Tahmina Susan Achekzai1, Luis Loza2, Stephen Kadlecek2, Kai Ruppert2, Faraz Amzajerdian2, and Rahim R. Rizi1
1Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States
1Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States
In this study we demonstrated the performance of XTC imaging in wildtype and transgenic free-breathing mice, while exploring the relationship of delay time and number of saturation pulses on the optimizing depolarization of GP Xe.
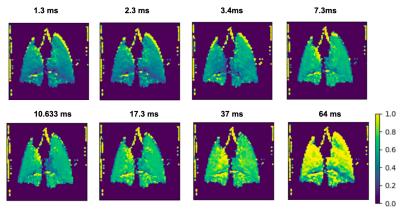
Maps representing ratio of depolarized/control image in a wild-type mouse, with increasing delay times (1.3, 2.3, 3.4, 7.3, 10.633, 17.3, 37, 64) and decreasing pulses (50, 40, 30, 20, 15, 10, 5, 3), for a same total of saturation time. Highest depolarization reached is about 30%, at a 3.4 ms delay.
