Sunrise Session
Microstructure: Non-Diffusion
Session Topic: Educational Q&A: fMRI/Diffusion/Perfusion Sunrise
Session Sub-Topic: Microstructure: Non-Diffusion
Sunrise Session
ORGANIZERS: Jongho Lee, Masaaki Hori
| Tuesday Parallel 1 Live Q&A | Tuesday, 11 August 2020, 13:45 - 14:30 UTC | Moderators: |
Skill Level: Intermediate
Session Number: S-Th-04
Overview
This intermediate-level Sunrise course is part of the four-day series on modelling, spanning from fMRI to perfusion microstructure and diffusion/non-diffusion microstructure modelling. The focus of this session is on the models of white matter microstructure in non-diffusion methods, which are myelin water imaging or magentic susceptibility imaging. The aim is to provide curious researchers who want to learn modelling details of non-diffusion micostructural imaging. Two lectures, one focused on the model for myelin water imaging and the other on the model for "hollow cylindrical fiber" in magnetic susceptibility imaging, will be described with the scope and limitations of each model.
Target Audience
Any researchers who want to learn imaging methods for non-diffusion microstructural imaging.
Educational Objectives
As a result of attending this course, participants should be able to:
- Describe the basics of white matter microstructure and non-diffusion models for white matter microstructure;
- Describe imaging methods for non-diffusion white matter microstructure; and
- Explain the scope and limitations of these models.
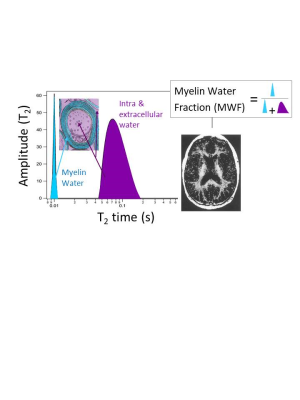 |
Myelin Water Imaging: Multiple Compartmental Model
Irene Vavasour
Myelin is composed of alternating layers of lipid bilayers with water in between. The multiple proton compartments in white matter can be modeled as four pools (myelin water, intra/extracellular water, myelin non-aqueous and non-myelin non-aqueous) which have different exchange properties. The water within the myelin bilayers can be measured using its shorter T1 and T2 relaxation time.
|
|
| Magnetic Susceptibility Imaging: White Matter Fiber Model
Daeun Kim
In MRI, magnetic susceptibility-induced contrast has been widely used due to its sensitivity and accessibility to magnetic properties of biological tissues. For example, in white matter of the brain, magnetic susceptibility variations are affected by both microstructural and molecular arrangements, which provides unique insights into understanding biologically important tissue features such as myelin. The main goal of this lecture is to 1) understand the magnetic susceptibility effects of white matter microstructure and 2) review a hollow cylinder fiber model for white matter that characterizes the magnetic susceptibility effects to explain susceptibility-induced contrast in white matter.
|

 Back to Program-at-a-Glance
Back to Program-at-a-Glance Watch the Video
Watch the Video Back to Top
Back to Top