New Developments in Cancer Imaging & Spectroscopy
| Power Pitch Session: How it Works | |
|
1st Hour: 2-minute Power Pitches inside the Power Pitch Theater. 2nd Hour: 60-minute Digital Poster Presentations at the numbered plasma screens outside the Power Pitch Theater. |
1st Hour
Pitch: New Developments in Cancer Imaging & SpectroscopyPower Pitch
General Cancer Imaging
Tuesday, 14 May 2019
Power Pitch Theater B - Exhibition Hall
15:45 - 16:45
Moderators: Christian Farrar, Vikram Kodibagkar
2nd Hour
Poster: New Developments in Cancer Imaging and SpectroscopyPower Pitch Poster
General Cancer Imaging
Tuesday, 14 May 2019
Power Pitch Theater B - Exhibition Hall
16:45 - 17:45
| Plasma # | |||
0575. 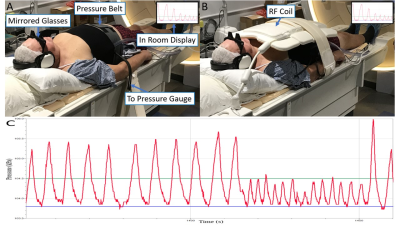 |
16 | Respiratory Motion Management in MR-guided Radiotherapy treatment and assessment with IVIM.
Benjamin Lewis, Robert Cadrain, Christopher Chipko, Armando Vera, Emma Fields, Siyong Kim, Taeho Kim
In radiotherapy (RT), respiratory motion induced target displacement can cause the treatment beam to miss the target, irradiating normal tissue instead. This study introduces a novel pressure based motion management system with biofeedback, compatible with MRI, CT, and megavoltage RT. A belt, wrapped around the abdomen, with a pressure sensor provided respiratory traces and guidance to subjects during MR acquisition. Superior-inferior liver dome motion could be reduced from 30.6mm under free breathing to 5.6mm with a small guiding window. This device provides significant motion reduction and a surrogate to internal organ motion for use across the RT treatment process.
|
|
0576. 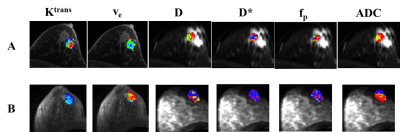 |
17 | Comparison and Integration of DCE- and IVIM-MRI for Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Preliminary Study
Kurt Li, Archana Machireddy, Alina Tudorica, Brendan Moloney, Karen Oh, Neda Jafarian, Savannah Partridge, Xin Li, Wei Huang
The goal is to compare DCE-MRI PK parameters with IVIM-MRI parameters and ADC in breast cancer diagnostic accuracy, and assess if integration of DCE and IVIM markers further improves diagnostic performance. Twenty-two patients with 23 suspicious breast lesions underwent pre-biopsy DCE- and DW-MRI with 12 b values. PK parameters were estimated using the Shutter-Speed model. IVIM parameters and ADC were derived with biexponential and monoexponential modeling of the DW-MRI data, respectively. Both DCE- and IVIM-MRI, with individual or combined markers, outperformed clinical MRI reading in breast cancer diagnosis. The integration of DCE and IVIM markers provided the best diagnostic performance.
|
|
0577. 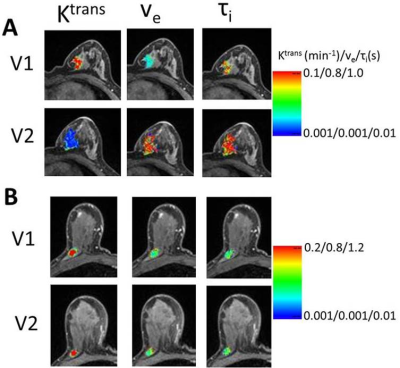 |
18 | Integration of DCE-MRI and Molecular Markers for Improved Early Prediction of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Alina Tudorica, Karen Oh, Yiyi Chen, Neda Jafarian, Arpana Naik, Kathleen Kemmer, Megan Troxell, Eric Goranson, Aneela Afzal, May Mishal, Wei Huang
The goal is to determine if integration of DCE-MRI and molecular markers improves early prediction of breast cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT). 49 patients undergoing standard of care NACT had DCE-MRI before and after the first NACT cycle, with 12 of them achieving pathologic complete response (pCR) after NACT. Pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis of DCE-MRI data was performed using the shutter-speed model. Changes in PK parameters were superior to changes in tumor size for early prediction of pCR. The improvement in predictive performance by combining DCE and HR, HER2 molecular markers was statistically significant compared to using MRI markers alone. |
|
0578. 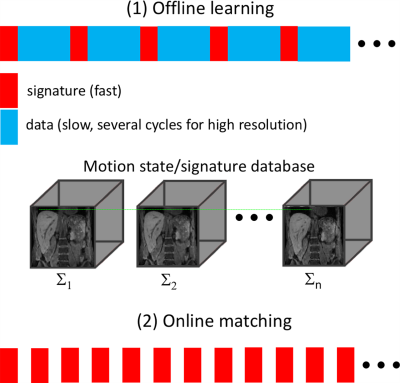 |
19 | Magnetic Resonance SIGnature MAtching (MRSIGMA) for Real-Time Volumetric Motion Tracking
Li Feng, Ricardo Otazo
New MR-Linac systems allow for simultaneous imaging and radiation-treatment, and hold great promise for adaptive radiation-treatment of moving organs. However, even with the latest MRI acquisition and reconstruction technologies, tracking volumetric motion in real-time is still challenging. This work describes a novel technique called MR SIGnature MAtching (MRSIGMA), which consists of (1) offline learning, where 3D motion states and corresponding unique rapid signatures are learned; and (2) online matching, where only rapid signature data are acquired to determine corresponding motion states. Initial implementation using golden-angle radial sampling is shown for liver motion tracking with a latency of < 200ms.
