James W. MacKay1,2, Joshua Kaggie1, Graham M. Treece3, Stephen M. McDonnell4, Wasim Khan4, Alexandra R. Roberts5,6, Rob L. Janiczek5, Martin J. Graves1, Tom D. Turmezei2,7, Andrew W. McCaskie4, and Fiona J. Gilbert1
1Department of Radiology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2Norwich Medical School, University of East Anglia, Norwich, United Kingdom, 3Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 4Department of Surgery, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 5Clinical Imaging, GlaxoSmithKline, London, United Kingdom, 6Antaros Medical, Uppsala, Sweden, 7Department of Radiology, Norfolk & Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, United Kingdom
1Department of Radiology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2Norwich Medical School, University of East Anglia, Norwich, United Kingdom, 3Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 4Department of Surgery, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 5Clinical Imaging, GlaxoSmithKline, London, United Kingdom, 6Antaros Medical, Uppsala, Sweden, 7Department of Radiology, Norfolk & Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, United Kingdom
We propose a novel approach to analysis of cartilage MRI
data in knee osteoarthritis which improves responsiveness and reduces analysis
burden vs standard methods. This could improve our ability to detect treatment
effects in shorter, smaller studies.

Figure 2:
Fig 2A: Outline of initial steps in 3D-CaSM pipeline, from image acquisition to thickness measurement. Femur used for demonstration purposes – 3D-CaSM is also performed for tibial cartilage surfaces.
Fig 2B: Outline of cartilage composition measurement process. In this example, a T1rho map is used. Note focal area of increased T1rho values on the medial femoral condyle (black arrowhead) corresponding to an area of partial thickness cartilage loss on the 3D SPGR images (white arrowhead).
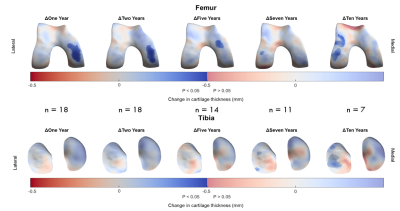
Figure 5: Implementation of 3D-CaSM in a clinical study of knee
joint distraction using statistical parametric mapping to detect effects at
group level. Surface data represent mean change from baseline mapped to the canonical
surface and masked for statistical significance. Significant increases in
cartilage thickness are seen over the weight-bearing medial femoral condyle at
up to 5 years follow-up, with a delayed compensatory response in the lateral
compartment at 7 years & 10 years follow-up.