Catherine A Spilling1, Franklyn A Howe1, and Thomas R Barrick1
1Neurosciences Research Centre, Molecular and Clinical Sciences Research Institute, St George's University of London, London, United Kingdom
1Neurosciences Research Centre, Molecular and Clinical Sciences Research Institute, St George's University of London, London, United Kingdom
Quasi-diffusion image (QDI) is a
new high b-value MRI technique providing standard and non-Gaussian diffusion
images. We identify an optimal 6 diffusion direction tensor QDI sequence which allows
clinical acquisition in approximately 2 minutes.
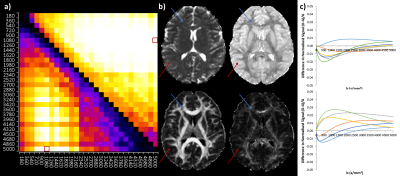
Figure
2: The optimisation matrix (a) shows subject average median χ2 values (upper
triangle) and rank (lower triangle) for each b-value pair. Hot colours
(yellow/white) indicate lower χ2 values and higher rank. The optimal b-value pair
was b = 1080, 5000 s mm-2
(red box). Mean and anisotropy D1,2
and α maps (b) are shown with graphs of the normalised difference between gold standard
(G) and optimal b-value decay curves (O) for the grey (top) and white matter (bottom)
voxels shown in Figure 1 (c).
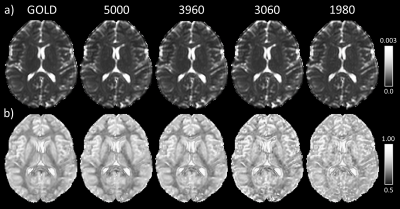
Figure 4: Single-subject QDI parameter maps of
(a) mean D1,2 and (b) α computed
from the gold standard
and optimal acquisitions with maximum b-values of 5000, 3960, 3060 and 1980 s
mm-2. From left to right the optimal acquisitions were b = 0, 1080,
5000 s mm-2, b = 0, 1080, 3960 s mm-2, b = 0, 1080, 3060 s mm-2,
and b = 0, 1260, 1980 s mm-2).
