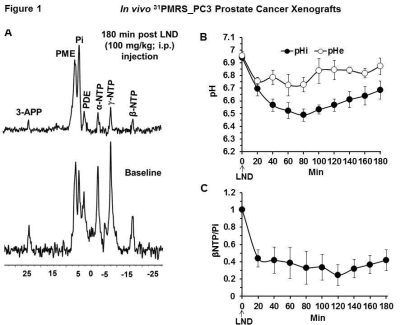
 Lonidamine-induced selective acidification and deenergization of prostate cancer xenografts: Enhanced tumor response to radiation therapy Lonidamine-induced selective acidification and deenergization of prostate cancer xenografts: Enhanced tumor response to radiation therapy
Kavindra Nath, Jeffrey Roman, David Nelson, Mary Putt, Stepan Orlovskiy, Ewere Azagidi, Violet Tu, Dennis Leeper, Jerry Glickson
Prostate cancer, when treated with external beam radiotherapy (RT) in the range of 78 Gy, is frequently associated with gastrointestinal (GI) & genitourinary (GU) toxicities. We hypothesize that tumor sensitization by lonidamine (LND) will enable the use of lower RT doses reducing the risk of side effects. LND effects detected in vivo by 31P and 1H MRS in androgen-independent (PC3) prostate cancer xenografts produced a sustained and tumor-selective decrease in intracellular pH, bioenergetics (βNTP/Pi), oxygen consumption rate and increase in lactate. Selective tumor acidification, deenergization and oxygenation induced by LND potentiated the radiation response in the PC3 prostate cancer model.
|
|
3801.
 |
10 |
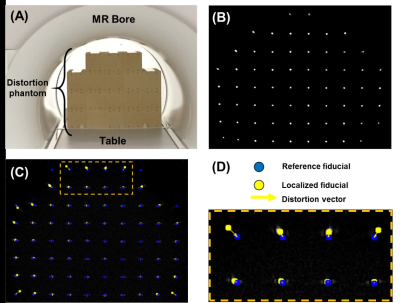
 Comparative Assessment of Geometric Distortion for an MR-Linac Versus Several Diagnostic Scanners Comparative Assessment of Geometric Distortion for an MR-Linac Versus Several Diagnostic Scanners
Jordan Slagowski, Yao Ding, Clifton Fuller, Caroline Chung, Mo Kadbi, Zhifei Wen, Jihong Wang
The integration of a MR scanner with a linear accelerator (MR-Linac) may improve image guidance in radiation therapy (RT). Spatial fidelity is an important consideration in RT and should be evaluated for MR-Linac imaging. This work presents a phantom and software developed in-house to measure geometric distortion across a large MR imaging field-of-view. A comparative assessment of geometric distortion within a 1.5T MR scanner integrated with a 7 MV linear accelerator is performed versus several commercial scanners with field strengths ranging from 1.5T-3.0T. The geometric distortion within the MR-Linac was comparable or less than that measured with the diagnostic scanners.
|
|
3802.
 |
11 |
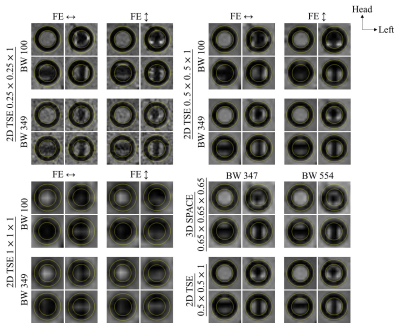
 Reduction of susceptibility artifacts in MR of permanent prostate gold seed for radiotherapy Reduction of susceptibility artifacts in MR of permanent prostate gold seed for radiotherapy
Abby Ding, Leon Ho, K.T Chan, Jing Yuan, Kin Yin Cheung, Siu Ki Yu
Stereotactic body radiation therapy for prostate cancer is a highly precise radiotherapy. Post-implant MR is important for target localization, contouring and treatment planning. A phantom was designed to investigate the susceptibility caused by gold seeds in different orientations relative to B0 field. 2D and 3D acquisition scheme at various resolution, bandwidth and frequency-encoding directions were examined. Our results show that for reduction of susceptibility artifacts and excessive local signal loss, resolution of higher than 0.5mm is recommended, increasing bandwidth with sufficient resolution is more practical than changing frequency-encoding directions. 3D is comparable to 2D sequence in susceptibility artifacts.
|
|
3803.
 |
12 |
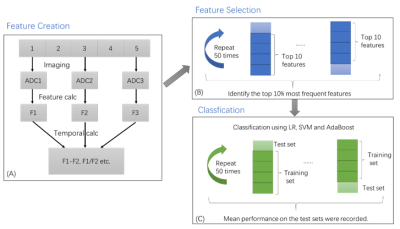
 Longitudinal diffusion MRI for predicting response to radiotherapy in sarcoma patients Longitudinal diffusion MRI for predicting response to radiotherapy in sarcoma patients
Yu Gao, Chunming Gu, Joong-hoon Kim, Minsong Cao, Anusha Kalbasi, Dan Ruan, Daniel Low, Peng Hu, Yingli Yang
In this work, we sought to predict the necrosis score, a surrogate of radiotherapy treatment outcome for sarcoma patients, using the longitudinal diffusion MRI data. Over three hundred features were extracted from the longitudinal diffusion data on twenty sarcoma patients. Minimum redundancy maximum relevance method with cross-validation was used to select the most relevant and stable features. Logistic regression, support vector machine and adaptive boosting were implemented to predict the necrosis score. AUC of 0.76 was achieved when using SVM with features from all three imaging time points. Features from before the treatment time point had better predictive power than data in the middle or after the treatment.
|
|
3804.
 |
13 |
Assessment Geometric Distortion in MRI for Gynaecological Brachytherapy Planning at 3T
Video Permission Withheld
Maria Schmidt, Eva Kousi, Georgina Hopkinson, Anne Gasnier, Kate Roberts, Alexandra Taylor, Susan Lalondrelle
MRI is increasingly used in radiotherapy treatment planning due to its superior soft tissue contrast. The growing interest in 3T MRI relates to the potential of higher signal-to-noise ratio and spatial resolution. However, geometric distortions associated with magnetic field inhomogeneity increase with field strength and may compromise geometric accuracy. We quantify the geometric distortion in MRI examinations for high dose rate brachytherapy planning for gynaecological cancer at 3T, and consider its clinical impact, taking into account the brachytherapy applicators, the subject’s susceptibility distribution and hardware-related distortions. We found localised areas of field inhomogeneity, and displacements of less than 1mm.
|
|
3805.
 |
14 |
 Practical Aspects of MRI-based Gel Dosimetry in RT Quality Assurance Practical Aspects of MRI-based Gel Dosimetry in RT Quality Assurance
Evanthia Kousi, Filipa Costa, Rollo Moore, Evangelos Pappas, Anne Gasnier, Emma Wells, Maria Schmidt
MRI-based gel dosimetry has been proposed as a part of a Radiotherapy QA programme and is of interest to Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy and Stereotactic Radiosurgery. MRI-related sources of error that may compromise the dosimetric accuracy need to be considered. R2 measurement variations associated with measurement timing after irradiation and SAR limitations were investigated using an anthropomorphic head phantom. Our results demonstrate gradual gel deformation and R2 variations that could have an impact on relative and absolute dose measurements.
|
|
3806.
 |
15 |
Use of a Rigidity Penalty to Improve MR-CT Image Registration
Did Not Present
Elizabeth McKenzie, Dan Ruan, Percy Lee, Ke Sheng
Attenuation coefficients of tissue must be known to accurately model dose in radiation therapy. MR-guided radiation therapy better visualizes soft tissue, but it does not inherently contain attenuation information in the same way as CT images. CT and MR images can be registered to pool information, but the bones can become severely distorted. This work applies a rigidity penalty to bones segmented in CT, such that the soft tissue is allowed to deform while the bones remain rigid during CT to MRI registration. We show that this technique improves the registration, making the deformations more anatomically feasible.
|
|
3807.
 |
16 |
 4D-MRI in radiotherapy: motion phantom study and automatic sorting based on internal surrogate for motion management during free breathing 4D-MRI in radiotherapy: motion phantom study and automatic sorting based on internal surrogate for motion management during free breathing
Soleakhena Ken, Oliver Bieri, Zarko Celicanin, Philippe Cattin, Laure Parent
4D-MRI sequence for radiotherapy (RT) application is validated in this study on a motion phantom and on healthy volunteers. 4D-MR imaging of a moving spherical target with different signal waveforms gave similar results as for classical 4D-CT used in RT planning. During free breathing 4D-MRI acquisitions, the internal surrogates, defined as the mean intensity inside a region of interest are relevant to detect the different respiratory phases for consistent retrospective automatic image sorting. Feasibility of integration into treatment planning system was also demonstrated, allowing picturing the dynamic behavior of the moving organ for treatment planning.
|
|
3808.
 |
17 |
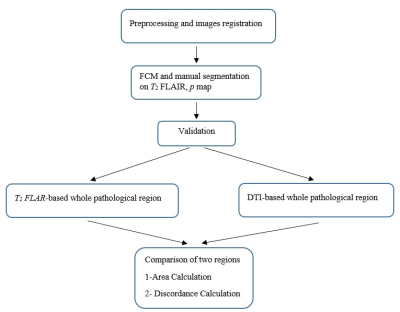
Comparative evaluation of DTI and FLAIR images in assessment of whole pathological region in GBM patients for RT planning; a semi-automatic segmentation approach
Did Not Present
Manijeh Beigi, Mojtaba Safari, Ahmad Ameri, Mohsen ShojaeeMoghadam, Hamidreza SalighehRad
Accurate determination of whole pathological region is still a challenging task and necessary prerequisite step in radiotherapy planning in GBM. This study attempted to propose semi-automatic segmentation method that can extract whole pathogenic tumor on T2-FLAIR and isotropic component (p-map) of diffusion tensor imaging(DTI) with over 90 % sensitivity, specificity and dice score. In addition, the extension of pathological region was compared. Results show that there is significant difference between segmented region on T2-FLAIR and p map. Beyond usual segmentation method for T2-FLAIR, we have highlighted DTI parametric maps because of its information on tumor infiltration.
|
|
3809.
 |
18 |
 A Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) compatible anthropomorphic pelvic phantom for MRI-guided radiotherapy. A Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) compatible anthropomorphic pelvic phantom for MRI-guided radiotherapy.
Kamal Singhrao, Yingli Yang, Thomas Wong, Geraldine Chee, Jie Fu, Daniel Low, John Lewis
We present an anthropomorphic pelvic phantom for MR-guided radiotherapy. Materials were selected to mimic bone, fat and muscle and produce tissue-like contrast with T1, T2 and T2* weighted MRI sequences and CT. MR and CT tissue quantification results are presented. A comparison between the phantom and patient images acquired using standard prostate radiotherapy MR sequences is presented. The study concludes with an example application of the phantom where we compare the visibility of an implanted gold fiducial marker in phantom and in vivo.
|
|
3810.
 |
19 |
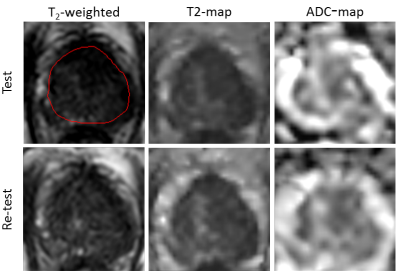
 Repeatability of Quantitative Imaging on the MR-Linac for Treatment Response Monitoring Repeatability of Quantitative Imaging on the MR-Linac for Treatment Response Monitoring
Ernst Kooreman, Petra van Houdt, Marlies Nowee, Vivian van Pelt, Folkert Koetsveld, Leon ter Beek, Johannes Peeters, Uulke van der Heide
The MR-Linac opens the possibility for accurate daily treatment response monitoring. Quantitative MR imaging is a promising tool to quantify day-to-day changes. Therefore the performance of quantitative imaging of the MR-Linac needs to be assessed. In this study, we investigated the repeatability of T2 and ADC mapping using test-retest data of patients with prostate cancer. We calculated the within-patient coefficient of variation (wCV) and compare this to data from a conventional diagnostic 3T scanner. The MR-Linac performs similar to the diagnostic scanner regarding T2 mapping as wCV values are comparable. However, the repeatability for ADC mapping is lower on the MR-Linac.
|
|
3811.
 |
20 |
 Susceptibility-based positive contrast for visualization and localization of implanted brachytherapy seeds in realistic prostate phantoms Susceptibility-based positive contrast for visualization and localization of implanted brachytherapy seeds in realistic prostate phantoms
Reyhaneh Nosrati, Matt Wronski, Ananth Ravi, Ana Pejovic-Milic, Gerard Morton, Greg Stanisz
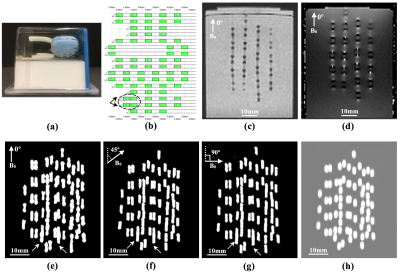
Employing susceptibility-based positive contrast for depiction and localization of closely implanted elongated paramagnetic objects (i.e. brachytherapy seeds) is very challenging due to the orientation dependence and/or size overestimation of reconstructed object. In this study, 321 brachytherapy seeds were implanted in four realistic prostate phantoms; all phantoms were scanned at three different angles on a 1.5T MR scanner. A novel susceptibility-based workflow was proposed for visualization and localization of the seeds. For all scanning angles the reconstructed seed shapes, centroids and orientations were identical and no significant difference was found between the proposed method and the current clinically used CT-based method.
