Mimi Tian1, Xiangtao Lin1,2, Shuwei Liu1, and Xiang Feng3
1Shandong Unversity, Jinan, China, 2Department of Radiology, Shandong Provincial Hosptial Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China
1Shandong Unversity, Jinan, China, 2Department of Radiology, Shandong Provincial Hosptial Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China
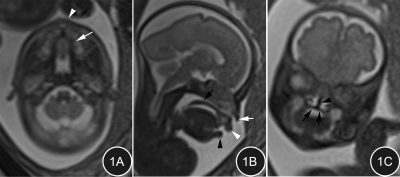
This is the frist prospective blinded study comparing the accuracy of US and MRI in diagnosing fetal facial cleft lip and palate. Compared to US diagnosis of fetal cleft lip and palate, MRI had obvious advantages and can be used as an effective alternative to US.
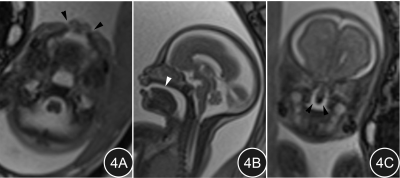
Fig.4A~C. Fetus with bilateral complete cleft lip and cleft palate, 29 weeks gestation. 4A: Continuous interruption of soft tissue in the upper lip bilaterally (arrow heads); the defect is filled with high-signal amniotic fluid. 4B: Absence of the fetal palatal plate and the connection between the nasal cavity and the oral cavity (arrow head). 4C: Continuous interruption of soft tissue in the bilateral palate (arrow head).