Puneet Bagga1, Laurie J Rich1, Abigail Cember1, Ravi Prakash Reddy Nanga1, Deepa Thakuri1, Mark Elliott1, Mohammad Haris2,3, John A Detre4, and Ravinder Reddy1
1Department of Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2Sidra Medicine, Doha, Qatar, 3LARC, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar, 4Department of Neurology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States
1Department of Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2Sidra Medicine, Doha, Qatar, 3LARC, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar, 4Department of Neurology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States
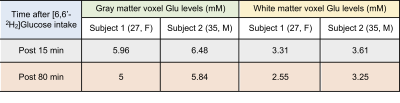
In this investigative study, we demonstrate the application of 1H MRS to detect glutamatergic neuronal metabolism in vivo in human brain at 3T. We exploited the fact that 2H is invisible on 1H MRS to detect the glutamate turnover from orally consumed [6,6'-2H2]glucose by healthy human subjects.
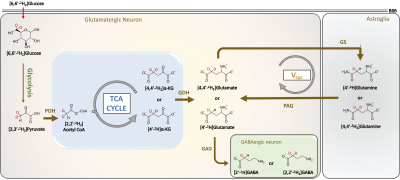
Metabolic Pathways of 2H label transfer from [6,6′-2H2]glucose in the brain. Schematic shows the pathway of exchange of deuterium from [6,6′-2H2]glucose to downstream metabolites that can be detected with 1H MRS. GABA g-aminobutyric acid, GAD glutamate decarboxylase, GDH glutamate dehydrogenase, GS glutamine synthetase, α-KG α-ketoglutarate