Yin Wu1, Jie Liu1, Qi Liu2, Hui Liu2, Jian Xu2, Yuanwei Xu3, Yucheng Chen3, Xin Liu1, and Hairong Zheng1
1Paul C. Lauterbur Research Center for Biomedical Imaging, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare America, Houston, TX, United States, 3Cardiology Division, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
1Paul C. Lauterbur Research Center for Biomedical Imaging, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare America, Houston, TX, United States, 3Cardiology Division, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
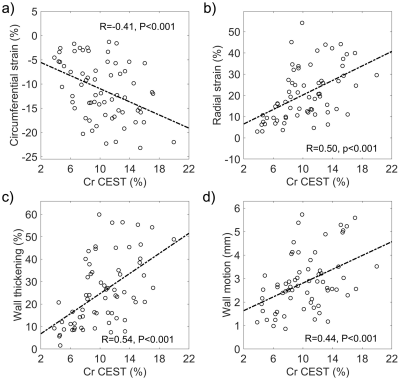
This study investigated the feasibility of Cr
CEST in evaluating cardiac dysfunction in acute infarct heart. Results show
moderate correlation between cardiac function and Cr CEST signal, demonstrating
the ability of Cr CEST in assessing heart functional impairment.

Figure
2.
(a) Cr CEST map overlaid on a CEST-weighted image
of a representative animal. Negative Cr CEST contrast was largely consistent with
the scar region shown on the T1w-LGE image (b). Segmental based
circumferential strain, (e) radial strain (f), wall thickening (g) and wall
motion (h) were measured from the respective cine images at
end-diastolic (c) and end-systolic (d) cardiac phases.