Contrast-Enhanced & Non-Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography
Oral
Cardiovascular
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
| S03 |
16:15 - 18:15 |
Moderators: Dariusch Hadizadeh Kharrazi, Ruth Lim |
16:15
 |
0913.
 |
 Highly Accelerated Steady State Ferumoxytol Abdominal MRA using Compressed Sensing Highly Accelerated Steady State Ferumoxytol Abdominal MRA using Compressed Sensing
Chengcheng Zhu, Joseph Leach, Sinyeob Ahn, Peter Speier, Michaela Schmidt, Christoph Forman, Gerhard Laub, David Saloner, Michael Hope
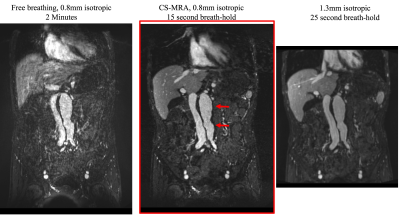
Clinical CE-MRA of the abdomen is limited in spatial resolution/coverage, or is excessively time consuming. We implemented a compressed sensing (CS) steady state MRA technique with an acceleration factor of 25, achievable in a 15 second breath hold, with 0.8mm isotropic resolution and a large 48cm coverage. In an investigation on 13 patients, we found CS-MRA had higher image quality scores and vessel sharpness compared with free breathing high-resolution MRA and clinical breath hold low-resolution MRA, with a reduced scan time. Our proposed CS-MRA technique is promising for the evaluation of abdominal vessels.
|
16:27
|
0914.
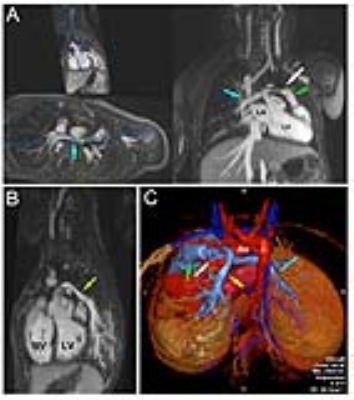 |
Ferumoxytol-Enhanced 4D MUSIC: Early Multi-Center Experience on Value-Added Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease
Video Permission Withheld
Kim-Lien Nguyen, Cynthia Rigsby, Kevin Whitehead, Mark Fogel, Peng Hu, J. Paul Finn
The value of MRI in congenital heart disease (CHD) is well-recognized. However, high time overhead and the requirement for expert oversight of image acquisition impede its more widespread use. Ferumoxytol-enhanced 4-dimensional multiphase imaging with contrast (4D-MUSIC) is a cardiac phase-resolved MR technique that generates highly detailed images under controlled ventilation. Our early multi-center experience demonstrates that 4D-MUSIC provides value-added imaging in CHD by shortening the examination time, simplifying the imaging protocol, and providing reliable, gadolinium-free, high spatial resolution, cardiac phase-resolved images. When combined with locally available velocity mapping, 4D-MUSIC enables comprehensive imaging of complex CHD in less than 40 minutes.
|
16:39
|
0915.
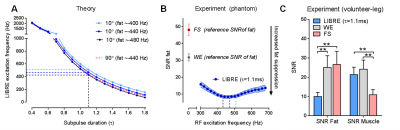 |
Lipid-insensitive 4D motion-resolved free breathing coronary MRA in heart transplant recipients at 3T
Video Permission Withheld
Jessica Bastiaansen, Lorenzo Di Sopra, Giulia Ginami, Hugues Vinzant, Juan Iglesias, Sophie Degrauwe, Samuel Rotman, Davide Piccini, Ruud Van Heeswijk, Roger Hullin, Jérôme Yerly, Matthias Stuber
The purpose of this study was to investigate coronary magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) at 3T as a possible alternative to invasive X-ray coronary angiography for the visualization of proximal and mid segments of the coronary arterial system in heart transplant recipients. Therefore, a lipid-insensitive binomial off-resonance excitation (LIBRE) pulse was optimized and combined with a 3D radial whole-heart sequence. Respiratory-self-navigated MRA was performed at 3T in heart transplant recipients during and after Gd infusion, and was compared with respiratory-motion compensation using compressed sensing (CS) to define the preferred acquisition and reconstruction protocol in this patient group.
|
16:51
|
0916.
