Ruiming Chen1, Sydney Nguyen2,3,4, Kai D. Ludwig1, Daniel Seiter1, Megan E. Murphy2,3,4, Kathleen M. Anthony2,3,4, Terry K. Morgan5, Ante Zhu6,7, Dahan Kim1, Sean B. Fain1,6,7, Oliver Wieben1,6, Thaddeus G. Golos2,3,4, and Kevin M. Johnson1,6
1Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Wisconsin National Primate Research Center, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Comparative Biosciences, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 4Obstetrics & Gynecology, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 5Pathology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, United States, 6Radiology, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 7Biomedical Engineering, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States
1Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Wisconsin National Primate Research Center, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Comparative Biosciences, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 4Obstetrics & Gynecology, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 5Pathology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, United States, 6Radiology, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 7Biomedical Engineering, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, United States
Feasibility of 2-D multi-slice VS ASL was shown. Differences in
pathology, # of cotyledons, and perfusion over gestational age were
observed for Zika subjects and controls. Visual inspection and quantitative
analysis demonstrate differences between single slice vs whole placenta
analysis.
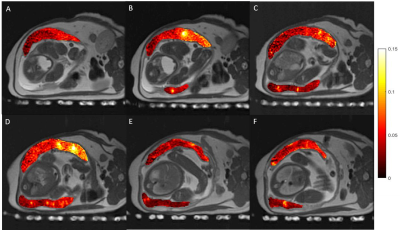
Figure 2. Six
consecutive anterior (A) to posterior (F) slices of rhesus macaque #2 on
gestational day 148. The VS ASL perfusion maps were calculated as ratio percentage
maps and are overlaid on top of the proton density images. Note that the spatial
variations in the VS ASL signal indicate the need for whole placenta assessment to improve measurement accuracy.
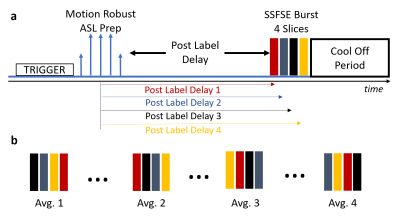
Figure 1. Interleaved multi-slice VS-ASL sequence paradigm
shown for 4 slices. (a) The sequence timing diagram (not drawn to scale) shows
how the respiratory trigger (expiration) initiates the motion robust VS-ASL
prep module followed by a post label delay (TI: ~1.2 s) and subsequent rapid
acquisition of 4 SSFSE slices and a cool off period. A total of 16 tag-on /
tag-off pairs are acquired and averaged for improved SNR. (b) The slice order
is cycled to mitigate signal differences from the different post label delays
differences, effectively averaging these effects.