Roozbeh Eskandari1, Arsen Mamakhanyan1, Michelle Saoi2, Kristin L Granlund1, Justin Cross2, Craig B Thompson3, and Kayvan Rahimi Keshari1,4
1Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 3Cancer Biology & Genetics Program Share, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 4Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering, New York, NY, United States
1Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 3Cancer Biology & Genetics Program Share, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 4Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering, New York, NY, United States
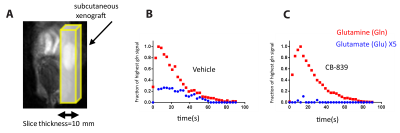
We developed a custom-synthesized compound, [5-13C,4,4-2H2,5-15N]-L-Glutamine, as a hyperpolarized MRI probe for glutaminase activity. We were able to detect in vivo conversion of hyperpolarized glutamine to glutamate in murine model of PDAC.