Poster: CV PowerBeat: Part 2
Electronic Power Pitch Poster
Cardiovascular
14:45 - 15:45
Wednesday, 20 June 2018
Power Pitch Theater B - Exhibition Hall
| |
|
Plasma # |
|
0758.
 |
16 |
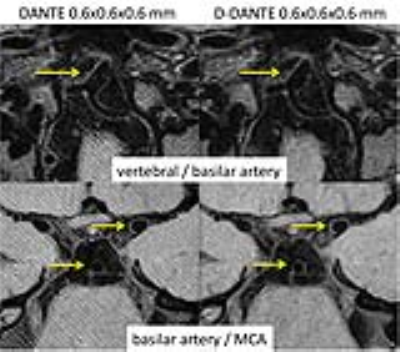
 Double DANTE: an improved method for high-resolution intracranial vessel wall imaging Double DANTE: an improved method for high-resolution intracranial vessel wall imaging
Bram Coolen, Jasper Schoormans, Ernst Kooreman, Qinwei Zhang, Olivia Viessmann, Gustav Strijkers, Aart Nederveen, Guillaume Gilbert, Jeroen Siero
We present the use of Double DANTE as an improved method for DANTE prepared 3D TSE imaging of intracranial arteries. DANTE preparation inherently leads to banding artifacts, which become increasingly visible at high-resolution imaging. We show that Double DANTE strongly reduces banding separation without changes in the DANTE pulse train duration, and more importantly, without compromising flow suppression of blood or CSF. Double DANTE therefore enables high-quality intracranial vessel wall MRI at 0.6mm isotropic resolution.
|
 |
0759.
 |
17 |
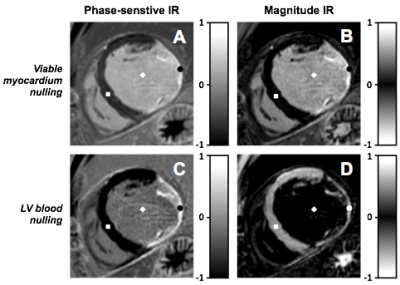
 Clinical value of dark-blood late gadolinium enhancement without additional magnetization preparation Clinical value of dark-blood late gadolinium enhancement without additional magnetization preparation
Robert Holtackers, Caroline van de Heyning, Muhummad Nazir, Imran Rashid, Ioannis Ntalas, Haseeb Rahman, René Botnar, Amedeo Chiribiri
Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) MRI often suffers from poor scar-to-blood contrast when used for detection of (sub)endocardial scar due to the bright signal of adjacent blood. We sought to validate a novel dark-blood LGE technique in a large cohort of 250 patients at both 1.5T and 3T. Combining left ventricular blood nulling with phase-sensitive inversion-recovery significantly improved both image quality and diagnostic confidence compared to conventional bright-blood LGE. As no additional magnetization preparation is used, clinical application on current MRI systems is readily available without the need for extensive simulations, software modifications and/or additional training.
|
|
0760.
 |
18 |
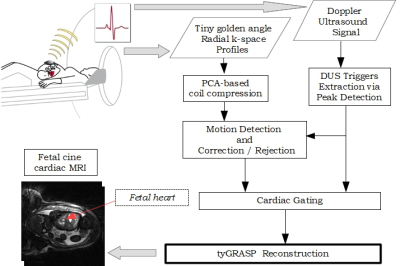
 Feasibility of Free-Breathing Fetal Cine Cardiac MRI based on Doppler Ultrasound, Compressed Sensing and Motion Compensation Feasibility of Free-Breathing Fetal Cine Cardiac MRI based on Doppler Ultrasound, Compressed Sensing and Motion Compensation
Kostas Haris, Erik Hedström, Fabian Kording, Sebastian Bidhult, Frederik Testud, Katarina Steding-Ehrenborg, Christian Ruprecht, Einar Heiberg, Håkan Arheden, Anthony Aletras
We investigated the feasibility of free-breathing fetal cine cardiac MRI using Doppler Ultrasound retrospective binning combined with continuous tiny golden angle radial sampling and compressed sensing via the tyGRASP reconstruction method. Motion due to maternal respiration and fetal movement was estimated by registration applied to reconstructed images of low temporal resolution. K-space radial profiles containing motion were either corrected or rejected from the reconstruction process. The reconstruction results demonstrated good image and diagnostic quality showing that the absence of fetal ECG can be bypassed in a computationally efficient way by Doppler Ultrasound even in the presence of motion.