|
|
0579. 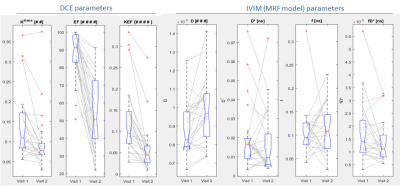 |
20 | DCE-MRI is more sensitive than IVIM-DWI for assessing therapy induced changes in tumour perfusion in colorectal liver metastases
Mihaela Rata, Khurum Khan, David Collins, Dow-Mu Koh, Nina Tunariu, Maria Antonietta Bali, James d'Arcy, Simona Picchia, Ian Chau, Nicola Valeri, David Cunningham, Martin O Leach, Matthew R Orton
This study evaluates response to anti-angiogenic treatment in 25 patients with colorectal liver metastases to determine whether the observed changes on dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE)-MRI are detectable by IVIM-DWI. Significant therapy response measured in this cohort by DCE and confirmed by tumour biopsies was not mirrored by the perfusion related IVIM parameters. No strong correlation was found between DCE and IVIM perfusion parameters. DCE-MRI is more sensitive than IVIM-DWI for assessing therapy induced changes in tumour perfusion in colorectal liver metastases.
|
|
0580. 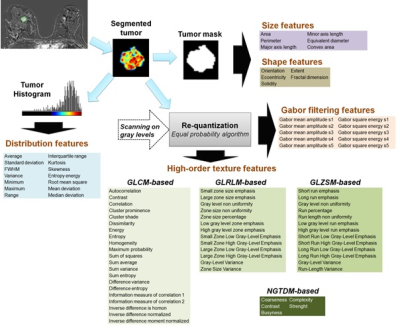 |
21 | Prediction of breast lesion malignancy in high-risk oncogenetic patients with MRI BI-RADS 4 lesion using multiparametric MRI-based radiomic
Benjamin Leporq, Camille Schreiner, Agnes Coulon, Olivier Beuf, Frank Pilleul
In this study a multiparametric MRI-based radiomic method to predict cancer in MRI BI-RADS 4 breast lesions, in high-risk oncogenetic patients is proposed. The results demonstrated that mpMRI-based radiomic can predict all malignant lesions among MRI BI-RADS 4 lesion and reduced the number of unnecessary biopsy by 86% in our population.
|
|
0581. 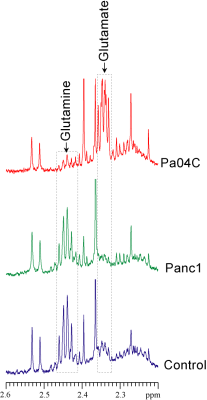 |
22 | Glutamine Metabolism Dysregulated in PDAC induced Cachexia
Santosh Kumar Bharti, Paul Winnard, Raj Kumar Sharma, Yelena Mironchik, Michael Goggins, Zaver Bhujwalla
Glutamine is one of the most abundant circulating amino acids that is critical for many fundamental functions in cancer cells, including synthesis of metabolites that maintain mitochondrial metabolism, protein synthesis, acting as a carbon source or as the primary nitrogen donor for multiple essential biosynthetic pathways, and in the activation of cell signaling. Here we have identified significant differences in glutamine in human plasma from pancreatic cancer patients that were also observed in tumor interstitial fluid from pancreatic cancer xenografts that induced cachexia. These results suggest that agents with glutaminolytic activity may be useful in treating cachexia.
