Jonathan Cuthbertson1,2, Trong-Kha Truong1,2, Jasmine Chen1,2, Fraser Robb3, Allen W. Song1,2, and Dean Darnell1,2
1Medical Physics Graduate Program, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 2Brain Imaging Analysis Center, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 3GE Healthcare, Aurora, OH, United States
1Medical Physics Graduate Program, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 2Brain Imaging Analysis Center, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States, 3GE Healthcare, Aurora, OH, United States
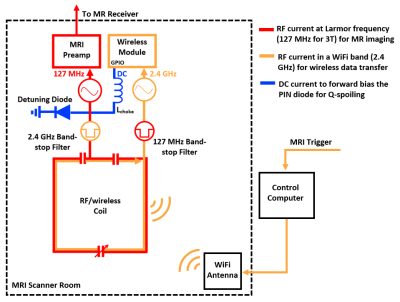
The experiments performed showed
that the integrated RF/wireless coil was able to provide wireless Q-spoiling
during MR image acquisition without significantly impacting SNR or wireless
performance.