|
|
0761.
 |
19 |
 Geometrical Characterization of Marfan and Bicuspid Aortic Valve Patients Using Finite Element Methods Geometrical Characterization of Marfan and Bicuspid Aortic Valve Patients Using Finite Element Methods
Julio Sotelo, Andrea Guala, Lydia Dux-Santoy, Aroa Ruiz-Muñoz, Arturo Evangelista, Joaquín Mura, Cristian Tejos, Daniel Hurtado, José Rodríguez-Palomares, Sergio Uribe
BAV patients and patients with MFS are predisposed to develop geometrical changes in the aorta. The geometrical assessment of the aorta using MRI in these patients generates an operator dependency and variability given by the 2D planer reformatting of the data. In this work, we propose finite element Laplace formulation, which allows us to obtain 3D maps of geometrical parameters in the aorta, avoiding the 2D reformatting process of the MRI data. We apply our method on volunteers, BAV and MFS patients. Our method allows applying it to any type of volumetric segmentation from MR or CT.
|
 |
0762.
 |
20 |
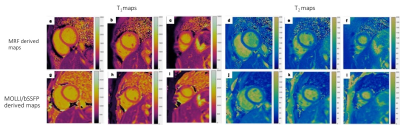
 Myocardial T1 And T2 Mapping Using MR Fingerprinting: Comparison to clinical standards Myocardial T1 And T2 Mapping Using MR Fingerprinting: Comparison to clinical standards
Shivani Pahwa, Jesse Hamilton, Joseph Adedigba, Sanjay Sridaran, Satyam Ghodasara, Rahul Thomas, Sadeer Al-Kindi, Gregory O'Connor, Sanjay Rajagopalan, Mark Griswold, Vikas Gulani, Nicole Seiberlich
Myocardial T1 and T2 relaxation times obtained with MRF were compared to values from traditional mapping sequences (MOLLI and T2-prep bSSFP) and evaluated for repeatability and reproducibility in 50 normal volunteers, as per SCMR consensus guidelines. MRF compared favorably with traditional sequences without significant proportional or systemic differences with fair to excellent repeatability and reproducibility, while providing better image quality.
|
|
0763.
 |
21 |
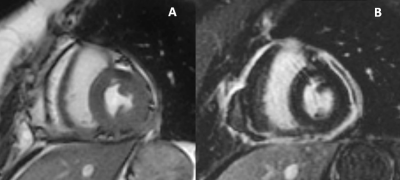
Pericardial Enhancement in Recurrent and Constrictive Pericarditis: Correlation with Pathology in 52 Patients
Did Not Present
James Glockner
Pericardial late gadolinium enhancement was correlated with pathologic specimens in 52 patients who had pericardiectomy performed for constrictive or chronic pericarditis. Pericardial LGE is an indicator of pericardial inflammation; however, it does not reliably distinguish inflammation from fibrosis: LGE was seen in 9/10 patients with pericardial fibrosis and minimal or no pericardial inflammation. Pericardial edema or early pericardial enhancement may be more useful biomarkers for pericardial inflammation.
|
|
0764.
