Breast Power Pitch
| Power Pitch Session: How it Works | |
|
1st Hour: 2-minute Power Pitches inside the Power Pitch Theater. 2nd Hour: 60-minute Digital Poster Presentations at the numbered plasma screens outside the Power Pitch Theater. |
1st Hour
Pitch: Breast Power PitchPower Pitch
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Tuesday, 14 May 2019
Power Pitch Theater C - Exhibition Hall
15:45 - 16:45
Moderators: Wolfgang Bogner
2nd Hour
Poster: Breast Power PosterPower Pitch Poster
Body: Breast, Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis
Tuesday, 14 May 2019
Power Pitch Theater C - Exhibition Hall
16:45 - 17:45
| Plasma # | |||
0590. 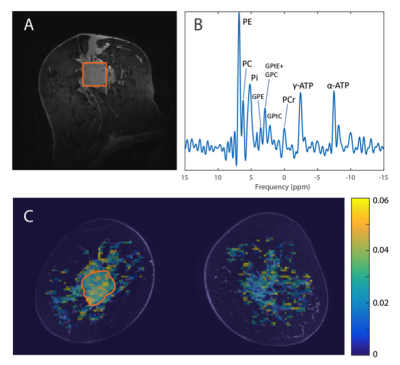 |
31 | Investigating the relation between amide signal and pH in breast cancer using CEST-MRI and 31P MRSI at 7T.
Erwin Krikken, Vitaliy Khlebnikov, Wybe van der Kemp, Hanneke van Laarhoven, Peter Luijten, Maurice van den Bosch, Dennis Klomp, Jannie Wijnen
In this study, we combine CEST-MRI and 31P-MRSI measurements, to better comprehend the underlying mechanisms of the measured changes in APT signal by relating it to the pHi. CEST-MRI and 31P-MRSI were acquired in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) treatment before and after the first cycle of NAC at 7T. We found a linear correlation between APT-CEST and pH and a linear correlation between PE/Pi and the pH in the tumor of breast cancer patients before the start of NAC treatment. We hypothesized that an increased pH results in an increased APT signal, yet we found the opposite. As APT mainly depends on mobile amide proton concentration and the exchange rate, this data suggest that the main contributor to the APT signal is the concentration of mobile amide protons.
|
|
0591. 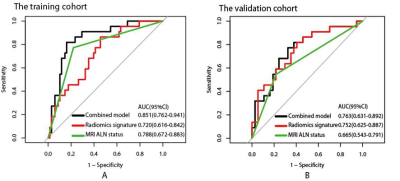 |
32 | Preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion in invasive breast cancer with DCE-MRI-based radiomics
Zhuangsheng Liu, Bao Feng, Yingjie Mei, Qinxian Chen, Changlin Li, Yehang Chen, Xiangmeng Chen, Zhuoyong Li, Wansheng Long
Preoperative assessment of lymphovascular invasion (LVI) plays an important role in the therapeutic planning for individual breast cancer patient. A few MRI features have been shown to be associated with LVI, but remain controversial. This prospective study explored DCE-MRI-based radiomics for preoperative prediction of LVI in breast cancer. The results suggested that radiomics signature and MRI based axillary lymph node status were significantly correlated with LVI. The combined model, which incorporated the radiomics signature and MRI based axillary lymph node status, could preoperatively predict LVI with acceptable performance in the training and validation cohorts.
|
|
0592. 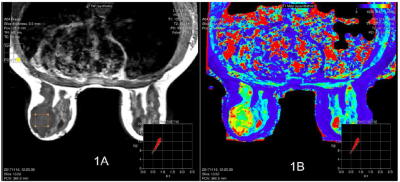 |
33 | Investigation of the use of T1 relaxation time map in synthetic MRI for diagnosis of breast cancer
Tie-bao MENG, Hui-ming LIU, Long Qian, Bing Wu, Hao-qiang HE, Chuan-miao XIE
It is known that benign and malignant breast cancer feature different T1 relaxation, the use of T1 relaxation in differential diagnosis has been reported. However accurate measurement of T1 relaxation requires knowledge of B1 distribution, which is inhomogeneous in breast. Synthetic MRI offers B1 corrected T1 relaxation time, its use breast cancer diagnosis has not yet been reported. Here, the use of the T1 mapping in synthetic MR in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant cancer is investigated. Our results demonstrated that T1 mapping offered by synthetic MR may be a potential quantitative biomarker for diagnosis of breast cancer.
