Scientific Session
Women's Imaging
Session Topic: Women's Imaging
Session Sub-Topic: Female Pelvis
Oral
Body
| Tuesday Parallel 3 Live Q&A | Tuesday, 11 August 2020, 14:30 - 15:15 UTC | Moderators: Victoria Chernyak & Nandita deSouza |
Session Number: O-31
0586.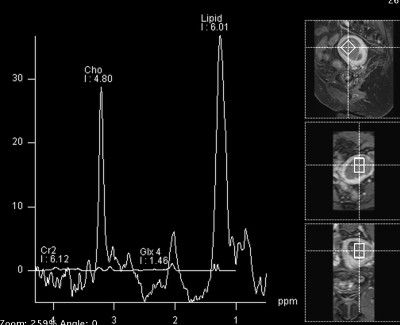 |
Total Choline Level on MRS Predicts Overall Survival for Endometrial Cancer and Correlates with Tissue Choline Metabolism
Gigin Lin1, Shang-Yueh Tsai2, Yu-Chun Lin1, Chiao-Yun Lin1, Ren-Chin Wu1, and Chyong-Huey Lai1
Video Permission Withheld
1Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou, Taiwan, 2National Chengchi University, Taipei, Taiwan
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic cancer in the developed countries but responses differently to the standard treatment. We aim to investigate and characterize the values of endometrial total choline levels on 1H MR spectroscopy in predicting overall survival, with tissue metabolomics and biochemistry corroboration. We found that increased total choline levels on MRS depicted high-risk cancer group for nodal metastasis, overall survival and disease-free survival for endometrial cancers, supported by increased tissue GPC levels and overexpression of EDI3.
|
|
0587.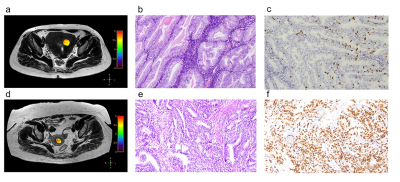 |
3D TSE Amide Proton Transfer and IVIM Imaging for Type I Endometrial Carcinoma: Correlation with Ki-67 Proliferation Status
Yong-Lan He1, Yuan Li1, Cheng-Yu Lin1, Ya-Fei Qi1, Xiaoqi Wang2, Hai-Long Zhou1, Hua-Dan Xue1, and Zheng-Yu Jin1
1Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Philips Healthcare China, Beijing, China
This study demonstrates the first attempt of 3D TSE APTw MR imaging for endometrial carcinoma with excellent inter-observer measurement agreement. APT values on 22 type I endometrial carcinoma lesions were moderately positively correlated with Ki-67 labelling index (r = 0.583, p=0.004). APT values of Ki-67 low-proliferation group were significantly lower than high-proliferation group (p=0.016) with AUC 0.768. However, no correlation was found between IVIM-derived parameters and Ki-67 labeling index (Dt, p=0.717; D* p=0.151; f, p=0.153).
|
|
0588.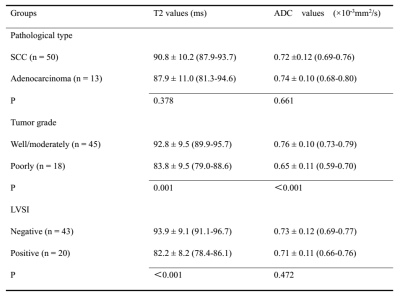 |
Accelerated T2 Mapping for Evaluating Cervical Cancer Features: A Preliminary Study
Shujian Li1, Jie Liu1, Jinxia Zhu2, Tobias Kober3, Tom Hilbert3, and Jingliang Cheng1
1Department of Magnetic Resonance, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China, 3Advanced Clinical Imaging Technology, Siemens Healthcare AG, Lausanne, Switzerland
This study investigated the feasibility of an accelerated T2-mapping sequence to evaluate cervical cancer (CC) pathological type, grade, stage and lymphovascular space invasion (LVSI) status. The results showed that quantitative T2 values can effectively grade and predict the CC LVSI status, and the ADC values can stratify CC grading. The synthetic T2-weighted (T2W) images showed comparable staging accuracy to the morphological T2W images acquired by a conventional sequence. This suggests that this accelerated T2-mapping sequence may facilitate CC staging and grading. Quantitative T2 values may be superior to ADC values in predicting the LVSI status of CC.
|
|
0589.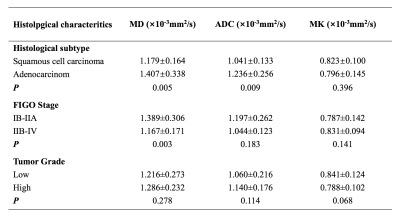 |
Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging of Cervical Carcinoma: Correlation between Imaging Parameters and Histological Findings
Qi Zhang1, Xiaoduo Yu1, Jieying Zhang1, Han Ouyang1, Xinming Zhao1, and Lizhi Xie2
1Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical, Beijing, China, 2GE healthcare, China, Beijing, China
Cervical cancer is the leading cause of death in gynecological malignancy around the world. The most important prognostic factors include stage at diagnosis, histological subtype, tumor differentiation and et al, which are critical to make the optimal treatment strategies. However, there are still huge challenges in accurate assessment tumor characteristics even by clinical examination and biopsy. DWI has showed promising results in assessment tumor characteristics in cervical cancer. Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI), an extension of DWI, is more sensitive to tissue heterogeneity and water exchange. This study demonstrated that DKI-derived parameters are helpful in assessment histological features of cervical cancer.
