Diffusion MRI: Signal Reconstruction & Representation
Oral
Diffusion
Tuesday, 19 June 2018
| N03 |
13:45 - 15:45 |
Moderators: Stamatios Sotiropoulos, David Atkinson |
13:45
 |
0463.
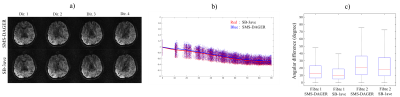 |
 Diffusion Acceleration with Gaussian process Estimated Reconstruction (DAGER) Diffusion Acceleration with Gaussian process Estimated Reconstruction (DAGER)
Wenchuan Wu, Peter Koopmans, Jesper Andersson, Karla Miller
Diffusion acceleration is a challenging task, particularly when using simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) imaging with in-plane acceleration. In this work, we develop a method termed DAGER: Diffusion Acceleration with Gaussian process Estimated Reconstruction, to improve SMS with in-plane acceleration, achieving a total acceleration factor of 12 (MB=4, R=3). In addition, DAGER reconstruction doesn't cause major degradation of angular resolution, indicating the Gaussian process model used in DAGER can accurately estimating the degree of local smoothness in q-space.
|
13:57
 |
0464.
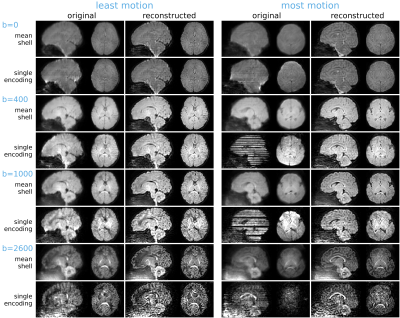 |
 Multi-shell SHARD reconstruction from scattered slice diffusion MRI data in the neonatal brain Multi-shell SHARD reconstruction from scattered slice diffusion MRI data in the neonatal brain
Daan Christiaens, Lucilio Cordero-Grande, Maximilian Pietsch, Jana Hutter, A. David Edwards, Maria Deprez, Joseph V. Hajnal, J-Donald Tournier
Diffusion MRI (dMRI) offers a unique probe into neural connectivity in the developing brain. However, analysis of neonatal brain imaging data is complicated by inevitable subject motion. Here, we develop a method for reconstructing multi-shell HARDI data from scattered slices, jointly estimating an uncorrupted data representation and per-excitation (slice or multiband package) motion parameters. The reconstruction relies on orthogonal decomposition of multi-shell dMRI data using a bespoke spherical harmonics and radial decomposition (SHARD), together with outlier rejection, distortion, and slice profile correction. We evaluate the method on publicly-released datasets for 40 neonatal subjects from the developing Human Connectome Project.
|
14:09
 |
0465.
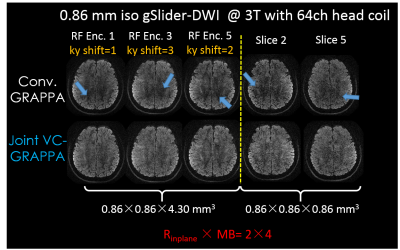 |
 Joint Virtual Coil Reconstruction with Background Phase Matching for Highly Accelerated Diffusion Echo-Planar Imaging Joint Virtual Coil Reconstruction with Background Phase Matching for Highly Accelerated Diffusion Echo-Planar Imaging
Congyu Liao, Mary Manhard, Berkin Bilgic, Qiuyun Fan, Haifeng Wang, Sohyun Han, Daniel Park, Fuyixue Wang, Jianhui Zhong, Lawrence Wald, Kawin Setsompop
We proposed a joint-virtual-coil (VC) acquisition/reconstruction method to improve accelerated single-shot EPI (SS-EPI) in diffusion imaging (DI). A background phase correction scheme for matching the phase of reference training data with accelerated diffusion-weighted data was developed for robust reconstruction. Additional Gy prewinding-blips were added to the EPIs, to create complementary shifted-ky sampling strategy across TRs, which help better utilizes smooth-phase and joint-information priors in the joint-virtual-coil (jVC) reconstruction. The proposed method was demonstrated in highly-accelerated DI with SS-EPI and extended to generalized slice dithered enhanced resolution (gSlider) acquisition to achieve efficient high-resolution DI.
|
14:21
 |
0466.