|
|
0593. 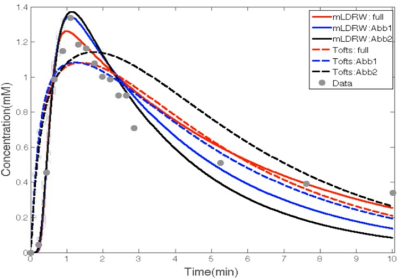 |
34 | Breast Pharmacokinetic Mapping using an Abbreviated Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) MRI Protocol
Linxi Shi, Jianmin Yuan, Bruce Daniel, Brian Hargreaves
The morphologic and kinetic information of a breast lesion can be quantified using pharmacokinetic models enabled by DCE MRI, which often has
|
|
0594. 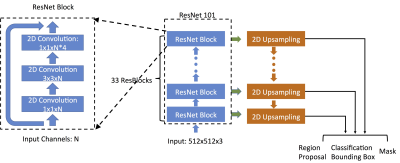 |
35 | Automatic Search in Breast MRI Dataset For Detection of Suspicious Lesions Using Mask R-CNN
Yang Zhang, Kai-Ting Chang, Siwa Chan, Peter Chang, Daniel Chow, Jeon-Hor Chen, Min-Ying Su
A Mask R-CNN algorithm was implemented to search the entire dataset of breast MRI to identify suspicious lesions for further diagnosis. A total of 102 patients with confirmed cancer were analyzed. There were a total of 2,314 positive cases (i.e. imaging slices containing lesion); and 8,512 slices without lesion as negative cases. The search results show 1,943 true positives; 6,149 true negatives; 2,363 false positives; and 371 false negatives, with sensitivity 0.83, specificity 0.72, and the overall detection accuracy 0.75. The Dice Similarity Coefficient of the tumor segmented in the detection box compared to ground truth is 0.84.
|
|
 |
0595 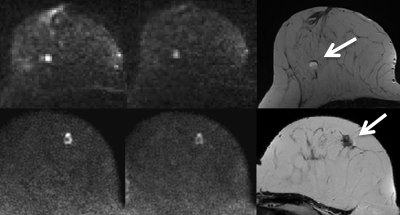 |
36 | Influence of residual fat signal on diffusion kurtosis MRI of suspicious mammography findings Video Permission Withheld
Anna Mlynarska-Bujny, Sebastian Bickelhaupt, Franziska König, Frederik Laun, Wolfgang Lederer, Heidi Daniel, Stefan Delorme, Heinz-Peter Schlemmer, Tristan Kuder
One of the factors determining the success of diffusion-weighted imaging of the female breast is complete fat suppression, especially when using high b-values. In this study, modified diffusion kurtosis models accounting for residual fat signal were compared to conventional DWI approaches. The comparison was based on a MR mammography dataset acquired in two study centers. The dataset comprised 198 patients with suspicious lesions detected during X-ray mammography screening. The ROC analysis shows significantly better performance of the modified diffusion kurtosis model in discriminating between malignant and benign lesions. This could improve the diagnostic accuracy regarding ambiguous mammography findings.
|
0596. 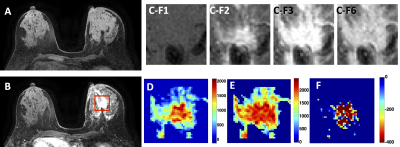 |
37 | Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions Based on DCE-MRI by Using Radiomics and Deep Learning with Five Different Networks
Jiejie Zhou, Yang Zhang, Kai-Ting Chang, Peter Chang, Daniel Chow, Ouchen Wang, Meihao Wang, Min-Ying Su
A total of 152 patients receiving breast MRI for diagnosis were analyzed, including 93 patients with 103 malignant cancers, and 59 patients with 73 benign lesions. Three DCE parametric maps corresponding to early wash-in, maximum, and wash-out were generated. Radiomics analysis based on texture and intensity histogram, and deep learning using 5 networks, were performed for differential diagnosis. The accuracy of radiomics was 0.80, and the accuracy of deep learning varied in the range of 0.79-0.94 depending on the network. The smallest bounding box containing the tumor with small amount of per-tumor tissue has the highest diagnostic accuracy.
