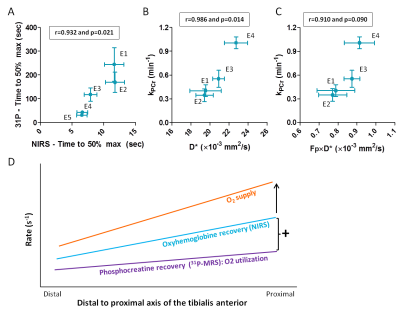It Takes a Muscle
Oral
Musculoskeletal
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
| S04 |
13:45 - 15:45 |
Moderators: Jung-Ah Choi, Charles Hutchinson |
13:45
 |
0813.
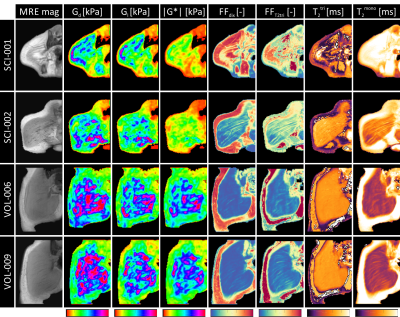 |
Elastography, T2-mapping, and Dixon MRI of the gluteus maximus muscle in spinal cord injured and able-bodied subjects
Video Permission Withheld
Jules Nelissen, Dorien Verschuren, Maurits Sloots, Larry de Graaf, Jitsha Monte, Sandra van den Berg, Kevin Moerman, Klaas Nicolay, Mario Maas, Sicco Bus, Ralph Sinkus, Jurgen Runge, Christof Smit, Thomas Janssen, Cees Oomens, Gustav Strijkers, Aart Nederveen
Gluteus maximus biomechanical properties and composition are altered in spinal cord injured (SCI) subjects and increase the risk of deep tissue injury type of pressure ulcers. For this purpose, a multi-parametric MRI study of the gluteus maximus of SCI and able-bodied subjects was performed. The protocol consisted of MRE, T2-mapping, and Dixon. The gluteus maximus of SCI subjects had a lower stiffness, which was accompanied by a higher fat fraction, as compared to the able-bodied subjects. The proposed protocol has great potential in providing personalized information on deep tissue injury risk.
|
13:57
|
0814.
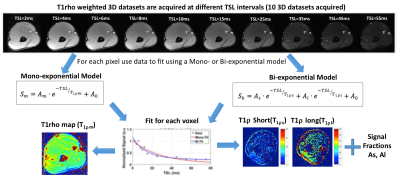 |
 3D-T1rho mapping of upper arm muscles in post-stroke patients 3D-T1rho mapping of upper arm muscles in post-stroke patients
Rajiv Menon, Preeti Raghavan, Ravinder Regatte
In this study, we evaluate the use of 3D-T1rho (T1ρ) relaxation mapping of the upper arm muscle glycosaminoglycan (GAG) content in healthy controls, and post stroke patients with pre and post hyaluronidase injections. Healthy controls (n=5) and post-stroke patients (n=5, pre and post treatment) were recruited. Dixon based water-fat imaging and T1ρ mapping were performed. Mono- and bi-exponential modeling was used to process the data. While water-fat distributions were not significantly different between the two groups, significant differences were noted in T1ρ values using mono- and bi-exponential analysis. T1ρ imaging shows significant changes that reflect the reduction of GAG’s following the treatment with hyaluronidase injection.
|
14:09
 |
0815.
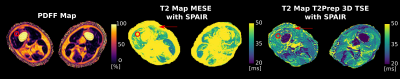 |
 Water T2 mapping in fatty infiltrated thigh muscles of patients with neuromuscular diseases using a T2-prepared 3D TSE with SPAIR Water T2 mapping in fatty infiltrated thigh muscles of patients with neuromuscular diseases using a T2-prepared 3D TSE with SPAIR
Sarah Schlaeger, Dominik Weidlich, Elisabeth Klupp, Federica Montagnese, Marcus Deschauer, Benedikt Schoser, Sarah Bublitz, Claus Zimmer, Ernst Rummeny, Jan Kirschke, Dimitrios Karampinos
In patients with neuromuscular diseases muscle water T2 is an important biomarker to monitor disease activity and therapy effectiveness. Especially, the thigh is of interest showing disease-characteristic patterns of involvement. Different T2 mapping approaches, routinely based on MESE, have been developed to minimize the effect of confounding factors. An alternative method is the T2Prep 3D-TSE combined with SPAIR. However, it remains unknown, how T2Prep 3D-TSE performs in the presence of fat. This work simulates the effect of SPAIR and T2preparation on the 3D-TSE readout in the presence of fat and compares T2Prep 3D-TSE and 2D-MESE to MRS in 34 patients.
|
14:21
 |
0816.
