Predictive & Prognostic Cancer Imaging
Oral
General Cancer Imaging
Thursday, 21 June 2018
| S04 |
13:15 - 15:15 |
Moderators: Wei Huang, Kei Yamada |
13:15
|
1157.
 |
 Investigating Oxygen Sensitive MRI to Provide Prognostic Biomarkers for Tumor Radiation Response Investigating Oxygen Sensitive MRI to Provide Prognostic Biomarkers for Tumor Radiation Response
Tatsuya Arai, Donghan Yang, James Campbell III, Tsuicheng Chiu, Strahinja Stojadinovic, Ralph Mason
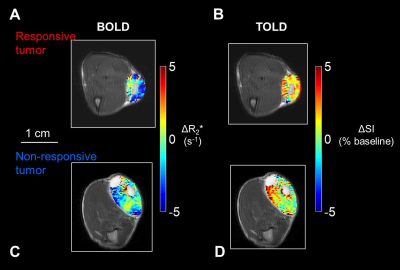
Prognostic imaging biomarkers to assess tumor hypoxia remain a Holy Grail. We present evidence that T1-weighted signal response to an oxygen breathing challenge before a single high dose of radiation is related to long term tumor control. Specifically, Dunning prostate R3327-AT1 tumors showing a small signal response showed poor control for relatively lower doses (30-50 Gy). Meanwhile, higher doses overcame the radio resistance, which we associate with hypoxia. A large BOLD response (ΔR2*) was associated with poor outcome irrespective of radiation dose. These results provide further evidence for the potential utility of oxygen sensitive MRI in guiding radiation therapy.
|
13:27
 |
1158.
 |
 Multi-modality molecular imaging with hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRSI and 18FDG-PET of early tumor response to a novel TRAIL agonist (MEDI3039) Multi-modality molecular imaging with hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRSI and 18FDG-PET of early tumor response to a novel TRAIL agonist (MEDI3039)
Richard Hesketh, Jiazheng Wang, Alan Wright, Maria Fala, Susana Ros, Jodi Miller, David Lewis, Kevin Brindle
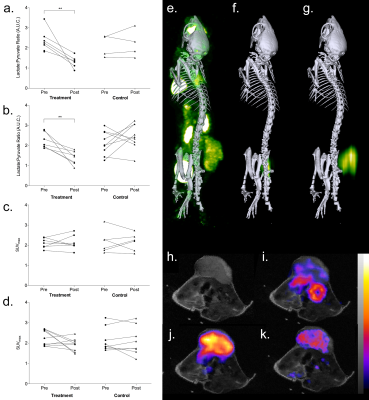
This study compared the capability of 3D magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) of hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate metabolism and 18FDG-PET to detect early responses to a TRAIL agonist (Medimmune MEDI3039) in Colo205 colorectal cancer and MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer xenograft models expressing luciferase and mStrawberry fluorescent protein. 24 hours after treatment, bioluminescence and hyperpolarized lactate/pyruvate ratio decreased significantly in all treated animals, preceding decreases in tumor volume. Conversely, 18FDG-PET did not detect treatment response. This suggests that for some tumors hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate may be an improvement on 18FDG-PET and RECIST for the early detection of treatment response.
|
13:39
|
1159.
 |
 Tracking the evolution of individual prostate cancer metastases in patients under the selective pressure of Radium-223 treatment using whole-body radiomics. Tracking the evolution of individual prostate cancer metastases in patients under the selective pressure of Radium-223 treatment using whole-body radiomics.
Matthew Blackledge, Dow Koh, David Collins, Matthew Orton, Erica Scurr, Julie Hughes, Chris Parker, Martin Leach, Nina Tunariu
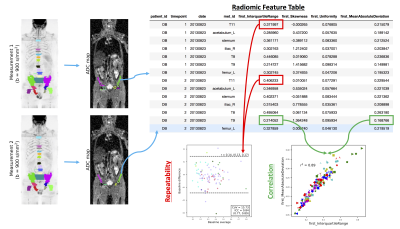
Whole-Body Diffusion-Weighted-MRI is emerging as an imaging response biomarker in metastatic bone disease. Tumour heterogeneity resulting in differential response to therapy is a well-recognized phenomenon. We propose that calculating radiomic features from the apparent diffusion coefficients within individual lesions can identify differential response patterns in whole-body bone disease. Robust statistical assessment of radiomic features based on repeatability assessment aids identification of significant changes.
