Value of MRI
Traditional Poster
MR Value
Thursday, 21 June 2018
| Exhibition Hall 2627-2647 |
08:00 - 10:00 |
|
2627.
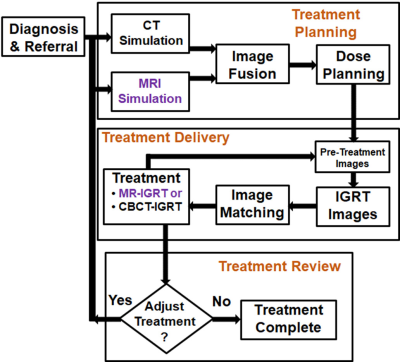 |
The value of MRI in radiation therapy
Olga Green, Hiram Gay, Paragh Parikh, Stacie Mackey, Sasa Mutic, Thomas Dvergsten, Mo Kadbi, H Michael Gach
During the last decade, the role of MRI in radiation therapy (RT) grew dramatically. The soft-tissue benefits from MRI simulations complement the geometric accuracy and photon attenuation maps from computed tomography in RT treatment planning. MR for calculating attenuation (MRCAT) is being used for MRI-only treatment planning. The clinical utilization of hybrid MRI-guided radiation therapy (MR-IGRT) systems began in January 2014. MR-IGRT enables real-time tracking of tumors and highly conformal treatments that enable improved patient outcomes. Hence, the value of MRI in RT is rapidly rising. Examples of MRI's role in, and value to, RT are presented.
|
|
2628.
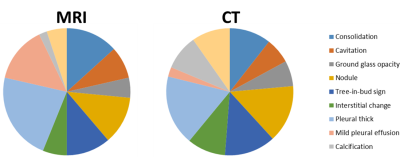 |
Comparison of MRI and CT Characterizations of Lung Lesions from Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Liya Wang, Zhou Liu, Lijian Liu, Zhiqing Wu, Yuzhong Zhang, Hui Mao
Lung MRI can be applied to imaging and characterize the abnormalities and lesions in patients with history of pulmonary tuberculosis (TB). By comparing with the images obtained from the routine clinical CT from the same patients, this work shows that MRI is comparable to CT as a non-radiation alternative for lung imaging with good diagnostic image quality. In addition, MRI can provide additional information on lung soft tissue properties not available from CT.
|
|
2629.
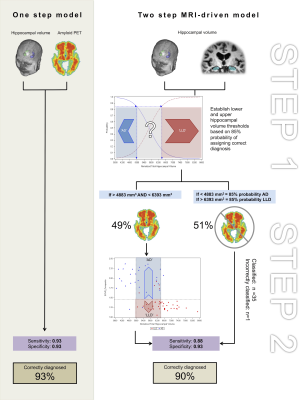 |
An optimised, MRI-PET based clinical protocol for improving the differential diagnosis of Late-life Depression and Alzheimer's Disease
Louise Emsell, Kristof Vansteelandt, François-Laurent De Winter, Filip Bouckaert, Lene Claes, Danny Christiaens, Lies Van Assche, Jan Van den Stock, Rik Vandenberghe, Stefan Sunaert, Mathieu Vandenbulcke
Owing to overlapping symptomatology, differentiating between late-life depression (LLD) and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), is clinically challenging. Amyloid PET may be used to improve AD diagnosis, however it is expensive and not widely available. Here we apply a two-step MRI driven approach exploiting the different degree of hippocampal volume loss that is present in both disorders to derive hippocampal volume thresholds for identifying patients who could be diagnosed without a PET exam. Using the more cost-effective hippocampal volumetry approach, we could correctly classify half of the patient sample. This increased to 90% when adding 18F-flutametamol PET for the remaining patients.
|
|
2630.
 |
Do MRI structured reports? for diabetic foot contain concise information for clinical application?
