Molecular & Metabolic Imaging
Molecular & Metabolic Imaging
Oral
Oral
Molecular Imaging
Thursday, 16 May 2019
| Room 510A-D | 13:45 - 15:45 | Moderators: Silvio Aime, Jack Miller |
13:45 |
1125. 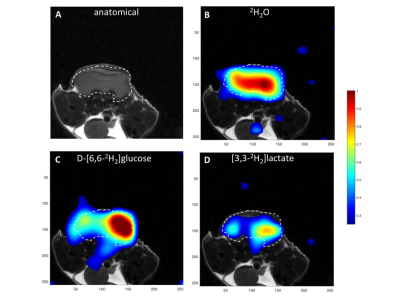 |
Monitoring treatment response in a murine lymphoma with Deuterium Metabolic Imaging and Spectroscopy
Felix Kreis, Alan Wright, Maria Fala, De-en Hu, Kevin Brindle
We investigated whether Deuterium Metabolic Imaging (DMI) with 2H-labeled glucose can be used to monitor treatment response in a pre-clinical murine lymphoma model (EL4). Localized 2H spectra were acquired from tumors, with a time resolution of ~1min, following a bolus injection of labeled glucose. These showed inhibition of lactate labeling following treatment of the tumors with etoposide. 2D chemical shift images (2D CSI) were acquired from the tumors, but imaging treatment response may need faster image acquisition. Studies with a respiratory chain inhibitor in vitro suggested that labeling of water in EL4 tumor cells may be due, at least in part, to TCA cycle activity.
|
13:57 |
1126. 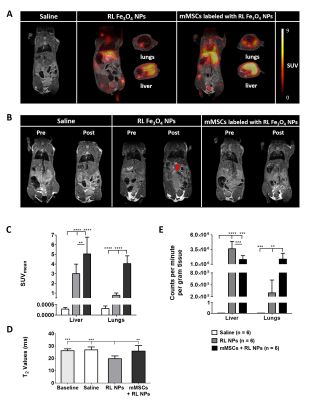 |
Novel Fluorine-18 Labeled Fe3O4@Al(OH)3 Nanoparticles as Dual Contrast Agents for Simultaneous PET/MRI
Sarah Belderbos, Manuel Antonio González-Gómez, Yolanda Piñeiro, Frederik Cleeren, Jens Wouters, Bella Manshian, Stefaan Soenen, Christophe Deroose, Willy Gsell, Guy Bormans, Jose Rivas, Uwe Himmelreich
The emergence of (pre)clinical PET/MRI scanners is accompanied by the development of novel contrast agents. Aluminum hydroxide magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@Al(OH)3 NPs) can overcome limitations of iron oxide NPs after labeling with Na18F, allowing visualization with PET (high sensitivity, low background) and MRI (high resolution, longitudinal NP follow-up). In this study, labeling of novel Fe3O4@Al(OH)3 nanostructures with Na18F was rapid. In vivo, radiolabeled NPs accumulated in liver of healthy mice, while cells labeled with radiolabeled NPs were also seen in lungs. Our results indicate the potential of these novel nanostructures for cell tracking with high sensitivity, specificity and resolution using PET/MRI.
|
| 14:09 |
1127. 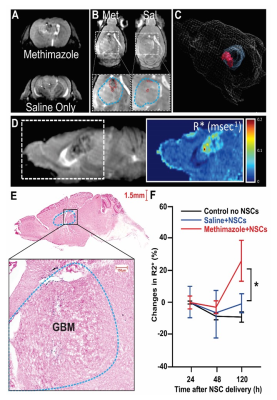 |
Longitudinal & quantitative 3D-R2* MRI validates methimazole-enhanced intranasal delivery of labeled neural stems cells for treatment of glioblastoma.
Daniele Procissi, Nicola Bertolino, Drew Spencer, Dou Yu , Katarzyna Pituch, Maciej Lesniak, Irina Balyasnikova
Longitudinal and quantitative 3D-R*2 MRI provides a unique platform for tracking labeled cells in vivo, across subjects and time-points following treatment. In this study we use this approach to demonstrate how FDA approved methimazole can enhance intranasal delivery and accumulation of labeled and therapeutically enhanced neural stem cells in glioma xenografts. 3D rendering of the high resolution quantitative maps across different sessions enhances visualization of the NSC accumulation and provides a unique tool to track the homing-pathway of the stem cells. Results were confirmed by survival data for different groups with the Met+NSC treated group exhibiting increased survival trends.
