High-Risk, High-Reward Translations
Oral
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Thursday, 21 June 2018
| W05/06 |
15:30 - 17:30 |
Moderators: Catherine Hines, Denis Le Bihan |
15:30
|
1261.
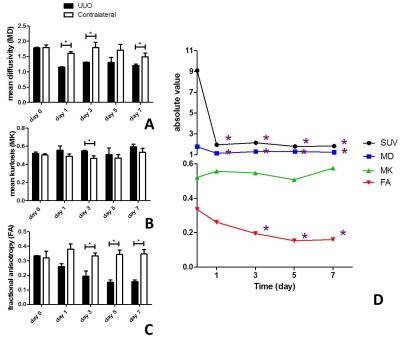 |
 Assessment of Renal Fibrosis in a Rat Model of Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction with Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging: Comparison with a-SMA Expression and 18F-FDG PET Assessment of Renal Fibrosis in a Rat Model of Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction with Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging: Comparison with a-SMA Expression and 18F-FDG PET
Anqin Li, Zhen Li, Jiali Li, Yao Hu, Daoyu Hu
To evaluate the value of diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) in renal fibrosis using a rat model of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Differences of DKI parameters among the time points and between the sides were compared. The correlation of DKI parameters with positron emission tomography (PET) renal function and expression of the fibrosis maker α-SMA were determined. There were significant differences on mean diffusivity (MD) and fractional anisotropy (FA) among days and between two sides. FA was moderate correlated with SUV and α-SMA. Therefore, quantitative DKI could be considered a useful and noninvasive method to help assess renal fibrosis.
|
15:42
|
1262.
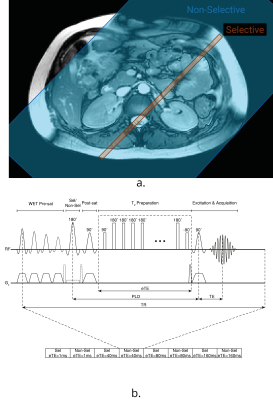 |
 Applying T2 Relaxation Under Spin Tagging (TRUST) to assess renal oxygenation in the kidney Applying T2 Relaxation Under Spin Tagging (TRUST) to assess renal oxygenation in the kidney
Alexander Daniel, Eleanor Cox, Charlotte Buchanan, Chris Bradley , Susan Francis
T2 Relaxation Under Spin Tagging (TRUST) provides a method to measure oxygenation in venous vessels within the brain. Here, a TRUST scheme is adapted for use within the body, specifically to assess oxygenation in the renal vein, using a respiratory-triggered Flow-sensitive Alternating Inversion Recovery (FAIR) labelling technique. This FAIR-TRUST variant has been tested in the brain, its reproducibility assessed in the kidney, and used to measure a change in blood oxygenation during an oxygen challenge. Changes in renal vein oxygenation could be measured more robustly than changes in BOLD T2*, the current MRI standard tissue oxygenation assessment within the kidney.
|
15:54
|
1263.
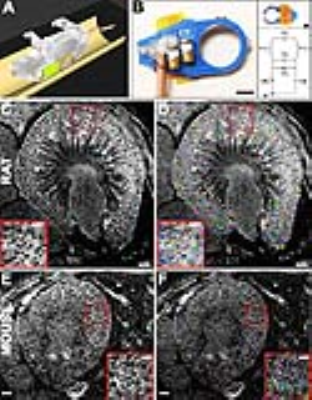 |
 Principles for measuring whole kidney nephron endowment in mice with in vivo MRI Principles for measuring whole kidney nephron endowment in mice with in vivo MRI
Edwin Baldelomar, Jennifer Charlton, Kevin Bennett
Nephron endowment is a strong predictor for renal health and nephron loss is a hallmark of early development of chronic kidney disease, but there are no techniques to measure nephron endowment in vivo. Here, we performed CFE-MRI in rats and mice to determine the limits of in vivo measurements of nephron endowment in vivo. We correlated in vivo measurements with measurements from ex vivo, high-resolution images of same kidneys. This work lays the foundation for consistent and accurate whole kidney glomerular number and size measurements in the mouse and rat kidney, in vivo.
|
16:06
|
1264.