|
|
0582 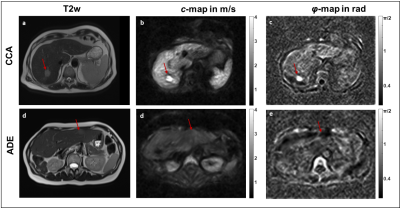 |
23 | Tomoelastography for the detection and characterization of liver tumors Video Permission Withheld
Mehrgan Shahryari, Georg Böning, Uli Fehrenbach, Jing Guo, Heiko Tzschätzsch, Jürgen Braun, Timm Denecke, Ingolf Sack
Tomoelastography is a full field-of-view multifrequency MR elastography technique for high-resolution mapping of stiffness and viscosity of in-vivo tissues. We applied tomoelastography to patients with hepatic lesions and analyzed the accuracy of the method for tumor detection (contrast between lesion and liver tissue) and characterization (difference between malignant and benign tumors). Our results show that shear-wave-speed and phase angle of the complex shear modulus have good accuracy for detection (AUC=0.90 and 0.93, respectively) and characterization (AUC=0.92 and 0.88, respectively) of hepatic lesions. Tomoelastography can add important quantitative information about the biophysical constitution of liver tumors.
|
|
 |
0583. 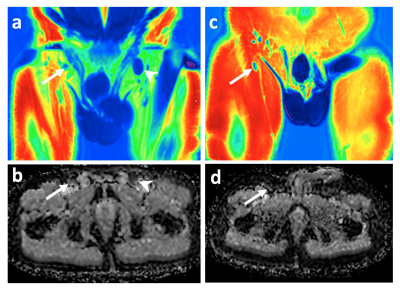 |
24 | Whole body 3.0 T MRI in Adult Lymphomas: Assessment of Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers for Nodal Disease Assessment
Arash Latifoltojar, Mark Duncan, Maria Klusmann, Alan Bainbridge, Deena Neriman, Francesco Fraioli, Jonathan Lambert, Kirit Ardeshna, Shonit Punwani
Whole-body MRI (WB-MRI) is being increasingly advocated as an alternative/adjunct imaging platform in range of cancers including lymphomas. In this study we investigated the application of quantitative imaging biomarkers (QIBs) from a multi-parametric WB-MRI protocol for nodal disease assessment in adults’ lymphomas. We have shown that signal fat fraction (sFF) is more accurate for delineation of positive and/or negative disease compared to apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and might be a useful addition to widely used ADC quantitation.
|
 |
0584. 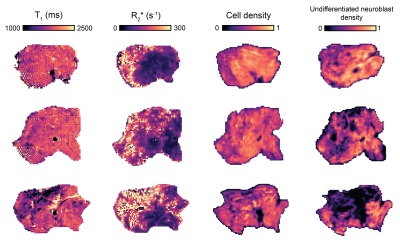 |
25 | T1 mapping of neuroblastoma pathology: insight from a computational pathology study in the Th-MYCN transgenic mouse model
Konstantinos Zormpas-Petridis, Matthew Blackledge, Matthew Clarke, Louis Chesler, Yinyin Yuan, Simon Robinson, Yann Jamin
A reduction in T1 has been reported as a generic biomarker of successful treatment in the Th-MYCN model of neuroblastoma, a childhood tumor of the developing nervous system. The aim of this study was to decipher the pathological determinant(s) contributing to global and regional variations in native T1 by comparison with R2* maps and registered computed density maps of both segmented cells and classified cells, extracted from whole-slide digital pathology images in tumors arising in the Th-MYCN transgenic model of neuroblastoma.
|
0585. 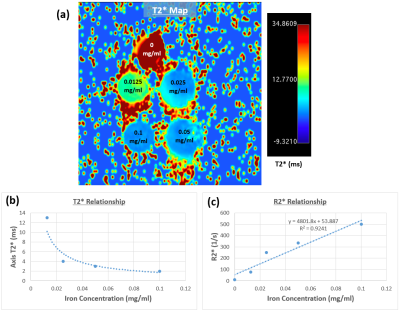 |
26 | Magnetic resonance imaging for confirmation of catheter-selective tumor-targeting liposomes distribution Presentation Not Submitted
Venkateswara Gogineni, El-Sayed Ibrahim, Dilip Maddirela, Dong-Hyun Kim, Sarah White
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form of primary liver cancer, and globally it is the sixth most common cancer. In this study, we use liposomes that can co-encapsulate the therapeutic agent (oxaliplatin or gemcitabine) in addition to iron oxide nanoparticles to enable MRI-monitored local delivery of the therapeutic agent to limit proangiogenic responses in non-resectable liver tumors following transcatheter embolotherapies. The results showed increased R2* values in the tumor regions at one week post-infusion, compared to the surrounding liver parenchyma and to same regions immediately after infusion, which allows for confirmation of procedural success and proper catheter-selective tumor targeting.