|
|
3812.
 |
21 |
 Response Assessment in Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy of Recurrent High Grade Glioma through Characterization of Tumor Vascularization and Perfusion using DCE MRI Response Assessment in Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy of Recurrent High Grade Glioma through Characterization of Tumor Vascularization and Perfusion using DCE MRI
Charlotte Debus, Maximilian Knoll, Ralf Floca, Sebastian Adeberg, Jürgen Debus, Amir Abdollahi
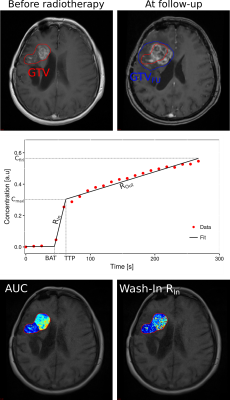
Carbon-ion radiotherapy holds great potential for treatment of recurrent high-grade glioma, where re-irradiation is difficult due to prior dose burden. We investigated effects of carbon RT on tumor micro-vascularization and micro-circulation, by evaluating semi-quantitative parameters derived from DCE MRI before and after irradiation. Results show augmented perfusion parameters AUC, maximum enhancement and wash-out after therapy compared to pre-RT scans, and lower AUC, wash-in, wash-out and final uptake for responders to therapy compared to non-responders. Additionally, significantly lower values for AUC, wash-out, maximum enhancement and final uptake could be observed for progressed tumor volumes compared to irradiated tumor volumes.
|
|
3813.
 |
22 |
 Changes in Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) of the Dominant Tumor during Dose-Painted Radiotherapy and High Dose Rate (HDR) Brachytherapy for Prostate Cancer Changes in Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) of the Dominant Tumor during Dose-Painted Radiotherapy and High Dose Rate (HDR) Brachytherapy for Prostate Cancer
Sangjune Lee, Jenny Lee, Tim Craig, Alejandro Berlin, Peter Chung, Cynthia Ménard, Warren Foltz
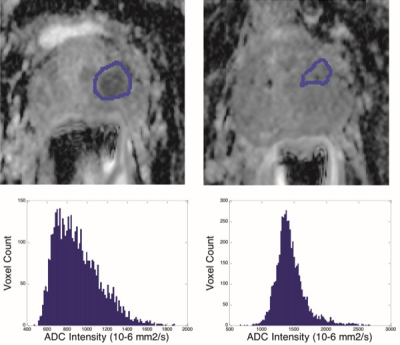
PIRADS-2 compliant Apparent Diffusion Coefficient mapping (ADC) and T2-weighted imaging was performed at baseline and week 6 of radiotherapy in 57 patients with localized prostate cancer. 101 radiomics features were calculated across the gross tumor volume (GTV) and whole prostate (WP). GTV ADC histogram metrics (10 percentile, median, mean) increased (p<1e-06) at equivalent maximum ADC values. High percentile WP ADC histogram metrics (90 percentile, maximum) decreased (p<2e-05) at equivalent 10 percentile/median/mean values. Between 44 (for GTV ADC) and 65 (for WP applied to T2w-weighted images) radiomics features were significantly different and will be explored as potential early predictive biomarkers of response.
|
|
3814.
 |
23 |
 Quantification of MRI visibility and artefacts at 3T of liquid fiducial marker in a pancreas tissue mimicking phantom Quantification of MRI visibility and artefacts at 3T of liquid fiducial marker in a pancreas tissue mimicking phantom
Sergej Schneider, Rasmus Jølck, Esther Troost, Aswin Hoffmann
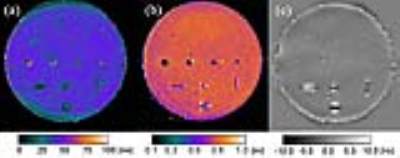
In image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), implanted fiducial gold markers are used for position verification and for registration of computed tomography (CT) and MRI scans used for delineation purposes. Recently, a liquid biodegradable carbohydrate based injectable soft tissue marker, compatible with CT and MRI, has been developed. Our aim was to quantitatively evaluate the tradeoff between visibility and artifacts of this marker on MRI and compare this with two solid fiducial gold markers commonly used in IGRT of PDAC.
|
|
3815.
 |
24 |
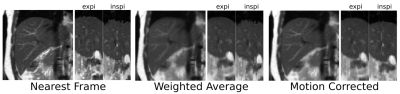
 Respiratory-Resolved Single-Shot Fast Spin Echo with Improved Volume Consistency Respiratory-Resolved Single-Shot Fast Spin Echo with Improved Volume Consistency
Anne Menini, Daniel Litwiller, Yuji Iwadate, Ersin Bayram
We present a motion-correction-based method for improving through-slice volume consistency for respiratory-resolved single-shot fast spin echo for the purposes of image-guided radiation therapy planning.
|
|
Endogenous Contrast Mechanisms in Cancer Imaging
Electronic Poster
General Cancer Imaging
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
08:15 - 09:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
3816.
 |
25 |
 Anisotropy of Anomalous Diffusion Helps in Grading of Gliomas Anisotropy of Anomalous Diffusion Helps in Grading of Gliomas
Boyan Xu, Lu Su, Zhenxiong Wang, Yang Fan, Bing Wu, Gaolang Gong, Wenzhen Zhu, Peiyi Gao, Jia-Hong Gao
Anomalous diffusion model has been introduced and shown to be beneficial in clinical applications, compared with conventional diffusion models. However, the anisotropy of anomalous diffusion was neglected and its clinical feasibility remains uncertain. In this study, the use of anisotropy of anomalous diffusion is investigated for differentiating low- and high-grade cerebral gliomas. Based on the results, it is shown that the anisotropy of anomalous diffusion offers advantages compared to that of conventional diffusion models, indicating its potential to facilitate future studies of neuropathological changes in clinical populations.
|
|
3817.
 |
26 |
The Restricted Diffusion Model for Differentiation of Tumor from Normal Tissue in Glioblastoma
Video Permission Withheld
Yuan Li, Michelle Kim, Theodore Lawrence, Parmar Hemant, Yue Cao
It is a challenge to differentiate non-enhanced solid tumor from edema in glioblastoma. This study applied the restricted diffusion model to high b-value diffusion weighted images to characterize glioblastoma. The formation of the restricted diffusion model was derived for bi-polar diffusion gradients. The parameters fitted by the restricted diffusion model can differentiate solid tumor from edema and normal-appearing white matter and grey matter, better than the conventional apparent diffusion coefficient and the bi-exponential model without accounting for diffusion restriction of intra-cellular water.
|
|
3818.
 |
27 |
 Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) provides reliable measures of blood volume in patients with metastases to the brain Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) provides reliable measures of blood volume in patients with metastases to the brain
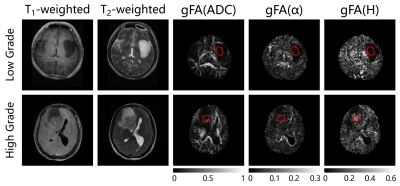
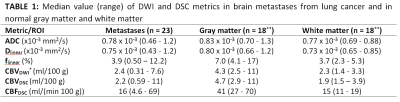
Line Nilsen, Knut Hole, Ingrid Digernes, Endre Grøvik, Oliver Geier, Edmund Reitan, Cathrine Saxhaug, Åslaug Helland, Kari Jacobsen, Birger Breivik, Dag Sætre, Kyrre Emblem
In this study, we aimed to assess the potential of using intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) for measuring cerebral blood volume (CBV) in brain metastases and normal brain tissue. DWI was acquired with b=0, 200, 300 and 1000s/mm2 in nineteen patients with 23 brain metastases from lung cancer. Asymptotic IVIM fitting yielded an estimation of the perfusion fraction, and subsequent estimation of CBV. CBVDWI in brain metastases and gray matter correlated significantly with CBV obtained from conventional DSC MRI. Our results suggest that IVIM may serve as an independent and reliable surrogate marker of blood volume in well perfused brain tissue.
|
|
3819.
 |
28 |
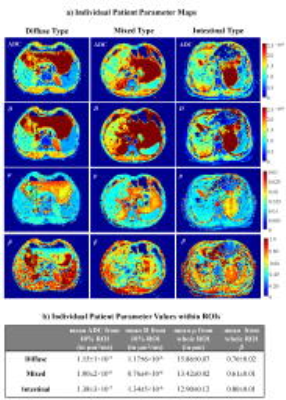
 In Vivo Assessment of Lauren Classification for Gastric Cancer Using Diffusion MRI with a Fractional Order Calculus Model In Vivo Assessment of Lauren Classification for Gastric Cancer Using Diffusion MRI with a Fractional Order Calculus Model
Muge Karaman, Lei Tang, Ziyu Li, Yu Sun, Jia Fu Ji, Xiaohong Zhou
Gastric cancer (GC) is the second most common cause of cancer-related mortality globally. Histological assessment of GC has been based on Lauren classification which categorizes the tumor according to its morphological features. In respond to the need for probing biological tissue complexity, a growing number of diffusion-weighted imaging studies have focused on revealing tissue microstructures by measuring non-Gaussian diffusion behaviors. One of these techniques is the fractional order calculus (FROC) model. In this study, we have used the FROC model to investigate non-invasive imaging-based assessment of GC, providing an alternative to histopathology-based Lauren classification.
|
|
3820.
 |
29 |
 Whole Body Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Paediatric Hodgkin’s Lymphoma; The Application of Quantitative Parameters for Nodal Staging Whole Body Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Paediatric Hodgkin’s Lymphoma; The Application of Quantitative Parameters for Nodal Staging
Arash Latifoltojar, Paul Humphries , Athar Haroon , Leon Menezes, Shonit Punwani
Nodal disease on whole-body MRI (WB-MRI) is mainly assessed using size criteria that could misclassify sub-centimeter lymphomatous nodes. In this study we investigated the comparative performance of anatomical WB-MRI derived nodal-size and signal-intensity; and whole-body diffusion-weighted-imaging (WB-DWI) nodal-size and apparent-diffusion-coefficient (ADC) measurements for determination of nodal-disease status. We showed that diseased nodes had significantly lower ADCs than benign nodes. We also noticed that for nodes deemed negative for disease based on size criteria (measuring 5-9 mm) ADC was significantly lower for FDG PET-CT -positive compared to FDG PET-CT -negative nodes. We also note that the performance of ADC was not greater than simple size measurement and concluded that there were no added advantage for quantitative measurements to simple size criteria on WB-MRI.
|
|
3821.
 |
30 |
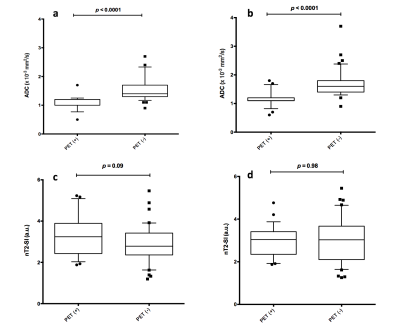
 Whole body 3.0 T MRI for Staging Lymphomas: An Assessment of Multiple Sequences Compared to Reference Standard Imaging Whole body 3.0 T MRI for Staging Lymphomas: An Assessment of Multiple Sequences Compared to Reference Standard Imaging
Arash Latifoltojar, Mark Duncan, Maria Klusmann, Alan Bainbridge, Deena Neriman, Francesco Fraioli, Jonathan Lambert, Kirit Ardeshna, Shonit Punwani
In lymphomas, whole-body MRI (WB-MRI), integrating structural / functional MRI sequences, offers an alternative radiation-free imaging method to standard radiological techniques. In this work, we evaluated multiple MRI sequences as part of a WB-MRI protocol for staging of 22 newly-diagnosed Hodgkin’s lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients compared to reference-standard 18F-FDG PET-CT. We found that the performance of WB-MRI for nodal / extra-nodal disease detection and Ann-Arbor staging were at best when the entire protocol was reviewed. We observed an inferior diagnostic performance of WB-MRI using diffusion-weighted-imaging and an improved diagnostic performance when T2-weighted / post-contrast WB-MRI were reviewed.
|
|
3822.
 |
31 |
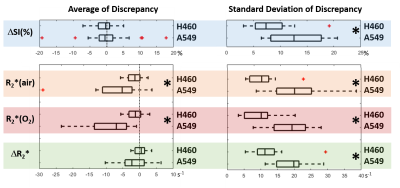
 The effect of flow suppression on BOLD MRI of lung tumor The effect of flow suppression on BOLD MRI of lung tumor
Heling Zhou, Olivier Belzile, Zhang Zhang, Jo Wagner, Chul Ahn, James Richardson, Debabrata Saha, Rolf Brekken, Ralph Mason
Blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) MRI is used to provide information on tumor oxygenation. However, the measurements are susceptible to blood flow changes, which often occur during hyperoxic gas challenge. This study investigated the extent of flow sensitivity by comparing BOLD measurements with and without flow suppression using two orthotopic lung xenograft tumor models. Flow suppression was found to affect multiple measurements including ΔSI(%) and R2*. The range of discrepancy was smaller in R2* than the ΔSI(%). High similarity was found in spatial patterns. ROI and spatial pattern analysis showed higher sensitivity to flow in A549 tumors than H460 tumors.
|
|
3823.
 |
32 |
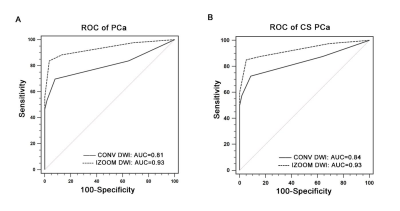
 High b value (2000 s/mm2) Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer Detection: Comparison between Zoomed Field of View (iZOOM) with a Two Dimensional Radiofrequency Pulse (2D-RF) Echo Planar Imaging (EPI) Sequence and Conventional ss-EPI DWI at 3.0 T High b value (2000 s/mm2) Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer Detection: Comparison between Zoomed Field of View (iZOOM) with a Two Dimensional Radiofrequency Pulse (2D-RF) Echo Planar Imaging (EPI) Sequence and Conventional ss-EPI DWI at 3.0 T
Shuai Ma, Kangjie Xu, Huihui Wang, Huihui Xie, Hongxia Sun, Juan Wei, Xiaodong Zhang, Xiaoying Wang
This study aims to evaluate diagnostic efficacy of high b value (2000s/mm2) zoomed field of view (iZOOM) with a 2D-RF EPI sequence, compared with conventional ss-EPI (CONV) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) for peripheral zone (PZ) prostate cancer (PCa) detection at 3.0 T. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System version 2 (PI-RADS v2) were used as evaluation tool and the TRUS-guided systematic plus targeted biopsies was considered as reference standard. It demonstrated iZOOM could provide excellent visual conspicuity as well as a better diagnostic performance compared with CONV DWI in PZ, especially in the small lesions and the lesions abutting the capsule.
|
|
3824.