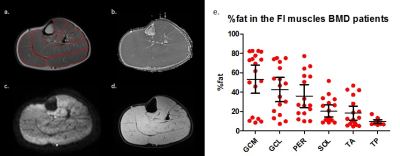 |
 Multi-parametric MR shows increased T2 heterogeneity in fat infiltrated muscles in Becker Muscular Dystrophy Multi-parametric MR shows increased T2 heterogeneity in fat infiltrated muscles in Becker Muscular Dystrophy
M.T. Hooijmans, C. Baligand, M. Froeling, J.J.G.M Verschuuren, A.G. Webb, E.H. Niks, H.E. Kan
Quantitative MR is increasingly used to assess muscle damage in muscular dystrophies, including BMD. Early markers that reflect changes in muscle tissue are becoming increasingly important with therapies aimed at preserving muscle tissue. This study used a multi-modal MR approach to examine diffusion properties, the average water T2 and SD of the water T2 in non-fat-infiltrated and fat-infiltrated muscles in BMD. Our results indicate that none of the proposed measures are sensitive to muscle tissue changes prior to the replacement of muscle tissue by fat and that only T2 heterogeneity is sensitive to muscle tissue changes in the presence of fat in patients with BMD.
|
14:33
 |
0817.
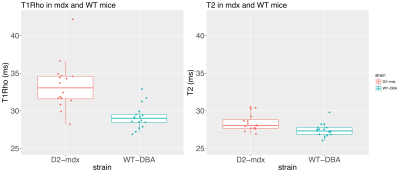 |
 Increased T1Rho relaxation in a Duchenne muscular dystrophy mouse model with increased muscle fibrosis Increased T1Rho relaxation in a Duchenne muscular dystrophy mouse model with increased muscle fibrosis
Bauke Kogelman, Kevin Adamzek, Ernst Suidgeest, Gustav Strijkers, Maaike Putten, Louise Weerd
A T1Rho sequence was used in a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy mouse model characterized by increased muscle fibrosis. Significantly higher T1Rho relaxation times were found compared to wild-type mice in which fibrosis was absent. Although both T1Rho and T2 values were increased, the increase was more pronounced for T1Rho than for T2 (14.2% vs 3.6%), indicating that T1Rho is affected by other processes than those resulting in increased T2 values. These data demonstrate the potential of T1Rho to assess muscle fibrosis in vivo.
|
14:45
|
0818.
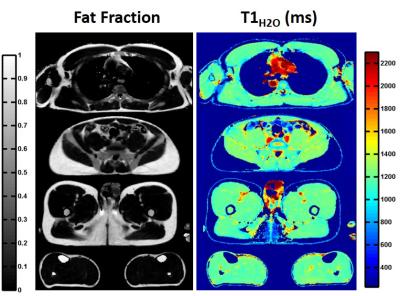 |
 Quantification of water T1 and fat fraction in skeletal muscle tissue using an optimal MR fingerprinting radial sequence (MRF-WF) Quantification of water T1 and fat fraction in skeletal muscle tissue using an optimal MR fingerprinting radial sequence (MRF-WF)
Benjamin Marty, Pierre Carlier
Quantitative T1-mapping might represent an efficient tool to monitor inflammation, necrosis or fibrosis processes in skeletal muscle tissues affected by neuromuscular disorders. However, standard T1-mapping sequences cannot separate the contribution of water and fat protons. If directly applied to fatty infiltrated skeletal muscles, a “global” T1 value would mainly reflect the degree of intramuscular fat and the other underlying processes would largely be hidden. Here, we proposed an optimal sequence allowing simultaneous estimation of water T1 and fat fraction. It was validated in phantom and in vivo acquisitions were performed on several subjects suffering from different neuromuscular diseases.
|
14:57
|
0819.
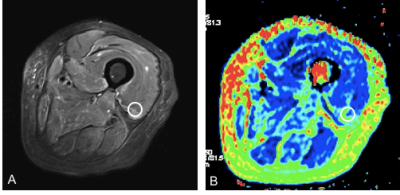 |
 Quantitative T2 mapping of the thigh muscles and its correlation with the ADC: a feasibility study in assessing inflammatory myopathy Quantitative T2 mapping of the thigh muscles and its correlation with the ADC: a feasibility study in assessing inflammatory myopathy
Fengdan Wang, Qian Wang, Haiping Zhang, Dong Liu, Tobias Kober, Tom Hilbert, Yi Sun, Yan Zhang, Zhengyu Jin
We investigated the use of the T2 mapping technique to quantitatively evaluate the thigh muscles of 18 dermatomyositis (DM)/polymyositis (PM) patients and 10 healthy control subjects. Moreover, the correlation of T2 values with apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values was also studied. The results showed significantly elevated T2 values with edematous muscles and increased T2 values with unaffected muscles (normal appearing in conventional MRI) in DM/PM patients, compared to the control group. The T2 values of the edematous muscles were found to be closely correlated with the ADC. This study demonstrated that T2 mapping may be successfully used in the quantitative evaluation of inflammatory myopathy.
|
15:09
|
0820.
