Ghoncheh Amouzandeh1, Dariya I Malyarenko1, Yuxi Pang1, Brian D Ross1, and Thomas L Chenevert1
1Radiology, University of Michigan, Ann arbor, MI, United States
1Radiology, University of Michigan, Ann arbor, MI, United States
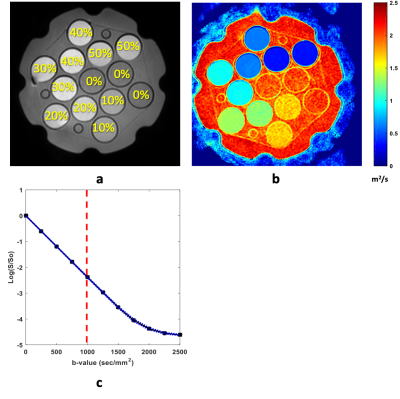
Temperature and concentration dependence of apparent diffusion coefficient for 0-50% PVP were studied for scanner room temperature range. Consistent with Arrhenius model, we showed that collision frequency factor and activation energy increase linearly with increasing [PVP] from 10-40%.