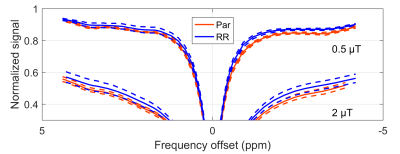 |
33 |
 Differentiation of Normal and Radioresistant DU145 Tumour Xenografts in Mice Using CEST MRI Differentiation of Normal and Radioresistant DU145 Tumour Xenografts in Mice Using CEST MRI
Wilfred Lam, Wendy Oakden, Leedan Murray, William Chu, Stanley Liu, Greg Stanisz
The differentiation of normal and radioresistant tumour potentially allows the tailoring of cancer treatment to the patient. DU145 prostate cancer cells from normal and radioresistant cell lines were injected in mouse hind limb and allowed to grow into tumours. The tumours were imaged within 48 h before and after x-ray therapy using CEST. The magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) was compared between tumours grown from each cell line and at both time points. The MTR was significantly different at a frequency offset of –3.3 ppm at both time points. T1 and T2 values were not found to be significantly different.
|
|
3825.
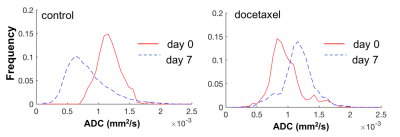 |
34 |
 Diffusion weighted MRI simplifies therapy monitoring in TRAMP mice Diffusion weighted MRI simplifies therapy monitoring in TRAMP mice
Jana Kim, Caroline Søgaard, Eugene Kim, Tone Bathen, Marit Otterlei, Siver Moestue, Deborah Hill
Transgenic mouse models of prostate cancer have advantages over xenograft tumor models as the cancer arises spontaneously and can be studied in immunocompetent mice, thus being highly biologically relevant. However, in vivo monitoring of cancer progression and treatment response is challenging and most studies rely on prostate volume measurements. Here we show that diffusion weighted imaging is a helpful tool for assessing response to chemotherapy in transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) mice.
|
|
3826.
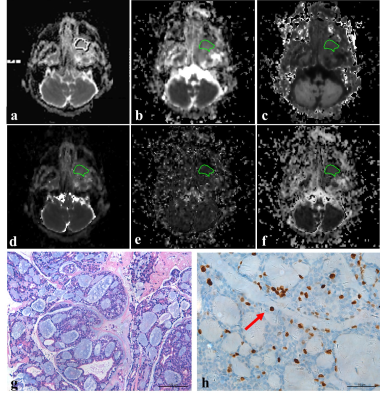 |
35 |
 Standard Diffusion-Weighted, Diffusion Kurtosis and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MR Imaging of Sinonasal Malignancies: Correlations with Ki-67 Proliferation Status Standard Diffusion-Weighted, Diffusion Kurtosis and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MR Imaging of Sinonasal Malignancies: Correlations with Ki-67 Proliferation Status
Zebin Xiao, Zuohua Tang, Jinwei Qiang, Yufeng Zhong, Rong Wang, Zhongshuai Zhang
This study aimed to explore the correlations between parameters derived from standard diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) with the Ki-67 proliferation status. Our preliminary study shows that DWI-derived parameters from different models are capable of providing different pathophysiological information. DWI, DKI and IVIM parameters are associated with Ki-67 proliferation status. Kmax derived from DKI is the strongest independent factor for the prediction of Ki-67 proliferation status.
|
|
3827.
 |
36 |
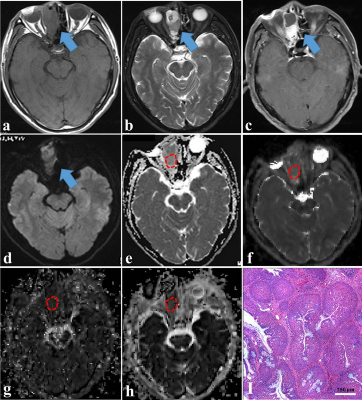
 Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MR Imaging in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant Sinonasal Lesions: Comparison with Conventional Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MR Imaging in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant Sinonasal Lesions: Comparison with Conventional Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
Zebin Xiao, Zuohua Tang, Jinwei Qiang, Yufeng Zhong, Rong Wang, Zhongshuai Zhang
This study aimed to evaluate the value of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in the differentiation between benign and malignant sinonasal lesions and to compare the diagnostic performance of IVIM with conventional diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Our preliminary study shows that ADC, D and f values may be considered as discriminating markers for identifying benign and malignant sinonasal lesions. The combination of D and f values demonstrates significantly higher sensitivity, specificity and accuracy than the ADC value, revealing that IVIM appears to be a more valuable tool than conventional DWI for distinguishing benign from malignant sinonasal lesions.
|
|
3828.
 |
37 |
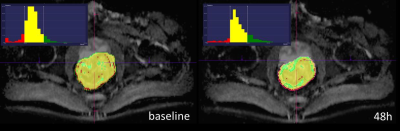
ADC histogram analysis of rectal cancer patients for early detection of therapeutic efficacy of neoadjuvant radio-chemotherapy: initial results.
Video Permission Withheld
Martin Buechert, Oliver Schäfer
Successful monitoring of neoadjuvant radiochemo therapy will allow early selection of responder and non-responder. Beside conventional morphological MRI additional functional MRI in combination with advanced analysis strategies like histogram analysis of ADC values are promising. Initial results of an ongoing clinical study are presented.
|
|
3829.
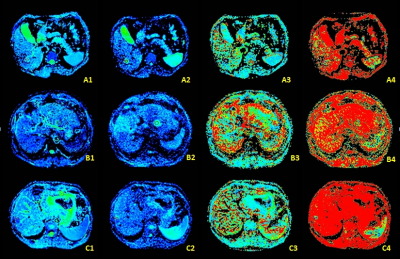 |
38 |
 Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging for differential diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hepatic hemangioma(HHA) and hepatic metastasis(HM). Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging for differential diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hepatic hemangioma(HHA) and hepatic metastasis(HM).
Ye Ju, Ailian Liu, Meiyu Sun, Lihua Chen, Lizhi Xie
The diffusion property of tumor tissues largely depends on cell density, which may also be predictive features of malignancy in some types of tumors. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging is an extension of diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) that can be used to investigate both diffusion and perfusion changes in tissues. Comparing the IVIM parameters between carcinoma (HCC), hepatic hemangioma and hepatic metastasis, we found that IVIM can facilitates understanding of tumor tissue characteristics of perfusion and diffusion, and it may provide more useful information to distinguish hemangiomas from other two malignant tumors.
|
|
3830.
 |
39 |
 Visualization of Peritumoral Fasciae by Dual-band Long-T2 Saturation UTE at 7T MRI Visualization of Peritumoral Fasciae by Dual-band Long-T2 Saturation UTE at 7T MRI
Yupeng Cao, Xiaohan Zhou, Yang Fan, Yuqing Wang, Wentao Liu, Dong Han
Fasciae are related with the tumor invasion. To investigate the alteration of peritumoral fasciae during tumor invasion, a novel dual-bandlong-T2saturation UTE sequence was proposed in this study. This sequence was applied to suppress the signal from long-T2 tissue components, consequently directly providing short-T2 contrast. Tumor-bearing Balb/c mouse was scanned on a 7T MRI scanner with the proposed sequence and standard FLASH to compare the quality of fasciae imaging. The results showed that the long-T2 signal was effectively suppressed and the peritumoral fasciae was visualized with this novel technique. This technique will give potential clinical feasibility of the fascia-related diseases.
|
|
3831.
 |
40 |
 Detecting Glioblastoma invasion using Multi-parametric MRI and Quantitative Assessment with in-plane Histology Detecting Glioblastoma invasion using Multi-parametric MRI and Quantitative Assessment with in-plane Histology
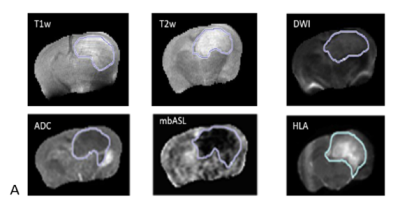
Haitham Al-Mubarak, Antoine Vallatos, Jim Birch, Lindsay Gallagher, Joanna Birch, Lesley Glmour, John Foster, William Holmes, Anthony Chalmers
We evaluate the ability of a range of MRI techniques to probe glioblastoma invasion in a mouse model by comparison with in-plane stacked histology, enabling a direct voxel-to-voxel comparison between MRI and histology (HLA stain). We used the G7 mouse model which exhibits highly invasive tumour margins and scanned using T1 weighted, T2 weighted, T2map, Diffusion Tensor Imagining (DTI) and Perfusion Weighting Imaging (PWI). Registration of MRI datasets with stacked in-plane histology allows direct quantitative validation using DICE and ROC analysis, showing that PWI gave the best indication of tumour cell invasion.
|
|
3832.
 |
41 |
 Non-linear Mechanics Allows Non-invasive Quantification of Interstitial Fluid Pressure Non-linear Mechanics Allows Non-invasive Quantification of Interstitial Fluid Pressure
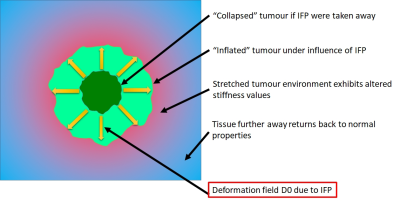
Daniel Fovargue, Jack Lee, Marco Fiorito, Adela Capilnasiu, Sweta Sethi, Stefan Hoelzl, Jurgen Runge, Jose de Arcos, Arnie Purushotham, Khesthra Satchithananda, David Nordsletten, Ralph Sinkus
Established tumour treatments include drugs and the emerging class of cell-based therapies. Individual tumours can counteract the delivery of the therapy, for example, they can feature high internal pressures (IFP) caused by blood vessels that are different from normal tissues. Furthermore, a drop in IFP is a well-established marker for successful therapy. Here we demonstrate in simulations, phantom experiments, fatty breast tissue, and a benign breast lesion that tissue biomechanics as quantified via MR-Elastography (MRE) allows in combination with non-linear mechanics to estimate IFP in absolute units non-invasively.
|
|
3833.
 |
42 |
 Pilot Study of Rapid MR Pancreas Screening for Patients with BRCA Mutation Pilot Study of Rapid MR Pancreas Screening for Patients with BRCA Mutation
Giuseppe Corrias, Andrea Agostini, Gabriella Carollo, Luca Saba, Lorenzo Mannelli
Patients with BRCA mutations are offered breast MRI because of their increased risk of breast cancer, but no screening strategy is available for other BRCA-associated malignancies including pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. In this protocol, we optimize the use of several recent developments in body MRI for a rapid pancreatic screening in BRCA mutation carriers: first, rapid relatively motion insensitive T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and navigator triggering (NT), where real-time tracking of the diaphragm position is performed. Secondly advances in diffusion-weighted-imaging (DWI). These techniques have changed our ability to screen for malignancies, in specific organs, such as the pancreas.
|
|
3834.
 |
43 |
Monitoring the Growth of Individual Tumours in the Mouse Lung using Cardio-Respiratory Synchronised bSSFP MRI
Video Permission Withheld
Ana Gomes, Paul Kinchesh, Danny Allen, Veerle Kersemans, Stuart Gilchrist, Luiza Madia-Lourenco, Anderson Ryan, Sean Smart
bSSFP imaging is used in-vivo to image small tumours in the mouse lung, at an isotropic resolution of 200µm in under 10 minutes per scan. Cardio-respiratory synchronisation using prospective gating control is used to minimise motion artefacts efficiently, and a 4 step RF phase cycle is used to eliminate banding artefact. Growth of individual tumours in multi-focal lung cancer can be measured with a throughput of >4 mice per hour.