|
|
0590.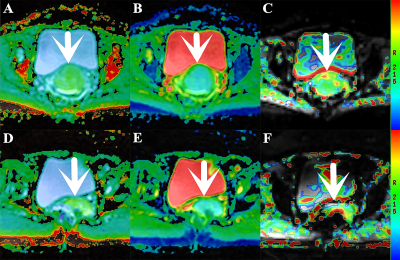 |
Comparative Analysis of the Value of APTWI and DKI in Evaluating the Histological Features of Uterus Cervical Cancer
Nan Meng1, Xuejia Wang2, Dongming Han2, Xiaoyue Ma1, Yan Bai3, Kaiyu Wang4, and Meiyun Wang*3
1Department of Radiology, Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital & Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Academy of Medical Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2Department of MRI, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Weihui, China, 3Department of Radiology, Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital & Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 4GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China
Amide proton transfer-weighted imaging (APTWI) has unique advantages in displaying the metabolism of diseased proteins. Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) can quantify the diffusion state water molecules in tissues with a non-gaussian model, thus correcting the deviation of the DWI model and improving the detection of lesions. Our results show that compared with APTWI, the DKI is more effective in evaluating the pathological and physiological characteristics of uterus cervical cancer (UCC).
|
|
0591.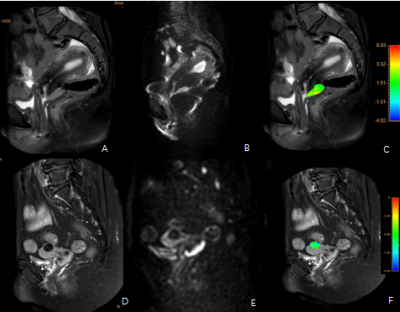 |
Application of amide proton transfer in differential diagnosis of mass cervical carcinoma and typical uterine leiomyoma
Xing Meng1, Ailian Liu 1, Shifeng Tian1, Zhiwei Shen2, Yishi Wang2, Yaxin Niu1, and Wan Dong1
1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Amide proton transfer (APT) imaging technology has been applied in the diagnosis of central nervous system tumors to some extent. However, it is only used in the diagnosis of cervical carcinoma in uterine tumors, and there is no study on the differentiation of cervical carcinoma and related tumors with APT. We investigated the value of APT in the differential diagnosis of mass cervical carcinoma and typical uterine leiomyoma.
|
|
0592.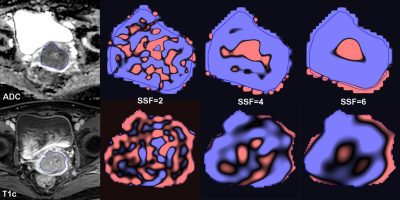 |
MRI Texture Analysis in the Characterization of Cervical Carcinoma
Mandi Wang1, Jose Angelo Perucho1, Queenie Chan2, and Elaine Lee1
1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2Philips Healthcare, Hong Kong, China
MRI texture analysis was performed in 100 patients with cervical carcinoma. TexRAD software was used for texture extraction and analysis on ADC maps and T1c images. Texture features were compared between histological subtypes, tumour grades, FIGO stages and nodal status. Feature selection was achieved with AUC ≥ 0.70. ADC-derived MPP5 was significantly lower in SCC than ACA, Entropy6 derived from both ADC and T1c increased from FIGO I~II to FIGO III~IV, and ADC-derived Entropy3 was higher in positive nodal status than negative. No texture features could differentiate tumour grades with acceptable diagnostic efficiency.
|
|
 |
0593.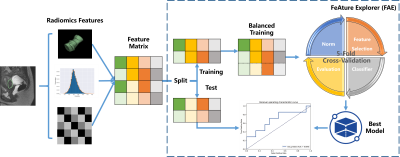 |
Prognosis of Focused Ultrasound Ablation Therapy Adenomyosis by Radiomics
Jing Zhang1, Zhicong Li2, Yang Song1, Han Wang2, Yefeng Yao1, and Guang Yang1
1Shanghai Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, Department of Physics, East China Normal University, shanghai, China, 2Department of Radiology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, shanghai, China
Patients with adenomyosis can be treated using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)-guided Focused Ultrasound Surgery (MRgFUS). However, note all patients have a good response to MRgFUS, some even equire pain management such as with Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) following MRgFUS. To evaluate the prognosis of MRgFUS using only MRI images, we used radiomics features together with clinical features to build a machine learning model with our homemade open-source software, namely FeAture Explorer (FAE), based on scikit-learn. We obtained a candidate model with AUC of 0.806 in test cohort.
|

 Back to Program-at-a-Glance
Back to Program-at-a-Glance Watch the Video
Watch the Video Back to Top
Back to Top