Tatsuhiro Wada1, Chiaki Tokunaga1, Osamu Togao2, Masami Yoneyama3, Yasuo Yamashita1, Kouji Kobayashi1, Toyoyuki Kato1, and Hidetake Yabuuchi4
1Division of Radiology, Department of Medical Technology, Kyushu University Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan, 2Department of Clinical Radiology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Fukuoka, Japan, 4Department of Health Sciences, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
1Division of Radiology, Department of Medical Technology, Kyushu University Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan, 2Department of Clinical Radiology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Fukuoka, Japan, 4Department of Health Sciences, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
CS-SENSE enables acceleration of the acquisition time for
3D CEST imaging. Assessments using multi-slice CEST imaging for clinical study
would thus be feasible using 3D CEST imaging combined with CS-SENSE.
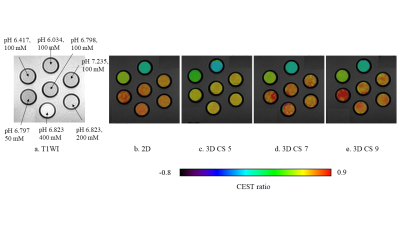
Fig. 5 The T1-weighted image
of the phantom (a) and CEST ratio images (b-e) were observed by all methods.
The signal intensity of the CEST ratio image varied with pH, but the intensity
was little affected by the concentration of iopamidol in all methods.
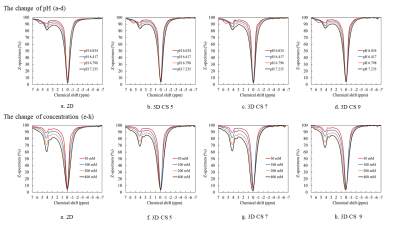
Fig. 2
A comparison of the z-spectrums obtained with 2D and
each 3D CEST imaging. The z-spectrums of upper phantoms were obtained at
100 mM concentration, and those of lower phantoms were obtained at pH 6.793–6.823.
In all the methods, the CEST
effects were observed at +4.2 and +5.6 ppm in lower pH phantoms,
and they changed according to the pH condition (a-d); the CEST effects also
increased with concentration in each method (e-h).