|
|
3835.
 |
44 |
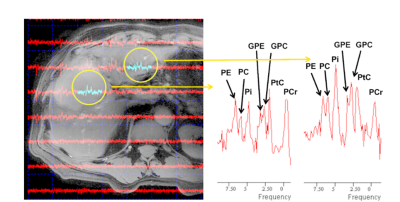
 Towards an ultra-high field virtual biopsy for hepatic cancers using phospholipid metabolism Towards an ultra-high field virtual biopsy for hepatic cancers using phospholipid metabolism
Deb Rivera, IML van Kalleveen, Catalina Arteaga de Castro, Hanneke Laarhoven, Dennis Klomp, Wybe van der Kemp, Jaap Stoker, Aart Nederveen
At 7T 31P spectroscopy becomes possible on clinically relevant scales. Here we tackle the greatest challenge in multi-parametric imaging at high-field – creating localizers and radiological-grade images in the body in the absence of a bore body coil. By using antennas rather than loop coils, we image the full extent of the liver (n=10). Combining antennas with parallel transmit, allows radiological-grade images. Although technically feasible, it is not yet possible to obtain multi-nuclear spectra and parallel transmit images within the same scan session. We combine the methods by rebooting the scanner mid-exam, and demonstrate the method can be used for imaging patients.
|
|
3836.
 |
45 |
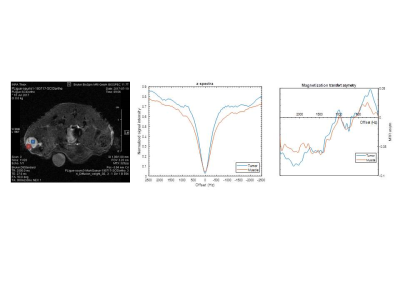
CEST MRI to contrast chondrosarcoma tumors: two contrasts in one acquisition.
Video Permission Withheld
Leslie Mazuel, Aurélien Voissière, Valérie Weber, Yvain Gérard, Sophie Besse, Jean-Marie Bonny, Elisabeth Miot-Noirault, Caroline Peyrode, Guilhem Pagès
This study aims to develop a non-invasive CEST MRI method to evaluate simultaneously pH and glycoaminoglycans (GAG) as a new imaging method for assessing hypoxic and chondrogenic status in chondrosarcoma in vivo.
|
|
3837.
 |
46 |
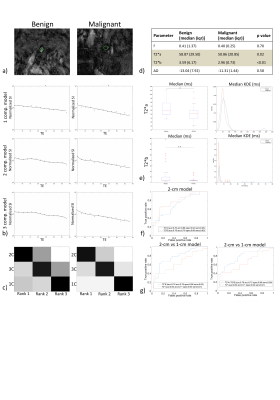
 Multi-exponential T2* mapping distinguishes benign/malignant lymph nodes in rectal cancer patients: an ex-vivo and in-vivo experiment Multi-exponential T2* mapping distinguishes benign/malignant lymph nodes in rectal cancer patients: an ex-vivo and in-vivo experiment
Inês Santiago, João Santinha, Andrada Ianus, Nickolas Papanikolaou, Celso Matos, Noam Shemesh
In rectal cancer patient management, quality-of-life compromise due to unnecessary neoadjuvant chemoradiation is a major concern and may be driven by false positive lymph node(LN) staging. We sought to distinguish benign LNs from LNs with different patterns of malignant infiltration by investigating multi-exponential decay in multi-gradient-echo(MGE) MRI ex-vivo, at 16.4T. The experiment was translated to the clinic and performed at 1.5T during rectal cancer staging. We found that the 2-compartment model of T2* decay allows malignant and benign LNs to be distinguished in clinical images with a higher specificity than that of conventional criteria, namely short-axis>5mm, border irregularity and mixed signal intensity.
|
|
3838.
 |
47 |
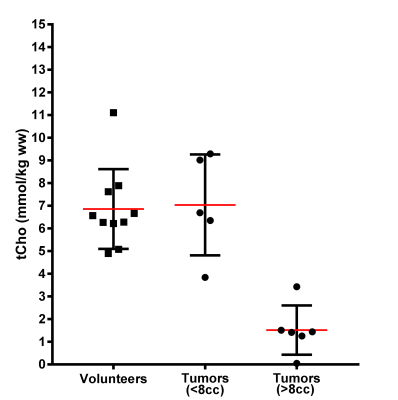
 Levels of choline-containing compounds are not increased in human liver metastases of colorectal cancer: an assessment by 1H MR spectroscopy Levels of choline-containing compounds are not increased in human liver metastases of colorectal cancer: an assessment by 1H MR spectroscopy
Edwin ter Voert, Linda Heijmen , Jack van Asten , Alan Wright , Iris Nagtegaal , Cornelis Punt , Johannes de Wilt, Hanneke van Laarhoven , Arend Heerschap
The commonly observed relative signal increase of choline-containing compounds (tCho) in 1H MR spectra of tumors may serve as a diagnostic biomarker. Here we evaluate the potential of this tCho signal in 1H MR spectra of the human liver to assess metastases of colorectal cancers. An increased tCho signal was not observed for these metastases. With increasing tumor volumes, the tissue levels of tCho decreased. The likely reason is a larger necrotic voxel fraction as it correlated with more higher ADC values assessed by diffusion weighted imaging. A Bland-Altman analysis revealed average repeatability in normal livers and poor repeatability in tumors.
|
|
3839.
 |
48 |
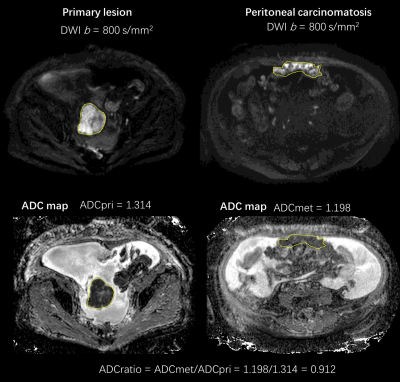
 Relationship of apparent diffusion coefficient on diffusion-weighted imaging and tumour burden in ovarian cancer Relationship of apparent diffusion coefficient on diffusion-weighted imaging and tumour burden in ovarian cancer
He An, Elaine Lee, Queenie Chan
To investigate the relationship of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and tumour burden in ovarian cancer. The ADC of primary ovarian tumour (ADCpri), peritoneal carcinomatosis (ADCmet), and the ratio of ADCmet/ADCpri (ADCratio) were correlated with the total tumour volume (TV) contoured on T2WI as representation of tumour burden in ovarian cancer. Significant correlations were found between ADCmet and TV, and between ADCratio and TV. Our study suggested that the analysis of ADC might provide important information on tumour burden in OC.
|
|
Predictive Cancer Imaging
Electronic Poster
General Cancer Imaging
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
09:15 - 10:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
3912.
 |
1 |
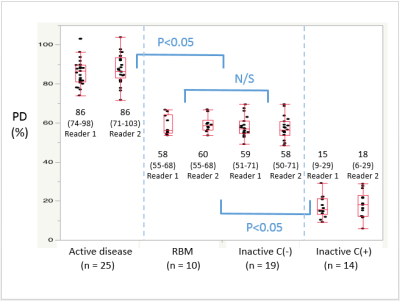
 Synthetic MRI of bone metastases in castration-resistant prostate cancer: detection of tumor activity and calcifications. Synthetic MRI of bone metastases in castration-resistant prostate cancer: detection of tumor activity and calcifications.
Yuki Arita, Taro Takahara, Soichiro Yoshida, Thomas Kwee, Tatsuaki Kobayashi, Chikako Ishii, Jun Kurasawa, Kazuya Sugimoto, Nobuya Higuchi, Yasuhisa Fujii
We quantified T1, T2, and proton density (PD) of bone metastases in castration-resistant prostate cancer with synthetic MRI (SyMRI). Bone foci of interest were classified into four groups; active disease, red bone marrow (RBM), inactive disease without calcification (Inactive C(-)), and inactive disease with calcification (Inactive C(+)). Active disease group showed very high PD, and Inactive C(+) group showed very low PD. Both Inactive C(-) and RBM showed medium values. Significant differences were noted among these three divisions. SyMRI thus shows clinical potential to differentiate active/inactive lesions, calcifications, and red bone marrow in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
|
|
3913.
 |
2 |
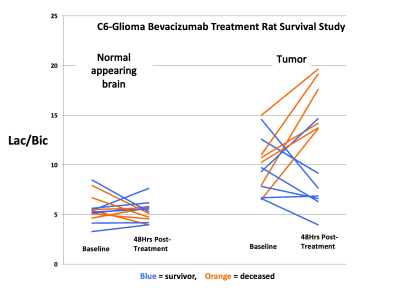
 Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate Imaging Predicts Survival in Rat C6 Glioma Model Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate Imaging Predicts Survival in Rat C6 Glioma Model
Keshav Datta, Mette Lauritzen, Milton Merchant, Taichang Jang, Shie-Chau Liu, Ronald Watkins , Ralph Hurd, Lawrence Recht, Daniel Spielman
The [1-13C]Lactate/[1-13C]Bicarbonate ratio at 48 hrs post-treatment, as measured in a hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate experiment, was found to accurately predict the survival in rat C6 glioma model treated with a single dose of the anti-VEGF drug Bevacizumab.
|
|
3914.
 |
3 |
 Radiomics: a novel MRI-based method of predicting recurrence in chordoma Radiomics: a novel MRI-based method of predicting recurrence in chordoma
Wei Wei, Ke Wang, Kaibing Tian, Zhenyu Liu, Liang Wang, Junting Zhang, Zhen Wu, Jie Tian
In order to find the relationship between MRI image and the postoperative recurrence of chordoma, we used a novel radiomics method for quantitative analysis of MRI image. Finally successfully predicted the probability of postoperative recurrence of chordoma.
|
|
3915.
 |
4 |
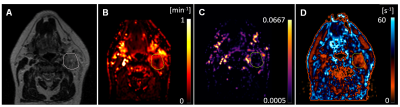
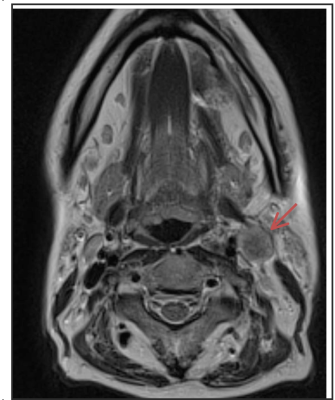
 Low nodal plasma volume is associated with poor treatment response in head and neck cancer treated with induction chemotherapy. Low nodal plasma volume is associated with poor treatment response in head and neck cancer treated with induction chemotherapy.
Rafal Panek, Kee Wong, Liam Welsh, Alex Dunlop, Dualta Mcquaid, Angela Riddell, Dow-Mu Koh, Martin Leach, Shreerang Bhide, Kevin Harrington, Christopher Nutting, Kate Newbold, Maria Schmidt
Impaired tumour perfusion results in decreased efficacy of cancer treatment. In this work we investigated the optimal timing and predictive value of early chemotherapy induced changes, measured by dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) and longitudinal intrinsic susceptibility (IS) MRI. We observed lower plasma volume in metastatic nodes responding poorly to the treatment. We found that for HNSCC patients treated with induction chemotherapy, combining DCE and IS-MRI methods improves early predictive value. This methodology could be used to aid patient stratification and subsequent radiotherapy treatment planning.
|
|
3916.
 |
5 |
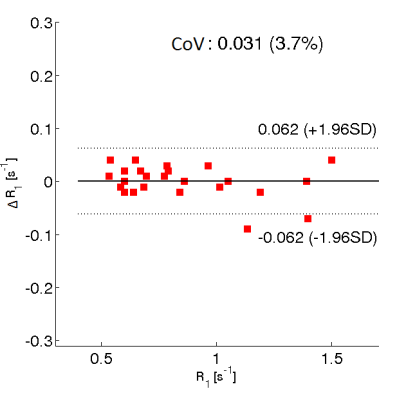
 Oxygen-Enhanced MRI for the Detection of Hypoxia in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Oxygen-Enhanced MRI for the Detection of Hypoxia in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Rafal Panek, Kee Wong, Liam Welsh, Angela Riddell, Dow-Mu Koh, Veronica Morgan, Shreerang Bhide, Kevin Harrington, Christopher Nutting, Maria Schmidt, Martin Leach, James O’Connor, Kate Newbold, Simon Robinson
Tumour hypoxia is a recognized cause of treatment failure. Noninvasive methods to quantify distribution and extent of hypoxia remain an unmet clinical need. Quantitation of the longitudinal relaxation rate, R1, using oxygen-enhanced MRI (OE-MRI), can be used to monitor differences in levels of paramagnetic molecular oxygen in plasma. In this study, we report a significantly reduced hyperoxia-induced ΔR1 response in HNSCC in comparison to the healthy lymph nodes, revealed by OE-MRI. Such a reduction can be attributed to regions of impaired tumour vasculature and hypoxia, the presence of which may be linked to a poorer outcome.
|
|
3917.
