Minjie Zhu1, Aditya Jhajharia1, and Dirk Mayer1
1Diagnostic Radiology & Nuclear Medicine, University of Maryland Baltimore, Baltimore, MD, United States
1Diagnostic Radiology & Nuclear Medicine, University of Maryland Baltimore, Baltimore, MD, United States
Metabolic
imaging of hyperpolarized(HP) 13C pyruvate in healthy rat brain with
flow suppression provide
evidence that majority of the HP lactate observed in brain was indeed produced in
the brain, making metabolic imaging of HP pyruvate a useful tool for the
investigation of brain metabolism.
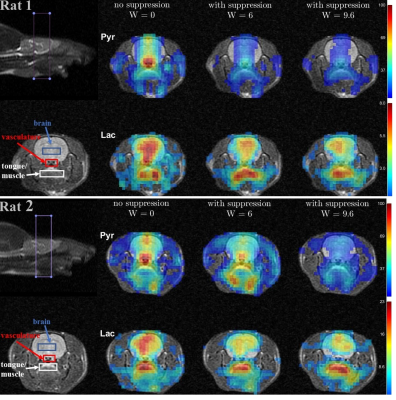
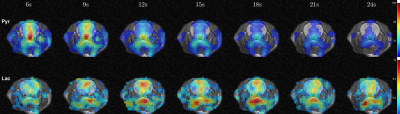
Figure 1. Metabolic maps for the
two rats, each scanned three times with different bipolar gradient
width:0/6/9.6ms respectively. For each map data were averaged over 6 time
points ranging from 9s to 24s with respect to the start of injection. Three regions
of interest – brain, vasculature, and tongue/muscle tissue were used for
quantitative analysis. For each column, image intensity is normalized with mean lactate
intensity in the muscle/tongue ROI to correct for the differences in
polarization level between the three injections.