Scientific Session
Multiple Sclerosis & Myelin
Session Topic: Multiple Sclerosis & Myelin
Session Sub-Topic: Myelin Imaging
Oral
Neuro
| Monday Parallel 2 Live Q&A | Monday, 10 August 2020, 13:45 - 14:30 UTC | Moderators: Catherine Lebel |
Session Number: O-07
0045.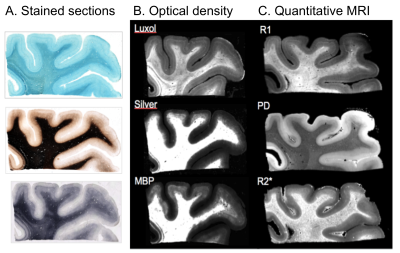 |
Differences in cortical and white matter myelination: a challenge for MRI myelin biomarkers.
Evgeniya Kirilina1,2, Ilona Lipp1, Carsten Jäger1, Markus Morawski3, Merve N. Terzi4,5, Hans-Jürgen Bidmon6, Markus Axer4, Pitter F. Huesgen5, and Nikolaus Weiskopf1,7,8
1Department of Neurophysics, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany, 2Center for Computational Neuroscience, Free University Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 3Paul Flechsig Institute of Brain Research, University of Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany, 4Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine, Forschungszentrum Jülich, Juelich, Germany, 5Zentralinstitut für Engineering, Elektronik und Analytik, Forschungszentrum Jülich, Juelich, Germany, 6C. und O. Vogt-Instituts für Hirnforschung, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Duesseldorf, Germany, 7Felix Bloch Institute for Solid State Physics, Leipzig University, Leipzig, Germany, 8Wellcome Centre for Human Neuroimaging, University College London, London, United Kingdom
Quantitative MRI parameters in the brain provide unique information on tissue myelination. However, the validation studies performing quantitative comparisons between MRI metrics and tissue myelin content are very limited, mainly due to the to the lack of methods for histological myelin quantification. Here, we explore lipid imaging using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) and multiple histological myelin stains in post-mortem human brain tissue samples for validation of MRI based myelin biomarkers. We show that tissue lipid composition vary across different cortical layers and white matter pathways, potentially reflecting differences in myelin structure and may impact MRI-based myelination metrics.
|
|
 |
0046.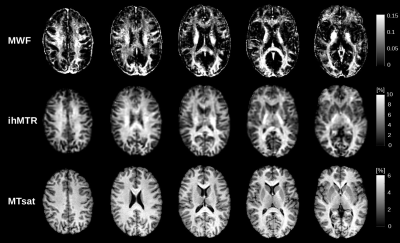 |
Towards advanced microstructural analyses of white matter: Quantitative regional comparison of different myelin measures
Ronja Berg1, Aurore Menegaux1, Guillaume Gilbert2, Claus Zimmer1, Christian Sorg1, Irene Vavasour3, and Christine Preibisch1
1School of Medicine, Department of Neuroradiology, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany, 2MR Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Markham, ON, Canada, 3Radiology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Microstructural parameters of the brain such as the myelin concentration or g-ratio (average ratio between axonal and fiber diameter) can provide important information on the pathophysiology of demyelinating diseases. Several myelin sensitive MRI methods exist. However, correlations between different myelin sensitive measures and the best choice for g-ratio mapping is not yet fully explored. Therefore, we compared MWF, ihMTR, and MTsat in white matter and found the highest correlation between MWF and ihMTR. Those measures also varied more strongly across WM regions compared to MTsat, which suggests that they could be more reliable for further analyses such as g-ratio imaging.
|
 |
0047.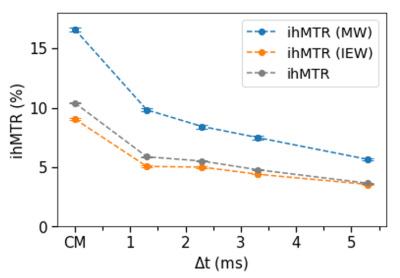 |
A study on Inhomogeneous Magnetization Transfer in Myelin and Intra-/Extra-cellular Water at 7T
Michelle H Lam1,2, Valentin H Prevost2, Andrew Yung2, and Piotr Kozlowski1,2,3,4
1Physics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2UBC MRI Research Centre, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3Radiology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4International Collaboration on Repair Discoveries, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Inhomogeneous magnetization transfer (ihMT) is a novel MR imaging technique that could be used for myelin-specific imaging if the sequence is properly tuned to filter components with short dipolar relaxation time (T1D). It is believed that ihMT’s dependence on T1D serves as a method to extract the myelin-related signal, due to its longest dipolar order among the brain structures. Here, we have combined two myelin imaging techniques, ihMT and myelin water imaging (MWI), to study myelin and intra-/extra-cellular water’s contribution to the overall ihMT signal.