 |
6 |
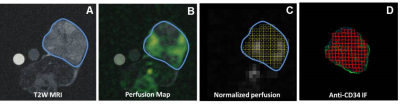
 Correlation of CD31-Based Microvessel Density and Percent Area Measurements against 13C-tert-butanol MRI Perfusion Mapping in a Sunitinib-Resistant RCC Xenograft Correlation of CD31-Based Microvessel Density and Percent Area Measurements against 13C-tert-butanol MRI Perfusion Mapping in a Sunitinib-Resistant RCC Xenograft
Patricia Coutinho de Souza, Aaron Grant, Xiaoen Wang, Rupal Bhatt, Gopal Varma, David Alsop, Leo Tsai
Tumor heterogeneity is deeply associated with regional perfusion. Improved evaluation of local perfusion, by imaging or histology, can be useful for tracking tumor progression and treatment. Here we use h13C-tert-butanol, a high-SNR quantitative MRI perfusion marker, to map perfusion in untreated (UT) and sunitinib-resistant (SR) renal cell carcinoma (RCC) xenografts. This study investigates the correlation between these perfusion maps with histologic measures of vascularity using CD31-labeled sections.
|
|
3918.
 |
7 |
 Hydrogen magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a technique for predicting clinical outcome in patients with head & neck squamous cell cancer with locally advanced cervical nodal disease Hydrogen magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a technique for predicting clinical outcome in patients with head & neck squamous cell cancer with locally advanced cervical nodal disease
Sola Adeleke, Marianthi-Vasiliki Papoutsaki, Harbir Sidhu, Alan Bainbridge, David Price, Dawn Carnell, Martin Forster, Ruheena Mendes, Shonit Punwani
Hydrogen magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) is a technically challenging modality. It has the potential to provide specific metabolic information that could guide clinical decision making. In this study we assess feasibility of performing 1H MRS in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) prior to treatment and explore its correlation with post-treatment outcomes.
|
|
3919.
 |
8 |
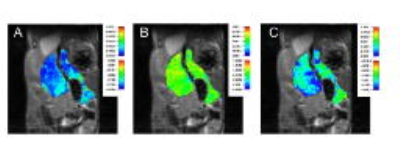
Noninvasive prediction of tumor-fibrosis using texture analysis of multiparametric MRI in pancreatic cancer model
Video Permission Withheld
Dae Chul Jung, Ravneet Vohra, Seon Young Lee, Kyunghwa Han, Helen Hong, Donghoon Lee
Authors want to evaluate the correlations between texture features of tumor on multi-parametric MRI (mp-MRI) and tumor-fibrosis in animal model of pancreatic cancer. mp-MRI was performed in a genetically engineered mice model of human pancreatic cancer. Texture features of tumors were extracted from each parametric map using texture analysis. Linear regression with LASSO method was used to evaluate the correlations between the texture features and percentage of fibrosis on histologic slides. Several texture features were correlated with tumor fibrosis. Statistical learning showed preliminary prediction model. Texture analysis of mp-MRI is helpful for predicting and monitoring tumor-fibrosis in pancreatic cancer model.
|
|
3920.
 |
9 |
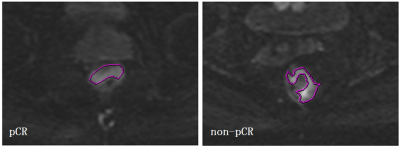
 Prediction of pathological complete response of rectal tumor by radiomics method based on diffusion kurtosis imaging results before neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy Prediction of pathological complete response of rectal tumor by radiomics method based on diffusion kurtosis imaging results before neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
Xiaoyan Zhang, Haitao Zhu, Xiaoting Li, Yanjie Shi, Yingshi Sun, Aijun Zhang, Haoyu Li
Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy is the standard treatment for locally advanced rectal cancer. Patients with pathological complete response (pCR) after NCRT (15~21% of the total) could benefit from either less invasive surgery or a “wait-and-see” strategy. A radiomics model is proposed in this work based on diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) result before NCRT is used to predict pCR of rectal cancer.
|
|
3921.
 |
10 |
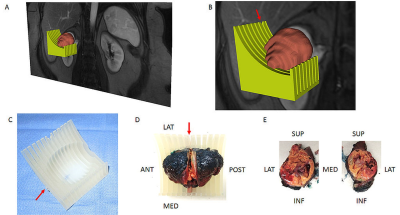
 Development of a Patient-specific Tumor Mold using MRI and 3D Printing Technology for Targeted Tissue Procurement and Radiomics Analysis of Renal Masses Development of a Patient-specific Tumor Mold using MRI and 3D Printing Technology for Targeted Tissue Procurement and Radiomics Analysis of Renal Masses
Durgesh Dwivedi, Yonatan Chatzinoff, Qing Yuan, Jeffrey Cadeddu, Payal Kapur, Ivan Pedrosa
To implement a platform for co-localization of in vivo quantitative multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) features with ex vivo surgical specimens of patients with renal masses using patient-specific 3D-printed tumor molds, which may aid in targeted tissue procurement and radiomics/radiogenomic analyses. Volumetric segmentation of 6 renal masses was performed with 3D Slicer (http://www.slicer.org) to create a three-dimensional (3D) tumor model. All patients successfully underwent partial nephrectomy and adequate fitting of the tumor specimens within the 3D mold was achieved in all tumors. Distinct in vivo MRI features corresponded to unique pathologic characteristics in the same tumor.
|
|
3922.
 |
11 |
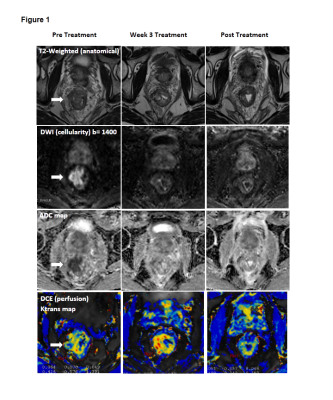
 Rectal cancer: multi-parametric MRI 3-dimensional assessment of intra-tumour heterogeneity and chemoradiotherapy response prediction Rectal cancer: multi-parametric MRI 3-dimensional assessment of intra-tumour heterogeneity and chemoradiotherapy response prediction
Trang Pham, Gary Liney, Karen Wong, Christopher Henderson, Robba Rai, Petra Graham, Malcolm Hudson, Nira Borok, Minh Truong, Mark Lee, Joo-Shik Shin, Michael Barton
This study investigated 3D quantitative histogram assessment of diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MRI in the prediction of chemoradiotherapy (CRT) response in locally advanced rectal cancer. Histopathologic response assessment was centralised and defined according to AJCC tumour regression grade. A whole tumour histogram analysis and combined multiparametric scatterplots of ADC and Ktrans were used to assess tumour heterogeneity and prediction of CRT response. Post-CRT ADC 75th and 90th histogram quantiles were the most promising parameters for prediction of CRT response. However, DCE-MRI and multi-parametric scatterplots combining ADC and Ktrans did not add value in predicting response.
|
|
3923.
 |
12 |
 Early Prediction of Soft Tissue Sarcoma Response to Preoperative Therapy Using DCE-MRI Texture Features Early Prediction of Soft Tissue Sarcoma Response to Preoperative Therapy Using DCE-MRI Texture Features
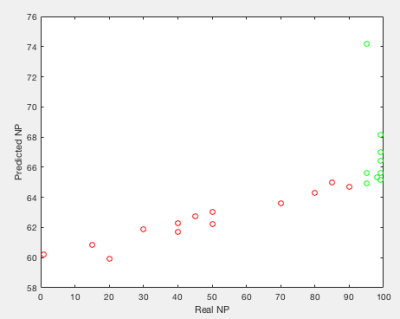
Tristan Xiao, Archana Machireddy, Xubo Song, Alina Tudorica, Aneela Afzal, May Mishal, Brooke Beckett, Megan Holtorf, Torrie Aston, Christopher Ryan, Wei Huang, Guillaume Thibault
23 patients with soft tissue sarcoma (STS) (25 tumors) underwent DCE-MRI before and after one cycle of preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Extended Tofts model (ETM) and Shutter-Speed model (SSM) were used for pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis of DCE-MRI data and generating voxel based PK parametric maps, from which texture features were extracted using different statistical matrix methods. Changes in SZM and RLM features consistently provided good early prediction of therapy response, while more features from the SSM PK maps were good predictors of response than the ETM maps.
|
|
3924.
 |
13 |
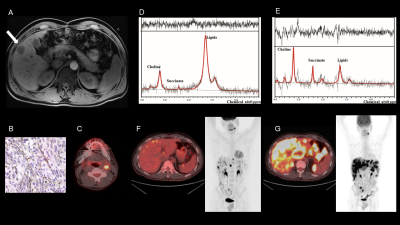
 MRS measurement of succinate in vivo as a biomarker in succinate dehydrogenase deficient tumours MRS measurement of succinate in vivo as a biomarker in succinate dehydrogenase deficient tumours
Mary McLean, Ruth Casey, Benjamin Challis, Rogier ten Hoopen, Thomas Roberts, Graeme Clark, Deborah Pittfield, Helen Simpson, Venkata Bulusu, Kieran Allinson, Lisa Happerfield, Soo-Mi Park, Alison Marker, Olivier Giger, Basetti Madhu, Eamonn Maher, Ferdia Gallagher
We performed respiratory-gated single-voxel 1H-MRS (TE = 144ms; voxel size 2.2-100ml; 96-512 averages) at 3T in tumours with suspected mutations in the mitochondrial enzyme succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) in 15 patients, analysed using LCModel. A germline mutation or epimutation in one of the SDH genes was identified in 11/15 subjects, with concordant MRS findings in 9 subjects, data rejection as technical failure in 4, and equivocal results in 2. Referencing succinate peaks to choline was an important quality control for discrimination of true from false negatives. MRS may provide a useful biomarker of SDH activity in this patient group.
|
|
3925.
 |
14 |
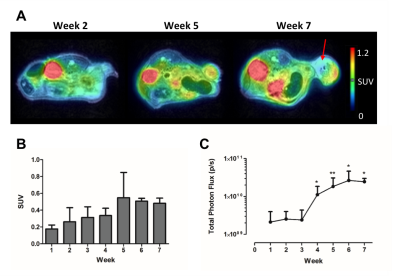
 Assessment of Tumor Microenvironment to Determine the Most Suitable Therapeutic Window in an Ovarian Cancer Model Assessment of Tumor Microenvironment to Determine the Most Suitable Therapeutic Window in an Ovarian Cancer Model
Sarah Belderbos, Kristof Govaerts, Anca Croitor Sava, Jens Wouters, Bella Manshian, Christophe Deroose, Sabine Van Huffel, Stefaan Soenen, Willy Gsell, Uwe Himmelreich
Multimodal imaging, i.e. combining (simultaneous) positron emission tomography (PET)-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and bioluminescence imaging (BLI) allows in-depth assessment of changes in tumor microenvironment over time. In this study, the development of human ovarian xenografts in mice was longitudinally monitored using BLI and PET-MRI to identify the most suitable time window to test nanomaterial-based therapies. Under these conditions, xenografts are viable, vascularized and metabolically active tumor masses with leaky blood vessels after four weeks, indicating a suitable time point for nanomaterial administration. This suggests that a combination of PET, MRI and BLI allows the identification of potential therapeutic windows.
|
|
3926.
 |
15 |
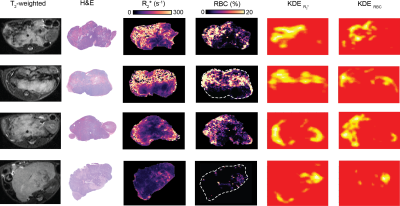
 Spatial comparison of in vivo MRI with digital histology validates R2* as a biomarker of vascular hemodynamics in the Th-MYCN model of neuroblastoma Spatial comparison of in vivo MRI with digital histology validates R2* as a biomarker of vascular hemodynamics in the Th-MYCN model of neuroblastoma
Konstantinos Zormpas-Petridis, Matthew Blackledge, Louis Chesler, Yinyin Yuan, Simon Robinson, Yann Jamin
This study explores the use of automated image analysis pipelines and kernel density estimation (KDE) analysis for hotspot mapping as a generic methodology to spatially evaluate MRI biomarkers with corresponding high-resolution whole-slide digital histology, used here to validate the transverse relaxation R2* as a biomarker of vascular hemodynamics in the Th-MYCN transgenic mouse model of childhood neuroblastoma.
|
|
3927.
 |
16 |
 Imaging immunotherapy resistance in melanoma in vivo and in vitro employing magnetic resonance Imaging immunotherapy resistance in melanoma in vivo and in vitro employing magnetic resonance
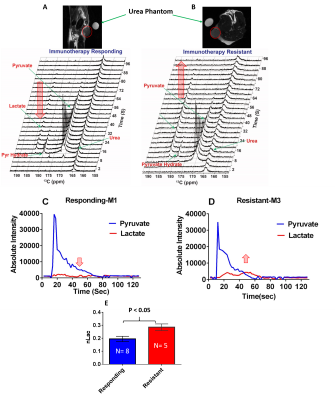
Shivanand Pudakalakatti, Ashvin Jaiswal, Prasanta Dutta, Michael Curran, Pratip Bhattacharya
Identifying immunotherapy resistance and underlying molecular mechanisms of resistance will help in stratifying immunotherapy treatment effectively. However, identifying immunotherapy resistance and its causative mechanisms are elusive. Here we have developed mouse models of immunotherapy resistance and identified molecular mechanisms indicating immunotherapy resistance employing magnetic resonance. In vitro studies showed adaptations in metabolic pathways of glycolysis, fatty acid and purine synthesis in resistant cell lines. In vivo experiments with 1-13C hyperpolarized pyruvate revealed higher pyruvate to lactate conversion in immunotherapy resistant mice compared to responding ones. Hence, pyruvate to lactate ratio can be a potential biomarker to identify immunotherapy resistance in vivo.