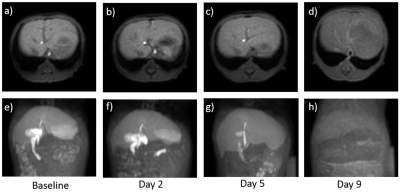 |
Multiphase Hepatocyte-Specific Contrast Enhanced MRI of Liver in a Non-Human Primate Model of Ebola
Video Permission Withheld
Ji Hyun Lee, David Thomasson, Jeffrey Solomon, Joseph Laux, Katie Hagen, Robin Gross, Peter Jahrling, Irwin Feuerstein, Reed Johnson
The purpose of this experiment was to assess the impact of Ebola virus infection on liver function during the acute phase of Ebola virus disease (EVD) in the rhesus macaque model in vivo imaging in a Biosafety level-4 facility. Multiphase liver-specific contrast, Eovist, enhanced MRI technique could detect the EVD liver failure. We observed a decreasing trend of Eovist uptake in the liver and biliary execution, and an increasing trend of liver volume with disease progression. Our findings highlight the spatiotemporal differences in Eovist uptake in a non-human primate model of Ebola.
|
16:18
|
1265.
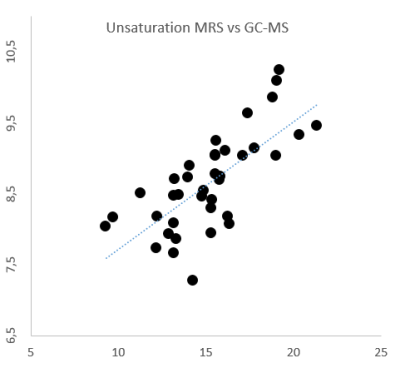 |
Comparison of long TE 1H-MRS to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for analysis of adipose tissue fat composition
Did Not Present
Jesper Lundbom, Kálmán Bodis, Daniel Markgraf, Julia Szendrödi, Michael Roden
Long TE 1H-MRS of fat results in an improved baseline and more narrow peaks but may be impacted by J-coupling effects. Here we compare long TE 1H-MRS of adipose tissue fat composition to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) of adipose tissue biopsies. There was a close correlation between the two methods for both unsaturation =CH/CH2 (R = 0.719, P < 0.00001) and saturated chain length CH2/CH3 (R = 0.782, P < 0.00001). MRS overestimated unsaturation and underestimated saturated chain length. Long TE 1H-MRS allows assessment of adipose tissue fat composition, however correction factors are needed for comparison to other methodologies.
|
16:30
|
1266.
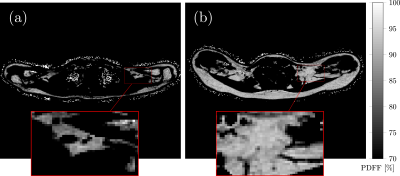 |
 The presence of brown adipose tissue is associated with thyroid function in subjects with low and normal BMI The presence of brown adipose tissue is associated with thyroid function in subjects with low and normal BMI
Daniela Franz, Dominik Weidlich, Jan Syväri, Maximilian Diefenbach, Christina Holzapfel, Theresa Drabsch, Thomas Baum, Holger Eggers, Ernst Rummeny, Hans Hauner, Dimitrios Karampinos
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) is important for energy and glucose metabolism in humans. Thyroid hormones regulate BAT development and function. Proton density fat fraction (PDFF) mapping based on a multi-echo gradient echo acquisition enables spatially-resolved fat quantification and can be indicative of the presence of BAT in adults. This study investigates the relationship between supraclavicular PDFF as surrogate marker for BAT, and serum levels of free thyroxine and free triiodothyronine with body mass index (BMI) as grouping variable.
|
16:42
|
1267.
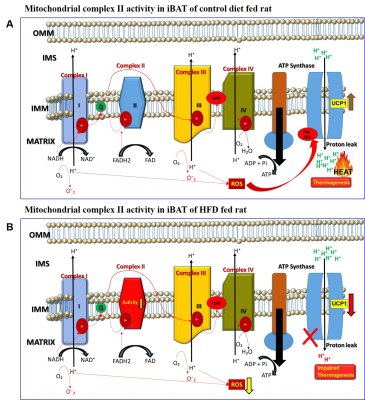 |
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based Assessment of High Fat Diet Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction Mediated Impaired Lipid Oxidation in Brown Adipose Tissue: Novel Mechanistic Insights Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based Assessment of High Fat Diet Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction Mediated Impaired Lipid Oxidation in Brown Adipose Tissue: Novel Mechanistic Insights
Jadegoud Yaligar, Rengaraj Anantharaj, Giang Le Thi Thu , Ritu Chawla, Sanjay Kumar Verma, Venkatesh Gopalan, Houchun Hu, Karthik Mallilankaraman, S. Sendhil Velan
Understanding the functional aspects of BAT under obese and overweight conditions is important to improve metabolic dysfunction. Mechanisms that regulate the quality of BAT are influenced by dietary lipids and plays a vital role in fat oxidation. Our imaging and molecular biology data suggests that lipid oxidative capacity of the mitochondria in iBAT is compromised with increased accumulation of lipids. High fat dietary feeding did not affect the mitochondrial content. However, the mitochondrial function was profoundly impaired. The novel finding in this study is the reduction in the activity of complex II in HFD fed rats leading to mitochondrial dysfunction.
|
16:54
|
1268.