 |
22 |
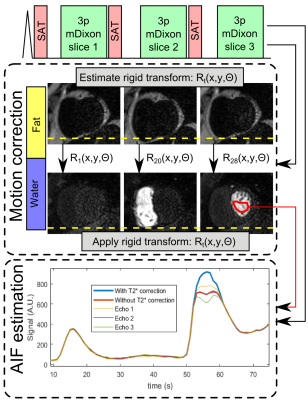
Quantitative myocardial perfusion using multi-echo Dixon for respiratory motion correction and arterial input function estimation
Video Permission Withheld
Markus Henningsson, Alexandre Farias, Adriana Villa, Cian Scannell, Torben Schneider, Amedeo Chiribiri
A quantitative myocardial first-pass perfusion approach is proposed using multi-echo Dixon acquisition. The fat images (unaffected by contrast bolus) are used to estimate respiratory motion and the transformations are applied to the corresponding diagnostic water images. The three echo images are also used to perform T2* correction of the arterial input function. Evaluation was performed in 8 patients during free-breathing rest perfusion. Motion correction reduced quantiation variability, while T2* correction of the arterial input function reduced the myocardial blood flow by 0.7ml/g/min across all patients.
|
 |
0765.
 |
23 |
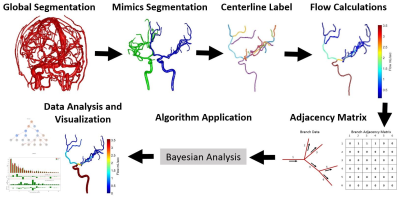
 Automated 4D Flow Conservation Utilizing Adjacency Matrices Automated 4D Flow Conservation Utilizing Adjacency Matrices
Carson Hoffman, Oliver Wieben, Gabe Shaughnessy
4D flow magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide a way to analyze both the anatomical and hemodynamic properties related to complex vessel networks. Using basic principles related to flow conservation the entire vessel networks data can be used to help improve local flow calculations. A Bayesian approach is utilized with a Markov Chain Monte Carlo where flow conservation is enforced to obtain, for a complete vascular network, estimates of mean flow and flow uncertainty. The estimated data results in a lower flow uncertainty overall and can allow for localization of potential erroneous branches in the initial data.
|
 |
0766.
 |
24 |
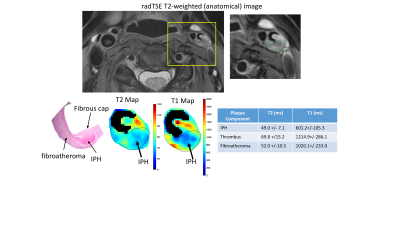
 Rapid Carotid Artery T2 and T1 Mapping Using a Radial TSE and IR-FLASH Approach Rapid Carotid Artery T2 and T1 Mapping Using a Radial TSE and IR-FLASH Approach
Maria Altbach, Sagar Mandava, Kevin Johnson, Zhitao Li, Mahesh Keerthivasan, Jennifer Becker, Ali Bilgin, Craig Weinkauf
Defining carotid plaque characteristics predictive of stroke using non-invasive MR imaging is clinically relevant, but has been mostly limited to qualitative visualization of signal intensity in multi-contrast MR images. Here we present two robust and fast T2 and T1 mapping techniques based on radial data acquisition and demonstrate them in terms of carotid plaque characterization.
|
 |
0767.
 |
25 |
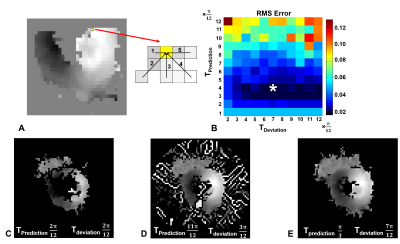
 Improved phase unwrapping algorithm for automatic cine DENSE strain analysis using phase predictions and region growing Improved phase unwrapping algorithm for automatic cine DENSE strain analysis using phase predictions and region growing
Daniel Auger, Xiaoying Cai, Changyu Sun, Frederick Epstein
Displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) measures myocardial displacements using the signal phase. Phase wrapping generally occurs during systolic phases, thus spatiotemporal phase unwrapping algorithms are required to compute motion trajectories and strain. Current DENSE analysis methods are aided by user-defined myocardial contours. A fully automatic DENSE analysis method is proposed where phase predictions using multiple pathways and region growing are used to simultaneously unwrap and segment the myocardium. Compared to a prior automatic method, this method selects fewer extramyocardial pixels, reducing the computation time, and has a greater phase unwrapping success rate.