|
0048.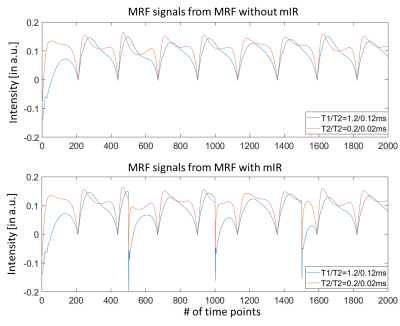 |
A Multi-Inversion-Recovery (mIR) Myelin Water Mapping (MWF)-MRF Sequence
Peng Cao1, Di Cui1, Queenie Chan2, and Edward S. Hui1
1Diagnostic Radiology, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Hong Kong, China
We proposed a new multi-inversion-recovery (mIR) myelin water mapping (MWF)-MRF sequence that allows 24 s/slice scan speed for four-compartment (myelin water, cerebrospinal fluid, gray matter and white matter) brain mapping on clinical 3T MRI.
|
|
0049.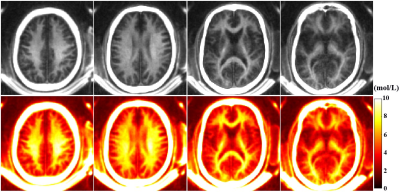 |
Quantitative Myelin Mapping in Human Brain Using a Short TR Adiabatic Inversion Recovery Prepared Ultrashort Echo Time (STAIR-UTE) Sequence
Yajun Ma1, Hyungseok Jang1, Zhao Wei1, Zhenyu Cai1, Yanping Xue1, Eric Y Chang2, Jody Corey-Bloom1, and Jiang Du1
1UC San Diego, San Diego, CA, United States, 2VA health system, San Diego, CA, United States
To quantitatively image myelin on clinical scanners, we propose a Short TR Adiabatic Inversion Recovery prepared UTE (STAIR-UTE) sequence for in vivo brain imaging. With STAIR technique, long T2 tissues with a broad range of T1s can be sufficiently suppressed. Healthy volunteer has a higher myelin proton density in white matter than that in patient with multiple sclerosis.
|
|
 |
0050.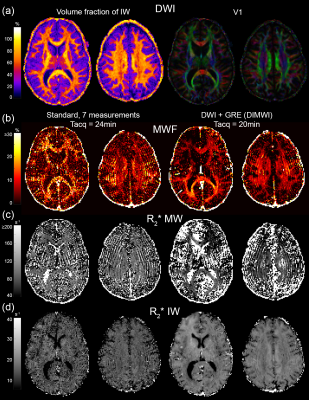 |
Diffusion informed Myelin Water Imaging
Kwok-Shing Chan1, Renaud Hedouin1, and José P. Marques1
1Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behaviour, Radboud University, Nijmegen, Netherlands
In this study, we propose an extension of the formalism of gradient echo based myelin water imaging by incorporating diffusion-weighted imaging data and an analytical white matter fibre model of signal evolution in a hollow cylinder. Voxel-wise analysis illustrated that the proposed model can significantly reduce the noise in the MWF estimation compared to the standard model, providing robust estimation even on high resolution data.
|
 |
0051.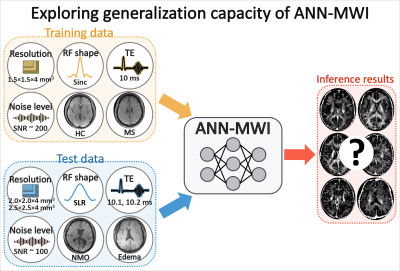 |
Exploring generalization capacity of artificial neural network for myelin water imaging
Jieun Lee1, Joon Yul Choi2, Dongmyung Shin1, Se-Hong Oh3, and Jongho Lee1
1Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Cleveland Clinic, Epilepsy Center, Neurological Institute, Cleveland, OH, United States, 3Division of Biomedical Engineering, Hankuk University of Foreign Studies, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea
In this study, the generalization capacity of the artificial neural network for myelin water imaging (ANN-MWI) is explored by testing datasets with different (1) scan protocols (resolution, RF shape, and TE), (2) noise levels, and (3) types of disorders (NMO and edema). The ANN-MWI results show high reliability in generating myelin water fraction maps from the datasets with different resolution and noise levels. However, the increased errors are reported for the datasets with the different RF shape, TEs, and disorder type.
