Yavuz Muslu1,2, Ty A. Cashen3, Sagar Mandava4, and Scott B. Reeder1,2,5,6,7
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Department of Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Global MR Applications and Workflow, GE Healthcare, Madison, WI, United States, 4Global MR Applications and Workflow, GE Healthcare, Atlanta, GA, United States, 5Department of Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 6Department of Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 7Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Department of Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Global MR Applications and Workflow, GE Healthcare, Madison, WI, United States, 4Global MR Applications and Workflow, GE Healthcare, Atlanta, GA, United States, 5Department of Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 6Department of Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 7Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States
Stack-of-stars, inversion recovery MRI is a promising method for T1 mapping in the abdomen due to its low motion sensitivity, strong T1 contrast and flexibility to different acquisition strategies for confounder correction.

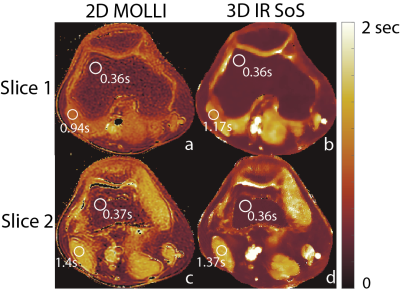
Figure 5: 2D MOLLI is a breath-held T1 mapping method, that is often corrupted by the motion artifacts. Shown is the comparison of T1 maps generated with 2D breath-hold MOLLI and 3D free breathing IR-SoS in the liver. T1 measurements in liver parenchyma from two methods show good agreement. Proposed method shows estimation inaccuracies in longer T1 species due to lack of sequence optimization.