Li Guo, Xiaoying Wang, Xin Qi, Yufeng Xu, Yong Huang, Xueying Li
The aim of this study is to evaluate if structured reporting of MRI in diabetic foot(DF) contain concise information for clinical application compared with nonstructured reporting. Thirty nonstructured foot MRI reports of patients with DF were included, and another structured report was written for each patient. Three readers (A, B&C) evaluated the nonstructured and structured reports. Statistical analysis included Wilcoxon signed ranks tests and chi-square tests. All readers needed shorter time to understand the structured reports. For the 8 features for DF, two readers could understand bone edema significantly more often when reading structured versus nonstructured reports. All readers needed to evaluate images when reading nonstructured reports, 2 radiologists (reader A&C) needed to evaluate images when reading structured reports, and reader B(doctor of burn & plastic surgery) only needed 4(13.3%) to evaluate images when reading the structured reports. All readers missed Charcot joint and fracture when reading nonstructured reports, but only reader A missed fracture and reader C missed Charcot joint when reading structured reports. All readers found another abscess when reading structured reports. In conclusion, structured reports of MRI in patients with DF provided more concise information for clinical application than nonstructured reports.
|
|
2631.
 |
Scanner Status Tool (STATS): towards increasing the value of MR
Ed Mojahed
Scanner Status tool (STATS) is a light Perl-based script that runs on the MR scanner's Host computer and picks up critical information about the status of the background processes and informs users when everything is OK or when there is an error detected so they could subsequently take an informed action. This will result in a smoother workflow, reduction in wasted time, promotion of First Time Right imaging, and increased value of MR.
|
|
2632.
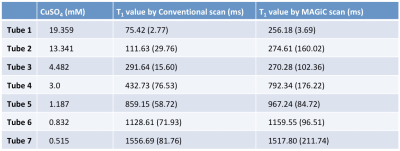 |
Quantitative validation of the image contrast generated by MAgnetic Resonance image Compilation (MAGiC) technique
Chia-Wei Li, Chien-Yuan Lin, Ai-Ling Hsu, Wing P. Chan
MAGiC scan could provide several different clinical relevant weighted images and quantitative tissue relaxation time with use of a multi-slice, multi-echo, and multi-delay acquisition in the single scan. In this study, a homemade phantom containing 7 tubes with various concentrations of aqueous CuSO4 was used to quantitatively validate the image quality of a MAGiC scan. Results show that overall diagnostic image quality using MAGiC is comparable to that using conventional scanning, but a slight contrast difference is seen where T1 values are low (outside the range of brain T1 values, less than 500 ms)
|
|
2633.
 |
Feasibility of high throughput scanning at 7T: 13 subjects per hour
Tijl van der Velden, Erwin Krikken, Catalina Arteaga, Fredy Visser, Dennis Klomp
While substantial acceleration in MRI acquisitions have been demonstrated in the last decades (particularly at high fields where SNR is not limited), substantial patient and scan preparation time have been reported that seem to prohibit high patient throughput for clinical MRI. In this study we demonstrate that robust head MRI can be obtained at a throughput of more than 13 subjects per hour, including patient management and scan preparations (even faster than typical X-ray exams). Increased throughput may be an alternative way to “killer applications” in making high field MRI economically viable.
|
|
2634.
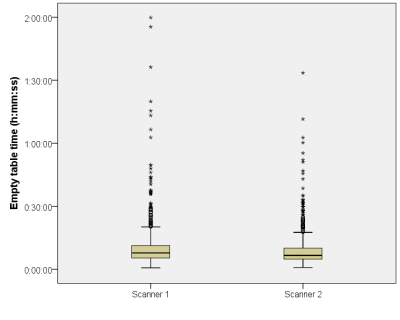 |
Added value of a management software tool for optimization of clinical MRI workflow
Timo De Bondt, Mahdi Kalai, Floris Vanhevel, Olivier Morhedec, Florian Sarrazin, Donat Thery, Federica Zanca, Paul Parizel
MRI has important drawbacks like slow speed and high cost, which makes it a challenge to maintain cost-effectiveness in context of the changing healthcare economic environment. We show that a management software tool, giving easy access to operational and clinical data, can provide insights into everyday clinical workflow. Additionally, it has the potential to facilitate optimization of protocols, and improve patient safety.
|
|
2635.