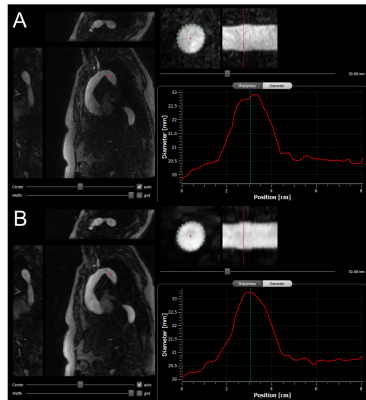 |
 Iterative Reconstruction for Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography of the Thoracic Aorta: Quantitative Assessment of SI Parameters and Impact on Quantitative Vessel Characteristics Iterative Reconstruction for Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography of the Thoracic Aorta: Quantitative Assessment of SI Parameters and Impact on Quantitative Vessel Characteristics
Luigia D'Errico, Jens Wetzl, Michaela Schmidt, Aurelien Stalder, Christoph Forman, Bernd Wintersperger
Iterative reconstruction methods can improve vessel depiction in thoracic contrast-enhanced MR angiography, particularly in small vasculature. This improvement can be ascribed to the reduced temporal footprint for iterative reconstruction compared to view sharing for standard reconstruction. An investigation of the effects of this new reconstruction on quantitative vessel characteristics found no bias in vessel diameter measurements compared to the reference.
|
17:03
|
0917.
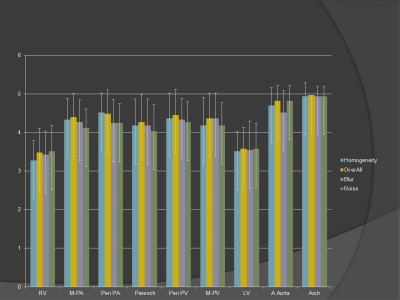 |
Time-resolved dynamic contrast enhanced MR imaging of the pulmonary vasculatures and parenchyma using Fat-sat DISCO with Gadobutrol
Video Permission Withheld
Takayuki Masui, Motoyuki Katayama, Mitsuteru Tsuchiya, Masako Sasaki, Kenshi Kawamura, Yuki Hayashi, Takahiro Yamada, Naoyuki Takei, Yuji Iwadate, Kang Wang
Fat-sat DISCO is modified version of DISCO, based on LAVA with view-sharing, which can be used for dynamic contrast MR imaging with high temporal resolutions. Gadobutrol has higher concentration of Gadolinium and its single bolus injection might induce T2 shorting effects. Simultaneous bolus injection of Gadobutrol and saline may suppress T2 shorting effects and will facilitate enhancement on T1-weighted imaging. Using fat-sat DISCO with simultaneous bolus injection of Gadobutrol and saline, dynamic contrast MR imaging of the lung can steadily provide selective visualization of pulmonary vasculatures and parenchymal enhancement.
|
17:15
 |
0918.
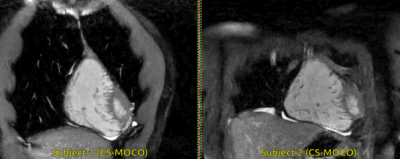 |
 Whole-Heart Cartesian Coronary MRA with Sub-Millimeter Isotropic Resolution in Four-Minute Acquisition Whole-Heart Cartesian Coronary MRA with Sub-Millimeter Isotropic Resolution in Four-Minute Acquisition
Aurelien Bustin, Giulia Ginami, Imran Rashid, Teresa Correia, Tevfik Ismail, Radhouene Neji, Rene Botnar, Claudia Prieto
Whole-heart coronary magnetic resonance angiography (CMRA) with isotropic resolution allows reformatting in any desired imaging plane without loss of resolution. However, achieving sub-millimeter isotropic resolution with a conventional 1D diaphragmatic navigator gated CMRA is very challenging due to long and unpredictable scan times. In this study, we sought to achieve sub-millimeter CMRA by combining 2D image-based navigator motion correction with highly accelerated compressed sensing reconstruction in concert with variable density Cartesian spiral-like k-space sampling to significantly accelerate the scan. The proposed technique enables CMRA acquisitions with 0.9mm isotropic spatial resolution in about 4 minutes. Ultimately, this technique might be useful for rapid screening of the coronaries in patients with suspected coronary artery disease.
|
17:27
|
0919.