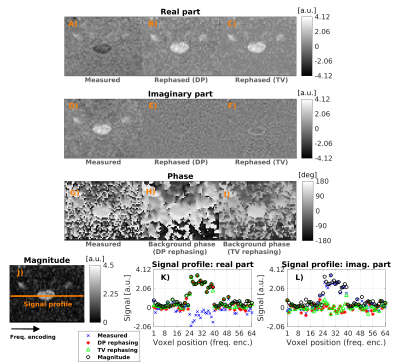 |
 Magnitude versus complex-valued images for spinal cord diffusion MRI: which one is best? Magnitude versus complex-valued images for spinal cord diffusion MRI: which one is best?
Francesco Grussu, Jelle Veraart, Marco Battiston, Torben Schneider, Julien Cohen-Adad, Manuel Jorge Cardoso, Claudia Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott, Els Fieremans, Daniel Alexander, Dmitry Novikov
Advanced diffusion imaging of the spinal cord is hampered by low signal-to-noise ratio, leading to strong Rician bias in magnitude images. Here, we investigate how to mitigate such bias studying complex-valued 3T diffusion scans of the cervical cord. We test two approaches, based on decorrelated phase (DP) and total variation (TV) filtering, corroborating results with simulations. The DP and TV methods, proposed for the brain, can be applied successfully also in the cord. Moreover, they appear useful pre-processing tools for image denoising, as state-of-the-art noise removal based on Marcenko-Pastur principal component analysis (MP-PCA) performs better on complex-valued as opposed to magnitude data.
|
14:33
|
0467.
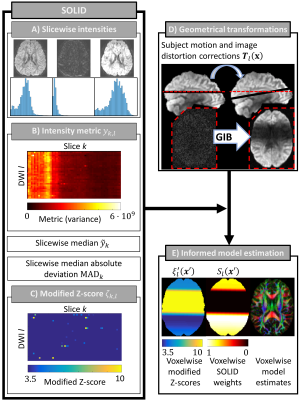 |
 Robust estimation of diffusion MRI metrics based on slicewise outlier detection (SOLID) Robust estimation of diffusion MRI metrics based on slicewise outlier detection (SOLID)
Viljami Sairanen, Alexander Leemans, Chantal Tax
The accurate characterization of diffusion process with MRI is compromised by various artefacts including intensity related errors. If not appropriately accounted for, model estimates can become significantly biased resulting in erroneous metrics. Slicewise intensity errors, in particular, are often handled by excluding the entire image or slice information, or by voxelwise robust estimators that experience difficulties in partial volume regions. In this work, we describe a fast and accurate algorithm to detect slicewise outliers and a framework to incorporate this information as data uncertainty in model estimation algorithms.
|
14:45
|
0468.
 |
 Influence of the lipids on the quantification of IVIM parameters in the vertebral bone marrow. Influence of the lipids on the quantification of IVIM parameters in the vertebral bone marrow.
Caroline Le Ster, Jérémy Lasbleiz, Hervé Saint-Jalmes, Raphaël Guillin, Giulio Gambarota
The aim of this study was to assess the effect of the lipids on the quantification of IVIM parameters in the vertebral bone marrow. Diffusion sequences were acquired with and without fat suppression on healthy volunteers. The results of our study show that fat is a confounding factor for the quantification of the diffusion coefficient and perfusion fraction; whereas it has no significant effect on the quantification of the pseudo-diffusion coefficient.
|
14:57
 |
0469.
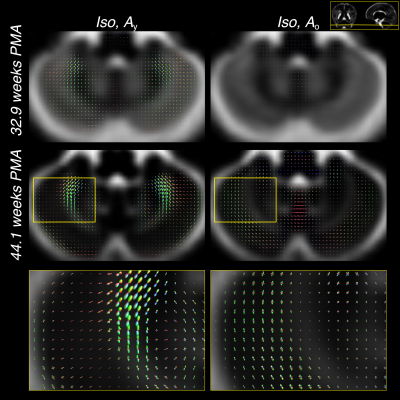 |
 Longitudinal multi-component HARDI atlas of neonatal white matter Longitudinal multi-component HARDI atlas of neonatal white matter
Maximilian Pietsch, Daan Christiaens, Jana Hutter, Lucilio Cordero-Grande, Anthony Price, Emer Hughes, A. David Edwards, Joseph Hajnal, Serena Counsell, J-Donald Tournier
We describe a method for creating a longitudinal atlas of developing white matter (WM) of neonates using the multi-shell multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution technique and multi-contrast registration on high-quality high angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI) data. We present an atlas that consists of one isotropic and two orientationally-resolved components. The atlas reveals fibre-specific patterns of WM maturation that are consistent with regional differences in maturation previously described in histological studies of the developing brain.
|
15:09
|
0470.