|
 |
0052.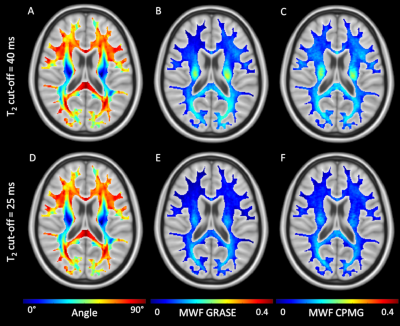 |
Myelin water imaging is sensitive to white matter fiber orientation in the human brain
Christoph Birkl1,2, Jonathan Doucette1,3, Enedino Hernández-Torres1, and Alexander Rauscher1,3,4
1UBC MRI Research Centre, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2Department of Neurology, Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria, 3Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4Department of Pediatrics (Division of Neurology), University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
We demonstrated that the measurement of MWF is considerably influenced by the angle between the white matter fiber tracts and the main magnetic field. Furthermore, we showed that the traditionally used cut-off between myelin water and intra- and extracellular water of 40 ms overestimates MWF.
|
0053.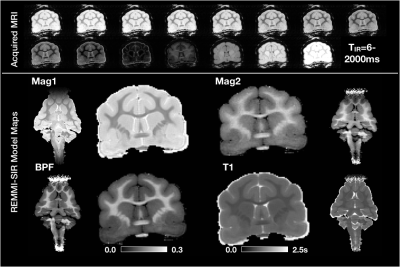 |
Quantitative myelin imaging in the ferret brain for traumatic brain injury research
JP Galons1, Kevin Harkins2, Mark Does2, Theodore Trouard1, and Elizabeth Hutchinson1
1University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States, 2Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States
MRI tools for mapping myelin content could provide useful markers of injury and repair in neurologic disorders that preferentially affect white matter such as traumatic brain injury (TBI). In this study, we apply two novel myelin water mapping approaches - bound pool fraction (BPF) from selective inversion recovery MRI and myelin water fraction (MWF) from multiple spin echo MRI - in the ex-vivo ferret brain with and without injury in order to develop these myelin mapping markers for pre-clinical TBI research. We demonstrate high quality BPF and MWF maps and describe metric behavior in a region of focal injury.
|
|
0054.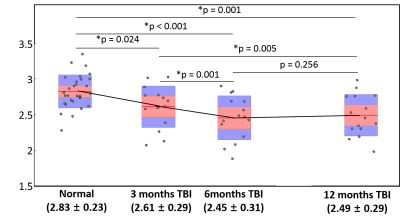 |
Longitudinal changes of myelin water fraction during the first year after moderate to severe diffuse traumatic brain injury
Joon Yul Choi1, John Whyte2, Amanda R Rabinowitz2, Vincent L Chow3, Se-Hong Oh4, Jongho Lee5, and Junghoon J Kim3
1Epilepsy Center / Neurological Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Moss Rehabilitation Research Institute, Elkins Park, PA, United States, 3Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Biomedical Sciences, CUNY School of Medicine, The City College of New York, New York, NY, United States, 4Division of Biomedical Engineering, Hankuk University of Foreign Studies, Yongin, Korea, Republic of, 5Laboratory for Imaging Science and Technology, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Institute of Engineering Research, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Reliable MRI biomarkers of white matter degeneration can be useful for monitoring post-traumatic progressive neurodegeneration and identifying potential treatment targets. We report that myelin water signal can be measured reliably during the first year after moderate to severe traumatic axonal injury. We also report that apparent myelin water fraction from the whole brain white matter continued to decrease beyond 3 months post-injury, reflecting progressive axonal degeneration and demyelination.
|

 Back to Program-at-a-Glance
Back to Program-at-a-Glance Watch the Video
Watch the Video Back to Top
Back to Top