Rick J van Tuijl1, Ynte M Ruigrok2, Birgitta K Velthuis1, Irene C van der Schaaf1, Gabriël J. E. Rinkel2, and Jaco J.M. Zwanenburg1
1Radiology, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Neurology and Neurosurgery, Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands
1Radiology, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Neurology and Neurosurgery, Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands
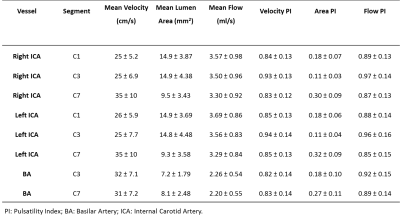
The bony carotid canal
constrains the distensibility of the internal carotid artery, yielding locally
increased velocity pulsatility. Velocity pulsatility is significantly higher in
men compared to women and increases with ageing.