|
|
3928.
 |
17 |
 Multi-Resolution Fractal Analysis of DCE-MRI Parametric Maps for Early Prediction of Breast Cancer Therapy Response Multi-Resolution Fractal Analysis of DCE-MRI Parametric Maps for Early Prediction of Breast Cancer Therapy Response
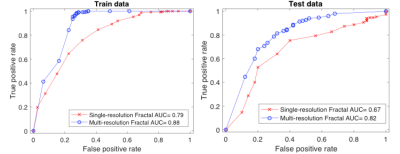
Archana Machireddy, Guillaume Thibault, Alina Tudorica, Aneela Afzal, May Mishal, Kathleen Kemmer, Arpana Naik, Megan Troxell, Eric Goranson, Karen Oh, Nicole Roy, Neda Jafarian, Megan Holtorf, Wei Huang, Xubo Song
DCE-MRI data from 54 breast cancer patients collected before and after one cycle of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were subjected to Shutter-Speed pharmacokinetic analysis. A new texture feature, multi-resolution fractal dimension (FD), was extracted from DCE-MRI parametric maps and compared with single-resolution FD for early prediction of therapy response. The multi-resolution approach appears to provide a richer description of the underlying tumor heterogeneity in perfusion/permeability than the single-resolution FD method, and has higher accuracy in early discrimination of pathologic complete response (pCR) from non-pCR.
|
|
3929.
 |
18 |
 PERFUSION MRI AS A MARKER OF GLIOBLASTOMA INFILTRATION INTO HEALTHY TISSUE PERFUSION MRI AS A MARKER OF GLIOBLASTOMA INFILTRATION INTO HEALTHY TISSUE
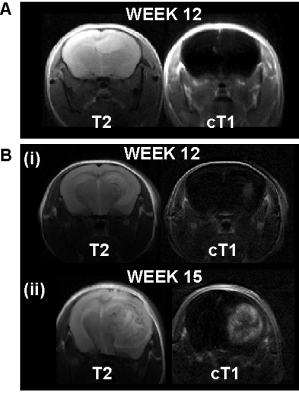
Antoine Vallatos, Haitham Al-Mubarak, Joanna Birch, Lindsay Gallagher, James Mullin, Lesley Gilmour, William Holmes, Anthony Chalmers
We investigate the ability of perfusion MRI to probe glioblastoma infiltration into healthy brain tissue, on a patient-derived mouse model presenting infiltrative tumour margins. Using a high SNR Arterial Spin Labelling sequence and a multiple slice in-plane histology method, we show that perfusion imaging can probe lower tumour cell density regions than conventional MRI. Voxel-to-voxel comparison between perfusion and tumour cell density images, allows identifying a negative relation between tumour cell burden and perfusion at the invasion margins. This relation, related to vascular co-option mechanisms, could be used as a marker of tumour cell infiltration into healthy tissue.
|
|
3930.
 |
19 |
 Diffusion-Weighted MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Histogram Changes In Primary Rectal Cancer Treated With Chemotherapy + Anti-Angiogenic Therapy Versus Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Diffusion-Weighted MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Histogram Changes In Primary Rectal Cancer Treated With Chemotherapy + Anti-Angiogenic Therapy Versus Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation
N. Jane Taylor, Davide Prezzi, J. James Stirling, James d'Arcy, Rob Glynne-Jones, Vicky Goh
Changes in the apparent diffusion co-efficient (ADC) histogram parameters in primary rectal cancers treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy + anti-angiogenic therapy (NAC) differ substantially to those treated with chemoradiation (CRT), reflecting the differing mechanisms of action of these therapies. Higher diffusivity and lower variance post-CRT compared to NAC in responders likely reflects radiotherapy-related inflammation.
|
|
3931.
 |
20 |
 Multi-parametric imaging based differentiation of primary CNS lymphoma from Glioblastoma using T1-Perfusion, Diffusion and Susceptibility-weighted MR Imaging Multi-parametric imaging based differentiation of primary CNS lymphoma from Glioblastoma using T1-Perfusion, Diffusion and Susceptibility-weighted MR Imaging
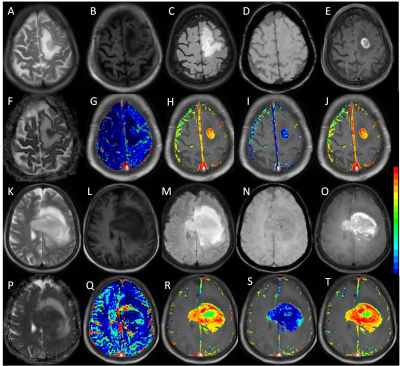
Pradeep Kumar Gupta, Jitender Saini, Ashish Awasthi, Chandra Pandey , Shreelekha Mohapatra, Anup Singh, Rana Patir, Sunita Ahlawat, Manish Beniwal, Anita Mahadevan , Rakesh Kumar Gupta
Glioblastoma and primary CNS lymphoma (PCNSL) need differentiation on pre operative imaging as management strategies for these two pathologies are diverse. Due to the presence of atypical imaging findings in a significant number of cases, it becomes difficult to differentiate these two pathologies on conventional MRI. We utilized multi-parametric imaging methods (T1-perfusion, DWI, and SWI) for possible differentiation of these two entities. In linear discriminant analysis using various imaging parameters we achieved 84% accuracy with AUC 90.14%. We conclude that multi-parametric imaging may prove to be useful in accurate preoperative discrimination of these two pathologies.
|
|
3932.
 |
21 |
 Towards quantitative multiparametric evaluation of response to treatment following loco-regional treatment for HCC- pilot study. Towards quantitative multiparametric evaluation of response to treatment following loco-regional treatment for HCC- pilot study.
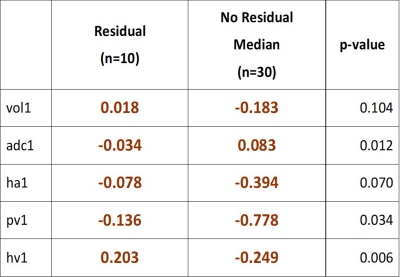
Sonal Krishan, Amit Mehndiratta
The aim of the present study was to explore the feasibility and utility of quantitative volumetric change in ADC, tumor volume and percentage differential enhancement in the various phases in being able to predict response to treatment following loco-regional therapy (LRT).This IRB approved pilot study included 40 consecutive patients following LRT for HCC .Patients with baseline imaging, 1,3 and 6 months follow up dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI were included in our study. Percentage change in arterial, portal venous and hepatic-venous differential enhancement, as well as change in ADC and tumor volume at 1 and 3 months, was calculated for all values. There was global reduction in the percentage of mean volume and differential enhancement is seen in all phases in completely treated study group.In patients with residual tumor, there is paradoxical decrease in ADC and
increase in hepatic venous enhancement at 1 month.Our pilot study has shown that volumetric quantitative evaluation of differential enhancement of the treated lesion in various phases combined with ADC and change in tumour volume are feasible. This has potential to act as surrogate markers for evaluating response to treatment
|
|
3933.
 |
22 |
Functional diffusion maps to assess treatment response in head and neck tumors using SPLICE.
Video Permission Withheld
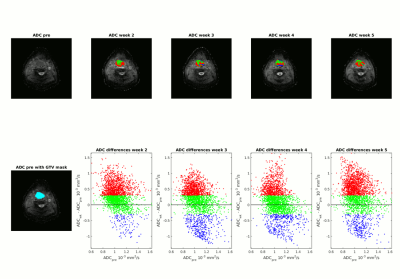
Boris Peltenburg, Tim Schakel, Chris Terhaard, Remco de Bree, Marielle Philippens
ADC changes during chmoradiation treatment might be of prognostic value in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and allow for treatment modification. To overcome decrease in tumor visibility and increase in delineation variation by observers, functional diffusion maps provide an objective measure to follow response on DW-MRI during treatment provided a good geometric accuracy as is offered by the SPLICE technique.
|
|
3934.
 |
23 |
 Multiparametric MRI as a biomarker of response to neoadjuvant second-generation hormone therapy for localized prostate cancer- a pilot study Multiparametric MRI as a biomarker of response to neoadjuvant second-generation hormone therapy for localized prostate cancer- a pilot study
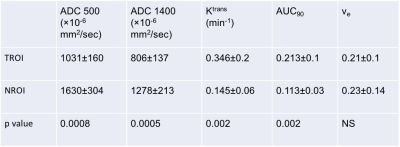
Fiona Fennessy, Andriy Fedorov, Mark Vangel, Robert Mulkern, Rosina Lis, Maria Tretiakova, Clare Tempany, Mary Ellen Taplin
Advanced prostate cancer (PCa) is driven by androgen receptor (AR) signaling, and as such the AR is an important therapeutic target to prevent PCa progression. The aim of this pilot study was to explore a role for prostate multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) as a biomarker for treatment response of localized prostate cancer to neoadjuvant treatment with the second-generation AR inhibitor enzalutamide. We demonstrate that quantitative mpMRI may play an important role as a biomarker of response to neoadjuvant treatment of localized PCa, and MRI-based tumor volumetrics may act as a surrogate for RCB at prostatectomy. These findings are worthy of investigation in a larger clinical setting.
|
|
3935.
 |
24 |
 MEMRI-guided preclinical trial of an experimental TAM-targeted therapy in mouse medulloblastoma MEMRI-guided preclinical trial of an experimental TAM-targeted therapy in mouse medulloblastoma
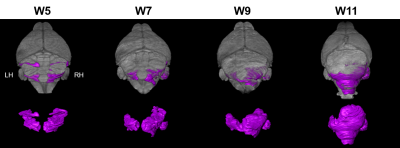
Hari Rallapalli, I-Li Tan, Alexandre Wojcinski, Alexandra Joyner, Daniel Turnbull
Using our high-throughput MEMRI pipeline, presented previously, we tested an experimental anticancer drug in mouse models of sporadic medulloblastoma.
|
|
Exogenous Contrast Mechanisms in Cancer Imaging
Electronic Poster
General Cancer Imaging
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall |
09:15 - 10:15 |
| |
|
Computer # |
|
3936.
 |
25 |
 Evaluation of Pharmacokinetic Models for Perfusion Imaging with Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Skeletal Muscle Using Low-Molecular-Weight Contrast Agents Evaluation of Pharmacokinetic Models for Perfusion Imaging with Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Skeletal Muscle Using Low-Molecular-Weight Contrast Agents
Stefan Hindel, Giorgos Papanastasiou, Peter Wust, Marc Maaß, Anika Söhner, Lutz Lüdemann
Pharmacokinetic models for perfusion quantification with DCE-MRI using a low-molecular-weight contrast agent (LMCA) in skeletal muscle of pigs were validated. This in vivo study included compartmental and distributed parameter models which allow estimation of the functional and structural composition of heterogeneously perfused tissues. The different tracer kinetic models, which measure transport parameters in physically meaningful units in heterogeneous tissue, were compared to identify a method that allows reliable quantitative determination of physiological parameters. Double-contrast agent DCE-MRI using LMCA and intravascular CA in combination with the 2-compartment exchange model extended by a nonnutritive arteriolar compartment yields the most reliable results.
|
|
3937.
 |
26 |
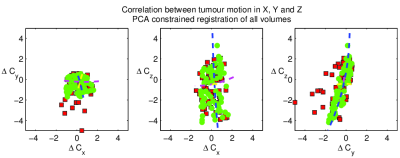
 Locally constrained registration of dynamic contrast enhanced MRI time series improves tracer kinetic model voxel-wise fit repeatability in liver tumours Locally constrained registration of dynamic contrast enhanced MRI time series improves tracer kinetic model voxel-wise fit repeatability in liver tumours
Michael Berks, Ross Little, Yvonne Watson, Sue Cheung, Gordon Jayson, James O'Connor, Geoff Parker
DCE-MRI enables the estimation of clinically useful parameters of tissue microvasculature, and is frequently used in trials of anti-angiogenic drugs. However tissue movement can lead to inaccurate parameter estimation. Rapidly changing contrast and limited spatial structure within tumours makes DCE-registration a challenging task. We present a novel algorithm that estimates a model of local tumour motion from the most stable part of the time-series and uses this to constrain registration of the whole series. We demonstrate statistically significant improved extended Kety-model fits and improved parameter repeatability for a set of 59 liver tumours in 40 patients, at two baseline scans.
|
|
3938.