|
 |
0768.
 |
26 |
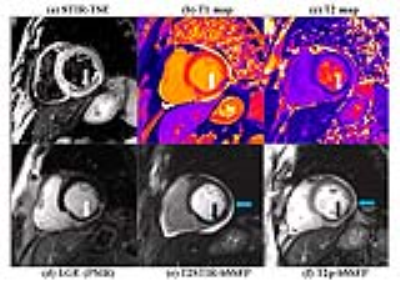
 Myocardial Edema Imaging – A Comparison of Three Techniques Myocardial Edema Imaging – A Comparison of Three Techniques
Yanjie Zhu, Lixian Zou, Yucheng Chen, Dong Liang, Xin Liu, Yiu-Cho Chung
Myocardial edema is commonly imaged using T2 based imaging technique, such as T2w-TSE, T2p-bSSFP and T2 mapping. Noting its elevated T1 and T2 value, a single-shot technique using T2 prepared STIR called T2STIR-bSSFP has been proposed for edema imaging. This study compared the contrast of T2p-bSSFP, T2 mapping and the newly proposed T2STIR-bSSFP methods via simulation, phantom experiment and patient study. The results showed that T2STIR-bSSFP has the highest contrast in myocardial edema image among the three methods at a shot scan time. It may provide a fast edema imaging technique for the whole heart covering.
|
|
0769.
 |
27 |
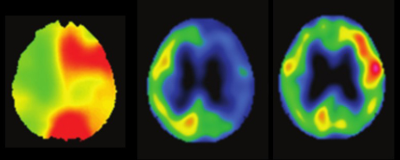
 Prediction for development of cerebral hyperperfusion after carotid endarterectomy using cerebral oxygen extraction fraction map based on quantitative susceptibility mapping at 7T Prediction for development of cerebral hyperperfusion after carotid endarterectomy using cerebral oxygen extraction fraction map based on quantitative susceptibility mapping at 7T
Jun-ichi Nomura, Ikuko Uwano, Makoto Sasaki, Kohsuke Kudo, Fumio Yamashita, Kenji Ito, Shunrou Fujiwara, Yoshiyasu Matsumoto, Kohki Oikawa, Kohei Chida, Kazunori Terasaki, Masakazu Kobayashi, Kenji Yoshida, Kuniaki Ogasawara
The aim of this study was to validate whether preoperative QSM-based OEF (OEFQSM) map at 7T could predict the development of postoperative hyperperfusion (HP) after carotid endarterectomy (CEA) in patients with internal carotid artery stenosis. In quantitative assessment, OEFQSM was significantly higher in the presence group than that in the absence group of HP. Receiver operating characteristic analysis showed the OEFQSM was a good indicator for predicting the development of HP after CEA when the suitable cut-off value. Finally, the present study demonstrated that preoperative OEFQSM map at 7T can identify patients at risk for HP after CEA.
|
|
0770.