|
| 14:21 |
1128. 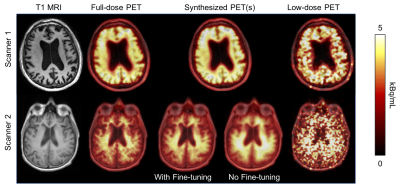 |
Transfer Learning of an Ultra-low-dose Amyloid PET/MRI U-Net Across Scanner Models
Kevin Chen, Matti Schürer, Jiahong Ouyang, Enhao Gong, Solveig Tiepolt, Osama Sabri, Greg Zaharchuk, Henryk Barthel
Reducing the radiotracer dose of amyloid PET/MRI will increase utility of this modality for early diagnosis and for multi-center trials on amyloid-clearing drugs. To do so networks trained on data from one site will have to be applied to data acquired on other sites. In this project we have shown that after fine-tuning, a network trained on PET/MRI data acquired from one scanner is able to produce diagnostic-quality images while achieving noise reduction and image quality improvement for data acquired on another scanner.
|
| 14:33 |
1129. 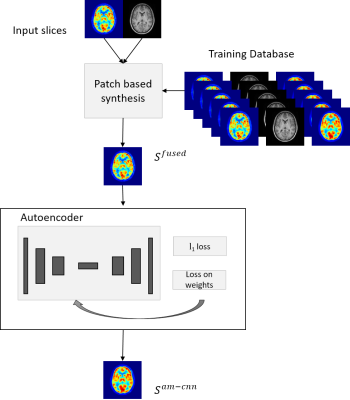 |
Synthesis of standard dose FDG PET images from low dose acquisition using a combination of atlas and CNN based method
Viswanath P. Sudarshan, Anthony Fernandez, Kamlesh Pawar, Shenpeng Li, Gary F. Egan, Suyash Awate, Zhaolin Chen
Radiation exposure in positron emission tomography (PET) examination is a major issue for patient safety. PET image quality is severely degraded if low dose of radioactive tracer is administered. With a simultaneous magnetic resonance (MR)-PET scanner, MR anatomical priors can potentially improve PET image reconstruction. In this work, we introduce a framework to synthesize high quality standard dose PET images from the low dose PET and T1 MR images using an atlas guided convolutional neural network (CNN) approach. Compared with the conventional methods, the introduced method demonstrates improved PET image quality for datasets acquired with ten-fold PET dose reduction.
|
| 14:45 |
1130. 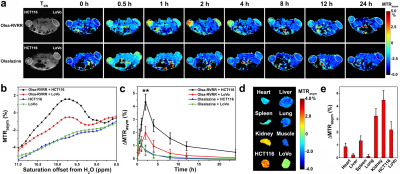 |
Tumor-Specific Self-Assembly of DiaCEST Nanoparticles as Theranostic Agents
Yue Yuan, Jia Zhang, Xiaoliang Qi, Shuoguo Li, Guanshu Liu, Xiaolei Song, Michael McMahon, Jeff Bulte
We employed a tumor-specific enzyme (furin)-mediated conversion of the anti-cancer and CEST MRI-visible drug olsalazine (Olsa), which resulted in the formation of self-assembled intracellular nanoparticles in tumor cells. In vivo studies using high-furin and low-furin expressing human xenografts showed that the OlsaCEST signal and anti-tumor therapeutic effect were 5 to 6-fold increased compared to single olsalazine molecules. An excellent “theranostic correlation” (R2 = 0.97) could be observed between the magnitude of the CEST MRI signal and therapeutic response (normalized tumor size).
|
| 14:57 |
1131. 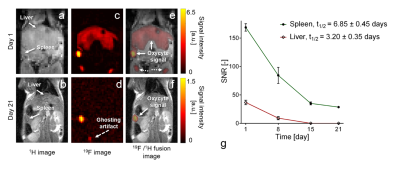 |
A fluorine-19 MR characterization of ABL-101 - a novel tracer with high biocompatibility and MR sensitivity
Emeline Darçot, Roberto Colotti, David Brennan, Graeme Deuchar, Celestine Santosh, Ruud van Heeswijk
A major challenge that slows down the translation of fluorine-19 (19F) MRI for inflammation monitoring and cell tracking into clinical practice is the need for perfluorocarbons (PFCs) that have good biocompatibility while also being suitable for 19F MRI. We therefore characterized ABL-101, a perfluoro(t-butylcyclohexane) emulsion, as a 19F MRI tracer. ABL-101 had T2/T1 ratios and detection limits similar to PFCs developed specifically for MRI. This combined with the short clearance half-life of this intravenous emulsion make ABL-101 a very promising candidate as a tracer in future clinical trials that use 19F MRI.