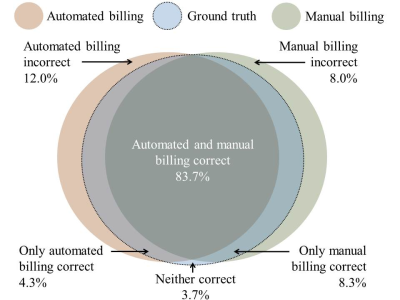 |
Automated Billing Code Prediction from MRI Log Data
Jonas Denck, Wilfried Landschütz, Knud Nairz, Johannes Heverhagen, Andreas Maier, Eva Rothgang
We developed an algorithm that is capable of retrieving MRI billing codes from MRI log data. This proof-of-concept work is applied to Tarmed, the Swiss fee-for-service tariff system for outpatient services, and is tested on two MRI scanners, a MAGNETOM Aera and a MAGNETOM Skyra (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany), of a single radiology site. A machine learning approach for automated MRI billing code retrieval from MRI log data is implemented. The proposed algorithm reliably predicts medical billing codes for MRI exams (F1-score: 97.1%). Integrated in the clinical environment, this work has the potential to reduce the workload for technologists, prevent coding errors and enable scanner-specific expense and turnover analysis.
|
|
2636.
 |
Patient Acceptance on a Compact 3T is Generally Superior to a Whole-Body Scanner
Erin Gray, John Huston III, Yunhong Shu, Myung-Ho In, Shengzhen Tao, Joshua Trzasko, Eric Fiveland, Thomas Foo, Matt Bernstein
A compact 3T scanner was developed under a Bioengineering Research Partnership as a technology demonstrator. To assess patient acceptance on the compact 3T compared with a whole-body 3T MR, 33 consecutive patients completed a series of survey questions to report their subjective experience. The survey results demonstrate that the Compact 3T is equal or superior to a whole-body scanner for patient acceptance.
|
|
2637.
 |
Synthesis and analysis of low b value Diffusion Weighted Images at 10mT
Seema Bhat, Pavan Poojar, Marta Ferreira, Hanumantharaju M C, Rita Nunes, Sairam Geethanath
DWI MRI is a well established method for stroke imaging, within the critical operating window of approximately four to six hours. This requires an accessible, portable and cost effective MR solution typically achieved at very low magnetic fields. In this work, simulation of low b value DWI images at 10mT has been performed in comparison with 1.5T. Also, the affect of pulse sequence design parameters has been explored to arrive at a potentially useful DWI acquisition scheme. Future work includes prospective implementations of the sequence on a 10mT scanner and; denoising and reconstruction of low field images using deep learning.
|
|
2638.
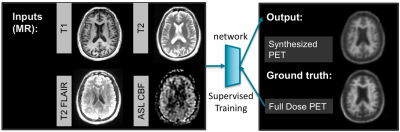 |
Mapping metabolic activation as FDG-PET/Amyloid-PET using Contrast-free MRI and Deep Learning
Enhao Gong, Kevin Chen, Jia Guo, Audrey Fan, John Pauly, Greg Zaharchuk
MRI has great clinical values to distinguish soft-tissues without contrast or radiation. By using the hybrid-modality information from MRI and PET, here we developed deep learning method to synthesize metabolic activity mapping from contrast-free multi-contrast MRI images. Trained on clinical datasets, we demonstrated the feasibility to estimate metabolic biomarker from contrast-free MRI and validated on both FDG-PET/MRI and Amyloid-PET/MRI in-vivo datasets. This technique can be used for more efficient, low-cost, multi-tracer functional imaging, exploring anatomy-function relationship, visualizing new bio-markers and improving the workflow for both MRI and PET/MRI.
|
|
2639.
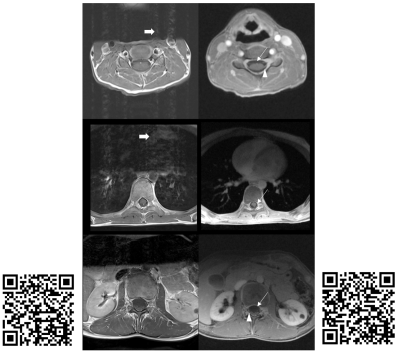 |
Free-Breathing Motion Insensitive T1-Weighted Spine MRI in Children Using a Radial Acquisition at 3 Tesla
Houchun Hu, Thomas Benkert, Mark Smith, Jerome Rusin, Aaron McAllister, Jeremy Jones, Ramkumar Krishnamurthy, Kai Tobias Block
MRI methods that are insensitive to physiological motion are attractive in pediatric applications. In this work, we compare a 3D T1-weighted radial acquisition with conventional multi-slice TSE in post-contrast spine imaging at 3T in seven patients. Images were rated by three neuroradiologists. Radial data were perceived as more diagnostic than TSE and Cartesian TSE data were significantly more impacted by motion and pulsation. Qualitatively, radial images yielded improved spinal cord to CSF signal contrast and better conspicuity of nerve roots than TSE data. In evaluating secondary CSF tumor spread, radial spine MRI provides a confident "first-time-right" protocol than TSE scans.
|
|
2640.