|
13:51
|
1160.
 |
 Predicting the spatio-temporal evolution of tumor vasculature and cellularity following whole brain radiation therapy Predicting the spatio-temporal evolution of tumor vasculature and cellularity following whole brain radiation therapy
David Hormuth II, Angela Jarrett, Thomas Yankeelov
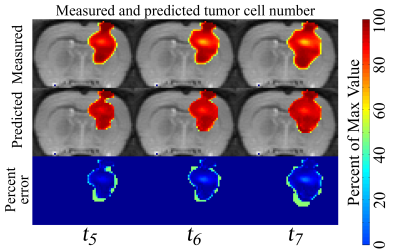
A fundamental challenge in the care of patients with brain tumors is the limitation of standard radiographic measurements to accurately evaluate, let alone predict, patient response. To address this challenge, we have developed a biophysical model of tumor growth, angiogenesis, and response to radiation therapy that is calibrated on a subject-specific basis using diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI data. We evaluated the predictive accuracy of the model in rats with C6 gliomas receiving whole brain radiation. The model accurately predicted future tumor volume (error ranged from 12.1 to 18.5%).
|
14:03
 |
1161.
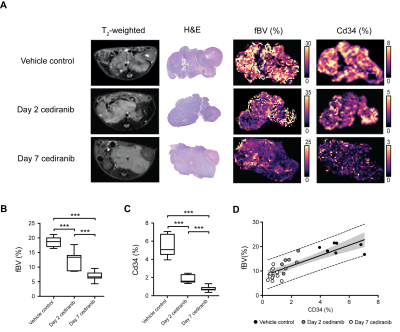 |
 Susceptibility contrast-MRI predicts response to the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor cediranib in the Th-MYCN model of neuroblastoma Susceptibility contrast-MRI predicts response to the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor cediranib in the Th-MYCN model of neuroblastoma
Konstantinos Zormpas-Petridis, Matthew Blackledge, Louis Chesler, Yinyin Yuan, Simon Robinson, Yann Jamin
In this study we demonstrate that fractional blood volume, measured by susceptibility contrast-MRI, predicts response to the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor cediranib in the Th-MYCN genetically-engineered mouse model of neuroblastoma.
|
14:15
|
1162.
 |
 The Effect of Altered Glucose Utilization on Dynamic GlucoCEST in a Preclinical Model of Glioblastoma The Effect of Altered Glucose Utilization on Dynamic GlucoCEST in a Preclinical Model of Glioblastoma
Xiang Xu, Jing Liu, Jiadi Xu, Linda Knutsson, Huanling Liu, Yuguo Li, Bachchu Lal, John Laterra, Peter van Zijl, Kannie Chan
To investigate the origin of glucoCEST contrast, we altered glucose utilization using an mTOR inhibitor (rapamycin) and studied dynamic glucoCEST signals in a human glioblastoma mouse model. By inhibiting glucose transport, cellular uptake and metabolism are suppressed and the perfusion of vessels and leakage into extravascular extracellular space highlighted. A great increase in glucoCEST contrast was seen in tumors in mice with the inhibitor compared to without. This provides evidence of a large extracellular glucose contribution to glucoCEST, and suggests that we can use glucoCEST to monitor the efficacy of rapamicin with respect to its inhibitory effect.
|
14:27
|
1163.
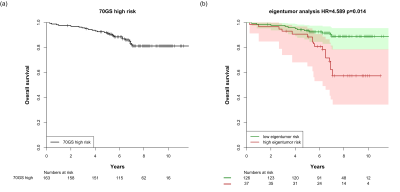 |
 Radiomics of DCE-MRI to selectively down-stage the risk of breast cancers with a high-risk 70-gene signature Radiomics of DCE-MRI to selectively down-stage the risk of breast cancers with a high-risk 70-gene signature
Hui Shan Chan, Tycho Bismeijer, Bas van der Velden, Jelle Wesseling, Esther Lips, Claudette Loo, Lodewyk Wessels, Kenneth Gilhuijs
The 70-gene signature (70GS) is a prognostic marker for patient survival that is used to guide treatment decisions. For a dataset of early-stage breast cancer patients, the 70GS were established retrospectively. We investigated the potential of DCE-MRI to stratify patient survival within the high-risk 70GS group. Eigentumor analysis and 3D lesion texture features from washin and post-contrast images were compared in survival analysis and hazard ratios were computed. Results show that the investigated features are able to significantly stratify survival, and suggest that radiomics of DCE-MRI may have complementary value to the 70-gene signature to reduce overtreatment.
|
14:39
|
1164.