|
|
0597. 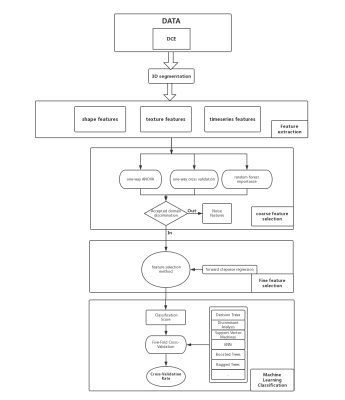 |
38 | Radiomics Signature on preoperative MR imaging:To predict pathological complete response and disease-free survival in patientes with Triple-negative breast cancer(TNBC) to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC)
Zhe Wang, He Wang, Bing Qing Xia, Yajia Gu
To investigate whether radiomics based on contrast-enhanced MRI can predict pathological complete response(pCR) and disease-free survival(DFS) of locally advanced TNBC undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy(NAC).
|
|
0598. 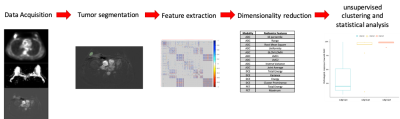 |
39 | Unsupervised Hierarchical Clustering of PET/MRI Radiomics Features Might Be Helpful to Predict Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy of Breast Cancer
Cindy Xue, Jing Yuan, Victor Ai, Helen HL Chan, Gladys Lo
|
|
0599. 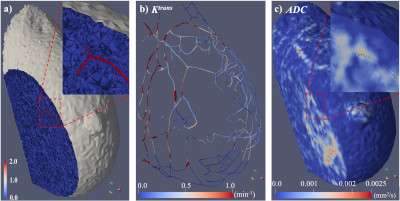 |
40 | Patient-specific characterization of breast tumor-associated flow using image-guided computational fluid dynamics
Chengyue Wu, David Hormuth, Todd Oliver, Federico Pineda, Gregory Karczmar, Robert Moser, Thomas Yankeelov
Tumor blood supply and interstitial flow play an essential role in tumor growth, invasion, and treatment response. In this contribution, we employ quantitative DCE-MRI and DWI data to constrain a patient-specific, computational fluid dynamics model of blood flow within breast tumors. To the best of our knowledge, this represents the first attempt at employing non-invasive imaging data to enable
|
|
0600. 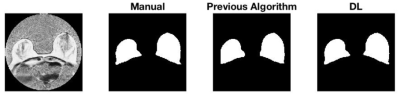 |
41 | Deep learning-based whole breast segmentation to support automated breast density measurements from fat-water decomposition MRI
Karl Spuhler, Jie Ding, Maria Altbach, Jean-Philippe Galons, Patricia Thompson, Alison Stopeck, Chuan Huang
Breast density monitoring has become a clinically interesting topic in the past several years. MRI-based methods are attractive because they allow for frequent monitoring without ionizing radiation. Here, we present evidence that a convolutional neural network can replace manual or algorithmic breast segmentation in such pipelines.
|
|
0601. 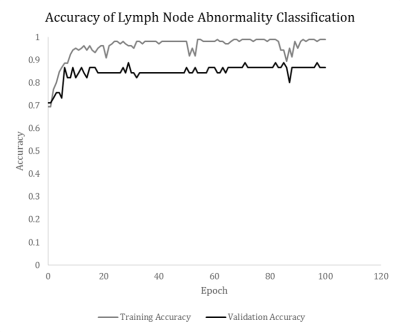 |
42 | Convolutional neural network classification of axillary lymph node metastasis on MRI of breast cancer patients
Thomas Ren, Hongyi Duanmu, Renee Cattell, Rami Vanguri, Mousumi Roy, Michael Liu, Vincent Zhang, Sachin Jambawalikar, Fusheng Wang, Tim Duong
The majority of breast cancer metastasis spreads through the axillary lymph nodes. It is challenging to classify whether there is disease or no-disease axillary lymph nodes because they are small and cluster together. We implemented a convolutional-neural network for automatic classification of diseased versus non-diseased axillary lymph nodes by analyzing data from standard clinical breast MRI. Data were assigned randomly to 70/30 as training/validation set. The results showed the remarkable agreement with ground truths, with 86.7% accuracy. This approach may prove useful for automatically detecting lymph nodes metastasis on MRI in clinical settings in breast cancer patients.
