Xiao Gao1, Xiaowei Wang2, Kai Qiao1, Cassandre Labelle-Dumais2, Douglas Gould2, and Myriam M. Chaumeil1
1Department of Radiology, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States, 2Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States
1Department of Radiology, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States, 2Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States
Multi-modal MRI at 14.1 Tesla revealed that Col4a1 mutant mouse models faithfully recapitulate the radiological manifestations of cSVDs. Notably, we show that allelic heterogeneity influences disease severity as well as the nature and distribution of lesions.

(A) All mice were imaged under 1.3-1.8% isoflurane using 4 optimized sequences whose parameter settings have been listed here, with total scan time of ~55 min/animal. (B) An atlas-based imaging data analysis pipeline was used to register mouse brain anatomical and pathological information to the Allen Brain Reference Atlas while K-means algorithm was used to cluster and quantify different lesion types.
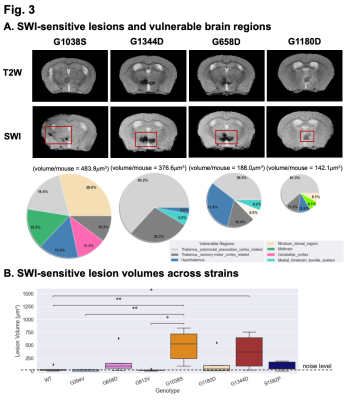
(A) SWI detected hypointense lesions overlooked by T2W imaging. As shown in the pie chart, where the pie radius reflects the total lesion volume per mouse, allelic heterogeneity was shown to influence disease severity and regional distribution of brain regions. Notably, lesions in cortical regions were only observed in the G1038S cohort. (B) The volume of SWI-sensitive lesions was significantly higher in mutant groups (G1038S and G1344D) compared to WT (as expected), and differ between Col4a1 mutant strains.
