Joana R. A. Loureiro1, Ashish K. Sahib1, Megha Vasavada1, Antoni Kubicki1, Shantanu Joshi1, Benjamin Wade1, Amber Leaver2, Roger Woods1, Randall Espinoza3, and Katherine Narr1
1Neurology, Ahamason-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Radiology, Center for Translational Imaging, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, United States, 3Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States
1Neurology, Ahamason-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Radiology, Center for Translational Imaging, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, United States, 3Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Serial-ketamine reduces functional connectivity
between the cerebellum and the default and somatomotor networks during response
inhibition, highlighting the role of this circuitry in MDD and its treatment.
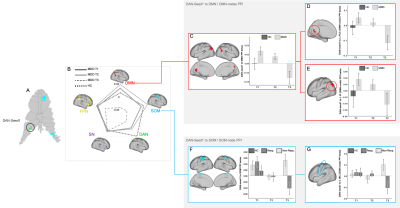
PPI analysis using DAN-seed1. A) DAN-seed1
mapped into cerebellum surface; B) Radar-plot representing the mean PPI betas obtained
between the DAN-seed1 and the 5 selected networks for MDD patients (at T1,T2,T3)
and for HC. C) Mean PPI betas for DAN-seed1 to DMN for HC and MDD; D,E) Mean PPI
betas for DAN-seed1 to DMN-nodes: posterior cingulate(D), Inferior parietal(E),
for HC and MDD patients; F) Mean PPI betas for DAN-seed1 to SOM, for HC and for
responders and non-responders; G) Mean PPI betas for DAN-seed1 to motor cortex (SOM-node), for
HC and for responders and non-responders.
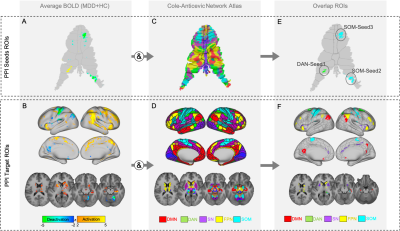
PPI seeds and target
ROIs. A, B) Average zstat maps obtained for HC and MDD at T1 for the
response-inhibition task fMRI NoGo-Go contrast mapped on the cerebellum surface
(A) and in cortical and subcortical regions (B); C,D) Cole-Anticevic network
Atlas adapted from [11] mapped on the cerebellar surface (C) and for cortical
and subcortical regions (D); E,F) Final ROIs obtained from the overlap between
the map in A,B and selected networks in C,D. Resulting ROIs located in the
cerebellum were used as seeds (E) and the ROIs obtained in the cerebrum were
used as targets (F) for the PPI analysis.