Weekend Educational Session
MR Physics for Scientists II
Session Topic: MR Physics for Scientists II
Session Sub-Topic: MR Physics for Scientists II
Weekend Course
ORGANIZERS: Jose Marques, Hua Guo, Ivana Drobnjak
| Saturday Parallel 4 Live Q&A | Saturday, 8 August 2020, 14:30 - 15:00 UTC | Moderators: MR Physics of Applications: Daniel Gallichan & Rui Pedro Teixeira |
Session Number: WE-01B
Overview
This course will describe the physics of the magnetic resonance, as well as the machineries (hardware or pulse sequence based) available to the MR physicist to manipulate the evolution of magnetization.
In the second part, there will be an emphasis on the mechanisms that drive relaxation properties in in vivo MRI and the image contrast observed in structural imaging (be it T1-, T2-, or T2*-weighted imaging).
The third section of the course will be dedicated to understanding the basic physics of a set of common MRI applications, namely: fMRI, flow, diffusion, and perfusion imaging.
Last, but not least, the interaction of static field, radiofrequency waves, and currents with the human body will be addressed both from a contrast opportunity and safety perspective.
Target Audience
MR physicists and engineers, pulse sequence developers, and clinicians who want to deepen their understanding of the MRI acquisition process and how MRI contrast can be optimized for different goals.
Individuals who will likely benefit most from the course are those who have recently completed or are currently following a graduate educational program in MR physics, chemistry, applied mathematics, or engineering, and those practitioners of MR with extensive practical experience who seek to obtain a more systematic foundation of MRI.
Educational Objectives
As a result of attending this course, participants should be able to:
- Express a systematic understanding of pulse sequence building blocks and MR system components;
- Demonstrate an in-depth understanding of advanced methods to explore image contrast;
- Describe the physical process behind a wide range of contrast mechanisms (chemical exchange saturation transfer, quantitative susceptibility mapping, BOLD, flow, and diffusion among others); and
- Critically describe the forms of interactions between the fields used in MRI with subjects tissues or implants and the safety constraints arising from such interactions.
| MR Physics of Applications | ||
| Physics of Flow Imaging
Rui Li
|
||
 |
Physics of Diffusion Imaging
Zhe Zhang
Diffusion imaging can non-invasively probe tissue microstructures and has been widely adopted in clinical diagnosis and neuroscience research. In this section, we will briefly review the diffusion imaging contrast mechanisms and discuss the workhorse diffusion imaging sequence, which is single-shot spin-echo EPI. We will also discuss some recent diffusion imaging techniques such as multi-shot diffusion imaging, simultaneous multi-slice imaging, 3D imaging, etc. This section aims to give a comprehensive overview on diffusion imaging physics.
|
|
| Physics of functional MRI: GE, SE BOLD
Klaus Scheffler
|
||
| Physics of Perfusion Contrast
Susan Francis
|
||
| Opportunities & Challenges of Interaction of Fields & Tissues | ||
| Principles of QSM & Applications
Jongho Lee
|
||
| Principles of EPM & Applications
Rosalind Sadleir
This course will present methods of imaging and mapping tissue electrical properties (Electric Properties Mapping, EPM) using MRI. An overview of the characteristics underlying tissue electrical properties will be given followed by a brief summary of methods that have been used to measure them. Finally, the diverse approaches, present applications and emerging areas within EPM using MRI will be presented and described.
|
||
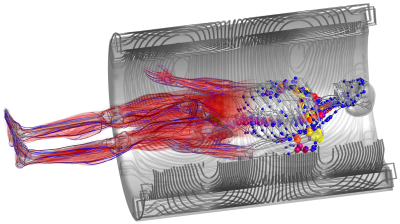 |
Modeling Tissue Interactions with Gradients and RF Fields
Mathias Davids
The time-varying magnetic fields used in MRI induce electric fields (E-fields) in the human body that can have adverse effects. The radio-frequency (RF) coils induce high-frequency (MHz range) E-fields that cause tissue heating and potentially irreversible tissue damage in the conductive tissue (SAR). The gradient coils induce low-frequency (kHz range) E-fields that can stimulate peripheral nerves (PNS), leading to involuntary muscle contraction of touch perception. Understanding SAR and PNS effects is important to allow developing mitigation strategies to overcome their impact on image acquisition, such as reduced excitation fidelity, longer scan times, and reduced spatiotemporal image resolution.
|
|

 Back to Program-at-a-Glance
Back to Program-at-a-Glance Watch the Video
Watch the Video Back to Top
Back to Top