 |
28 |
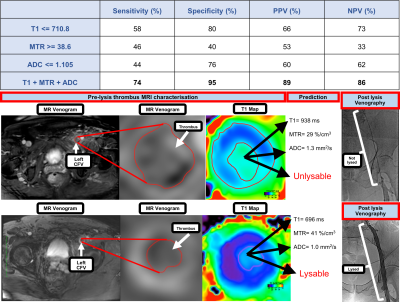
 Investigating the use of non-contrast enhanced Magnetic Resonance Multi-Sequence Thrombus Imaging (MSTI) to direct therapy in patients with acute iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis Investigating the use of non-contrast enhanced Magnetic Resonance Multi-Sequence Thrombus Imaging (MSTI) to direct therapy in patients with acute iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis
Justinas Silickas, Prakash Saha, Alberto Smith, Stephen Black, Adam Gwozdz, Marcelo Andia Kohnenkampf, Ashish Patel, Bijan Modarai, Rene Botnar, Alkystis Phinikaridou
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) affects 1 in 1000 people and when the ilio-femoral segment is involved, over half will develop post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS). PTS can be debilitating for the patients and carries a huge health cost burden. Thrombolysis reduces the incidence of PTS, but is only successful in 60% of patients. There is no reliable method of identifying thrombi susceptible to lysis. We have developed a non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance multi-sequence thrombus imaging (MSTI) protocol that provides information on the structural composition of the thrombus and may be a reliable method of predicting thrombus lysability.
|
|
0771.
 |
29 |
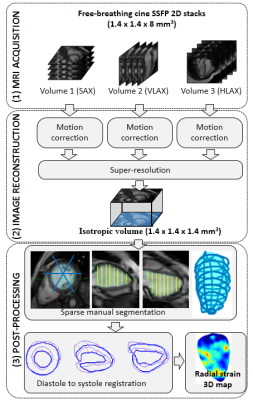
 Strain Measurements from 3D Isotropic Cine MRI: Relation with Fibrosis in a Duchenne Patient Population Strain Measurements from 3D Isotropic Cine MRI: Relation with Fibrosis in a Duchenne Patient Population
Freddy Odille, Shufang Liu, Bailiang Chen, Aurélien Bustin, Jacques Felblinger, Laurent Bonnemains
A method is proposed for myocardial strain estimation, based on 3D isotropic cine MRI. A free-breathing, motion-corrected super-resolution acquisition is used to obtain the 3D isotropic cine dataset. Then the left ventricular (LV) myocardium is manually segmented using a sparse segmentation technique. Finally a registration-based technique is used to obtain displacement fields that best match diastolic and systolic 3D isotropic masks of the LV, and subsequent Lagrangian strain estimates. The method was evaluated in 20 Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. Segment-wise analysis showed that the proposed radial strain estimates correlated well with the presence of fibrosis.
|
|
0772.
 |
30 |
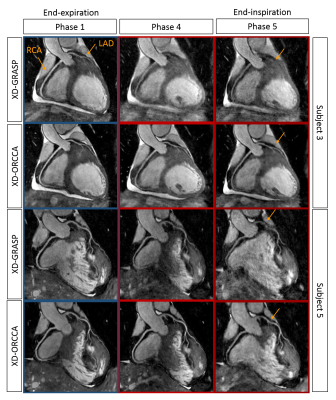
 Optimized respiratory-resolved motion-compensated 3D Cartesian coronary MRA Optimized respiratory-resolved motion-compensated 3D Cartesian coronary MRA
Teresa Correia, Giulia Ginami, Radhouene Neji, Gastao Cruz, Rene Botnar, Claudia Prieto
Conventionally, free-breathing whole-heart 3D coronary MR angiography (CMRA) uses navigator-gated acquisitions to reduce respiratory motion, by acquiring data only at a specific respiratory phase, which leads to prolonged scan times. Respiratory-resolved reconstruction approaches have been proposed to achieve 100% scan efficiency using mainly non-Cartesian acquisitions and exploiting sparsity in the respiratory dimension. Here, a robust framework for Cartesian imaging is proposed, which provides high-quality respiratory-resolved images by incorporating motion information from image navigators (iNAV) to increase the sparsity in the respiratory dimension. Furthermore, iNAV motion information is used to compensate for 2D translational motion within each respiratory phase.
|
|

 Watch the full Pitch Session Here
Watch the full Pitch Session Here