|
|
0602. 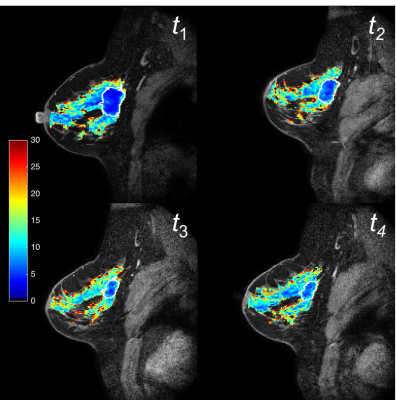 |
43 | Quantitative magnetization transfer imaging of breast cancer: Initial results at 3T
Lori Arlinghaus, Richard Dortch, Hakmook Kang, David Wharton, Richard Abramson, Thomas Yankeelov
Quantitative MT (qMT) techniques provide measurements of the ratio of macromolecular to free water protons, or pool-size-ratio (PSR), which may be useful for detection of changes in macromolecular content of breast tumors early in the course of treatment. Here we report preliminary qMT data acquired as part of an ongoing study employing quantitative MRI to predict the response of breast tumors to neoadjuvant therapy. PSR measurements in tumors were found to be significantly reduced compared to the surrounding fibroglandular tissue in patients diagnosed with invasive breast cancer.
|
|
0603. 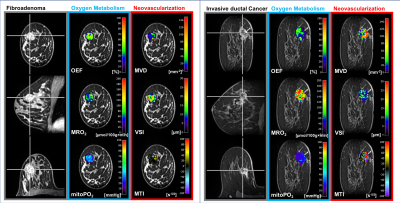 |
44 | First-in-human: tackling the hypoxic challenge in breast cancer with advanced MRI
Katja Pinker-Domenig, Barbara Bennani-Baiti , Thomas Helbich, Max Zimmermann, Pascal Baltzer, Paola Clauser, Pangiotis Kapteas, Zsuzsanna Bago-Horvath, Peter Dubsky, Rupert Bartsch, Andreas Stadlbauer
To develop a novel MRI approach for the non-invasive assessment of hypoxia and neovascularization in benign and malignant breast tumors and to provide insights into the intratumoral heterogeneity of breast cancer. 76 patients with a BI-RADS 4/5 lesion underwent 3T MRI of the breast with Vascular Architecture Mapping (and quantitative Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent (qBOLD) imaging. Our approach demonstrated that breast cancer consumes more oxygen and is more hypoxic and neovascularized than benign tumors. This non-invasive approach can be easily integrated in a diagnostic MRI protocol and has the potential to improve tumor characterization and facilitate tailored breast cancer treatment.
|
|
0604. 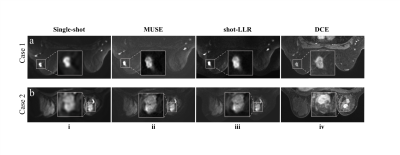 |
45 | Multi-shot DWI with multiplexed sensitivity encoding (MUSE) versus single-shot DWI in the breast
Yuxin Hu, Arnaud Guidon, Lloyd Estkowski, Bruce Daniel, Brian Hargreaves, Catherine Moran
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has shown strong potential for clinical impact in breast MRI but is limited by low resolution and image distortion. Multi-shot acquisitions can help to address these limitations. Here we assess a multi-shot diffusion acquisition utilizing two different reconstructions in comparison to single-shot DWI in breast cancer patients. The assessment includes quantified perceived resolution and ratings of qualitative image characteristics with respect to the DCE-MRI acquisition.
|
 Back to Program-at-a-Glance |
Back to Program-at-a-Glance |  Back to Top
Back to Top