|
15:09 |
1132. 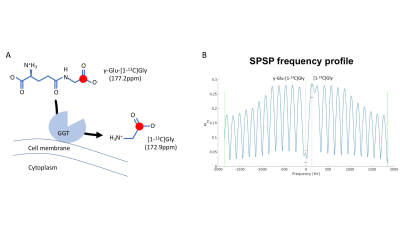 |
Detection of ?-glutamyl-transferase activity up-regulation in orthotopic glioma using hyperpolarized ?-glutamyl-[1-13C]glycine
Georgios Batsios, Chloé Najac, Peng Cao, Pavithra Viswanath, Elavarasan Subramani, Yutaro Saito, Anne Marie Gillespie, Hikari Yoshihara, Peder Larson, Shinsuke Sando, Sabrina Ronen
γ-glutamyl-transferase (GGT) is a key enzyme in the γ-glutamyl cycle, which regulates glutathione homeostasis. Previous studies reported that the enzyme is upregulated in many human malignancies including glioblastoma, but remains low in normal brain. Here, we demonstrate the potential of hyperpolarized γ-glutamyl-[1-13C]glycine as a probe for GGT activity in the brain by demonstrating that its conversion to [1-13C]glycine is significantly higher in animals with orthotopic glioblastoma tumors when compared to healthy animal brains.
|
| 15:21 |
1133. 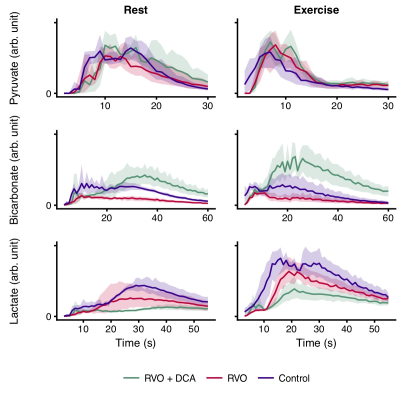 |
Hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate spectroscopy assessment of the metabolic reserve in a porcine model of compensated cardiac overload
Nikolaj Bøgh, Esben Hansen, Camilla Omann, Jakob Lindhart, Per Nielsen, Robert Stephenson, Christoffer Laustsen, Vibeke Hjortdal, Peter Agger
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of heart failure undetectable by current clinical techniques. We examined pigs with cardiac overload using hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate magnetic resonance spectroscopy at rest and under stress. Mitochondrial function was determined in-vitro. Pyruvate oxidation rates were decreased in overloaded hearts, especially under stress. In-vitro mitochondrial respiration rates were decreased in tissue from overloaded hearts. In one group, we pharmacologically increased pyruvate oxidation, which led to decreased hypertrophy, increased contractile reserve and better mitochondrial respiration. Our work underlines the importance of metabolism in heart failure and suggests that stress hyperpolarized imaging may be a marker of mitochondrial dysfunction.
|
| 15:33 |
1134. 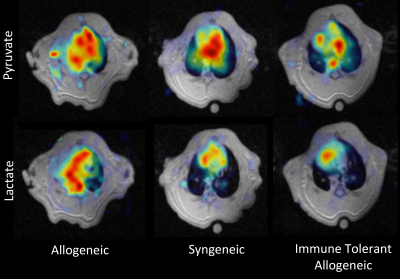 |
Imaging Post-Transplant Allogeneic Rats with Acquired Immune Tolerance Using Hyperpolarized [1-13C] Pyruvate MRI
Sarmad Siddiqui, Federico Sertic, Mehrdad Pourfathi, Susan Rostami, Yi Xin, Ian Duncan, Stephen Kadlecek, Ali Naji, Rahim Rizi
Post-transplant, lungs are clinically monitored using regular radiography and/or CT scans to detect rejection. We previously demonstrated that lactate-to-pyruvate ratio derived via hyperpolarized (HP) [1-13C]-pyruvate MRI is an earlier predictor of lung rejection than microCT in an orthotopic rat lung transplantation model. In this study, we imaged transplanted allogeneic lungs in a recipient rats with acquired immune tolerance to resolve the signal contribution of ischemia-reperfusion injury from that of tissue rejection. Transplanted rat lungs with acquired immune tolerance exhibit similar behavior to that of syngeneic lung transplants before abolishing their acquired tolerance.
|
 Back to Program-at-a-Glance |
Back to Program-at-a-Glance |  Back to Top
Back to Top