 |
27 |
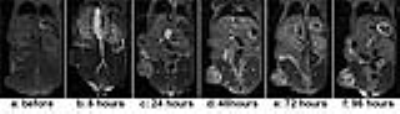
 Monitoring theragnostic drug delivery in tumors using Fe(III) metal crosslinked-micelles at 7T Monitoring theragnostic drug delivery in tumors using Fe(III) metal crosslinked-micelles at 7T
William Dominguez-Viqueira, Tara Costich, Epifanio Ruiz, Kevin Sill, Suzanne Bakewell, Gary Martinez
Stabilized micelles have shown prolonged blood circulation and targeting to solid tumors through enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. It has been demonstrated that Intezyne's Versatile Encapsulation and Crosslinking Technology (IVECT™) has the advantage of allowing the micelles to be crosslinked via a pH-sensitive Fe(III) metal coordination reaction that permeates xenografted tumors and clears from circulation without retention in the kidneys or liver. In this work we developed a theragnostic method to study drug delivery over time of IVECT by T1-weighted image histogram and image intensity in the tumor, kidneys, liver and muscle in a HCT116 Xenograft Model.
|
|
3939.
 |
28 |
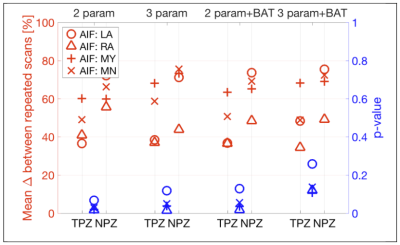
 In Search of Repeatable and Useful Prostate DCE In Search of Repeatable and Useful Prostate DCE
Sharon Peled, Michael Schwier, Mark Vangel, Clare Tempany, Ron Kikinis, Andrey Fedorov, Fiona Fennessy
This work aims to improve the practical utility of DCE derived quantitative biomarkers by comparing the repeatability of DCE calculated parameters across analysis methods, and across AIF choices. The data consists of two scans each from a set of 15 patients with suspected prostate cancer, repeated within 14 days without intervening therapy.
|
|
3940.
 |
29 |
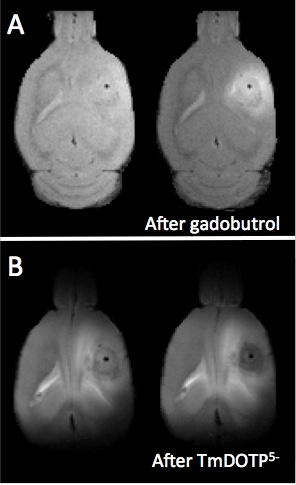
 Tumorigenesis in glioblastoma multiforme: Longitudinal mapping of glioma growth and extracellular pH Tumorigenesis in glioblastoma multiforme: Longitudinal mapping of glioma growth and extracellular pH
John Walsh, Lucas Adam, Maxime Parent, Daniel Coman, Samuel Maritim, Fahmeed Hyder
Tumorigenesis in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is complex and depends on interactions of tumor cells with the tumor microenvironment. A limiting factor in translating preclinical GBM treatment studies is being able to longitudinally and non-invasively map the tumor microenvironment in the same tumor over days and weeks. Here we describe a multi-modal MRI study of glioma growth and metabolism in human-derived models of GBM that differ in levels of hypoxia, angiogenesis, and necrosis. We demonstrate successful longitudinal mapping of tumor growth and extracellular pH in the same U87 and U251 gliomas. We find that despite significant tumor growth, acidosis plateaus early.
|
|
3941.
 |
30 |
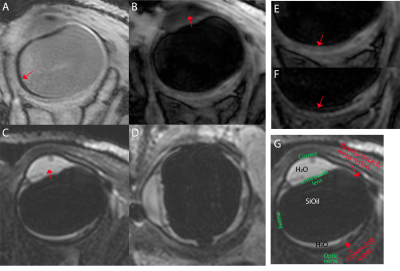
 MRI for vitrectomized eyes MRI for vitrectomized eyes
Jan-Willem Beenakker
Retinal detachment is a common complication of ocular tumours and is treated by replacing the original vitreous liquid with a silicon oil (SiOil). This SiOil hinders regular ophthalmic imaging, preventing follow-up after radiotherapy. MRI could offer the necessary imaging, but the strong off-resonance of SiOil impedes normal scan protocols. We determined the MR-characteristics of SiOil and developed a corresponding MR-imaging protocol. This protocol was evaluated on an eye tumour patient, who also suffered from retinal detachment. The protocol resulted in high quality MR-images of the eye, allowed a diagnosis of the multiple ocular lesions and averted surgical removal of the eye.
|
|
3942.
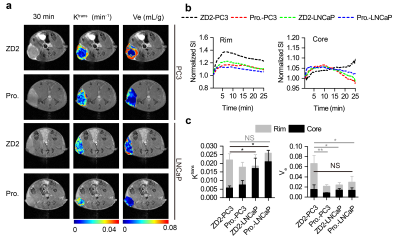 |
31 |
DCE-MRI with a targeted contrast agent for characterizing prostate cancer aggressiveness
Did Not Present
Zheng-Rong Lu, Zheng Han
Conventional dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) has been used for tumor characterization based on tumor vascularity and permeability using non-targeted small molecular contrast agents. In this study, we investigate the effectiveness of DEC-MRI with a targeted MRI contrast agent for characterization of prostate cancer of different aggressiveness in comparison with a clinical agent. Distinctive Ktrans and Ve values were obtained between the high-risk PC3 and low-risk LNCaP tumors using the targeted agent, but not for the clinical agent, Gd(HP-DO3A). DCE-MRI with this targeted contrast agent could increase accuracy in characterizing prostate cancer aggressiveness.
|
|
3943.
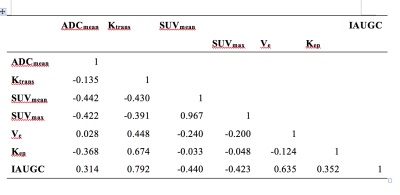 |
32 |
PET/MR in tumor differentiation of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a Preliminary Study of Multi-modality Imaging including PET, DWI, DCE and the combination
Did Not Present
Haodan Dang, Yu Chen, Bo Hou, Huadan Xue, Zhengyu Jin
The purpose of our study was to evaluate the diagnostic efficiency of multiple parameters and the combination with PET/MR in tumor differentiation of HNSCC. The patients with clinical suspicion or diagnosis of HNSCC were included and had the PET/MR examination with 18F-FDG PET and multiple MR sequences. The results showed that there was no significant correlation among different parameters. The differences among groups of tumor differentiation were obvious with ADCmean and SUVmean. Finally, our study suggested that the multiple parameters of PET / MR could be complementary in diagnosis of tumor differentiation and the combination can further improve the performance.
|
|
3944.
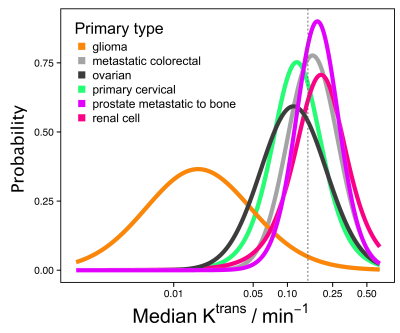 |
33 |
 Population variation in tumour microvascular characteristics Population variation in tumour microvascular characteristics
Ross Little, Hervé Barjat, Jennifer Hare, Mary Jenner, Yvonne Watson, Susan Cheung, Katherine Holliday, Weijuan Zhang, James O'Connor, Simon Barry, Sanyogitta Puri, Geoff Parker, John Waterton
It is unclear from the literature whether microvascular characteristics vary according to primary tumour type, although this is important for e.g. patient selection in drug development. DCE-MRI data were obtained covering 342 tumours and 13 tumour types. Median Ktrans for non-glioma tumours had geometric mean (95% CI) of 0.15 min-1 (0.05 min-1, 0.45 min-1). There was insufficient separation between posterior densities to predict tumour Ktrans given primary tumour type. This demonstrates that where microvascular characteristics are relevant for inclusion in a clinical trial or for beginning a specific treatment, it is not generally possible to select on tumour type alone.
|
|
3945.
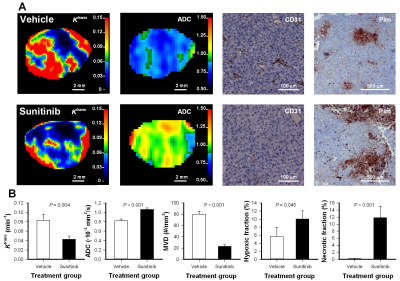 |
34 |
 The effect of sunitinib on human melanoma xenografts assessed with MRI and intravital microscopy The effect of sunitinib on human melanoma xenografts assessed with MRI and intravital microscopy
Jon-Vidar Gaustad, Trude Simonsen, Einar Rofstad
We evaluated the effect of sunitinib on melanoma xenografts with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI), diffusion weighted MRI (DW-MRI), intravital microscopy, and immunohistochemistry. An MR-compatible dorsal window chamber was used to compare parametric MR images with high resolution intravital microscopy images of the tumor vasculature. Sunitinib treatment reduced vessel density, increased the hypoxic tumor fraction, and induced necrosis, and DCE-MRI and DW-MRI were sensitive to these microenvironmental effects. The MR-compatible window chamber allowed daily assessment of both the morphology and function of tumor vasculature and may be a valuable tool to verify treatment-induced effects observed in parametric MR images.
|
|
3946.
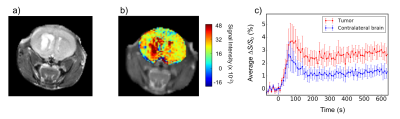 |
35 |
 CEST MRI of 3-O-Methyl-D-Glucose uptake and accumulation in brain tumors CEST MRI of 3-O-Methyl-D-Glucose uptake and accumulation in brain tumors
Akansha Sehgal, Yuguo Li, Bachchu Lal, Nirbhay Yadav, Xiang Xu, Jiadi Xu, John Laterra, Peter van Zijl
Glucose weighted chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging has garnered a lot of interest in the past few years as it can be a safe alternative to gadolinium contrast based MRI for tumor diagnosis. 3-O-methyl glucose (3-OMG) is a structural analog of glucose which, because of its apparent non-toxicity and its property to not get metabolized, has been shown to be another promising CEST contrast agent. Here we explore its application as a CEST contrast agent for assessing brain tumors.
|
|
3947.
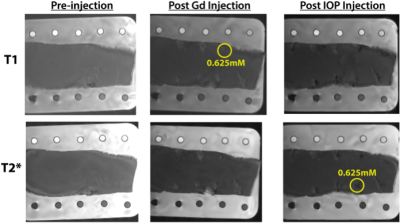 |
36 |
Bio-orthogonal MR imaging – A novel method proposed for metastatic cancer detection
Did Not Present
Tanner Ravsten, William Pitt, Neal Bangerter, Randy Hartley, Forrest Howell, Jessica Doud
Metastatic tumors (METs) cause 90% of cancer deaths since their small size makes detection difficult. A bio-orthogonal method is demonstrated where two distinct detection molecules and mechanisms are employed with minimal interference. Gadolinium (Gd) and Iron-Oxide-Particles (IOP) with respective MRI T1 and T2* scans were hypothesized to produce orthogonality in the resulting images. In vitro experiments showed respective minimum detectability limits of Gd and IOP at 1µL, 0.25µM and 0.5µL, 6µM. Ex vivo experiments demonstrated Gd and IOP detection at 0.313-0.625mM. Thus the plausibility of bio-orthogonal MET detection to reduce the likelihood of false positive and negative diagnoses is very high.
|
|
3948.
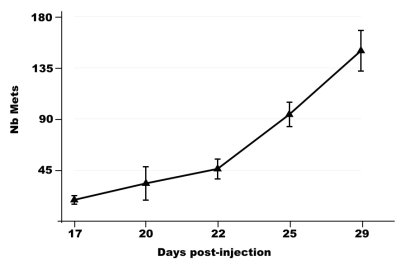 |
37 |
 A 3D Spiral/Radial sequence for both anatomical and DCE imaging of pulmonary metastases in mice A 3D Spiral/Radial sequence for both anatomical and DCE imaging of pulmonary metastases in mice
Emeline RIBOT, Charles Castets, Wilfried Souleyreau, Lin Cooley, Andreas Bikfalvi, Aurélien Trotier, Sylvain Miraux
In order to detect and characterize pulmonary metastases in small animals, a 3D UTE sequence using a hybrid radial/spiral encoding, was employed while free breathing. Due to the high contrast and the high spatial resolution (125μm isotropic), early-growing metastases (representing less than 10 voxels) were detected in mice in only 12min. In parallel, through the acceleration of the acquisition by 4, the same sequence was used to perform, for the 1st time, DCE-MRI on pulmonary metastases in mice. The new pulmonary-dedicated sequence enables to obtain either anatomical or DCE-MRI information in mice.
|
|
3949.
