Andrei V. Manzhurtsev1,2,3, Peter Bulanov3, Maxim Ublinskiy1,2, Petr E. Menshchikov2,4, Alexey Yakovlev1,2, Tolib Akhadov1,3, and Natalia Semenova1,2,3,5
1Radiology, Clinical and Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Trauma, Moscow, Russian Federation, 2Emanuel Institute of Biochemical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russian Federation, 3Moscow State University, Moscow, Russian Federation, 4Philips Healthcare, Russia, Moscow, Russian Federation, 5Semenov Institute of Chemical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russian Federation
1Radiology, Clinical and Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Trauma, Moscow, Russian Federation, 2Emanuel Institute of Biochemical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russian Federation, 3Moscow State University, Moscow, Russian Federation, 4Philips Healthcare, Russia, Moscow, Russian Federation, 5Semenov Institute of Chemical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russian Federation
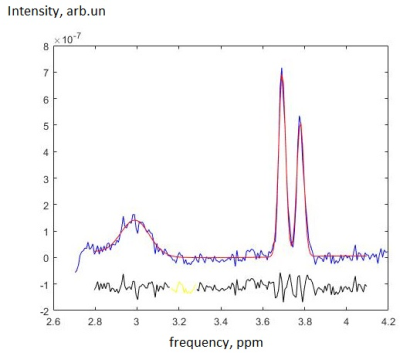
The increase in Glu without glutamine
contribution and the stability of GABA without macromolecule contamination are
revealed in the posterior cingulate cortex of acute mTBI pediatric patients. The excitatory-inhibitory
neurotransmitter balance is shifted towards excitation.