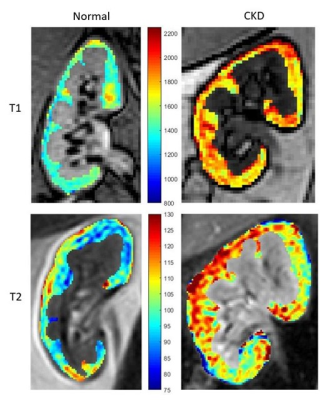 |
Renal Relaxivity Mapping at 3.0 T for the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease – Initial Experience
Muditha Bandara, Chirath Sulalith, Narayana Rolla, Indrajit Saha, Aruna Pallewatte, Janaka Wansapura
Detection of early stage Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is essential to improve patient outcome but remains a challenge. In this study we generated T1 and T2 maps of renal cortex at 3.0 T in CKD patients and healthy volunteers (n=16). Modified Look-Locker sequence with simulated ECG and a multi-echo Gradient and Spin-Echo sequence were used to generate T1 and T2 maps respectively. T1 of CKD kidney (1752 ± 45 ms) was significantly higher (P < 0.001) than that of healthy kidney (1538 ± 37 ms). There was no significant difference between the groups in T2, FWHM and skewness of T2.
|
|
2641.
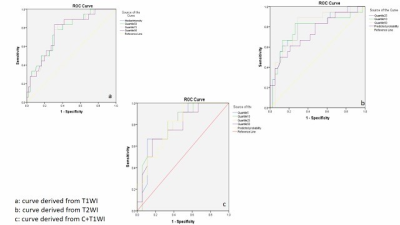 |
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING TEXTURE ANALYSIS (MRTA) ON T1WI, T2WI AND T1WI CONTRAST: DIAGNOSTIC ACCURACY OF CEREBRAL GLIOMA.
Mame KEITA, Liang Han, YANWEI MIAO, Mahammed MOHAMUD
Cerebral gliomas are the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults and include Astrocytoma, Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma. Due to its multi-parametric approach, MRI was used to quantify tumor heterogeneity with Texture Analysis (TA). To avoid unnecessary surgeries and set-up good treatment’s plan, the analysis of conventional MRI sequences was performed and showed a strong level of discrimination between the three gliomas on each sequence. TA has shown promise in the discrimination between lesions on MR images and provided satisfactory results.
|
|
2642.
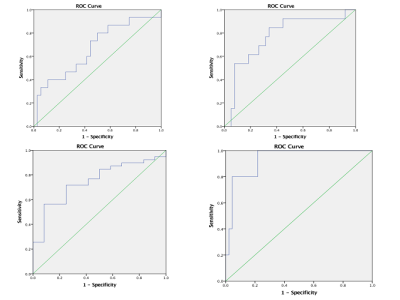 |
MRI TEXTURE ANALYSIS: DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF CEREBRAL GLIOMAS FOLLOWING WHO 2016 CLASSIFICATION OF CNS TUMOURS
Mame KEITA, Liang Han, YANWEI MIAO
For the first time in 2016, the World Health Organisation (WHO) Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System used molecular parameters in addition to histology to define many tumour entities, thus formulating a concept for how CNS tumour diagnose should be structured in the molecular era and in that way is both a conceptual and practical advance over its 2007 predecessor. The strength of non-invasive diagnosis using textural analysis of conventional MRI sequences was evaluated and gave satisfactory results comparing grade II, III and IV including their genetic status.
|
|
2643.
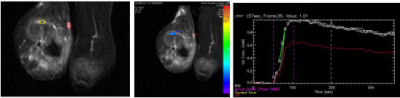 |
Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of rabbit VX2 bone tumor: Model Selection, repeatability and Validation
Wei Gong, Yunfei Zha
To compare the repeatability and availability of the quantitative parameters for dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging that is based on the Reference-Region model and Tofts model with the microcirculation perfusion and permeability characteristics in rabbit VX2 bone tumor.
|
|
2644.