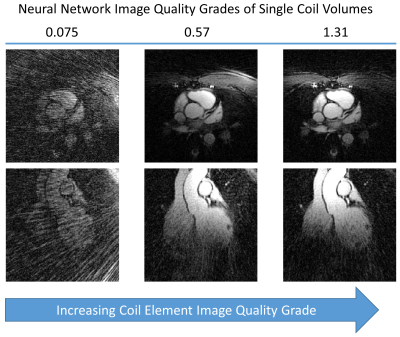 |
 Automated Coil Ranking using a Neural Network for Image Quality Assessment: An Explorative Study in Coronary MRI Automated Coil Ranking using a Neural Network for Image Quality Assessment: An Explorative Study in Coronary MRI
John Heerfordt, Robin Demesmaeker, Jérôme Yerly, Tobias Kober, Matthias Stuber, Davide Piccini
A novel method that uses a neural network to rank individual coil elements of phased arrays based on their image quality is proposed. With a ranking of the coil elements, the specific subset of coils that leads to the best image reconstruction can be selected. Alternatively, the contribution of coils with high levels of artifacts and noise to the final image can be reduced. We show that both selection and weighting of coil elements can reduce the level of image artifacts while maintaining a high signal intensity in the region of the examined organ.
|
17:39
|
0920.
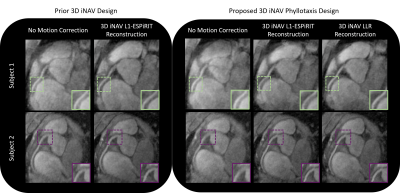 |
 Improved Design and Reconstruction of 3D Image Based Navigators for Coronary MR Angiography Improved Design and Reconstruction of 3D Image Based Navigators for Coronary MR Angiography
Mario Malavé, Srivathsan Koundinyan, Christopher Sandino, Joseph Cheng, Dwight Nishimura
We present a novel method to acquire whole-heart 3D image-based navigators (iNAVs) for tracking and correction of localized motion in free-breathing coronary angiography. More specifically, a variable-density, phyllotaxis-based trajectory is utilized for homogeneous sampling of the desired k-space extent. To reconstruct the 3D iNAVs, a locally low rank regularized iterative scheme is implemented. Across all volunteer studies, compared to 3D iNAVs generated with prior design and reconstruction strategies, the proposed 3D iNAVs provide superior delineation of the structures of interest. Application of the proposed 3D iNAVs for motion correction in volunteer studies yields improved depiction of the coronary arteries.
|
17:51
|
0921.
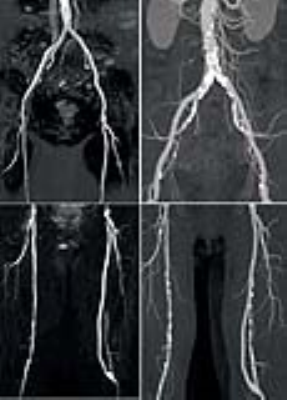 |
Accuracy of ECG-triggered Non-contrast Enhanced MRA (TRANCE) versus CT Angiography for diagnosis of peripheral artery disease: Comparison with DSA
Did Not Present
Lan Zhang, Zhi Zheng Zhuo
There is an increasing clinical need for implementing a Non-contrast enhanced MRI technique for patients with PAD or contraindications for the use of contrast medium, especially patients with renal insufficiency. We optimized TRANCE with best performance at 3.0T and compared image quality and diagnostic accuracy versus CTA and DSA for evaluation of low extremity PAD.
|
18:03
|
0922.
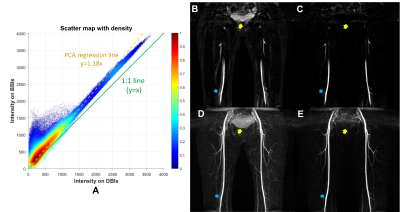 |
 An optimised subtraction approach for subtractive NCE-MRA techniques based on principal component analysis An optimised subtraction approach for subtractive NCE-MRA techniques based on principal component analysis
Hao Li, Shuo Wang, Andrew Priest, Martin Graves, David Lomas
An optimised subtraction approach is developed to improve the background signal suppression in subtractive Non-Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography (NCE-MRA) and Venography (NCE-MRV) techniques. Principal component analysis (PCA) is used to correct the intensity difference of background tissue in dark-blood images (DBIs) and bright-blood images (BBIs). Compared with the direct subtraction operation, the proposed approach significantly improved the background signal suppression in all the evaluated cases including femoral Fresh Blood Imaging (FBI)-MRA, iliac Flow-Sensitive Dephasing (FSD)-MRV and FSD-MRA for the thoracic central veins.
|
|