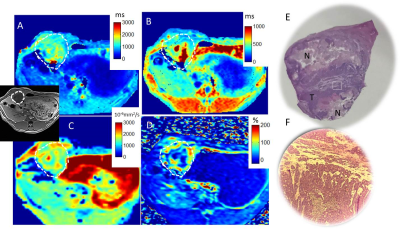 |
38 |
 Correlation of Native Liver T1 mapping to post contrast T1 mapping, Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) and Dynamic Contrast Enhancement (DCE) Maps in a Rabbit Model for Liver Cancer Correlation of Native Liver T1 mapping to post contrast T1 mapping, Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) and Dynamic Contrast Enhancement (DCE) Maps in a Rabbit Model for Liver Cancer
Dana Peters, Daniel Coman, Julius Chapiro, John Walsh, Fahmeed Hyder, Tsa Shelton, Johanna van Breugel, Tabea Borde, Lynn Savic, MingDe Lin, Albert Sinusas, Jean-Francois Geschwind, Douglas Rothman, R. Todd Constable, James Duncan, Steffen Huber
We investigated native T1 mapping for detection of liver tumors in comparison to multi-parametric MRI. In 13 rabbits with implanted 2 week VX2 tumor, 9 of which underwent transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), native T1 mapping showed a similar spatial pattern compared to dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) imaging, apparent diffusion coefficient maps (ADC), and post-contrast T1 maps. Native T1 is highest in central necrosis, intermediate in viable hypervascular tumor, and lowest in normal liver.
|
|
3950.
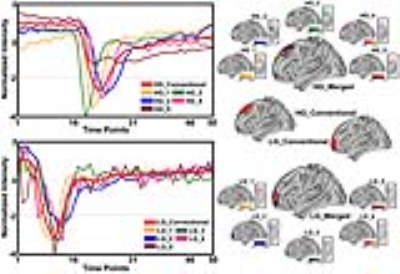 |
39 |
 Feature decomposition based examining tumor heterogenity on dynamic susceptibility contrast enhansed MRI data Feature decomposition based examining tumor heterogenity on dynamic susceptibility contrast enhansed MRI data
Bing Ji, Silun Wang, Liya Wang, Xiaofeng Yang, Hui Mao
Dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DSC MRI) is widely used for studying blood perfusion in brain tumors. We report use of a model free approach combining with a feature extraction strategy to interrogate time course data from DSC MRI of brain tumor patients. The results reveal the spatial and temporal heterogenity of brain tumors based on features of time course profiles. The number of features/patterns in DSC data indicating the heterogenity of the tumor is associated with the tumor grade. The new method can potentially extract more tumor physiology information from DSC MRI comparing to the traditional model-based analysis.
|
|
3951.
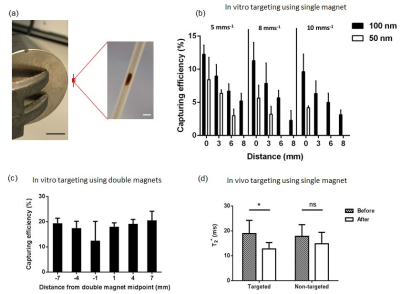 |
40 |
Magnetic targeting and imaging of super-paramagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles to subcutaneous tumour models
Video Permission Withheld
Mohammad Mohseni, John Connell, Stephen Patrick, Chris Payne, Yichao Yu, May Zaw-Thin, Tom Roberts, Bernard Siow, Tammy Kalber, Quentin Pankhurst, Mark Lythgoe
Magnetic targeting of iron-oxide nanoparticles using a MRI system could play an important role for future advances in delivery and non-invasive monitoring of therapeutic interventions. Currently, there is limited information on the effect of magnetic field gradients on the distribution of particle accumulation in the target region. This study shows that the delivery of individual 100nm particles can be enhanced in tumours using an external magnetic field after intravenous injection in vivo. Using quantitative non-invasive imaging we found that the distribution of nanoparticles within the tumour depends on the shape of the magnetic field gradient applied across the tumour.
|
|
3952.
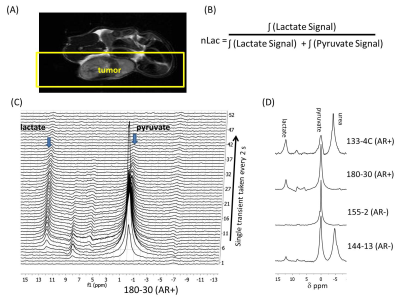 |
41 |
 Androgen receptor signaling in castration resistant prostate cancer tumor alters real-time lactate flux and lactate levels in vivo Androgen receptor signaling in castration resistant prostate cancer tumor alters real-time lactate flux and lactate levels in vivo
Niki Zacharias, Jaehyuk Lee, Sumankalai Ramachandran, Sriram Shanmugavelandy, James McHenry , Sankar Maity , Mark Titus , Pratip Bhattacharya
Non-invasive imaging of castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) subtypes remains a challenge in the clinic. CRPC can be subdivided grossly into two phenotypes 1) a morphologically small cell, chemosensitive, and androgen receptor (AR) negative subtype and 2) AR-dependent CRPC characterized by dysregulation of AR signaling. Employing hyperpolarized pyruvate conversion to lactate in vivo as well as lactate measurements ex vivo, we determined the difference in glycolysis between patient derived xenograft (PDX) animal models of these two CRPC subtypes. We have found increased pyruvate to lactate conversion (P <0.04) and higher lactate levels in AR-dependent compared to AR negative PDX models.
|
|
3953.
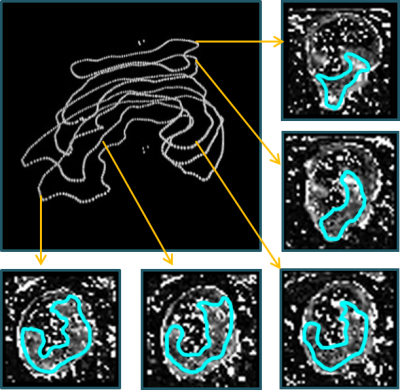 |
42 |
 Comparison of 2D and 3D dynamic contrast enhanced perfusion magnetic resonance imaging in patients with colorectal cancer Comparison of 2D and 3D dynamic contrast enhanced perfusion magnetic resonance imaging in patients with colorectal cancer
Tanja Uhrig*, Christina Korth*, Sonja Sudarski, Lothar Schad, Frank Zöllner
This study investigated the influence of quantitative 3D volume dynamic contrast enhanced-MRI in rectal cancer on perfusion parameters compared to the data obtained by a selecting a single tumor slice as typically performed in clinical routine. Data analysis of five patients showed deviations of up to 28 % for Plasma Flow, 28 % for Plasma Volume and 36 % for Mean Transit Time. An examination of the entire tumor volume is therefore advisable in order to additionally guarantee intra-observer reproducibility.
|
|
3954.
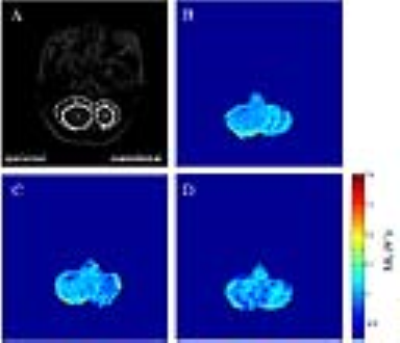 |
43 |
 In vivo monitoring of oxygen levels in the brain tumor between fractionated radiotherapy using oxygen-enhanced MR imaging In vivo monitoring of oxygen levels in the brain tumor between fractionated radiotherapy using oxygen-enhanced MR imaging
Junchao Qian, Xiang Yu, Suhong Wu, Hongzhi Wang
Response of tumor cells to radiation is closely related to oxygen level and fractionated radiotherapy allows reoxygenation of hypoxic tumor cells. Dynamic monitoring of tissue oxygenation is important for precise radiotherapy. Oxygen-enhanced MRI may directly reflect tissue oxygenation, has shown promising applications in the measurement of hypoxia. Therefore, in this study we explored the possibility to monitor oxygen level in the brain between fractionated radiotherapy using oxygen-enhanced MRI. The results showed ΔR1 increased in tumor 30 minutes after first fractionated radiation compared to pre-radiation levels. Thus, oxygen-enhanced MRI can noninvasively monitor oxygen levels in brain tumor between fractionated radiotherapy.
|
|
3955.
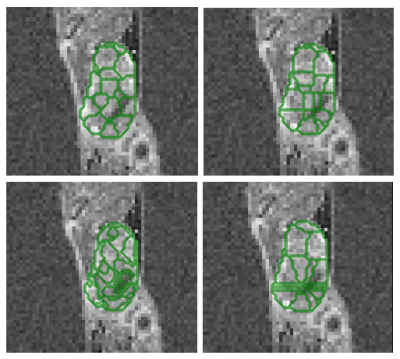 |
44 |
 Variation-guided supervoxels for subregional tumour analysis in DCE-MRI Variation-guided supervoxels for subregional tumour analysis in DCE-MRI
Jola Mirecka, Benjamin Irving, Danny Allen, Paul Kinchesh, Stuart Gilchrist, Ana Gomes, Veerle Kersemans, Sean Smart, Michael Chappell, Julia Schnabel, Mark Jenkinson
In nature and real life application domains it is common to encounter varied or textured areas, therefore in many cases it is of greater interest to partition the image into similarly varied, as opposed to similarly homogeneous subregions. We propose a novel, variation-guided approach to SLIC clustering, that has a potential to provide a useful alternative to standard supervoxels due to it’s ability to retain local variation information. We evaluate the method on a longitudinal DCE-MRI dataset of 10 mice scanned over 10 days. The method was able to produce contiguous segmentations, while significantly reducing computational complexity.
|
|
3956.
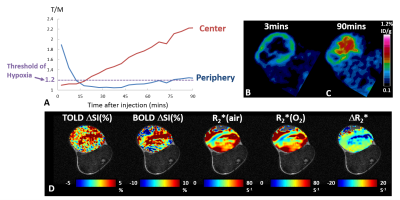 |
45 |
 Hypoxia in Rat Prostate Tumors: Correlation of BOLD/TOLD MRI with [18F]FMISO PET Hypoxia in Rat Prostate Tumors: Correlation of BOLD/TOLD MRI with [18F]FMISO PET
Heling Zhou, Srinivas Chiguru, Rami Hallac, Donghan Yang, Guiyang Hao, Peter Peschke, Ralph Mason
18F-fluoromisonidazole ([18F]FMISO) has been exploited in positron emission tomography (PET) as an imaging radiotracer for tumor hypoxia. The accumulation of [18F]FMISO must depend on both hypoxia and perfusion. In this study, we investigated [18F]FMISO activity in the AT1 tumor rat model and found that [18F]FMISO produced conflicting results in the poorly perfused hypoxic tumors. The preliminary results indicate that BOLD and TOLD MRI can provide complimentary information for interpretation of the [18F]FMISO results.
|
|
3957.
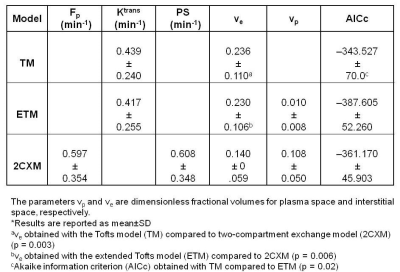 |
46 |
 Assessment of tumors aggressiveness in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) using DCE-MRI Assessment of tumors aggressiveness in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) using DCE-MRI
Ramesh Paudyal, Yonggang Lu, Vaios Hatzoglou, David Nunez, Andre Moreira, Yousef Mazaheri, Mithat Gonen, Joseph Deasy, Ashok Shaha, R. Tuttle, Amita Shukla-Dave
In this study, pretreatment dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE-MRI) data was analyzed using the Tofts model (TM), extended Tofts model (ETM), and two compartment exchange model (2CXM) to quantify perfusion-related quantitaive imaging metrics in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) patients. The histopathological features of aggressiveness were used as the standard of reference. The results indicated that the ETM provided better fit among the models. The ETM Ktrans values were able to distinguish between aggressive and non-aggressive tumors. The study concludes that pretreatment perfusion-related metric can be useful biomarkers for stratifying tumor aggressiveness in PTC patients.
|
|
3958.
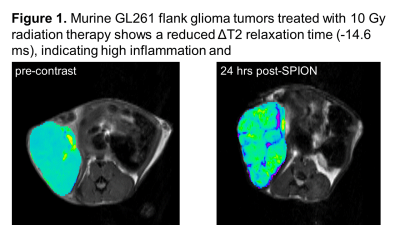 |
47 |
 Iron Oxide-Based T2-weighted MRI and NMR Metabolomics of Radiation and Chemotherapy Induced Inflammation in Glioma Models Iron Oxide-Based T2-weighted MRI and NMR Metabolomics of Radiation and Chemotherapy Induced Inflammation in Glioma Models
Heather Caulkins, Paul Hong, Ksenia Serdukova, Kendra Huber, Denise Davis, Jenna Steiner, Natalie Serkova
Radio- and chemotherapy for gliomas cause a macrophage-driven inflammation called pseudoprogression (PsP) which appears as abnormal MRI enhancement mimicking treatment response. Our quantitative NMR metabolomics in murine glioma models show a significant increase in amino acid uptake and metabolism (glutamine, glycine, methionine, and tyrosine), lactate and phospholipids in actively proliferating untreated gliomas. Iron oxide is taken up uniquely by inflammatory macrophages, as shown by decreased T2-MRI contrast and an increase in the F4/80 macrophages during treatment-induced PsP. This imaging platform may provide a promising discernment of PsP (iron oxide qT2MRI) and true progression (amino acid PET) for gliomas.
|
|
| Back |
| The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians. |

































































