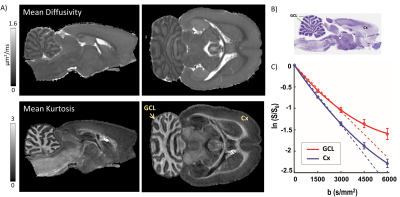 |
 Probing microstructural heterogeneity and mild traumatic brain injury-induced gray matter alterations in the rat brain using diffusion kurtosis imaging Probing microstructural heterogeneity and mild traumatic brain injury-induced gray matter alterations in the rat brain using diffusion kurtosis imaging
Manisha Aggarwal, Isabel San Martin, Alejandra Sierra
In heterogeneous brain tissue microenvironments, the probability distribution of spin displacements deviates from Gaussianity. Examining the non-Gaussian behavior of the diffusion-encoded signal with diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) could potentially allow probing cellular heterogeneity and injury-induced changes that are not discernible in the limited (q,t)-regime that pulsed-gradient DTI with conventional b-values explores. Here, we investigated the sensitivity of DKI to intrinsic cellular heterogeneity and mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI)-induced gray matter (GM) alterations in the rat brain. The results demonstrate distinct contrasts in mean kurtosis maps reflecting microstructural heterogeneity in GM regions, and detection of region-specific alterations in the cortex and thalamus.
|
15:21
|
0471.
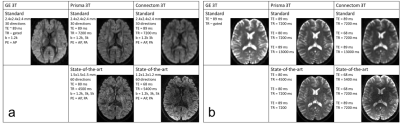 |
 Cross-vendor and Cross-protocol harmonisation of diffusion MRI data: a comparative study Cross-vendor and Cross-protocol harmonisation of diffusion MRI data: a comparative study
Chantal Tax, Francesco Grussu, Enrico Kaden, Lipeng Ning, Umesh Rudrapatna, John Evans, Samuel St-Jean, Alexander Leemans, Santi Puch, Matt Rowe, Paulo Rodrigues, Vesna Prckovska, Simon Koppers, Dorit Merhof, Aurobrata Ghosh, Ryutaro Tanno, Daniel Alexander, Cyril Charron, Slawomir Kusmia, David Linden, Derek Jones, Jelle Veraart
We present a comparison of five different methods that estimate mappings between scanners for diffusion MRI data harmonisation. The methods are evaluated on a dedicated dataset of the same subjects acquired on three distinct scanners with ‘standard’ and ‘state-of-the-art’ protocols, with the latter having higher spatial and angular resolution. Our results show that cross-vendor harmonisation and spatial/angular resolution enhancement of single-shell diffusion data sets can be performed reliably, although some challenges remain. The dataset is available upon request and can serve as a useful testbed for future method development in cross-site/cross-hardware and cross-vendor diffusion MRI harmonisation.
|
15:33
|
0472.
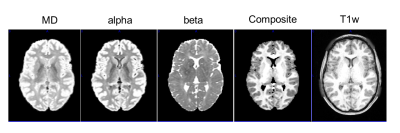 |
 Segmentation of the brain using direction averaged signal in DWI images Segmentation of the brain using direction averaged signal in DWI images
Hu Cheng, Sharlene Newman, Maryam afzali
A novel segmentation method using the direction-averaged DWI signal is proposed. Two images can be obtained from the fitting of the direction-averaged DWI signal: one with superior contrast between the gray matter and white matter; one with prominent CSF contrast. A pseudo T1 weighted image can be constructed and standard segmentation tools can be applied. The method was tested on the HCP subjects in SPM12 and FSL, and showed good agreement with segmentation using the T1 weighted image with the same resolution.
|
|