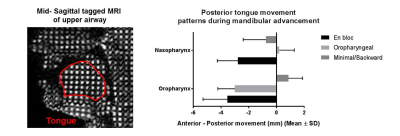 |
 Tongue deformation during mandibular advancement, as determined using tagged-MRI, may help to predict mandibular advancement treatment outcome in Obstructive sleep apnoea. Tongue deformation during mandibular advancement, as determined using tagged-MRI, may help to predict mandibular advancement treatment outcome in Obstructive sleep apnoea.
Lauriane Jugé, Fiona Knapman, Peter Burke, Elizabeth Brown, Jane Butler, Danny Eckert, Jo Ngiam, Kate Sutherland, Peter Cistulli, Lynne Bilston
Tongue deformation during mandibular advancement, as characterised by tagged-MRI, may be helpful to predict mandibular advancement splint (MAS) therapy for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). 68 OSA patients untreated underwent a MRI scan prior to trialling a MAS and treatment outcome was determined. Preliminary results identified 3 possible tongue deformations (en bloc, oropharyngeal and minimal/backward) with variable impact on the upper airway size. Over all participants, tongue deformation was not associated with treatment outcome, but among obese participants, “en bloc” tongue deformation was associated with positive treatment outcomes. This may also improve the understanding of the mechanisms underpinning MAS therapy effectiveness.
|
17:06
|
1269.
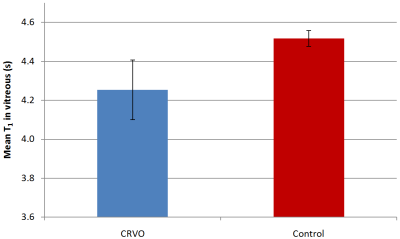 |
 Non-invasive T1 mapping of the vitreous humour can detect central retinal vein occlusion and may discriminate between other forms of retinal ischaemia Non-invasive T1 mapping of the vitreous humour can detect central retinal vein occlusion and may discriminate between other forms of retinal ischaemia
Nicholas Dowell, Andrew Simpson, Samira Bouyagoub, Edward Hughes
In this work we demonstrate that careful T1 mapping of the vitreous humour can identify disease in the retina. We studied a cohort of patients with central vein retinal occlusion (a type of retinal ischaemia) and show that significant decreases in T1 of the vitreous humour are observed compared to healthy control eyes. We speculate that the decreases may be the result of increased pO2 that could arise when the oxygen demand of the retina is reduced as a consequence of damage. We show preliminary data from patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy and ocular ischaemic syndrome that suggest that it may be possible to discriminate different forms of retinal ischaemia completely non-invasively with MRI.
|
17:18
 |
1270.
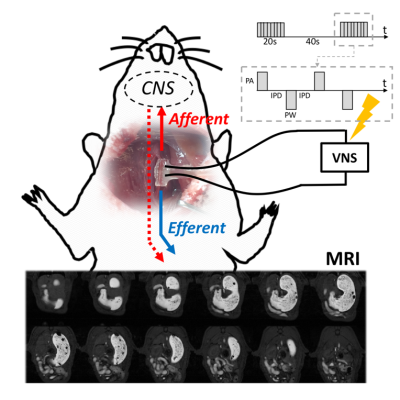 |
 Vagus Nerve Stimulation Promotes Gastric Emptying in Rat Measured by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Vagus Nerve Stimulation Promotes Gastric Emptying in Rat Measured by Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Kun-Han Lu, Jiayue Cao, Steven Oleson, Matthew Ward, Terry Powley, Zhongming Liu
We developed in vivo contrast-enhanced MRI and an image processing pipeline to image and assess the therapeutic effect of cervical vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) on gastric emptying and motility in rat. We found that: (1) VNS significantly promoted the rate of gastric emptying. (2) VNS significantly increased the degree to which the pyloric ring opened, and this outcome was correlated to the rate of gastric emptying. (3) The VNS parameters used in this study did not alter antral motility significantly. The proposed method allows non-invasive and repeated preclinical imaging of gastric physiology and diseases given electroceutical treatments.
|
|












