Paul Kyu Han1, Yanis Djebra1,2, Thibault Marin1, Georges El Fakhri1, Jinsong Ouyang1, and Chao Ma1
1Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 2LTCI, Télécom Paris, Institut Polytechnique de Paris, Palaiseau, France
1Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 2LTCI, Télécom Paris, Institut Polytechnique de Paris, Palaiseau, France
The results from the simulation study show that the dynamics of ASL signal display low-rank property. The results from the in vivo experiment show that the scan time of multi-delay ASL imaging can be accelerated using the proposed low-rank-based acquisition and image reconstruction method.
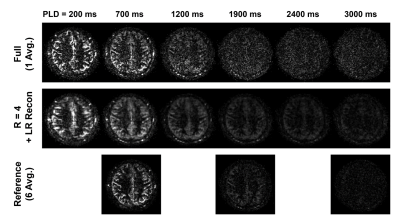
Figure 2. Low-rank reconstruction of multi-delay ASL signal. ASL subtraction map from fully-sampled single-average data, down-sampled (r=4) single-average data with low-rank reconstruction, and reference 6-average scan are shown at representative post-labeling delay (PLD) times.
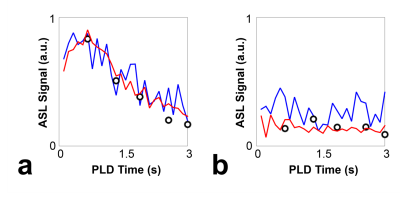
Figure 4. Comparison of signal dynamics of ASL subtraction signal. a: ASL subtraction signal dynamics from the gray matter region for fully-sampled single-average data (blue line), down-sampled (r=4) single-average data with low-rank reconstruction (red line), and reference 6-average scan (black circle) are shown. b: ASL subtraction signal dynamics from the white matter region for fully-sampled single average data (blue line), down-sampled (r=4) single-average data with low-rank reconstruction (red line), and reference 6-average scan (black circle) are shown.
