Jing Liu1, Yingxue Gao1, Hailong Li1, Xuan Bu1, Lingxiao Cao1, Lianqing Zhang1, Suming Zhang1, Xinyu Hu1, and Xiaoqi Huang1
1Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Functional and molecular imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China, Chengdu, China
1Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Functional and molecular imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China, Chengdu, China
Both static and dynamic ALFF/fALFF can detect certain cerebral region with abnormal activity.
Dynamic ALFF/fALFF can demonstrate additional brain regions that are ignored by static ALFF/fALFF.
There is significant correlation between cerebellum activity and clinical scale
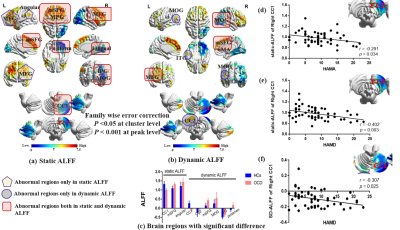
Figure 1. Brain regions with significant group differences in s-ALFF (a) and d-ALFF(b). Histogram (c) represents the mean value and standard error of s-ALFF/d-ALFF in the significant difference area between OCD group and HCs. The s-ALFF in the right CC1 correlated negatively with HAMA(d) and HAMD(e); The d-ALFF in the right CC1 correlated negatively with HAMD(f). Warm colors indicate regions showing higher s-ALFF/d-ALFF value in the OCD group comparing to HCs and cool colors indicate regions showing lower value. IPG, inferior parietal gyrus.
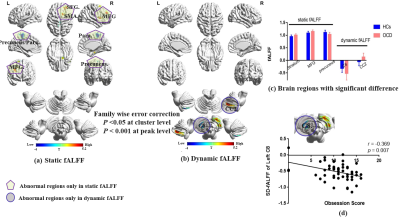
Figure 2. Brain regions with significant group differences in s-fALFF(a) and d-fALFF (b) Histogram (c) represents the mean value and standard error of s-fALFF/d-fALFF in the significant difference area between OCD group and HCs,The d-fALFF in the left C8 correlated negatively with obsession score(d). Warm colors indicate regions showing higher s-fALFF/ d-fALFF value in the OCD group comparing to HCs and cool colors indicate regions showing lower value. Para,paracentral lobule.