Hitoshi Kubo1, Yuya Abe2, Tomoya Yokokawa2, Seira Yokoyama2, and Koji Hoshi2
1Fukushima Medical University, Fukushima, Japan, 2Hoshi General Hospital, Koriyama, Japan
1Fukushima Medical University, Fukushima, Japan, 2Hoshi General Hospital, Koriyama, Japan
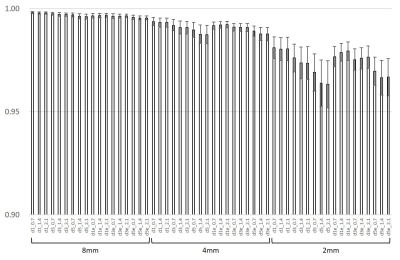
SNRs were increased higher
significantly by DLR in all SNR ranges. Increasing ratio of SNR was varied by
means of parameter settings. Combination of the DLR parameters affected varies
to SNR, SSIM, and spatial resolution of the images.