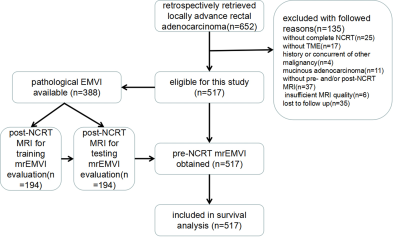 |
Baseline mrEMVI as an independent prognostic factor for locally advanced rectal cancer with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy: recommendations for risk stratification
XIAO-YAN ZHANG , SHUAI WANG, XIAO-TING LI, YING-PING WANG, YAN-JIE SHI, LIN WANG, AI-WEN WU, YING-SHI SUN
Extramural venous invasion status is a potential prognostic factor for identifying rectal cancer patients with a high risk of distant metastasis or local recurrence. It is currently unclear what impact extramural venous invasion status as defined by magnetic resonance imaging before neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (pre-NCRT mrEMVI) has on survival outcomes in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. Moreover, the incorporation of baseline mrEMVI into risk stratification is poorly understood.This study has demonstrated that pre-NCRT mrEMVI status can be reliably evaluated and can serve as an independent prognostic factor for distant and local recurrence and overall survival in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. We have provided important evidence that pre-NCRT mrEMVI status should be considered for managing risk stratification in baseline locally advanced rectal cancer. Finally, we recommend that mrEMVI evaluation be included in routine pre-NCRT MR reports to support an individualized treatment strategy, considering positive pre-NCRT mrEMVI may serve as an indicator for neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
|
|
2645.
 |
The treatment efficacy of novel adjuvant chemotherapy evaluated by bi-exponential model diffusion weighted imaging in breast carcinoma
Liang Yuyu, Zhu Rongrong, Yang Yong, Zhuo Zhizheng
This study aims to explore the efficacy of NAC assessed by quantitative multi-parameter utilized bi-exponential diffusion weighted imaging in breast cancer. In this study, there is significant difference in ΔFfast value between groups, mainly results from the rise of Ffast value of tumor because of chemotherapy. Nonetheless, the diagnosis efficacy is mild for NAC assessment using ΔFfast value.
|
 |
2646.
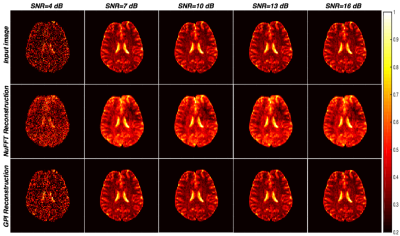 |
Evaluation of spiral trajectories for very low field MR imaging of the brain
pavan poojar, Imam Shaik, Girish Koulagi, Seema Bhat, Sairam Geethanath
Very low field (VLF) MRI systems provide cost effective, accessible solutions for brain imaging. However, VLF MRI typically suffers from significantly lower signal-to-noise ratio and hence longer acquisition times. This work explores the utilization of spiral acquisitions at VLF as it provides efficient sampling of kspace and accelerated acquisitions compared to Cartesian trajectories. Spiral trajectories were designed for 10mT without violating the hardware constraints resulting in potential accelerated acquisitions. Retrospective reconstruction of brain images was performed using Non uniform Fast Fourier Transform and Graphical Programming Interface. Future work involves prospective implementation on a home built scanner being currently pursued.
|
|
2647.
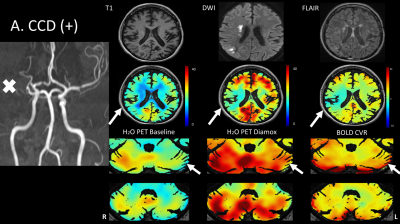 |
Crossed cerebellar diaschisis: diagnostic & prognostic value of BOLD fMRI cerebrovascular reactivity
Marco Piccirelli, Martina Sebök, Christiaan van Niftrik, Oliver Bozinov, Susanne Wegener, Giuseppe Esposito, Athina Pangalu, Antonios Valavanis, Alfred Buck, Andreas Luft, Luca Regli, Jorn Fierstra
Crossed cerebellar diaschisis (CCD) is associated with poorer stroke outcome and is traditionally measured with [15O]-H2O-PET. BOLD-CVR can detect CCD with high specificity and sensitivity. Furthermore, CCD subjects identified with BOLD-CVR also had a poorer clinical status at baseline and at three months follow-up. These encouraging results suggest that BOLD-CVR might be considered as a diagnostic and prognostic test for CCD subjects, comparable to the gold standard [15O]-H2O-PET – but without the ~1mSv radiation dose. |
|






















