Yu Guo1,2, Jiayu Xiao2, Zhongying Gong3, Wen Shen1, Shuang Xia1, and Zhaoyang Fan2
1Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, tianjin, China, 2BIRI, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 3Neurology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, tianjin, China
1Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, tianjin, China, 2BIRI, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 3Neurology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, tianjin, China
BZ+PI infarction has a higher degree of stenosis and distinct vulnerable
plaque characteristics compared with pure BZ infarction. IBZ infarction in BZ infarction caused by middle cerebral
arteriosclerosis is more common than CBZ infarction.
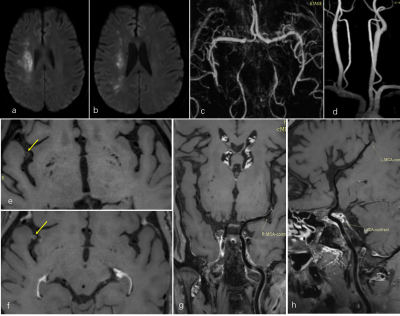
Male,58
years-old, right border-zone (BZ) infarction. (a-b) Diffusion weighted imaging
(DWI) showed disseminated spotty high signal intensity lesions in the right BZ
area of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory; (c-d) Magnetic resonance
angiography (MRA) of head and neck demonstrated no stenosis of the right vessels.
(e) Pre-contrast MR-VWI showed annular wall thickening and moderate stenosis of
MCA-M2 (arrow). (f, g) Post-contrast MR-VWI demonstrated plaque obvious
enhancement (arrow). (h) Post-contrast MR-VWI showed normal left vessels.
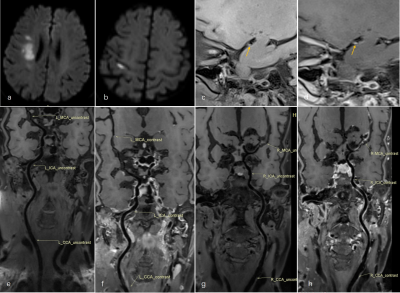
Female,75
years-old, right border-zone (BZ) infarction and pial infarct (PI) . (a-b)
Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) showed multiple high signal intensity lesions
in the right BZ area and cortex of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory. (c, g)Pre-contrast
MR-VWI showed wall thickening and a HIP (arrow) on the ventral side of MCA;
also revealed severe stenosis and occlusion in the MCA-M2. (d, h)Post-contrast
MR-VWI demonstrated plaque obvious enhancement.(e, f)Pre-contrast
and post-contrast MR-VWI showed normal left vessels.