|
|
0586. 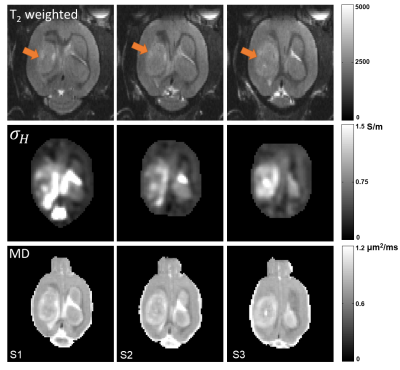 |
27 | High-frequency electrical conductivity imaging of rat brain tumor
Clementine Lesbats, Nitish Katoch, Atul Minhas, Hyung Kim, Eung Woo, Harish Poptani
Magnetic Resonance Electrical Property Tomography (MREPT) allowed the evaluation of the intra- and extracellular ionic changes in a rat model of brain tumor. A multi-echo T2-weighted pulse sequence was used with 10 echos to map the B1 field and reconstruct the tissue conductivity at 9.4T. Higher conductivity values were measured in the tumors compared to the healthy brain tissue, suggesting an increased ionic content and mobility in the tumor.
|
|
0587. 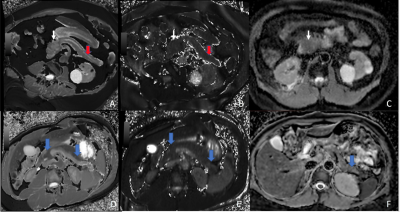 |
28 | Non-Contrast Multiparametric Mapping for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cancer (PDAC) Tissue Characterization
Lixia Wang, Yibin Xie, Srinivas Gaddam, Nan Wang, Zixin Deng, Zhengwei Zhou, Wensha Yang, Zhaoyang Fan, Tao Jiang, Simon Lo, Andrew Hendifar, Stephen Pandol, Debiao Li
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most-common malignant tumors and has poor outcomes. With increasing size, the mass causes obstruction of the main pancreatic duct which results in chronic pancreatitis of the upstream pancreas (towards the tail). However, the downstream pancreas (towards the head) does not have these changes. In this study, we quantitatively measured multiple MR parameters (T1, T2, and ADC) of PDAC, upstream, and downstream pancreas along with normal pancreas in healthy volunteers and found these values can be used to differentiate these tissue types. The combination of the three parameters improves overall accuracy in differentiating PDAC with upstream pancreas, downstream pancreas, and normal pancreas over single parameter.
|
|
0588.  |
29 | Assessment of Tumor Hypoxia response to sorafenib in Rabbit VX2 Liver Tumor xenografts by Tissue Oxygen Level Dependent MR imaging Presentation Not Submitted
Shuping Qin, Xinming Li, Zhendong Qi, Wen Liang, Yingjie Mei, Jingjing Huang, Xianyue Quan
Developing non-invasive methods that assess drug resistance, which causes tumor hypoxia, is a research hotspot. We applied tissue oxygen level dependent (TOLD) MRI to investigate the changes in tumor oxygen inhalation of rabbit liver VX2 tumor xenografts before and sorafenib treatment.
|
|
0589. 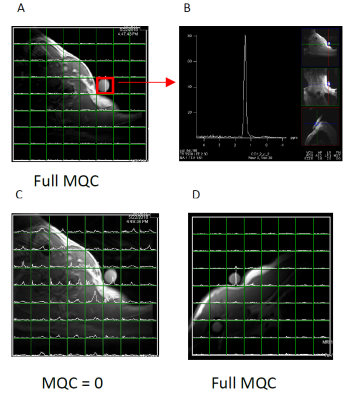 |
30 | Improvement and systematic analysis of the selective multiple quantum coherence 1H MRS lactate imaging pulse sequence for application to brain tumor and lymphoma patients
Seung-Cheol Lee, Hari Hariharan, Gabor Mizsei, Sanjeev Chawla, Kavindra Nath, Fernando Arias-Mendoza, Mark Elliot, Drew Torigian, Jakub Svoboda, Sunita Nasta, Stephen Schuster, Ravinder Reddy, Jerry Glickson
We have tested our revised Sel-MQC-CSI sequence for dependence of Lac/H2O on the B0 and B1 field inhomogeneity. The immunity of the Lac/H2O from our sequence on the above factors was demonstrated. We have improved lipid suppression from previously reported 100-fold to 22,000-fold while not losing the lactate signal. The revised sequence was applied to a glioma patient and a normal volunteer with a lactate phantom seated near the typical lymphoma occurring region of the body. In both human studies, satisfactory performance of the sequence was demonstrated.
|
 Back to Program-at-a-Glance |
Back to Program-at-a-Glance |  Back to Top
Back to Top