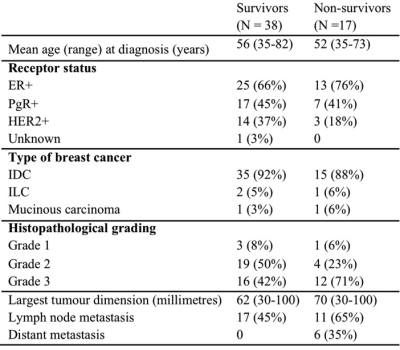 |
 Predicting breast cancer patient survival using textural features in CE MR images Predicting breast cancer patient survival using textural features in CE MR images
Beathe Sitter, Guro Giskeødegård, Ioanna Chronaiou, Jose Teruel, Roja Hedayati, Steinar Lundgren, Else Marie Huuse Røneid, Martin Pickles, Peter Gibbs, Tone Bathen
Treatment for women with locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) is determined with inadequate knowledge of the long-term outcome. We evaluated the prognostic value of textural features derived from pre-treatment CE-MRI in 55 LABC patients scheduled for neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Using overall survival at 7-years follow-up as endpoint, textural features derived from post-contrast pre-treatment images were significantly different. Using all textural features as input for multivariate analysis, we achieved a classification accuracy of 72% (p<0.001), which increased to 78% when including traditional prognostic factors (p<0.001). Textural features provide prognostic information, which can complement the stratification of patients to treatment.
|
14:51
|
1165.
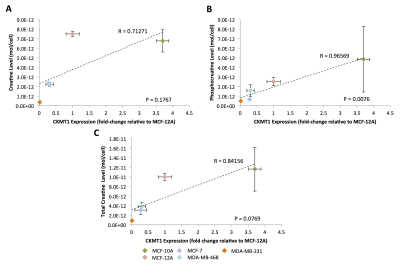 |
 Proton MRS-Detected Creatine Metabolic Profiles in Human Breast Cancer Cells Correlate with the Prognostic Indicator Ubiquitous Mitochondrial Creatine Kinase (CKMT1) Proton MRS-Detected Creatine Metabolic Profiles in Human Breast Cancer Cells Correlate with the Prognostic Indicator Ubiquitous Mitochondrial Creatine Kinase (CKMT1)
Vinay Ayyappan, Menglin Cheng, Ruoqing Cai, Caitlin Tressler, Kanchan Sonkar, Michael McMahon, Kristine Glunde
Ubiquitous mitochondrial creatine kinase (CKMT1) is an important mitochondrial membrane component responsible for the reversible conversion of creatine (Cr) to phosphocreatine (PCr). This study shows that in five breast cell lines of varying aggressiveness, 1H MRS-detected PCr levels correlated with CKMT1 mRNA expression. CKMT1 expression was significantly downregulated in triple-negative breast cancer cells compared to estrogen receptor (ER)/ progesterone receptor (PR)-positive cells, and nonmalignant cells. CKMT1 is a prognostic indicator in several cancers; thus, PCr holds promise as potential marker for improved cancer diagnosis, patient stratification, and theranostic treatment monitoring.
|
15:03
|
1166.
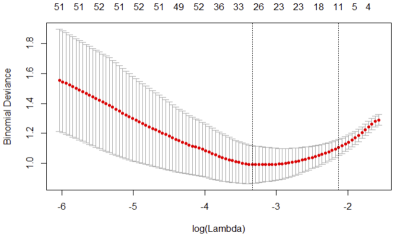 |
 Radiomics subtyping improves 5-year disease free survival prediction beyond key clinical and radiological characteristics in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) Radiomics subtyping improves 5-year disease free survival prediction beyond key clinical and radiological characteristics in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC)
Ke Nie, Peng Hu, Fei Peng, Tingyu Mao, Xiao Wang, Ning Yue, Jihong Sun
In this study, we have identified an 11-feature set from a large panel of radiomics signature (5248 features from pre-operative T1w, T2w, DCE and DWI images) that allows prediction of 5-year disease free survival of locally advanced rectal cancer patients underwent surgical resection. The selected radiomics signature demonstrates improved performance compared with that of established clinical and radiological risk models. The results were tested and validated on a consecutive 165-patient cohort with an average of 54±20 months follow-ups.
|
|