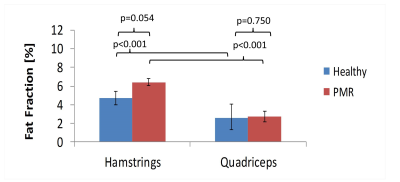 |
 Magnetic resonance measurements of fat content and water diffusion in muscles of glucocorticoid-treated patients with polymyalgia rheumatica compared with healthy volunteers. Magnetic resonance measurements of fat content and water diffusion in muscles of glucocorticoid-treated patients with polymyalgia rheumatica compared with healthy volunteers.
John Biglands, Steven Tanner, Ai Lyn Tan, Sarah Mackie, Elizabeth Hensor, John Ridgway, Paul Emery, Thorsten Feiweier, Emma Harris, Paul Stewart, Andrew Grainger
The purpose of this study was to assess differences in fat fraction and water diffusion between muscles in the healthy thigh and to assess differences between glucocorticoid treated patients with polymyalgia rheumatic (PMR) and healthy controls. Twenty five healthy volunteers and sixteen patients with PMR undergoing glucocorticoid treatment underwent MRI to assess muscle fat fraction and diffusion. The study found that the hamstrings have greater fat fraction and reduced diffusion compared to quadriceps in healthy individuals. Furthermore, alterations in fat fraction and diffusion parameters associated with glucocorticoid-treated PMR are more readily detectable in the hamstrings than the quadriceps.
|
15:21
 |
0821.
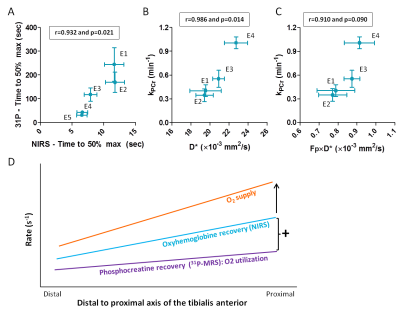 |
Both oxygen supply and phosphocreatine recovery rate show proximo-distal gradients along the human tibialis anterior after exercise
Video Permission Withheld
Linda Heskamp, Franciska Lebbink, Mark van Uden, Marnix Maas, Jurgen Claassen, Andreas Boss, Arend Heerschap
Since the rate of phosphocreatine recovery after exercise varied substantially within the tibialis anterior, we wondered if O2 supply also varied along this muscle. Therefore, we applied near infra-red spectroscopy to study the dynamic equilibrium of O2 supply and O2 utilization, intravoxel incoherent motion imaging for muscle perfusion and 31P-MRS during and after isometric exercise of the tibialis anterior. We observed higher post-exercise perfusion and faster phosphocreatine and oxyhemoglobin recovery proximally than distally in the tibialis anterior, indicating a proximo-distal gradient in O2 supply. This may be an adaptation to a higher proximal energy requirement.
|
15:33
|
0822.
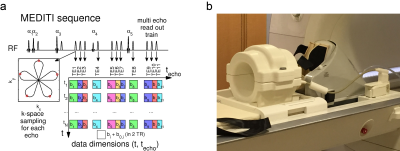 |
 Work dependence of calf muscle DTI exercise response from dynamic imaging Work dependence of calf muscle DTI exercise response from dynamic imaging
Eric Sigmund, Steven Baete, Mary Bruno, David Stoffel, Jenny Bencardino
We describe measurement of work dependence of exercise response of diffusion contrast in calf muscle with a multiple echo diffusion tensor imaging (MEDITI) in a clinical 3 T scanner. With radial imaging, accelerated diffusion encoding, and compressed sensing reconstruction, spatial resolution of 3.7 mm and temporal resolution of 16 s was achieved. Using an MR-compatible ergometer with pneumatic resistance and force/displacement monitoring, post-exercise recovery of T2 and DTI metrics following plantarflexion in gastrocnemius muscle were monitored as a function of total normalized work. Exercise response showed significant anisotropy, and trends of higher response with work were observed.
|
|